It’s as if bubbles are bursting in the ears: what is it?
The human body is a mechanism of complex action, and all changes in it indicate a certain failure of the usual life processes.
Sometimes symptoms arise that make it difficult to determine the nature of the pathology. Often, complaints of ear pain can be a direct hint of a disease that is associated with the ear canals. But sometimes it does not apply to the hearing organs. Many people do not realize that bursting bubbles in the ears can be associated with various types of disorders. The reason may lie in a disruption of the vestibular apparatus or the cardiovascular system. If bubbles seem to burst in your ears, and you don’t know what it is, it’s worth familiarizing yourself with this phenomenon in the body in more detail. As a rule, the feeling that something is bursting in the ear causes otosclerosis or influenza otitis media. In any case, visiting a doctor is mandatory.
Symptoms
Unlike other, more common forms of otitis, a symptom of bullous otitis is severe itching inside the ears. It stops only after the bullae burst with bloody exudate flowing out. In addition, there is a slight pain inside the ear canal, which intensifies when pressing on the tragus.
With hemorrhagic otitis media, pain and other unpleasant symptoms usually appear in only one ear.
Bullous otitis media may also present with the following symptoms:
- Sharp pain in the ears;
- Dizziness;
- Hearing loss;
- Feeling of fullness in the ears;
- Unpleasant sensations inside the ear;
- Redness and soreness of the skin of the ear;
- Clear, bloody or purulent discharge;
- Facial nerve paresis;
- The appearance of brown crusts in the ear canal.
In advanced forms of the disease, disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus appear: unsteadiness of gait, impaired coordination of movements, or loss of a sense of orientation in space. Children often show signs of intoxication such as nausea, vomiting, fever, and general malaise.
The appearance of symptoms such as severe dizziness, unsteadiness of gait and nausea means urgently seeking medical help.
Feelings and actions
Often the sensations in the body are difficult to explain, especially when you encounter a particular phenomenon for the first time. Sometimes the feeling of bubbles bursting in the ears is accompanied by additional symptoms: ear canal congestion, pain, noise of various types, clicking, ringing. But more serious manifestations are also possible: dizziness, hearing loss and impaired body coordination. All this can manifest itself with varying intensity in individual situations: flying on an airplane, hiking in the mountains, with a sudden change in body position.
Everything is individual
Before getting rid of the problem, you should consult a specialist. Situations are different, and perhaps not everything is as rosy as it may seem. If bubbles seem to burst in your ears, then treatment should be entrusted only to experienced specialists. Their task is to determine what is causing the noise. If the cause is infectious or inflammatory diseases, the doctor will prescribe a comprehensive treatment that is aimed at speedy recovery of the patient. If there is a connection with an allergic reaction, then you should pay attention to medications and diet, all of which can directly affect the internal disease.
Allergen influence
After identifying the allergen, it is necessary to exclude from the diet those foods or medications that provoke a malfunction in the body for a certain period. If it is impossible to exclude medications, the doctor may prescribe a medicine that will have the same properties as its predecessor. If bubbles seem to be bursting in your ears, but the doctor could not determine what it is and how to treat it the first time, you should not self-medicate. After all, the consequences for the human body can be irreversible. Introduction into the treatment process can cause complications not only in the ear canal, but throughout the body. You cannot introduce foreign objects into the ear or make any lotions, all this can only aggravate the problem. In this case, you need to seek help from an otolaryngologist, who will help identify the problem and prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
Bullous otitis - definition of the disease
Hemorrhagic or bullous otitis is an acute inflammatory disease of the middle or outer ear. Most often, the mildest, that is, external, form of the disease occurs. Ear pain with or without a cold, a sharp decrease in hearing and increasingly intensifying itching in the ears are all reasons to immediately seek help from an otolaryngologist.
Bullous otitis media is especially dangerous in children. This is due to the fact that frequently occurring viral infections quickly penetrate from the nasopharynx into the Eustachian tube.
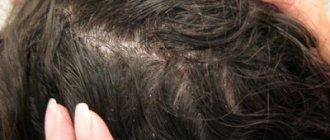
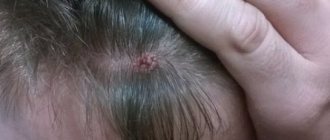
A characteristic feature of this particular form of the disease is the formation of pronounced blisters about 1 centimeter in size, filled with clear or bloody fluid. Over time, they burst, causing severe itching. Bursting blisters produce translucent or bloody discharge.
Bullous otitis is a type of acute viral otitis of purulent origin.
Bullae can form directly on the surface of the eardrum and the surface of the external auditory canal. At an advanced stage of the disease, the blisters can even spread to the outer surface of the auricle. Such purple bubbles on the surface of the ear are combined with severe redness and itching of the skin.
It's all because of ear plugs
No matter how trite it sounds, gurgling in the ears can occur from ordinary ear plugs. In this case, it is all due to lack of hygiene. Few people know that cleaning ears with a cotton swab is not recommended. In the depths of the ear canal, an obstacle is created when the wax is pushed deep into the ear canal. No matter how strange it may sound, if the Eustachian tube is blocked, then it is worth doing certain exercises that normalize internal processes in the body.
