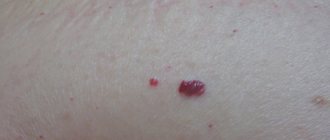
The presence of various neoplasms and warts on the skin indicates infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). It is very unpleasant when papillomas appear in the throat; a photo of the neoplasm is presented below. Despite the large variety of HPV, only some strains of the virus cause growths in the mouth. If at the very beginning the neoplasms are practically not noticeable, then over time the person begins to feel discomfort, difficulties arise with breathing and eating. In addition, papillomas in the mouth can become injured and infected, which will lead to their inflammation, so doctors recommend the only way out of the situation is to remove the tumors.
Short description
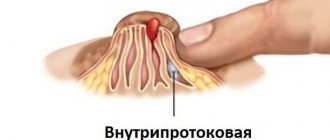
Papilloma is a specific benign neoplasm that is often found on the mucous membranes and internal organs. The virus can infect the esophagus, larynx, uvula and soft palate. Externally, papillomas are very similar to ordinary warts, which are attached to the surface of the epithelium by a thick or thin stalk. The growths are flat and round. The disease itself is called papillomatosis. In difficult situations, pathology not only interferes with speaking normally, but also makes breathing difficult.
During the examination, a specialist can identify either one wart or a whole scattering of warts in a patient. Due to the predominance of connecting elements, the growths have a characteristic pink color. Patients need to treat pathology with caution, since under the influence of unfavorable factors, neoplasms can degenerate into malignant melanoma.
Is it necessary to remove papilloma?
The peculiarity of papillomas is their unpredictability. In 40% of cases this is a harmless skin formation. In some cases, they contribute to degeneration into warts or malignant neoplasms.
Symptoms at the initial stage of the disease:
- slight discomfort in the throat;
- sensation of a foreign object;
- cough;
- frequent sore throats.
When the tonsils are affected by papilloma, sore throats are more severe: with swelling that blocks the airways.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Types of anesthesia in dentistry - local, infiltration, drugs
As the growth increases, the patient’s well-being worsens due to constant coughing. Papilloma makes breathing difficult and interferes with speaking.
But why tonsils in the holes can appear after a sore throat and what medications can cope with such a problem is described here.
In the video - is it necessary to carry out operations:
According to the degree of growth, papillomatosis is divided into:
- defeat in a separate area;
- on several;
- obstructive, blocking the windpipe.
Papilloma requires removal if there is a risk of its increase in size or the appearance of new growths.
You may also be interested in information about what stomatitis on the tonsils looks like and what pharmaceutical drugs should be used first.
The immune system can overcome single, small papillomas on its own within one to two years. In other cases, treatment is prescribed.
Types of papillomas
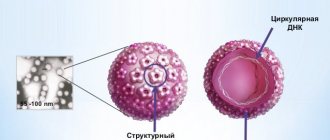
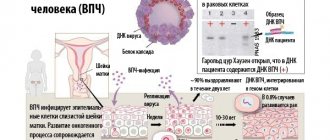
Experts have conducted many studies that have shown that more than 90% of the world's population are carriers of the HPV virus. After activation of the disease, a change in the structure of the epithelium occurs, which is why various growths and compactions appear. The case when the larynx is affected by multiple papillomas is considered difficult. In most cases, tiny growths do not show themselves. But the course of the disease is individual.
Today, experts count more than forty varieties of the papilloma virus that can infect the human throat:
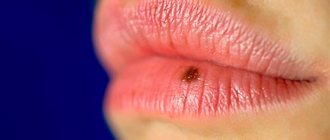
- Vulgar growths. These are common warts on the mucous membrane that often affect the oral cavity. Most often found on the surface of the palate or gums. The pathology is contagious. The disease does not depend on the person’s age and can be diagnosed in a small child.
- Squamous cell papillomas of the larynx. One of the most common benign neoplasms. During examination, growths can be found on the frenulum and tongue, the mucous surface of the lips and the palate. Such formations have a characteristic white color.
- Genital warts. Most often they affect the human genitals, which is why they are classified as sexually transmitted diseases. In the oral cavity, growths can be localized on the mucous surface of the lips, frenulum and soft palate. You can become infected with such a dangerous disease from your mother, as well as during oral sex. The pathology is practically untreatable.
- Specific epithelial hyperplasia. This is a focal growth of growths that often affects children. New growths are colored light pink. The growths can persist for several years, after which they resolve on their own. Relapses are recorded extremely rarely.
