Papillomavirus is a disease that activates the process of epidermal cell division, which results in skin growths. In women, it can provoke the progression of erosion to dysplasia, the development of which leads to cervical cancer. HPV is observed in 80% of the world's population. Treatment of human papillomavirus in women is carried out after an examination to determine the type of pathogen.
Which doctor should I contact if I have HPV infection in women?
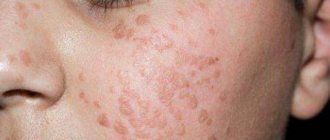
Papillomas appear on different parts of the body and have different shapes, colors, and sizes. To find out the type of formations, women should consult a doctor. First you need to consult a therapist, who, upon examination, will determine the direction of the examination. You may need specialist advice:
- dermatologist;
- gynecologist;
- oncologist;
- venereologist.
The dermatologist will determine the type of symptoms. The gynecologist will check the condition of the genital organs, the presence of erosion and other pathologies. The oncologist will do a test to determine the patient’s predisposition to developing malignant tumors.
An examination by a venereologist is necessary to exclude sexually transmitted diseases that can trigger the activity of the papillomavirus.
If they are, the doctor will select the appropriate treatment for the woman.
Diagnostic methods
For diagnosis, the patient can contact a gynecologist, urologist, proctologist, dermatologist, or even a therapist if he is not sure about the nature of his growths. The doctor can give an initial conclusion based on the external signs of the virus, but to clarify the details, different types of studies are prescribed. These include:
- Colposcopy. Thanks to a colposcope, the gynecologist is able to repeatedly enlarge the image showing the mucous membrane of the genital organs from the inside. The procedure allows you to examine the vagina and cervix in detail, so the doctor can notice the appearance of even small tumors. The peculiarities of the course of HPV are such that growths can form even on the internal genital organs, so examination with a colposcope is a mandatory diagnostic step.
- Cytology. This research method is based on taking a smear from the affected membrane at the site of exposure to the virus. After collection, the smear is examined under a microscope and checked for the presence of malignant cells. The results of cytology are interpreted as follows: group 1-2 indicates the absence of pathology, group 3 indicates the need for other studies, since the diagnosis is in doubt, group 4-5 indicates the presence of malignant changes.
- Histology. For the procedure, a piece of biomaterial is also taken from a certain area of the body, after which the data is examined under a microscope. The difference between this method and the previous one is that it is not a smear that is analyzed, but a small piece of growth. This way you can more clearly see whether oncological changes are occurring in a specific area.
- PCR diagnostics. One of the most common tests, based on taking a smear from the vagina or urethra. The method is considered quite sensitive and allows you to detect not only the presence of the virus, but also identify specific strains. The PCR test is also used to track the concentration of the virus, which helps to see how effective the treatment was.
- Digene test. Intended primarily for screening examinations of women, as it effectively detects precancerous conditions. The material for collection is a smear taken from the vagina. The test can also be used as an additional study to clarify the results of other tests.
Each test should only be performed under the supervision of a specialist. If diagnostic rules are not followed, there is a possibility of obtaining a false positive or false negative result, the latter being more common.
Video from our practicing dermatovenerologist:
What types of papillomavirus do not require treatment?
The infection is transmitted by contact: during intimate intimacy, when using other people's towels, through microtraumas on the skin. Favorable conditions for the growth of papillomas:
- Immunodeficiency.
- Pregnancy.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Weak immune system.
- Frequent colds.
- Chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys, genital organs.
- Diabetes.
- Abortion.
- Lack of vitamins, minerals.
Nursing mothers, women who began sexual activity early and often change partners, and those with AIDS are predisposed to contracting papillomatosis. The risk of the disease increases with alcohol abuse, drug addiction, and long-term smoking. A woman who has papillomas, condylomas on the vagina, the outer part of the vulva, during conception and childbirth can infect the child. Doctors recommend getting rid of growths and treating the cause.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
With a strong immune system, the body blocks the action of the virus, preventing it from spreading and forming dangerous growths. The degree of protection depends on the type of HPV, which is divided into three groups according to the level of oncogenicity. Determining the type of virus makes it possible to identify patients with an increased risk of developing cancer.
