Home / Papillomas
The human body is not at all protected from various infections and viruses.
Most viruses can be infected not only through everyday contact, but also through sexual contact.
One of these is the human papillomavirus .
HPV is directly involved in the formation of skin lesions - warts, condylomas and others.
Below in the article, we will look at what papillomas on the penis look like; the photos are not recommended for children.
Causes
After direct infection, HPV in men (photos available below) begins to appear on the skin of the foreskin, on the frenulum, and also on the head.
Consequently, the entire penis is covered with papillomas.
The main causes of papillomas in the groin and on the penis itself:
- A weakened immune system, which leads to activation of the pathogenic virus.
- Infection from one partner to another.
Based on this, the following routes of infection are distinguished:
- sexual intercourse without protection;
- kisses;
- all types of sex;
- during direct household contact, when several people use personal items.
You also need to be careful if you have skin lesions , because abrasions and scratches can lead to infection with the virus. It is also very important to be safe when shaving, as this can also lead to infection.
What causes the appearance of HPV?
Before you look at papillomas on the genitals, photos of formations, you should study what causes HPV.
The immunity of a completely healthy person is able to prevent the activation of the virus.
But with an incorrect lifestyle, HPV begins to actively develop and multiply.
Risk areas:
- Promiscuous sexual relations with several partners at once.
- Unprotected sex.
- After suffering from serious viral illnesses.
- In the presence of chronic diseases.
- Drinking alcohol, smoking and drug addiction.
- Irregular and unbalanced nutrition.
Methods of infection
Transmission of the pathogen occurs in different ways:
- during everyday communication, for example, the virus can be transmitted when using shared utensils, while visiting swimming pools, saunas, using personal hygiene items (razors, toothbrushes, towels, etc.);
- through cuts, cracks, scratched places;
- when kissing and more intimate unprotected sex, including unconventional methods.
Important! The main method of transmission of the virus is considered to be sexual contact.
What are the symptoms?
The human papillomavirus in men (see photo here) can remain in the latent period for up to nine months and only after this period can it appear visually.
Neoplasms are usually localized
- on the frenulum of the penis;
- in the urethra;
- on the head of the penis;
- on the coronal sulcus;
- on the body of the penis.
In appearance, the formation of papillomas can resemble cauliflower and be white or flesh-colored. Photos of papillomas on the penis are presented below in the article.
If there is no treatment and a complication occurs, the virus spreads throughout the body, as well as near the anus . This is what a papilloma looks like in an intimate place in men, photo:
The signs of papillomas are:
- phimosis;
- the penis begins to become inflamed;
- smegma begins to accumulate in the folds of the foreskin;
- urine entering the folds of the flesh provokes the development of infection;
- erosion occurs;
- formations can be single or localized on the head in the plural.
After identifying the virus in the body, it is necessary to urgently start taking medications aimed at increasing immunity, and also consult a doctor for a papillomas removal procedure. Launched HPV is fraught with the following consequences:
- Deterioration in quality of life due to a cosmetic defect.
- Psychological disturbance during sexual intercourse.
- Possible problems with reproductive function.
- If the tumors are located near the opening of the urethra, then difficulty urinating may occur.
- The presence of the virus in the body increases the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
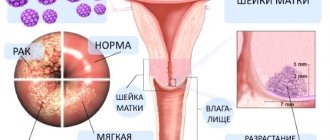
If an infected man comes into contact with his partner, then more serious consequences - pathological changes in the cervix and cancer.
The most common types of cancer that cause cancer are the following types of HPV virus (listed in order of decreasing oncogenicity):
Literally 3 days ago, material appeared online about doctors who specifically do not treat papillomas and condylomas in men (including on the genitals) in order to “pump out” more money!
What happened?
Red, white, brown warts - what does the color of the growth indicate?
Different types of warts differ in shape, location, and size. They can have different colors - flesh-colored, light, pinkish, brown. There are white and red growths.
Not all skin formations are warts. Their color may indicate the type of anomaly, the reasons for its occurrence, and also signal the degeneration of benign cells into oncogenic ones. Suspicious changes in the skin, noticed at an early stage, help to promptly seek medical help and avoid possible dangerous consequences for the body.
What does the appearance of red formations on the skin indicate?
If pink or red warts appear on the genitals or anus, this may indicate that a person is infected with papillomavirus, which causes genital warts. Their appearance on the genitals may be accompanied by discomfort, itching, and pain. HPV, which causes such growths, is transmitted through sexual contact.