Doctors rarely diagnose laryngeal papillomatosis. A benign tumor can be registered in 3 forms: widespread, limited, obliterating. High-quality treatment should be aimed at preventing recurrent laryngeal papillomatosis, as well as at restoring the previous functions of the vocal cords.
Reasons for appearance
There are many different factors through which a person can become infected with the dangerous human papillomavirus. Pathology provokes a change in the nature of epithelial tissues, which is why growths appear on the mucous membrane. Transmission of the virus occurs from a carrier to a healthy person:
- From mother to baby during passage through the birth canal (the baby takes a sip of contaminated amniotic fluid).
- Infection during sexual intercourse. Most often, the human papillomavirus with a low degree of oncogenicity is transmitted sexually.
- In the process of using someone else's toothbrush and microdamage to the oral mucosa. After such hygiene procedures, soft tissue infection may occur.
Every second inhabitant of the planet is a carrier of the human papillomavirus. The infection may not manifest itself for a long time. Activation of the dangerous HPV pathology occurs due to weakened immunity and under the influence of various unfavorable factors:
- chronic infections (sinusitis, tonsillitis, adenoiditis);
- decreased protective function of the immune system as a result of allergic reactions;
- regular infection of the upper respiratory tract (laryngitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis, tonsillitis, fibrous plaque on the vocal cords, glossitis);
- specific hormonal disorders (adolescence, lactation, pregnancy, menopause);
- abuse of bad habits (drug addiction, smoking, alcoholism);
- prolonged depression, frequent stressful situations;
- burn of mucous membranes by hazardous chemicals;
- radioactive exposure to x-rays;
- living in unfavorable conditions with poor ecology.
Main symptoms
Laryngeal papilloma can remain invisible to humans for a long time. The small size of the growth does not cause discomfort. Unpleasant symptoms appear if papillomas begin to grow significantly:
- even with a slight load, characteristic attacks of suffocation are observed;
- voice changes (it may become hoarse, rough, quiet or disappear completely);
- dry paroxysmal cough that does not bring relief;
- periodic breathing problems (severe wheezing during a deep breath, shortness of breath, whistling);
- release of small blood clots when coughing;
- constant feeling of a foreign object in the throat.
In children, all the symptoms of laryngeal papillomatosis are very similar to the signs of damage to the mucous membranes in adults. But the course of the pathology in a child is complicated by the fact that he has a narrower airway, and the throat itself is loose, which is why it is prone to swelling. Diffuse growth of growths can cause blockage of the lumen of the organ, and even suffocation. If an adult does not provide timely medical care to the baby, death is possible. Case histories of patients with the juvenile form of papillomatosis include more than 7% of deaths from suffocation.
The dangerous consequences of the disease in adults include the fact that the larynx is susceptible to scar damage as a result of frequent recurrence of the disease. Degeneration into a malignant form is recorded quite rarely; malignancy of neoplasms can occur with extensive damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth and bronchioles.
Methods of surgical intervention
Removal of papillomas in the throat is inevitable if they grow strongly or interfere with a person’s breathing or eating. There are several common methods for removing growths:
- Excision with a scalpel. The skin, subcutaneous fat, and trachea are cut. Next, the tracheostomy is fixed, and the formation is removed through it. The method is fraught with complications. An endoscope is used for intralaryngeal excision. The place where the growth was is generously covered with antiseptic and subjected to coagulation.
- Cryodestruction involves cauterizing the growth using liquid nitrogen. Cells that are frozen die and soon fall off. Relapses are very rare.
- Electrocoagulation involves removing papillomas with a special scalpel powered by electric current. The technique is highly effective. The positive point is that neighboring tissues are not affected.
- Laser surgery is appropriate for removing growths in hard-to-reach areas. The peculiarity is the absence of scars, which means there is no relapse. During the process, the growths are excised and the bleeding immediately stops. The tool works with maximum precision.
- X-ray therapy is a non-traumatic method. The disadvantage is the possible development of post-therapeutic damage to the laryngeal tissues. After the radio wave knife, the incision created is very quickly healed, and secondary infection is eliminated.
All indicated manipulations are performed using local anesthesia. After surgery, the patient must be treated with antibacterial and antiviral agents, as well as medications to eliminate inflammation and increase immunity, and steroid hormones. It is unacceptable to remove warts in the throat on your own. The growths can become injured and grow in size, becoming a malignant tumor.
Diagnosis of the disease
Localization of papillomas in the oral cavity and laryngeal area is only one of the options for the manifestation of a dangerous HPV infection. Infection can occur at home, through kissing, oral sex, and the use of personal hygiene items. Only a qualified otolaryngologist or oncologist can perform a high-quality diagnosis of the disease:
- Specific laryngoscopy in the light of the frontal refractor.