The first group includes viruses that are not capable of causing cancer and the proliferation of papillomas. They do not require specific treatment; they appear in single growths, which may disappear over time. The second group includes weak strains with low oncogenicity. They do not cause cervical cancer, but they do create the right conditions. The third group is types with a high level of oncogenicity. In women infected with this strain, 80% develop cervical cancer. Treatment is necessary, which involves timely and reliable blocking of HPV. The third option includes the viruses presented in the table.
| Virus index | View | Properties |
| 16 | A large number of flat, wide spots in the genital area. They have a rough, dense surface, gray, brownish color. | Destroys the body's natural defenses against tumors at the intracellular level. |
| 18 | Condylomas, papillomas in the armpits and genitals are prone to growth. Warts are red. | Interferes with the functioning of the immune system, provokes the occurrence of benign formations. |
| 31 | Papillomas near the vulva, in the vagina. | Symptoms do not appear for a long time. Causes pain during intimacy and bleeding. Promotes cervical cancer. |
| 33 | Pointed growths, warts on the genitals, with a wide stalk. | Activates the carcinogenic process, creating favorable conditions for the development of oncology. |
| 35 | Condylomas with an acute ending. Instantly grow, turn into spreading spots | They provoke chills, weakness, and high fever. |
| 39 | Papillomas, thin condylomas located on the walls of the vagina, in the area of the cervical canals. | Accompanied by malignant formations. |
| 45 | Warts, multiple small papillomas on the genitals. | Long latent state. Provokes the development of dysplasia and oncology in the cervical area. |
| 51 | Warts, flattened bright condylomas, dense pointed growths on the genitals, near the eyelids, in the armpits. | Benign tumors. |
| 56 | Warts, condylomas with a thin long stalk, growing on the walls of the vagina. | Has a short incubation period. |
| 59 | Warts, small papillomas growing on the genitals, in the anus. They have a rough, dense surface, torn edges, and large sizes. | Causes anorectal tumors. |
Mechanism of infection: causes and predisposing factors
Papillomavirus is a classic infection transmitted primarily through sexual contact.
There are more than 40 strains of viruses that infect the female genital tract.
Infection occurs directly through sexual contact, as well as through household means.
The latter option is possible when using public sanitary facilities where disinfection rules are not followed.
The virus can survive in baths, saunas or toilets for up to several hours.
However, more than 90% of cases of infection occur after unprotected sexual contact.
After entering a woman’s body, the virus penetrates the epithelium of the mucous membrane, where it multiplies.
From the moment of infection to the appearance of clinical symptoms, at least 1 month usually passes.
Formally, no person is protected from possible infection.
However, the infection can remain dormant for a long time.
Moreover, with strong immunity, the human body’s defense mechanisms destroy the papillomavirus.
However, there are predisposing factors that provoke the rapid proliferation of a dangerous microorganism.
These include:
- low level of hygiene
- chronic genital tract infections
- HIV
- vaginal candidiasis
- varicose veins of the pelvic organs
- alcohol abuse
- frequent change of sexual partners
The most important condition for the progression of the human papillomavirus is the presence of a reduced immune status of the female genital area.
Once the body's defenses are depleted, HPV multiplies.
Which leads to the appearance of clinically significant symptoms.
Treatment methods for papilloma virus in women
Growths on the outer layer of the epithelium, in the vagina, on the outer surface of the vulva and near it are noticeable upon superficial examination. The gynecologist must determine their presence inside the woman’s genital organs and, if necessary, send the patient to an oncologist. The following methods are used for medical diagnostics:
- Colposcopy.
- Blood and urine examination.
- PCR testing.
- Cytological tests.
Based on the results, a drug or surgical treatment regimen is selected.
Antiviral drugs
The fight against HPV involves the use of antiviral drugs, the course is set according to the degree of infection and localization. The drugs destroy the DNA of the virus and prevent its reproduction. Available in the form of tablets, ointments, injections, suppositories. They prevent papillomas from spreading on the mucous layer, the epidermis.
Valtrex and Groprinosin are prescribed. Valtrex contains valacyclovir, which blocks the DNA of the virus. Groprinosin has antiviral and immunomodulatory effects.