The appearance of red spots and growths often occurs due to problems occurring within the body. Such formations are not considered warts, and the cause of their development is not the human papillomavirus.
The occurrence of such anomalies can be provoked by:
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas. This will be indicated by numerous dots of red shades - burgundy, bright crimson. The distribution of such formations throughout the body has its own characteristic feature - they are localized only in the upper part. With exacerbations of hepatitis or pancreatitis, the red dots necessarily increase;
- Hematological problems. With such disorders, various hemorrhages often occur. They may leave red marks on the skin;
- Lack of vitamins C and K.
A pathological change in the color of an area of the epidermis can occur as a result of its mechanical damage.
A separate group of skin formations that are red in color are hemangiomas. This name is given to benign tumors that develop from lymphatic or blood vessels.
Hemangiomas can be located on the face and body. They reach two to three centimeters in diameter and bleed heavily when damaged.
Hemangiomas can appear even in newborns. It should be remembered that in a normal state they do not manifest themselves in any way. Therefore, if you experience discomfort in the area of red dots on the skin, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Why do white growths appear?
The appearance of white warts on the genitals may also indicate the spread of genital warts. These growths can be single or multiple. Their color varies from very light to burgundy.
If white formations appear not in the genital area, but on the body, this may be an indicator of the occurrence of achromia - discoloration of the skin. Pathology often manifests itself due to the presence of the following factors:
- Progression of autoimmune diseases;
- Dysfunction of the endocrine glands;
- Long exposure to the sun;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Stress, mental trauma;
- Vegetovascular diseases;
- Hormonal surges;
- Toxin poisoning;
- Bad habits;
- Traumatization of the skin;
- Lack of nutrients and vitamins.
This is interesting: Small papillomas: do growths need to be treated?
There are cases when initially dark warts turn white. Such a change in color may indicate the degeneration of benign skin cells into a cancerous tumor - melanoma. If you notice the growth of white spots, their itching, burning or change in shape, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What does the brown color of warts mean?
Lumps of very dark color can often be observed on different parts of the body in old people. Black and brown warts occur due to age-related changes in the body. They are completely harmless and cannot be transmitted to another person.
Senile warts begin to appear after forty-five years. At first, the skin becomes covered with characteristic light brown markings, which over time thicken, darken and become convex.
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
At the initial stage, brown and black warts can be confused with age spots of the same color. However, they are distinguished by a rough surface and keratinized structure.
Sometimes the wart is not completely dark. Black and brown dots (one or more) are visible on its surface. This phenomenon may not be noticed immediately, but several months after the appearance of the tubercle.
The presence of dark dots indicates the formation of a kind of “root” at the wart. Through it, the growth on the skin receives nutrients and oxygen. Such brown cores are especially noticeable on the spines (plantar seals).
Pink, yellow, flesh-colored warts may turn brown over time. If the modification occurs gradually (over many months or years), then this is considered normal.
It is natural for the wart to turn black after treatment begins. This is exactly how the process of death of its cells can manifest itself after exposure to external cauterizing agents, refrigerants or tablets.
If the skin formation becomes very dark very quickly (in a few weeks or days) for no apparent reason, this is a signal that you need to visit a doctor. Such a color change may indicate the following anomalies:
- Joining the process of progression of papillomavirus bacterial infection;
- The beginning of inflammation of the upper layer of the wart due to possible damage to its tissues;
- Degeneration of a benign tumor into a cancerous tumor.
If there are any suspicious visual changes in growths on the skin or the appearance of warts of a strange color, you should consult a doctor. Self-medication in these cases is strictly prohibited. A person without medical education cannot make a correct diagnosis, and, therefore, determine the need and methods of treating a wart.
What does papilloma on the penis look like?
Papillomavirus in men: photo of spiky growths.
Papillomas on the penis: photo of formations on the shaft of the male penis.
Papillomas: photos of growths on the head in men.
Advanced HPV on the penis: photo of a severe form.
Now you have seen everything, even what papillomas on the penis look like, the photos show that the disease needs to be treated as quickly as possible. If you notice something strange on your penis, run to a urologist or dermatovenerologist - they are well aware of the treatment of papillomas both on the body of the penis and on its head.
Why are growths on the penis dangerous?
When a papilloma appears on the penis as in the photo, the first thing a man should do is consult a specialist. While the tests are being prepared, the diagnosis is confirmed or refuted, it is necessary to use condoms to protect the partner. The papilloma virus is highly contagious. In women, infection with some strains of this virus can lead to the development of cervical cancer. Since this disease is asymptomatic, it is very difficult to diagnose it in time, therefore, among patients with this pathology there is a high percentage of deaths.
