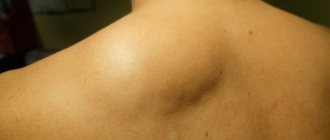
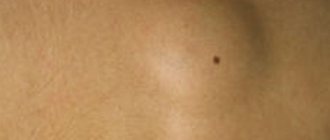
Breast lipoma is a benign tumor growing in the subcutaneous fatty tissue. Less commonly, a lump in the mammary gland can form closer to the surface of the skin. This problem is most often encountered by women after forty years of age, but there are also men among patients. Wen in the chest area can appear in girls and boys during adolescence. Lipoma can occur where there is adipose tissue, and in the mammary glands, all patients without exception have it to a greater or lesser extent.
Breast lipoma - what is it?
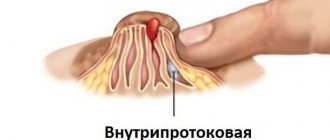
The formation of a wen is difficult to detect at an early stage and to distinguish from healthy adipose tissue in the mammary gland due to its structural features. The mammary gland, in addition to adipose tissue, includes glandular and connective tissue. The glandular tissue consists of alveoli (lobules), from which the thoracic ducts stretch towards the nipple.
A lipoma on the chest is a benign tumor that arises from fatty tissue. The main signs of breast lipoma are as follows:
- a node in the center of the tumor;
- the contours are quite clear;
- capsule containing fatty contents; can form on any part of the breast (wherever there is fatty tissue), as well as in the nipple halo;
- The symptoms of a lipoma in the chest area are similar to other lipomas; in most cases, the growth of the formation occurs in the absence of pain.
Symptoms
The development of symptoms occurs along with the passage of the tumor through certain stages of its growth and development.
At the first stage, the tumor does not have any effect on the lung. She is still small. The capsule does not allow it to grow quickly.
The second stage will be marked by compression of the bronchial tree, a rapidly growing formation. A person feels heaviness while breathing. Notes the appearance of shortness of breath. Feeling of tightness on one side of the chest. Possible chest pain.
On this topic
- Respiratory system
How to recognize and treat pleural fluid
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- February 28, 2021
At the third stage, narrowing of the main bronchi is possible. The cough may be mixed with blood and viscous sputum. Pulmonary hemorrhage may occur, which requires emergency care.
Injuries to the bronchial tubes by tumors lead to infection. Symptoms of fever appear. Intoxication of the body increases, urgent medical attention is required.
The clinical picture accompanying the development of formation is not the basis for making a diagnosis. Many respiratory system diseases are accompanied by the same symptoms.
Classification of fat formations
Lipoma in the mammary gland can be of one type or another, depending on the structure and characteristics of the contents. Highlight:
- If the basis of the lipoma is adipose tissue, but interspersed with connective tissue are present, we are talking about lipofibroma; if the latter predominates, we are talking about fibrolipoma.
- When the structure of the formation, in addition to fat, is dominated by muscle tissue, they speak of myolipoma.
- The structure of the tumor contains smooth muscle cells of the vascular wall - an angiolipoma is diagnosed.
- If there is mucus in the wen, we are talking about a mixolipoma.
Mostly wen forms in the thickness of adipose tissue, but they can also form directly under the skin or on its surface in any area, including in the area of the nipple circumference.
Most often, the wen is enclosed in a capsule (nodular formation), that is, it has a clear outline. By palpation, you can easily determine the location of the formation and its mobility. But there are also diffuse lipomas that do not have clear boundaries.
Diagnosis criteria
Lipoma is not diagnosed by clinical manifestations. The pulmonologist, having noted the clinical picture, will definitely refer the patient to a plain chest radiograph (CHX). The X-ray results clearly show the approximate location of the tumor.
Having suspected a lipoma, doctors will send the patient for further diagnostics. Usually, when it is detected, a bronchoscopy with a biopsy of tumor tissue is performed. Bronchoscopy allows you to determine the exact location of the lipoma, and the results of a biopsy will tell you about the nature of the tumor.
Doctors will make the final diagnosis after the results of the biopsy. Without tissue examination, a pulmonologist or oncologist cannot confirm or refute the diagnosis. Before this, the detected tumor is called a neoplasm.
Bronchoscopy with biopsy reveals centrally located tumors. They are found in large bronchi. If the tumor is located on the periphery, it does not manifest itself for a long time. It is discovered accidentally during routine preventive examinations.
Causes of growths
Lipomas in the breast, like those located on other parts of the body, form and begin to grow in the presence of one or several factors at once. The first and main one is genetic predisposition. Most patients with breast lipoma are over forty years old. But with poor heredity, a wen in the chest area can also appear in a young girl.
The risk of developing wen is higher among smokers and those who regularly experience severe stressful situations.
