Hidradenoma cutis is a benign tumor that appears as a single gray-pink nodule about 1-3 cm in diameter, which most often occurs on the head and neck, trunk, or, less commonly, on the extremities. These can be single or multiple nodules.
- Causes of cutaneous hidradenoma
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment of the disease
- Prognosis and prevention
The tumor is relatively safe for health and creates mainly aesthetic discomfort.
Symptoms
Depending on the cause of the lesions, they will look different. Red nodes on the skin often indicate the inflammatory nature of the disease. Such lesions are softer to the touch, painful, and sometimes the pain can be throbbing. In acute cases, an increase in local temperature may be observed. Painful nodes under the skin may be a symptom of the presence of a malignant tumor disease.
A typical non-inflammatory nodule has a dense consistency and is light pink or white in color. Usually it does not cause the patient any unpleasant physical sensations. The dimensions can reach up to 10 cm. Inflammatory nodes sometimes ulcerate, and after healing, scars form in their place.
Skin formations. What could it be?
Various types of formations often appear on human skin: pits, swellings.
Including nodules, the variety of which is also rich. They differ in color, shape, and also in their involvement in the disease, as a result of which they appear on the human skin. How to determine which disease a particular nodule belongs to? They come in different sizes. There is also a division of nodes into subcutaneous ones and those that grow directly on the human skin itself. So, let's look at the most common variations of formations.
The initial form of formation on human skin is called tubercles. They look dense. The color of the tubercles varies from flesh-colored to red, sometimes even black. The color depends on the person’s disease.
Since the tubercles are practically the initial stage of the formation of nodes, they practically do not cause discomfort. Basically, they are painless, but in some cases, with a serious form, they are painful and cause pain on palpation.
Papules usually come in several types. There are subcutaneous and tubercles directly on the skin itself. Subcutaneous nodes may be painless, but they often cause pain and discomfort when pressed.
What are papule and pustule
Papule is an element of the rash, localized in the upper layers of the skin; the attributes do not have a cavity with pus or liquid. They have a mild course, may be accompanied by inflammation, and there is no discomfort when touching the affected area.
After the development of papules and pustules is completed, there are no traces or scars left on the skin. Formations can appear with syphilis, meningitis, an allergic reaction, or occur after a scabies mite bite.
A pustule is a formation with a head, a capsule filled with purulent masses that provoke inflammation, unlike papules. When an element ruptures, a substance leaks out and a dry crust appears on the skin. If the formations are isolated in nature and are not accompanied by pathological processes, they disappear without a trace.
In case of profuse rashes with pronounced discharge, an examination is carried out for the presence of pathologies.
Modern methods of treatment
For basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer, in most cases, one can limit ourselves to surgical excision of the malignant tumor . It is removed using a scalpel, capturing a certain amount of surrounding healthy tissue. After surgery, it is important to obtain a negative resection margin: when examining the tumor under a microscope, no cancer cells should be present near the cut edge. Otherwise, the tumor is most likely not completely removed, and there is a risk of relapse.
, Mohs surgery is used . This is a more labor-intensive and complex intervention, during which the tumor is removed layer by layer, and each layer is immediately examined under a microscope. Removal continues until tumor cells are no longer detected in the next layer. Typically, Mohs surgery is used in cases where it is important to preserve as much healthy tissue as possible, for example, if a tumor is on the face.
Similar surgical interventions are used for melanoma.
In addition, in some cases, basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas can be removed in other ways:
- With the help of cryosurgery - by exposure to very low temperatures.
- Using photodynamic therapy. The patient is injected with a special drug - a photosensitizer - which accumulates in tumor cells. Then the tumor is exposed to light of a certain wavelength, the photosensitizer is activated and destroys the tumor cells.
Sometimes, after excision of skin cancer, curettage and electrocoagulation : the edges and bottom of the wound are scraped with a special instrument that cauterizes the tissue. This allows the remaining cancer cells to be destroyed.
If the tumor affects the lymph nodes, they are also removed. For melanoma in the later stages, palliative operations can be performed: removal of tumor foci in such cases does not lead to a cure, but helps to contain the progression of the disease and prolong the patient’s life.
In some cases, if surgery cannot be performed for some reason, the malignant tumor can be destroyed using radiation therapy. Most often, radiation is used as an addition to surgical treatment or independently in late stages to contain the growth of tumor foci, cope with pain or other symptoms.
For common malignant skin tumors, therapy is carried out with antitumor drugs. In addition to classical chemotherapy drugs, targeted drugs are used that block certain target molecules in tumor cells.
A breakthrough in the treatment of metastatic and inoperable melanoma occurred with the advent of innovative immunodrugs from the group of checkpoint inhibitors. These anticancer drugs block molecules that prevent immune cells from being activated and attacking cancer cells. Checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy helps improve survival among patients with advanced melanoma. It is much more effective than chemotherapy, causes fewer side effects and is better tolerated by patients.
All the latest generation antitumor drugs are available at the Medicine 24/7 clinic. Our doctors draw up treatment regimens in accordance with the latest versions of international protocols.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
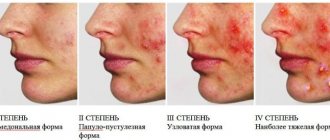
Nodular cystic acne: causes
The main signs that characterize the disease are the formation of cysts under the skin. They are filled with sebaceous plugs and purulent contents. The elements protrude above the surface of the skin, are accompanied by an inflammatory process, and have a bluish color. A common consequence of this form is scars that are difficult to heal.