The papilloma virus is easily transmitted during sexual intercourse
HPV negatively affects a man's health. The danger is the appearance of growths on the head of the penis. This is accompanied by:
- phimosis;
- genitourinary infections;
- erosions on the head;
- inflammatory diseases.
The appearance of warts on the glans leads to difficulty in moving the foreskin. Excess smegma and urine begin to accumulate in the folds, which creates a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microorganisms. The infection affects the head of the penis, resulting in bleeding erosion around the papilloma. The infection then spreads to the urethra and penetrates the testicles and prostate gland. Inflammation of the male genital organs is accompanied by pain, fever, and difficulty urinating.
Papillomas in men on the penis are well supplied with blood due to small blood vessels that feed the growth. Any mechanical damage leads to heavy bleeding. Due to its location, an injured papilloma is easy to become infected, which will lead to inflammation.
Any warts on the skin of the body, genitals and mucous membranes are easily rubbed with a cloth or when walking. Irritation of the growth is always accompanied by pain.
Frequent injuries, mechanical damage, rubbing during sexual intercourse or when wearing underwear are all dangerous factors that predispose to the development of a malignant process. Repeated damage to papillomas on the genitals can cause cancer, so if unsightly growths are detected, you should visit a specialist as soon as possible.
Signs of illness
After the papilloma virus enters a man’s body, visual manifestations do not begin immediately. HPV can remain in the incubation period for quite a long time - from two weeks to two months.
- When HPV is activated, it begins to manifest itself on the mucous membrane of the head in the form of neoplasms, which are accompanied by pain.
- At first, the rashes are subcutaneous and have a pink or yellowish color.
- Initially, such rashes resemble plaques.
- The subcutaneous tubercles are soft to the touch and do not cause any discomfort.
- Sometimes there may be a burning sensation and soreness.
- If the rash is in the urethra, urination will be difficult.
- Then, at an advanced stage, the papilloma grows.
- According to visual diagnostics, the neoplasms resemble warts, but are more dangerous.
- The convex growths have jagged edges and are very similar in appearance to cauliflower (the main sign that a person is infected with HPV).
- Papillomas tend to multiply very quickly and first appear in the form of massive pimples on the head of the penis.
- If left untreated, the formation will quickly increase in size and affect healthy areas of the skin.
- Most often, papilloma does not pose a threat to life, but if they are not eliminated in time, then this is fraught with degeneration into an oncological formation.
Classification
In medicine, such formations are classified into several types:
- extragenital papillomas and warts: flat, vulgar, non-warty skin formations, plantar warts, etc.;
- anogenital warts: genital warts in the form of papules, spots;
- papillomas of the mucous membranes: conjunctiva of the eye, oral mucosa, larynx, etc.
According to the course of the disease, forms are distinguished:
- latent (detected during laboratory testing);
- subclinical (erased manifestation);
- clinical (classic symptoms of infection - neoplasms, dysplasia).
It is worth noting that the asymptomatic (latent) form is most common. A separate group includes patients with severe immunodeficiency, severe condition after transplantation, as well as weakened patients. Treating the infection in such people is much more difficult.
Men's remedy against papillomas No. 1 on the market at a discount!
How to start living without papillomas right now? If you are still thinking about this question, you have come to the right place. There is an excellent remedy against papillomas and condylomas on the penis!
But there is a solution! PapillOFF, a remedy against papillomas and condylomas in men , is:
- disappearance of papillomas forever,
- quickly and painlessly (including removal from the penis),
- the result is already on the 3rd day.
And the best part! If you order today, one package costs 990 rubles! Order!
Papillomas on the penis are formations the appearance of which is caused by HPV. They are small in size and are located on the inner surface, as well as on the foreskin, on the frenulum, on the head and papillomas on the scrotum. Warts can be single or multiple.
They require mandatory treatment and removal, since their injury can cause the rash to degenerate into malignant tumors. You can learn more about papillomas on the penis in the photos that are presented on the Internet.
Diagnostics
The oncogenicity of human papilloma can be determined using various examinations. This disease is treated in men by an androgologist, urologist and dermatovenerologist.
