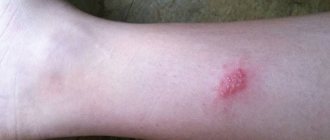
Papillomas on the chest are one of the manifestations of the disease caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Correct diagnosis and timely treatment will help get rid of unpleasant symptoms and prevent relapse.
Today, patients often consult a dermatologist with papilloma on the chest - this is a viral disease that causes skin changes. Externally, the neoplasm resembles a small limited nodule, sometimes prone to peeling and itching.
The disease itself, HPV (human papillomavirus), does not cause trouble for 90% of people who do not even suspect that they are infected. In the remaining 10%, the disease lasts a long time, most often throughout their lives.
The disease manifests itself in the formation of flesh-colored, yellow and brown growths consisting of epidermal cells and blood vessels. The latent period lasts from a month to six months.
Sometimes it lasts for several years. Before the appearance of papilloma, the place where the tumor grows begins to burn and itch. Most strains do not pose a health hazard, but some types of viruses can lead to cancer.
Favorable conditions for the occurrence of symptoms are a weakening of the body’s immune defense.
Papillomas on the chest appear due to:
- stressful situations, nervous overstrain;
- abortions;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- absence of pregnancies in women over 40;
- microtraumas;
- wearing tight, tight or strange underwear;
- the existence of bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking);
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- menopause, puberty;
- excessive physical activity;
- excess weight, sweating:
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- chronic, venereal, frequent colds.
Women are more susceptible to hormonal imbalances, depression, and are more likely to develop papillomas than men.
The virus is localized on the chest:
- on the nipple and areola;
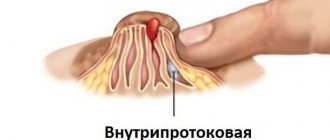
- in the milk ducts (cystadenoma);
- under the chest.
In the first case, the structure of the growths is granular. Papillomas come in round and pointed shapes. When injured, they multiply quickly, capturing the entire nipple, areola and surrounding areas.
The intraductal type consists of single or group cystic growths. The size varies from 3–5 mm to several centimeters.
The disease is identified by discharge from the nipple and treated surgically. Women with mastopathy after 40 years of age are most susceptible to the disease.
There are folds under the breasts and increased sweating, which creates favorable conditions for HPV. Papillomas are pedunculated or broad-based, with no skin pattern.
Mainly they create aesthetic inconveniences. If the growths are injured, a secondary infection may occur.
Papillomas in the chest area are caused by strains of viruses with low oncogenicity.
HPV infection occurs in several ways:
- Sexual contact, even protected. The virus can penetrate the epithelium if the integrity of the skin on any part of the body is damaged.
- During childbirth from mother to child.
- Household method. Through a handshake, dishes, using other people's personal hygiene products.
You can become infected while shaving or epilating if a person is a carrier of the virus.
Types of papillomas on the chest
If growths appear on the skin, there is no need to mask them or ignore them. By avoiding the removal procedure, unpleasant consequences are provoked in the future.
A papilloma on the chest can be small, elongated, or vice versa; we will describe the types of papillomas below.
Flat
They are small round seals. More often observed in children and adolescents. The appearance is due to increased production of hormones, frequent colds, and infection with helminths.
With the normalization of the endocrine system, juvenile papillomas disappear.
Filiform or acrochords
They have a leg and an elongated body. Color - from flesh to dark brown. Appear after 40 years in women and men. The disease occurs due to infection with the papilloma virus.
This is facilitated by diabetes, menopause, and thyroid dysfunction. Acrochords are not prone to degeneration into cancerous tumors, but are often injured. As a result, they become inflamed and spread to new areas of the skin.
Senile keratomas
They begin with the formation of age spots, which over time turn into irregularly shaped growths.
Keratomas are not related to HPV; they appear due to weakened immune defenses, metabolic disorders, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, and heredity.
If the growths are not treated, they can develop into malignant tumors.
What is this
The disease manifests itself in the formation of flesh-colored, yellow and brown growths consisting of epidermal cells and blood vessels. The latent period lasts from a month to six months. Sometimes it lasts for several years. Before the appearance of papilloma, the place where the tumor grows begins to burn and itch. Most strains do not pose a health hazard, but some types of viruses can lead to cancer.
Favorable conditions for the occurrence of symptoms are a weakening of the body’s immune defense. Papillomas on the chest appear in the following cases:
- stressful situations, nervous overstrain;
- abortions;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- absence of pregnancies in women over 40;
- microtraumas;
- wearing tight, tight or strange underwear;
- the existence of bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking);
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- menopause, puberty;
- excessive physical activity;
- excess weight, sweating:
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- chronic, venereal, frequent colds.
Women are more susceptible to hormonal imbalances, depression, and are more likely to develop papillomas than men.
The virus is localized on the chest:
- on the nipple and areola;
- in the milk ducts (cystadenoma);
- under the chest.