In dermatology, there is a classification of acne based on severity:
- Acne is localized in one area of the body, purulent pustules are rare;
- A large area of the face or body is affected, the ratio of comedones and ulcers is equal;
- The appearance of deep pimples filled with pus, which tend to scar;
- The formation of fistula entrances, the nodes acquire significant sizes.
As is the case with other forms of acne, the described variety occurs due to impaired functioning of the secretory glands. They produce excess sebum and cystic acne develops. The reasons for increased fat production lie in:
- Hormonal changes caused by adolescence, pregnancy, abortion, menopause and gynecological diseases in women;
- Thickening of the upper layer of the epithelium, preventing the normal outflow of “fat”;
- Weakened immune system;
- Dysfunction of the digestive system;
- Lack of hygiene, habit of touching your face with unwashed hands;
- Drug therapy, in particular supplements containing steroids;
- Exposure to stress and anxiety;
- The habit of squeezing out purulent pimples;
- Genetic predisposition to acne.
Reasons for appearance
Red or bluish-purple spots and nodules on the human body are medically called hemangiomas. The underlying physiological causes of vascular anomalies on the body have not yet been precisely established, but the following factors may serve as prerequisites for their appearance on the human body:
- Infectious diseases in women in the first trimester of pregnancy. In this case, there is a risk that the newborn will have small red moles on the body. The size of congenital angiomas, as a rule, does not exceed 1 cm. As they grow older, the spots gradually disappear without any treatment and by the age of seven they disappear completely. In girls, congenital red moles are several times more common than in boys.
- Hormonal changes in the body lead to the appearance of tumors in adults. Sometimes angiomas can appear on the abdomen of women after giving birth or during menopause. The size and shape of such neoplasms vary widely. Only a doctor should determine how dangerous these skin diseases are and whether they require treatment.
- Diseases of the internal organs are sometimes associated with the appearance of purple moles on the body. It is believed that their location indicates a problematic organ - a red nodule on the abdomen indicates problems with the liver, intestines or pancreas. The validity of this statement is debatable, but consulting a doctor would be a good idea.
- Trauma or thrombus-forming processes. Any disruption of the vascular network can cause the appearance of benign vascular formations.
- Red spots or nodules sometimes occur due to excessive exposure to ultraviolet light. Both natural and artificial tanning are dangerous for the skin in general and are fraught with the appearance of angiomas on the body of women.
Regardless of the reasons for which these formations appear in women, in most cases they cause damage only to appearance. But you need to carefully monitor them, especially if the nodule is voluminous and is at risk of injury. The most common causes of injury in women are jewelry, underwear, or a belt. In addition, long nails or hair can also accidentally get caught on the tumor and injure it.
Prognosis and prevention
With adequate treatment, the patient can forget about the removed tumor forever. If the node was a single one, the risk of its reoccurrence is extremely low. If multiple hidradenomas are observed, it is necessary to establish the cause of their occurrence and eliminate all the risk factors listed above, and perhaps at first recommend the patient to regular monitoring by a specialist.
Hidradenoma, as a rule, does not pose a threat to the patient’s health, however, it is important to make a correct diagnosis in a timely manner and carry out appropriate treatment. That is why in the European clinic this problem is dealt with by oncologists with extensive experience, and equipping the clinic with modern equipment allows for a comprehensive examination and adequate treatment.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Diagnostic methods
The main diagnosis of hidradenoma (as well as other oncological processes of the skin) is a biopsy of the contents of the node followed by microscopic examination of the taken material. To carry out this procedure, a section of the node is removed with a special needle or removed with a scalpel and sent to the laboratory to study the morphological characteristics of the tumor.
According to histological examination, several types of skin hydradenomas are distinguished. The main ones are the following:
- Hidradenoma clear cell.
- Hidradenoma nodosa.
- Hydradenoma cystica.
Based on the biopsy data, further treatment tactics are determined. If hidradenoma transforms into a malignant form (this happens extremely rarely), it is called hidradenocarcinoma.
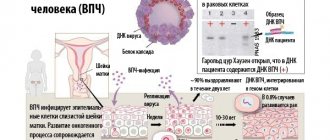
As part of the screening diagnosis of skin tumors, an analysis for the presence of human papillomavirus can be performed. If the test is positive, this may require regular monitoring. Other diagnostic methods, such as examination of the skin by a doctor, dermatoscopy and ultrasound are preliminary and are usually carried out at the initial stage of the diagnostic process.
Causes of cutaneous hidradenoma
Hydradenomas arise due to the degeneration of sweat gland cells. The specific cause of their occurrence has not been fully established. The main risk factors are the following:
- Skin contamination that blocks the flow of sebaceous or sweat glands.
- Previous inflammatory or infectious skin diseases.
- Exposure to direct sunlight on the skin.
- The use of certain chemical agents, creams.
- Trauma, surgical interventions or cosmetic procedures on the skin.
In addition, one of the risk factors is the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in the body. After suffering stress, systemic infection, hypothermia, or when the immune system is weakened, this virus can be activated and can cause the development of skin hidradenoma or other neoplasms.