Initially, the doctor examines the localization of the formations, after which he prescribes an additional examination, which includes:
- smear and scraping from the urethra;
- biopsy _ Examination of a tissue sample of condyloma, which is taken during removal of the growth;
- digene test . The most modern diagnostic method that determines the presence of the virus, its quantity and load on the body. Using this study, it is possible to predict the development of the disease with high probability;
- polymerase chain reaction . Allows you to determine the presence of a virus, its strain and the level of oncogenic danger;
- urethroscopy . Allows you to visually examine the changes occurring in the urethra;
- anal oncocytological smears . This test is recommended for hetero- and bisexual men.
Causes
Papillomas on the penis in men are of viral origin. Therefore, the main reasons for their appearance are infection of the body as a result of contact with a sick person. The virus enters the body in most cases during sexual intercourse. Therefore, it is important to use a condom during sex.
The following factors can also trigger the disease:
Other causes of HPV
- Infection can occur through household items used by an infected person: cutlery, spoons, forks, mugs;
- if a man’s work involves unfavorable environmental conditions. This could be the chemical, metallurgical industry, work with substances hazardous to health;
- if a man has chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- with a long history of smoking;
- the virus easily penetrates the body during infectious and colds;
- if a man suffers from insomnia, depression, or has chronic stress;
- Most often, men in old age are susceptible to HPV, when the immune system is weakened and chronic diseases of the reproductive system are exacerbated;
- for caries. Therefore, it is recommended to visit the dentist at least once every 6 months;
- with vitamin deficiency, when an insufficient amount of vitamins and microelements enters the body with food;
- with regular consumption of hot and spicy foods;
- infection occurs with AIDS and HIV.
To protect yourself from the virus, it is important to know the reasons that provoke infection in order to prevent the development of the disease in the initial stages.
How can you get infected?
The infection is usually transmitted sexually. There is also data on contact and household infection through a handshake, swimming pool, linen, and hygiene items. It is possible to transmit the infection during childbirth from mother to child (vertical route).
HPV infects epithelial cells, penetrates into the deepest layers of the skin or mucous membranes, and can persist in them for a long time. For many, the virus is eliminated from the body on its own within 12-24 months after infection.
Interesting! About half of the world's sexually active adult population is infected with some type of papilloma virus!
The peak incidence occurs between 17 and 29 years of age; at older ages, the risk of infection remains.
Treatment
The best way to treat HPV is to remove papillomas. After the diagnosis, the doctor decides how to get rid of the formations and how to treat the disease.
The most effective methods for removing growths are:
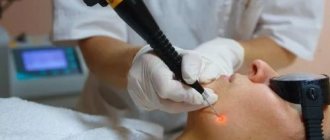
- Laser therapy, during which warts are exposed to laser beams. The growths are excised and disappear, and in their place there are no scars or scars.
- Electrocoagulation is a treatment in which growths are exposed to a certain frequency of current. Before the procedure, an anesthetic is administered to eliminate discomfort and pain.
- Cryotherapy is the treatment of warts with liquid nitrogen. As a result of such exposure, the papilloma dies and disappears on its own.
Treatment with one of the methods is prescribed only by a doctor after examination.
Some types of papillomas are dangerous because they cause cancer. In this case, the patient is examined by an oncologist and prescribed the necessary treatment.
Treatment with traditional methods
Treatment includes drug therapy and removal of papillomas. Medicines are prescribed to suppress the activity of the virus, putting it in a state of suspended animation and strengthen the immune system.
Papillomas, even small ones, cannot disappear on their own, so they are removed using one of the following methods:
- Electrocoagulation . Electric current is used to remove the build-up. A cheap but painful method that often leaves scars;
- Cryodestruction . Cauterization of papillomas with liquid nitrogen. A safer method that does not leave scars;
- Laser removal . The growths are burned off with a laser beam. Expensive, but safe and painless method of removal;
- Radiosurgery . A non-contact method of removing growths using waves of a certain frequency. An accurate and safe method that does not cause complications;
- Chemical removal . The growths are cauterized with special solutions, after several procedures they dry out and fall off;
- Surgical method . It is used for large condylomas, but rarely: it often leaves scars;
- Removal with ointments . Used to remove small, few growths. The ointment is prescribed by the doctor, but the patient can apply it independently.
The method is selected taking into account the individual characteristics and preferences of the patient. Most methods are reliable and do not require anesthesia, but in some cases there is a risk of relapse.
Prevention
Prevention of human papillomavirus plays an important role. It must be followed by infected patients, people who are susceptible to this disease. This will avoid infection or prolong remission after treatment.