In the first case, the structure of the growths is granular. Papillomas come in round and pointed shapes. When injured, they multiply quickly, capturing the entire nipple, areola and surrounding areas.
The intraductal type consists of single or group cystic growths. The size varies from 3–5 mm to several centimeters. The disease is identified by discharge from the nipple and treated surgically. Women with mastopathy after 40 years of age are most susceptible to the disease.
There are folds under the breasts and increased sweating, which creates favorable conditions for HPV. Papillomas are pedunculated or broad-based, with no skin pattern. Mainly they create aesthetic inconveniences. If the growths are injured, a secondary infection may occur.
Papillomas in the chest area are caused by strains of viruses with low oncogenicity.
HPV infection occurs in several ways:
- Sexual contact, even protected. The virus can penetrate the epithelium if the integrity of the skin on any part of the body is damaged.
- During childbirth from mother to child.
- Household method. Through a handshake, dishes, using other people's personal hygiene products.
You can become infected while shaving or epilating if a person is a carrier of the virus.
Diagnostics
Superficial papillomas are determined by visual examination. To determine the type of virus, a scraping of the epidermis is examined.
Diagnosis of HPV on the breast is carried out by a mammologist-oncologist. Intraductal papillomas are detected by palpation and contrast radiography (galactography). The location and size of cystic growths are clarified.
Methods for determining the disease include ultrasound examination of the mammary glands and mammography. Clear or bloody discharge from the nipple is taken for analysis.
Several methods are used to determine the type of HPV:
The inecologist takes a cytological smear from the cervical canal in women, the urologist - from the urethra of men using a special brush with rotational movements. Next, the biomaterial is sent for research using polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
The DNA standard of the pathogen is introduced into human DNA, which has a certain order. If HPV is already present in it, then it combines with the attached DNA and quickly begins to divide.
The presence of malignant neoplasms is shown by a Pap test . It is prescribed to women under 30 years of age. Older women are prescribed a Digen test , which, in addition to oncogenicity, determines the concentration of viruses.
Gynecologists recommend that women independently examine their breasts monthly to identify tumors and discharge from the nipples. This procedure is carried out after menstruation. Particular attention is paid during pregnancy, lactation, menopause.
By performing simple steps, cancer caused by HPV is detected at the initial stage.
Are such formations dangerous?
Papillomas on a woman’s sternum are less dangerous diseases. The risk of developing into cancer cells is minimal.
Formations on the mammary gland and nipples are subject to constant microtrauma due to friction with underwear and clothing. An infection penetrates through the cracks, causing inflammation. As a result, new lesions appear next to the growth.
If a woman has papilloma on the nipple, this interferes with lactation and increases the risk of infection for the child.
Such formations on the chest are associated with a virus and are transmitted from person to person.
Appeared during pregnancy?
While expecting a child, women undergo hormonal changes in their bodies, which reduce immunity and give impetus to the growth of tumors.
medical accurate 3d illustration of a fetus week 12
Significant deformation of the skin is observed in the second and third trimester, so HPV symptoms appear more often during this period. In most cases, papillomas disappear after childbirth. During pregnancy, you should not take radical measures to remove growths if they do not bother you or become inflamed.
Recommendations for pregnant women:
- Examine your breasts and get tested for HPV before conceiving a child to exclude the possibility of transmission of infection during childbirth.
- Avoid tight clothing and underwear to avoid chafing and chafing of the skin.
- Dress according to the weather, protect yourself from infectious colds.
- Watch your weight. Avoid eating fatty and spicy foods.
Medicines are not used for treatment. The doctor selects a vitamin complex to maintain the body’s immune defense.
Removal of growths is carried out in isolated cases, if there are significant indications. The procedure is performed without anesthesia in the first three months, since tumors grow faster in later stages.
Which doctor should I contact with a papillomatous problem?
If you do not understand why papillomas develop on your chest, it is better to visit a doctor in a timely manner and tell him about your problem.
In case of external growths, first of all, you need to go to a mammologist (if one is not available, you can be examined by a dermatologist or local therapist) and get a referral for a general and biochemical blood test and a PCR test. This procedure will reveal the occurrence of a hidden infection or inflammatory process. If papillomas form inside the duct or in the chest cavity, the specialist will prescribe an ultrasound or mammography, as well as an x-ray examination.
If you have completed a course of medical therapy, but the papillomas either dry up or reappear, be additionally examined by an immunologist and an infectious disease specialist.
The surgical removal of papillomas is performed by a surgeon.
Treatment and removal
There are no effective pills that can permanently get rid of papillomas. Medicines are prescribed that suppress the development of the virus and increase the body's immune defense. These include:
- Cycloferon;
- Isoprinosine;
- Viferon.
These medications are used separately from other treatment methods or in combination with hardware or chemical removal of growths on the chest.