- Taking a small piece of tissue (biopsy) for histological examination of the tumor. This procedure allows specialists to eliminate the possibility of malignancy of the growth.
- For hard-to-reach localization of papillomas, an x-ray with a contrast agent is performed.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- A specific blood test to detect HPV aggression (polymerase chain reaction).
Effective treatment
If, after all the diagnostic procedures, the specialist was able to determine that the growths are benign, the patient is prescribed effective treatment with antiviral medications. Thanks to this, the spread of growths stops, and the patient’s immunity also increases. It is better to remove single growths, as they serve as the main source for the spread of a dangerous infection. The formations are excised to reduce the risk of further growth.
If the patient plans to use traditional recipes, in order to avoid possible complications, it is better to consult a doctor in advance. It is better not to touch growths in the larynx yourself, but to entrust the treatment to specialists. To effectively treat HPV infection, you can use fresh potato juice, rosehip infusion, plantain decoction, and St. John's wort oil. But you should always remember that any attempts to independently remove even a tiny tumor in the throat can end tragically.
For professional excision of papillomas, surgeons use a regular scalpel, a laser knife, electric current, and liquid nitrogen. The final choice of one or another removal method depends on the age of the patient, the location of the growths, as well as the capabilities of the clinic.
If the biopsy confirms the presence of malignant neoplasms, the patient must be prescribed the following procedures:
- surgical excision followed by radiation;
- highly effective chemotherapy.
Modern radiation therapy necessarily involves the delivery of high levels of radiation. Due to this, it is possible not only to stop the growth of the growth, but also to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy is actively used to combat malignant neoplasms. Quite often, after excision of an oncological growth, additional surgery may be required to restore the missing part of the larynx (if body tissue has been removed).
Diagnostic measures
Detection of papillomas is not a complicated procedure. Already during a visual examination, the specialist sees the growths present in the throat, determines their size, shape, appearance, and specific location. The person does not feel any discomfort upon examination. In practice, the following diagnostic methods are widely used:
- histology (if the presence of a malignant body is suspected);
- laryngoscopy;
- electroglottography;
- laryngotracheoscopy;
- CT;
- microlaryngoscopy;
- radiography;
- laryngosroboscopy.
Possible complications
A deterioration in the patient's general condition is possible if the growths have an abnormal location on the larynx. In this case, a person may experience serious gastrointestinal disorders, bleeding when coughing, frequent infections, and anemia. After radical surgical excision and irreversible damage to the vocal cords, the patient may be assigned disability.
If treated incorrectly, the patient may experience relapses of papillomatosis. Tiny remnants of growths can grow. And against the background of a weakened immune system, a tumor of the larynx can form.
Are papillomas in the throat dangerous?
Papillomas in the throat and oral cavity are overwhelmingly benign, small in size, rarely impair speech, and interfere with food intake.
Despite this, clinicians recommend removal of papillomas for the following reasons:
- With regular food trauma, it spreads and increases the risk of cell malignancy;
- The gradual growth of papilloma promotes growth deep into the mucous membranes of the pharynx, which leads to the formation of a tumor;
- Localization in the larynx can lead to stenosis and suffocation.
The latter complication is especially dangerous in young children; it can be accompanied by sleep apnea, up to a state of acute suffocation.
Unfortunately, the infection is difficult to diagnose at an early stage of development due to the long absence of symptoms. Against the background of strong immunity, the body defeats pathogenic environments and leads to self-healing. Such people do not even notice the infectious process; they rarely develop papillomas.
With reduced immunity or against the background of serious chronic diseases, the body simply cannot fight the infection and over time the symptomatic picture manifests itself in the form of papillomatous foci of various locations.
Prevention measures
Experts believe that the main method of preventing papillomatosis in adults and children is to exclude infection with HPV infection. Adult patients should avoid questionable sexual contacts. If infection has already occurred, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Maintain a more gentle voice mode.
- Seek qualified help from doctors when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
- Limit contact with harmful substances.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Carry out high-quality sanitation of all chronic infections.
- Regular healing of the body (playing sports, eating a healthy diet, taking fortified medications).
Experts say that signs of laryngeal papillomatosis can give a person many unpleasant symptoms that can put life at risk. Only high-quality and timely prevention of chronic diseases, strengthening the protective functions of the immune system, as well as timely seeking help from doctors will help transform the pathology into a latent form and get rid of growths forever.