- During sexual intercourse, be sure to use a condom.
- It is recommended to have a regular sexual partner.
- Take a shower every day and keep your genitals clean.
- For minor rashes on the penis, visit a dermatologist, urologist, or oncologist.
- Have an individual towel, razor, toothbrush, washcloth.
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Monitor antibiotic intake.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Normalize your diet, change your eating habits.
- If you suspect infection in your partner, carry out diagnostic procedures.
- Normalize your work and rest schedule.
- Avoid stressful situations.
Conclusion
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. And HPV is an insidious disease. The virus can stay in the body for years without showing itself. The danger of the disease also lies in the fact that the growths can be oncogenic in nature.
Therefore, it is important to visit a doctor in a timely manner, take prescribed medications and strictly follow all prescribed recommendations. This will help avoid dangerous and serious complications in the future.
Papillomas on the penis are neoplasms in the form of a growth that appears on the surface of the phallus.
The pathology is viral in nature. The causative agent is considered to be human papillomavirus (HPV).
When the immune system is weakened, the virus enters the nucleus. The cell begins to change. Over time, this place thickens and grows in the form of papillae . Growths can form on the head of the penis, its crown, frenulum, and the inner part of the foreskin. Clinical manifestations of the disease do not appear immediately . The incubation period lasts from 1 to 12 months .
Symptoms
Once in the body, the papillomavirus may not manifest itself for quite a long time. The first signs of the disease are warts or papillomas. The incubation period of the infection lasts about 3-6 months, in rare cases it can increase to a year.
In 90% of all cases of infection, self-healing occurs. Another part of men develop clinical signs of the disease of varying severity. This is due to the type of virus, its titer and the state of the immune system.
Most often, men develop formations in the form of genital warts, papillomas, and warts.
Condylomas acuminata
They are light pink, elongated growths on the mucous membranes and skin, having a characteristic pattern and structure.
Most often they appear in places that are subject to the greatest friction during sexual intercourse: the head of the penis, the foreskin, the anal area (during anal sex). After infection, such formations form gradually. When merging, their sizes increase somewhat, which often causes unpleasant consequences (bleeding and injury). On palpation, condylomas are mobile, painless, the skin around them is unchanged.
Most often they appear in the groin, pubic area, and inner thighs.
A man may experience the following symptoms:
- burning, itching;
- cramps, pain and discomfort when urinating;
- bleeding of condylomas with the appearance of non-healing cracks;
- unpleasant (sometimes extremely painful) sensations during intimate relationships;
- when large condylomas appear in the urethra, there is difficulty in ejaculation and emptying the bladder.
Complications:
- trauma with possible secondary infection;
- phimosis (narrowing of the foreskin);
- bleeding.
Warts
In men, such formations can form on the body of the penis, on the foreskin, in the perineum, on the scrotum, near the anus. They look like papules (nodules) without growths or protrusions.
They can affect not only the mucous membranes of the genital organs and skin, but also be located on almost all parts of the body: torso, limbs, neck, head and face, soles and palms.
Types of warts:
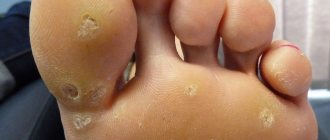
- palmar-plantar - have dark inclusions on their surface and cause discomfort when walking;
- thread-like - located on the skin of the face, eyelids, neck, chest, and forearms. They look like mobile protrusions of flesh color;
- flat and vulgar warts are up to 0.5 cm in size and often have multiple growths. They are found on the dorsum of the foot and cysts;
- cystic and mosaic are also localized on the surface of the foot. They differ from the palmoplantar ones in appearance and structure.
Why do papillomas appear on the penis?
There are two reasons for the formation of papillomas on the male penis and its head:
- infection with HPV from a person who is a carrier of the virus;
- decreased immunity in the carrier of the virus. HPV can be found in blood and saliva. You can become infected with it:
- with unprotected sex (vaginal, oral and anal);
- through a kiss;
- during blood transfusion;
- when carrying out medical work with non-sterile instruments;
- during everyday contact (for example, in a bathhouse, swimming pool, when using only hygiene items, clothing).
Mostly, papillomas on the penis (photos below) appear in men who have promiscuous intimate relations .
Constantly changing sexual partners and refusing to use protective equipment increases the risk of infection many times over . The body of a healthy man easily inhibits the vital activity of HPV.