The impetus for the development of lipomas is:
- Hormonal changes caused by dysfunction of the endocrine system.
- Irregular menstrual cycle in young girls and women.
- Decreased functionality of the ovaries, failure of metabolic processes during menopause. With the growth of adipose tissue in the breast (due to age-related involution of the glands), the lipoma may be mistaken for normal adipose tissue. Pathology is revealed with a more thorough examination.
- Long-term and incorrect use of oral contraception.
- Bruise of the mammary gland with damage to its tissue.
Why education is dangerous for women, men and children
Lipoma in the breast in most cases remains a benign formation. The risk that pathology will move into the field of oncology arises if:
- the formation is large in size;
- a wen on the nipple and there is a risk of mechanical damage to tissue (trauma, bruise);
- there is a chronic disease of internal organs;
- accompanied by decreased immunity or inflamed wen;
- During pregnancy, a woman developed clearly defined painful “bursting” sensations in the chest;
- on the man’s sternum, under the skin, a formed nodular formation of a spherical shape has formed, which increases in size and is accompanied by severe painful sensations.
It is important for men to pay no less attention to breast health than for women. In men, both benign formations (in the form of lumps, dense nodes) and malignant ones can form in the chest area, since in addition to fibrous tissue, the male mammary gland also consists of fatty tissue.
The chances of their development are higher in men suffering from gynecomastia - growth and thickening of breast tissue. The entire area may swell and become particularly painful. Infants also face a similar problem due to the effects of maternal hormones, as well as children during puberty.
Preventive measures
Lipoma is not considered a very dangerous disease, but it can lead to liposarcoma. The last disease is oncological, which requires immediate consultation and treatment. As a preventive measure, experts recommend examining your breasts yourself in the first week after the last day of menstruation. The mammary glands should be palpated while lying on your back. Next, you need to examine your breasts in the mirror for bulges and asymmetry. If a woman has a hereditary predisposition, then she should carefully monitor her condition. Otherwise, the disease can lead to serious complications that are difficult to get rid of.
Source of the article: https://fb.ru/article/402338/jirovik-na-soske-prichinyi-i-priznaki-sposobyi-lecheniya
Diagnosis of lipoma
You can identify a lump under the mammary gland and differentiate it from other formations by studying the results of mammography. An ultrasound is also prescribed.
If necessary, a biopsy, histological and cytological examination may be prescribed to clarify the results. Once the benign nature of the wen is confirmed, surgical removal is usually recommended.
Since lipoma is a benign formation, there are no direct indications for its removal. The need for the operation is due to the fact that there remains a small, but still risk of degeneration of the wen into one of the malignant neoplasms (liposarcoma).
How to treat
If the size of the wen is small and there are no changes over time, the attending physician will select an individual course of conservative treatment.
In case of multiple lipomas (lipomatosis), the presence of complications and the risk of degeneration of the lipoma into a malignant tumor, surgical intervention is indicated.
Conservative therapy
Fatty deposits in the mammary gland, if they are small in size, may not require immediate removal. In this case, the patient is taken under constant observation. Repeated studies to determine the dynamics of the development of the wen are carried out every three months.
In the case of a lipoma, conservative therapy is not considered in connection with the possibility of eliminating the tumor (in rare cases, the problem can be solved by administering the drug Diprospan, which has a resolving effect, near the lipoma), but is aimed at correcting the factors that provoke the formation and development of the lipoma.
Depending on what diseases are present, their stage and severity, the following is recommended:
- balance the diet, create a menu and monitor regularity (eating at the same time), calorie content, and sufficient fiber to ensure normal stool;
- normalize water balance and consume a sufficient amount of fluid daily to prevent slagging in the body;
- identify foci of chronic infection in the body and eliminate them;
- take control of existing chronic diseases and undergo treatment if necessary.
Surgical intervention
The main indications for breast lipoma removal are related to:
- rapid growth of the wen and severe pain in its localization;
- large-sized formations that noticeably deformed the shape of the nipple or the mammary gland as a whole;
- noticed tissue necrosis in the tumor;
- genetic predisposition to lipomatosis.
The fatty tissue on the chest is surgically excised. Lipoma removal must be as precise as possible. The surgeon will select the method that is appropriate for a particular case and cut out the tumor without damaging either its capsule with fatty contents (thus the formation is completely eliminated without the risk of relapse) or the surrounding healthy breast tissue.
Methods for removing a lump on the mammary gland vary depending on the size of the lipoma, the severity of the disease and the general health of the patient. Most often we are talking about sectoral resection of the mammary gland (with mandatory histological examination of the tissue), which is performed under local or general anesthesia.
It is recommended to get rid of a lipoma in the breast as soon as the next examination reveals that the formation is actively growing and has led to impaired blood circulation in the localization area, as well as disruption of the functioning of organs and systems.