The medicinal method of treating superficial papillomas also includes the removal of tumors using ointments and solutions.
You can cauterize growths after consultation with a doctor, under his supervision, and some drugs can only be used in a doctor’s office.
For chemical exposure the following means are used:
- Collomak;
- Super clean;
- Dermavit;
- Solcoderm;
- Feresol.
It is not recommended to use medications containing aggressive acids under the breast. The use of cauterization is unpopular due to possible complications.
Stories from our readers
Got rid of these terrible tumors at home. A month has already passed since I forgot about the bleeding and nasty growths in the most “prominent” places. Oh, I tried so many things - it helped, but only temporarily. How many times did I go to the clinic, but they prescribed useless medications over and over again, and when I returned, the doctors simply shrugged their shoulders. There were also folk remedies such as potatoes, which did not help. I also tried various celandines, which also turned out to be ineffective. I was already on the verge of a nervous breakdown and wanted to literally “cut” them, but then a miracle happened... Finally, there is not a single growth on my body and all thanks to this article. Anyone who has “unloved” growths should read this! You will forget about this problem forever, just as I forgot about it!
Read the full article >>>
For more information about intraductal papillomas, see our video:
Physical methods for removing growths.
Electrocoagulation
Papillomas are exposed to high frequency electric current. After cutting out the tumors, the edges of the incisions are sealed, which protects the patient from bleeding and infection from entering the bloodstream.
Cryodestruction
Papillomas are treated with low temperature liquid nitrogen. In less than a minute, the frozen cells are destroyed. Rehabilitation lasts up to a month, healthy tissues are affected.
Laser technology
The targeted impact of a carbon dioxide laser allows you to reach growths even on deep layers of tissue. The procedure is painless, leaves no scars, and excludes infection.
Radio wave destruction
Non-contact method of exposure to a beam of high-frequency radio waves. The papilloma is cut off in a gentle manner, and the incision is disinfected during the operation. The procedure is bloodless. Due to coagulation of nerve endings, it eliminates pain.
Surgical method
Used when other methods are ineffective. Performed under intravenous anesthesia. Used when cutting out an area of the mammary gland affected by intraductal papillomas. Disadvantages include a long recovery period and scars.
To prevent the disease, preventive measures are used in the form of vaccination, periodic medical examinations, and visits to the gynecologist.
You need to have one sexual partner, maintain personal hygiene, and wear comfortable underwear. Avoid physical contact with strangers and skin injuries.
Dermatologists of the Lasersvit clinic - we will get rid of small papillomas in 60 seconds
When you are looking for a place for treatment, be sure to read reviews about the doctors of the chosen clinic. Doctors with many years of experience have a better understanding of the different forms of growths. This means they can easily remove them.
These are the dermatologists who work with us - at the Lasersvit clinic.
We have been removing tumors for several years now. Many of our doctors have been treating skin diseases for over 14 years, and have examined more than 50,000 patients during this time.
In diagnosis, we rely not only on experience. We are helped by the Delta 20 T dermatoscope, which we use to check the most complex tumors. The device magnifies the image 16 times. So, with its help, we can easily identify even small signs of degeneration of moles and other neoplasms.
We can remove with laser:
- Moles
- Warts
- Papillomas
- Condylomas
- Spider veins
- Tattoos
- Dark spots
- Zhiroviki
- Lipomas
- Basaliomas
And this is not a complete list.
Come to Lasersvit and get rid of unpleasant and dangerous tumors without pain, scars and bleeding.
Useful video about papillomas
List of sources:
- Manykin A.A., Zavalishina L.E., Frank G.A., et al. The use of PCR and in situ hybridization methods for typing papillomaviruses in biopsy specimens of the human larynx // News of Clinical Cytology of Russia. -2001. -T.5. -No. 1-2. P. 91.
- Mynbaev OA, Eliseeva M.Yu., J. Doorbar, Manukhin KB. Epidemiology, molecular biology and principles of immunotherapy for human papillomavirus infection // Issues of gynecology, obstetrics and perinatology. 2009. - T.8. - No. 3. - P.69-79.
- Fletcher R., Fletcher S., Wagner E. Clinical epidemiology: foundations of evidence-based medicine. M.: MediaSfera, 1998. - 352 p.
Author
Denis Filin
Author of the portal Mama66.ru
Share
Prevention
In order to prevent infectious skin lesions on the chest, doctors recommend timely vaccination against the human papillomavirus. This procedure is relevant for children and women who are planning to become pregnant. Vaccination will help them avoid exacerbation of the disease during the period of hormonal fluctuations caused by adolescence or bearing a child. In addition, this way young mothers can protect their baby from unpleasant pathologies.
If infection cannot be avoided, you must begin to carefully monitor the state of the immune system and in no case allow it to decline. A balanced diet and taking vitamin complexes, the action of which is aimed at strengthening the protective properties of the body, helps to cope with this task.