Papillomas are activated due to a weakened immune system . This happens in the following cases:
- the presence of chronic infectious diseases (especially STDs);
- AIDS, HIV;
- taking antibiotics;
- persistent colds;
- hormonal disorders;
- stress;
- frequent hypothermia;
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- harmful working conditions.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection comes down to an initial examination of the affected area, collection of biomaterial for examination (smear from the urethra, biopsy of the formation). The resulting material is examined using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA hybridization (Digene-test). Tests can determine not only the presence of HPV, but also the genotype of the virus, as well as the viral load.
Less commonly, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is performed to detect antibodies to the human papillomavirus (immunoglobulins class G and M) in the patient’s blood.
What are the types of papillomas on the penis: types and features
Papillomas of the male genital organs are flat and pointed . The first type is similar in appearance to plaques. Flat formations rise slightly above the surface, are grouped and cause itching. The second type is also called condylomas . Sometimes they are called warts.
Usually, several elongated formations develop from the point, resembling a bouquet of flowers or cauliflower. Genital warts are easy to damage and cause additional infection in the wound. Most often they are located throughout the phallus.
There are many different human papillomaviruses known in medicine. Some affect intimate areas and cause cancer . All types of HPV are divided into 3 types according to the degree of risk:
- HPVs do not cause cancer . This group includes types 1, 2, 3, 5 of the virus. Formations of this type are warts that grow on the surface of the skin, creating an aesthetic defect and inconvenience.
- HPV that carries low levels of cancer . These include types 6, 11, 42, 43, 44. This group includes condylomas. Despite the low likelihood of developing cancer, it is worth carefully monitoring the condition of the body in the presence of these strains. Any injury to the papilloma can cause an infection, which, together with HPV, will affect healthy cells with enormous force.
- HPV carries a high degree of cancer . These are 16, 18, 31-35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68 types. These viruses, when the immune system is weakened, actively affect healthy cells and destroy their DNA, which subsequently leads to the development of cancer. They are less treatable and rarely go away on their own.
If you detect oncogenic type HPV on your penis, do not despair.
Contacting a specialist at the beginning of the development of the disease will allow you to avoid its further development and consequences.
Mechanism of disease development
The human papillomavirus is widespread among modern people. Experts believe that it is present in the body of the majority, but until a certain time it is in an inactive state. It begins to actively multiply and form papillomas when exposed to unfavorable external and internal factors:
- traumatization of mucous membranes and skin;
- decreased immune defense due to general weakening of the body, surgery, stress;
- exacerbation of any infectious and inflammatory processes;
- sexually transmitted diseases, urogenital infections;
- presence of herpes virus in the body;
- promiscuity.
All tumors that:
- often injured and inflamed;
- change color;
- hurt or itch;
- prone to group arrangement, massive fusion;
- grow quickly;
- have a high oncogenic risk;
- cause exacerbation of chronic infections of the genitourinary organs.
First of all, neoplasms whose oncogenicity has been confirmed by laboratory diagnostic results are subject to treatment. If skin growths are detected, specialists prescribe an examination - a PCR test, during which the type of virus can be determined and the degree of its oncogenicity can be determined. For any localization of papillomas, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, based on examination data.
Symptoms
Papillomas on the penis look like small neoplasms (cauliflower-shaped), single or multiple, flesh-colored without pronounced signs. The man complains only about the unaesthetic appearance.
When papillomas form on the head of the penis, a certain discomfort, itching and burning occurs during intimacy . Huge condylomas cause pain at the slightest touch of the affected area and have an unpleasant odor.
The following stages are distinguished in the development of pathology:
- Phimosis.
- Accumulation of smegma and development of infection.
- Inflammation of the head and leaves of the foreskin
- Formation of erosive defects on the head of the penis and foreskin. This manifestation is considered the first stage of cancer.
Features of the course of human papillomavirus infection in men
Under natural conditions, most viruses are low-pathogenic due to low infectivity and resistance of hosts to infection. Having penetrated a human cell, a DNA virus most often does not integrate into the cellular genome. Instead, a protein (or group of proteins) encoded by the viral genome rapidly activates the cell's DNA replication system. If the virus replicates synchronously with the cell without harming it, an infection of a non-productive type develops,” otherwise this process is called persistence or asymptomatic carriage.
If the virus multiplies rapidly in a cell, the process is called asymptomatic carriage, or releases thousands of active viral particles. This period is characterized by the appearance of rounded formations and growths on the skin and mucous membranes.