At the initial stages of HPV development in women, Famvir and Amiksin can be used. The drugs have no contraindications and do not require a long course of use. Effective treatments include: Viferon tablets, Allokin-alpha, Ganferon suppositories, Epigen-intim gel. Medicines are prescribed in combination and supplemented with vitamins and drugs to strengthen the immune system.
Detecting the virus and determining its type
HPV testing is considered a necessary measure, since 51 types of the virus and several other strains that are highly oncogenic after many years of dormancy can cause dysplasia, cervical tumors or penile cancer.
Timely diagnosis will help not only to detect the presence of papillomavirus, but also to prevent the development of a malignant process. The examination is normally not difficult and includes several stages:
- Examination of the patient to determine external signs of the virus.
- Collection of biomaterial for histological examination.
- Laboratory tests to confirm the presence of HPV, determine its type and viral load.
In the last century, the main way to detect the virus was to treat the lesion with a 5% solution of acetic acid. Over time, new methods for diagnosing papillomavirus were developed and introduced, which are successfully used today.
- Colposcopy. Examination of the entrance to the vagina, its walls and part of the cervix using a special device.
- Biopsy. Taking a sample of the affected tissue to determine the morphology.
- Histology. Determination of the structure of cells and the dislocation of their layers.
- Cytological screening of Pap smears. Detection of endometrial or cervical cancer by drying and microscopic examination of cellular structures.
- PCR. Genetic study of material to identify the type of pathogen.
- Digene test. Determination of the presence of one or more oncogenic types of papillomavirus.
The last two methods are considered highly informative and allow you to have a complete picture of the disease. Based on the results of the data obtained, the doctor prescribes effective treatment.
Can it be cured at home?
Those who intend to get rid of papillomas at home should remember: you cannot treat HPV on your own!
Cauterization, smearing with celandine, vinegar, garlic pulp and other folk methods can lead to complications of the disease.
Alternative medicine can only be used to improve the functioning of the immune system, not as a treatment. To do this, you can drink echinacea tincture, a decoction of elecampane roots, lemongrass, thyme, drink aloe juice, propolis, and honey. Long walks in the fresh air, light morning jogging, and gymnastics strengthen the immune system.
How to treat: drugs and topical products
Regardless of the type of strain, antiviral therapy combined with immunomodulators is prescribed. The preparation of tactical therapy for 16 and 18 viral strains is associated with the localization of papillomatous rashes.
Clinicians identify 2 main directions in the treatment of human papillomavirus infection:
- A course of drug therapy is the preferred and main method of treatment;
- Surgical intervention to eliminate external manifestations, as well as in case of dangerous localization of papillomas (urethra, cervix, bladder).
The general course of therapy for both types of strain is no different, and the duration of therapy is practically the same.
In both cases, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Immunomodulators: Transfer Factor, Cordyceps, Interferon, Genferon, Viferon, Derinat;
- Antiviral: Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Isoprinosine, Alpizarin.
Be sure to use topical agents for external rashes: Viferon, Acyclovir, Superchistotel, Panavir, Aldar. The use of drugs must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
In case of infection with the 16th strain of HPV, damage to the mucous membranes of the cervical canal, uterus, and vagina occurs, so doctors additionally prescribe drugs for vaginal administration:
- Laferomax,
- Genferon,
- Viferon,
- Panavir,
- Proteflazid.
When infected with strain 18 of HPV, the bladder and urethra are affected, and problems with urination may occur.
In this case, the following is prescribed:
- Uroseptics for urine sanitation: Furadonin, Furamag;
- Diuretics: Diuver, Hypothiazide;
- Suppositories: Laferomax, Proteflazid.
In the case when the neoplasm is damaged and a bacterial infection occurs, then the introduction of symptomatic antibacterial therapy is necessary. Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin are excellent for such purposes. These water-based preparations are suitable for douching.
How to prevent dangerous complications from occurring
HPV must be treated in full accordance with the doctor’s prescriptions, otherwise complications may arise. The course of taking medications for women is long and cannot be interrupted. If an allergy occurs, you should consult a doctor to avoid consequences.
It is important to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, maintain hygiene, and give up promiscuity, alcohol, and drugs. Learn to react calmly to stress, regularly visit a gynecologist, follow a diet that excludes fatty, salty, spicy foods.