This method is preferable if the lipoma is large and the risk of its degeneration into a malignant tumor is high. If such a risk is assessed as small, removal is performed by enucleation (cleansing, “taking out” the tumor). In some cases, it is possible to remove a lipoma by applying:
- puncture biopsy (aspiration puncture) - the contents of the wen are sucked out through a puncture and a thin needle;
- radio waves - the radio knife completely removes the lipoma, minimal trauma, after the operation the rehabilitation period is short;
- laser is a highly precise operation that does not affect surrounding healthy tissue.
ethnoscience
Even benign tumors of the mammary glands cannot be treated with traditional medicine. Plants and preparations prepared from them are certainly powerful medicines, but it is important to remember that lipoma cannot be eliminated by simply affecting the skin.
It is even more dangerous to do this in the nipple area, where the skin is especially sensitive and there is an opening for the release of breast milk.
The risk of complications and infection is extremely high when trying to puncture or otherwise open a small lipoma that has formed not in the thickness of the fatty tissue (as happens in the vast majority of cases), but directly under the skin or close to its surface. Under no circumstances should this be done.
Methods for safely getting rid of wen around the nipples
Before starting treatment, it is important to undergo an examination to identify the causes of the formation on the chest, its nature and shape. During the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a number of tests and additional studies:
- A biopsy of the contents of the wen will help identify the nature of the formation and eliminate the risk of cancer.
- Ultrasound and mammography make it possible to detect the location of the formation of the compaction, determine exactly its shape and size, and the presence of complications.
- MRI - prescribed after a biopsy confirming the malignancy of the tumor. During the examination, the doctor sees the full picture of what is happening around and in the middle of the wen, the presence of metastases.
The doctor examines the test data and makes a diagnosis. In most cases, surgery is prescribed.
Based on the overall picture, the specialist selects the most suitable method of getting rid of the problem on the chest. Several methods are used in medical practice:
- Surgery is indicated if the formation is large, has signs of malignancy and puts pressure on blood vessels and tissues. The operation takes place under anesthesia, during which the surgeon removes the seal along with the capsule. The effectiveness of the operation is justified; it is possible to completely remove the tumor and eliminate recurrence.
- Laser and radio wave therapy is used in cases where the formations are benign and small in size. The defect is eliminated with a beam that does not leave scars and reduces the likelihood of relapse.
- The operation is performed under local anesthesia using a needle that sucks out the wen or injects a special medicine that promotes resorption. The puncture is used after confirmation of benignity and only with small growths on the chest, but there remains a high percentage of the likelihood of reappearance. This is due to the fact that during the process of inserting the needle, only the contents are sucked out, and the capsule remains in place and, over time, is filled with fat cells again.
Getting rid of it with folk remedies and medications is ineffective; there is a high risk of re-formation of breast wen, and in some cases even growth throughout the body. The traditional method is dangerous due to the development of an allergic reaction and consequences that will have to be treated in a hospital.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
With timely diagnosis, control of lipoma development and correct treatment, the risk of relapse is extremely low in women. It is even more small in men, in whom malignant neoplasms in the breast account for less than a percent of the total number of detected cases and most patients have already crossed the 65-70-year-old mark.
Particular attention should be paid to patients over forty years of age who have been diagnosed with fatty tumors with connective tissue inclusions (lipofibroma, fibrolipoma). Large pathology leads to deformation of the mammary glands, and its rapid growth may be a sign of degeneration into a malignant formation.
If you miss the moment and diagnose angiolipoma late, the risk of bleeding during surgery or due to the presence of blood vessels in the structure increases.
Prevention measures
The most effective preventive measures are those that apply to general obesity:
- Rationality of nutrition. Even if you have a passion for fatty, high-calorie foods, you should periodically arrange fasting days/weeks for yourself. In general, it is better not to accustom your body to junk food, so that later you do not have to strictly limit yourself.
- Active lifestyle. This is a real problem, because men spend most of their lives in front of the TV or at the computer, when they should be walking, getting involved in some kind of sport, dancing, or hiking.
- Regular medical examinations. It is necessary to promptly identify diseases that lead to obesity - thyroid disorders, imbalance of the hormonal system, problems in the functioning of the adrenal glands.
We recommend reading about correcting inverted nipples.
From the article you will learn about the causes of inverted nipples in women, men and children, classification, and correction options. And here is more information about why nipples peel.
Lipomastia is a condition characterized by frequent relapses. If a man stops following the principles of proper nutrition and exercise, the problem will return in just 2-3 months. And even if after surgery there are violations of doctors’ recommendations, you can count on a relapse with 90% confidence. But the problem can be solved, it is only important to set yourself up correctly and change your eating habits and lifestyle.