However, HPV types 16 and 18 can integrate into the cell genome without hijacking cellular genes. This phenomenon is called “insertional mutagenesis,” and the gene thus changed is inherited by all descendants of a given cell. As a result, oncogenes are activated and a tumor appears. Thus, these cells are inherited by all descendants from the moment the fetus is formed, during the woman’s pregnancy and the birth of the child.
Diagnosis
If signs of papilloma are detected on the penis, you should immediately contact a urologist . The doctor evaluates the patient’s complaints, asks the necessary questions and conducts an examination. The urologist pays special attention to formations on the head of the penis, in the anus and in the perineum. To identify the cause of development and make an accurate diagnosis, a number of examinations are carried out. These include:
- microscopic examination;
- PCR diagnostics (determining the DNA of the virus and its type);
- cytological examination of smears and fluid;
- histological examination of tissues taken for biopsy (performed if oncogenic type HPV is detected).
Based on the results of examinations and visual examination, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment, which should be started immediately.
Diagnostic measures
The set of diagnostic procedures includes:
- Examination by a urologist. The doctor will examine the area where the formations are concentrated and determine the extent of the virus. The characteristics of the patient are taken into account: the age of the formations (when they arose), the presence of chronic diseases of the reproductive system, lifestyle;
- PCR tests are carried out to determine the presence of the virus and the number of its agents in the body. The analysis allows you to obtain comprehensive information about the type of HPV (oncogenic, non-oncogenic). Any biological fluid of the patient is suitable for the study: blood, urine, semen, secretions;
- Biopsy, which consists in taking a microscopic section of the body of the papilloma for the purpose of its detailed examination
How to get rid of papillomas on the penis
Treatment of papillomas on the glans and skin of the penis involves an integrated approach . It includes 2 methods: conservative and radical.
Conservative therapy
There are several ways to treat papillomas on the penis, they include:
- treatment of chronic diseases;
- treatment of viral diseases;
- increasing immunity with the help of immunomodulators and vitamin complexes.
Radical methods
Doctors recommend removing formations in intimate places. The radical method is selected individually for each case based on the results of a preliminary examination, tests and individual wishes of the patient. There are several ways to remove papillomas on the penis. This:
- surgical exposure;
- cryodestruction;
- laser beam removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- radiosurgery;
- Chemical destruction.
Surgical exposure
This method involves removing growths with special instruments under local anesthesia.
It is used only for condylomas of large parameters and if biological material is needed for further research. Preliminary preparation of the patient is required.
After the procedure, a suture is applied. Restoration of functionality usually occurs within a month.
Video of removal of papillomas on the penis:
Cryodestruction
Cryotherapy is the removal of papillomas on the penis with liquid nitrogen. When a small drop of the substance gets on the papilloma, its protein structure is destroyed and further falls off. A crust forms at the site of the removed condyloma.
Complete regeneration within 10–14 days. itself does not require preliminary preparation and does not last long . It can take place either under local anesthesia or without it. The method is affordable and effective.
Cryodestruction is used in the presence of genital warts in a single quantity. If there are many growths, several sessions are required. The disadvantage is the likelihood of condylomas re-growing if they are not completely cauterized.
Laser
When removed by a laser beam, it is exposed to a focused beam. Duration - no more than a minute.
Under the influence of a laser beam, the papilloma is dried . With preliminary anesthesia, the procedure is painless. At the site of removal, crusts remain, which disappear within 2 weeks. There is a risk of scarring .
The method is used for multiple condylomas or when they are densely concentrated at one point. Laser procedure is one of the most effective methods and is worth paying attention to if you are looking for how to get rid of papillomas on the penis . The most significant disadvantage is the high cost.
Electrocoagulation
This is the effect of electric current on the pedicle of condyloma acuminatum. As a result, the tumor disappears .
Under the influence of an electric discharge, the vessels are sealed. Before the procedure, it is advisable to perform superficial anesthesia. Pain is felt after the anesthesia wears off. The wound heals in 2 weeks . There is a risk of scar formation.
Electrocoagulation is recommended for use in difficult situations or when necessary to examine biological material.
Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery involves the removal of formations on the penis using radio waves from a special device “Surgitron”. The exposure process is similar to laser .
Anesthesia is first performed with a special agent. Using this method, all growths, even large ones, are removed in one session. Advantages: painlessness, short recovery period and absence of complications . But the procedure is expensive and for this reason is not used everywhere.
Chemical destruction
The method of chemical destruction involves the use of medications that contain organic acids and chemicals.