Viruses with high oncogenicity will not cause cancer if a woman receives the correct treatment and constantly takes care of her health. It is necessary to avoid stressful situations, overheating, hypothermia, periodically take a course of vitamins, and do not forget about preventive measures. After surgical removal of growths, it is necessary to keep the lesions sterile and treat them with anti-inflammatory drugs several times a day until complete healing. These tips will help prevent complications from occurring and bring the virus into a dormant state.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Features of the development of HPV 51 in the male body
When human papillomavirus is detected in a laboratory setting in a man, experts immediately note a high threat to his health and vital functions. The lack of adequate therapy in the presence of genotype 51 in the body several times increases the risk of normal cells degenerating into cancer cells.
The infection may remain hidden for many years. Doctors note the likelihood of developing malignant neoplasm of the anus. The most common location for condylomas is the head or shaft of the penis, the foreskin, the urethral opening, the corners of the mouth, the anal area, and the coronary groove. The virus initially manifests itself in the form of single papillae, which gradually grow, merging into a single whole.
If HPV 51 is detected in men, then treatment consists of removing growths and strengthening therapy.
Chemical destructive methods for removing papillomas
To implement therapy, concentrated solutions of acids, alkalis and other chemicals are used. Thus, Feresol, hydrogen peroxide, quinacrine and khingamine in liquid form, medications, including salicylic, lactic, acetic, nitric acids, juice of herbaceous plants - thuja, celandine - can be used. It is noteworthy that the effect of all these drugs is difficult to predict, as well as to predict possible side effects. There are very few full-fledged studies providing statistical data. At the same time, there are a number of drugs, the picture when used is more or less clear. Thus, foreign doctors and domestic specialists prescribe trichloroacetic and nitric acid without any particular concerns; in addition, an acid-containing medicine, solcoderm, is used.
Removal of papillomas with trichloroacetic and nitric acids
As for the first medication (TCU), when treating HPV it should be in a concentration of 80-90%. After application, it leads to local necrosis (death) of newly formed cells. A solution of nitric acid acts similarly. This destructive method is quite popular due to its low cost and ease of operation.
Indications for use are condylomas of the female external genitalia and the head of the male penis. Exposure to acid is also appropriate if there are contraindications to the use of cystotoxic methods or laser therapy. Also, with caution and only in extreme cases, TCA is prescribed when vaginal and urethral papillomas are detected. The percentage of effectiveness of such drugs reaches 70-80. A third of patients suffer from ulcers and weeping after treatment.
Removal of papillomas with solcoderm
An aqueous solution for external use, the active components are the decomposition products of several organic acids - oxalic, acetic and lactic, as well as nitric acid and metal ions. The drug stands out significantly from other medications used when using destructive methods of treatment. Solcoderm is characterized by the following properties and mechanism of action:
— leads to instant fixation of the tissue;
— affects only the application area;
— the damaged area changes color immediately after treatment with the solution;
- tissue, the development of which is suspended, undergoes a process of mummification - it dries out and darkens;
- the resulting necrotic tissue is rejected on its own.
At the same time, solcoderm rarely leads to any complications (infection or scarring), and the healing period of the area is short. The treatment does not require special conditions or equipment and is therefore carried out on an outpatient basis. Prescribed for genital warts of any location; a one-time application of the solution is sufficient.
What are immunomodulators
Immunomodulatory agents include drugs of a chemical and biological nature that can modulate (inhibit or stimulate) immune responses. At the same time, the immunological effect of immunomodulators depends on the initial state of a person’s immunity: these drugs reduce high and increase low levels of immunity. This postulate especially applies to interferon preparations. Immunotherapy also includes treatment methods based on the use of immunotropic agents for diseases in the pathogenesis of which there are disorders affecting the immune system.
The main criterion for prescribing immunomodulators is the clinical picture of the disease (acute or chronic infectious-inflammatory process), which is accompanied by a decrease in immune parameters and is difficult to treat. In this case, immunomodulators play the role of the main assistant, which promotes effective therapy and relieves the manifestations of many diseases.
Since HPV infection is also a disease that is quite difficult to combat, and the outcome of treatment depends on the state of the immune system, various immunomodulators are widely used in the treatment of this infection.