The product is applied to the papilloma. As a result, the cell is cauterized and destroyed . The main advantage is accessibility.
Now you know how to remove papillomas on the penis, all that remains is to choose the removal method.
Treatment and disposal of papillomas
Note! Typically, any neoplasms on the mucous membranes and skin in the genital area are recommended to be removed after examination to ensure that the papillomas are benign.
If warts that appear on the arms, legs, armpits, neck, etc. can not be removed, then it is most often recommended to get rid of tumors on the penis immediately: they are vulnerable and are always a source of danger for a man and his sexual partners.
The growths are removed exclusively using a radical method, using the following techniques:
- Laser therapy has almost no contraindications, is performed under anesthesia, and traces remain after removal.
- Electrocoagulation is the cauterization of papilloma using electric current, a rather painful procedure.
- Radio wave therapy is the safest and most effective intervention, does not leave scars, and is often used to remove multiple and fused papillomas.
- Chemical coagulation, cauterization with chemicals, is very painful, has a long rehabilitation period, and is rarely used when removing papillomas in the intimate area.
- Cryodestruction affects neoplasms with nitrogen, low temperatures affect pathological tissues without affecting healthy ones, and is well tolerated by patients.
- Surgical intervention is performed less and less often, after surgery there are always scars
Drug treatment
Along with surgical actions, drug treatment is prescribed aimed at suppressing the virus and increasing immunity . All immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs are prescribed only by a doctor.
Pharmacy products for removing papillomas are often very aggressive, and their use, especially in areas where the risk of contact with mucous membranes is quite high, is strictly not recommended.
Folk remedies for removing papillomas
Celandine, garlic juice, propolis, and rowan juice are often used as non-traditional methods for removing warts. Papillomas are lubricated with egg white, tea tree oil, and vinegar. To strengthen the immune system, take echinacea tinctures, rose hip decoctions, and ginseng tinctures.
Note! HPV is too serious a disease. Removing papillomas on your own can have disastrous consequences: burns, infection, relapses, proliferation of papillomas. Medicine does not recommend using traditional methods to get rid of any warts, especially those located in the intimate area.
Complications of the disease
The consequences of developing growths on the penis depend on the type of HPV. The most dangerous is cancer of the male genital organ .
A larger spread of papillomas can cause cancer in the prostate, urethra, bladder, scrotum or anus.
Papillomas on the penis in men cause inflammation, erosion of the head, and phimosis. There are also problems with potency, the functioning of the urinary system and the reproductive system.
Symptoms of HPV in men
A specialist can diagnose human papillomavirus infection only after the appearance of warts . Symptoms indicating human papillomavirus infection are obvious only when visible growths appear in the genital area.
Possible complications
The severity of the disease is that the papillomavirus penetrates deep into the tissue. HPV suppresses the immune system, weakening the body and making it vulnerable to other infections. Condylomas grow, become vulnerable, and begin to bleed at the slightest injury. Their growth can cause:
- reduction of the foreskin;
- concentration of the secretion of the sebaceous glands and urinary fluid in the folds of the flesh;
- problems with the mucous membrane and the appearance of erosions.
In a more severe form, papillomas cover the anal area.
A wart is a formation filled with microscopic vessels. Any mechanical injury results in bleeding and pain.
What is the danger of papillomas for men?
Treating growths on the penis only as an aesthetic nuisance is a big mistake.
Ignoring the problem leads to an increasing number of growths on the penis. And if in the early period these were single neoplasms, then later entire colonies appear on the skin.
Important! The resulting wounds do not heal well and can later turn into cancerous tumors.
Danger for women
During sexual contact, genital papillomas caused by oncogenic HPV can cause infection of the partner . For women, the presence of oncogenic types of virus in the body is directly related to cervical erosion and, as a consequence, a high risk of developing malignant processes.
Photo 2: The appearance of papillomavirus in a husband is dangerous not only for his other half, but also for unborn children. HPV can be transmitted in utero: from mother to fetus. Source: flickr (Alexander Balakin).
Preventive actions
Prevention of the occurrence of papilloma on the penis (photo shown above) includes:
- using a condom during sex;
- Contacts with one regular partner;
- careful care of the genitals;
- use of personal hygiene products;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- maintaining a proper diet;
- diagnosing viral diseases in yourself and your partner;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- regular preventive examinations with a urologist.
any disease than to treat it. A responsible attitude towards your health and a timely visit to a urologist when symptoms of the disease appear will help you avoid many serious complications.