They are as follows: the lower jaw moves forward, and then the direction changes and the jaw moves to the right and left. This simple exercise helps eliminate signs of congestion. You can also experiment with another exercise: close your nostrils with your fingers and draw air into your lungs, and then exhale it. This simple exercise will cause a small “click” to appear, which will cause ear congestion to disappear.
Repairing spaces
Remember that extraneous sounds in the ears are not a separate disease, but only a symptom that is accompanied by headache and weakness in the body. Therapy always depends on the cause and nothing else. In each case, the treatment is individual, which is prescribed by an experienced specialist. If the course of therapy that the doctor prescribed for you did not produce results, and bubbles seem to be bursting in your ears, and you don’t know what to treat, then you should pay attention to your blood pressure. When it increases, you should limit your consumption of salty foods, strong tea and coffee. Perhaps the cause of extraneous sounds is iron deficiency anemia. In this case, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment using drugs that contain iron. If tinnitus is caused by inflammation of the auditory tube, then the doctor should prescribe therapy using antimicrobial drugs.
How to treat if there is gurgling in the ear
When there is no pain when the sound occurs, but there is a feeling that congestion is present, you can try to fix the problem yourself.
Are you sure there is wax in your ear? It is possible to remove it, but you should immediately stop using cotton swabs. Trying to clear wax from the ear with their help is useless; the “clog” will only thicken, and the condition will worsen in the future.
A way to get rid of wax in the ear canal yourself:
- First you need to drip 3% hydrogen peroxide or Vaseline oil into the passage - hydrogen peroxide is better, it optimally softens the dense plug;
- After half an hour, you should try to insert a cotton wool into the ear canal. If there are sulfur particles left on it, then we can conclude that the plug has softened and proceed to the main stage of ear cleansing;
- Tilt your head to the side on which the stuffy ear is located;
- Use a syringe without a needle to rinse with warm water;
- When the plug comes out, apply ear drops with anti-inflammatory properties.
If the ear is stuffy due to swelling, and gurgling is caused by accumulated mucus, then you can try the following methods to solve the problem:
- apply dry heat to the tragus;
- insert a cotton wool soaked in warm camphor oil into the passage;
- add 1 drop of alcohol and then close the passage with a cotton swab;
- add Vaseline oil.
Under no circumstances should you resort to an alcohol compress. Intense heat treatments will increase the swelling and the sound will only get worse.
When carrying out all procedures that help remove extraneous sound in the ear, it is necessary to first clean the nasal passages. In some cases, to eliminate clicking or gurgling, it is enough to use vasoconstrictor drops. But it is not advisable to use them constantly. Swelling of the mucous membrane and unpleasant sound in the hearing organ are relieved by the usual rinsing of the nasal passages.
This can be done in various ways - using a syringe without a needle, drawing in saline solution through the nostrils, pouring in liquid with the spout of a teapot - this is how the nose is usually washed in Japan and India.
If mucus does not accumulate in the nasal passages and sinuses, there will be no noise in the eustachian tube. There is another specific reason that explains why water “gurgles” in the ear. The symptom is caused by an ENT disease – exudative otitis media. During it, liquid discharge accumulates in the tympanic cavity under the influence of external factors - trauma or inflammation in the middle ear.
It is impossible to treat this disease on your own - in some cases, minor surgical intervention is required - puncture of the eardrum to remove fluid. If it continues to accumulate, the pain syndrome may intensify.
Sources of extraneous noise
Among the reasons are:
- Damage to the auditory or vestibular system.
- Brain or ear injury.
- Ear infection.
- Drug poisoning.
- Sulfur plug.
- Vascular disease.
- Active heart work during additional physical activity.
There can be many possible reasons for the appearance of foreign phenomena in the ear canal, and there are no less treatment options. It is important not only to have the correct doctor’s opinion, but also to prescribe the right course of therapy. First of all, an experienced doctor should check the patient for ear inflammation, which may be associated with an infection or cold.
Possible causes of sounds
The feeling as if bubbles are bursting in the ear is characteristic of the following factors:
- Sulfur plug. If accumulated wax has formed in the ear, the patient feels some discomfort. With a “fresh” plug, a person is bothered by the sound of shimmering water or the feeling of bursting bubbles. If we are talking about an old plug, then only ear congestion occurs;
- Foreign body. If there is a foreign body in the ear canals, a sensation of bursting bubbles may occur. This usually happens when turning the head or changing position;
- Otitis. This symptom is characteristic of otitis media, which is accompanied by purulent discharge. When fluid accumulates, the patient has a feeling of bubbles that periodically burst. It should be noted that this factor is accompanied by pain.
Also, the symptom can manifest itself in pathologies of the vestibular apparatus or in the presence of vascular pathology.
Causes
This symptom is surprising; people are in no hurry to see a doctor and suffer from the feeling of squelching and gurgling. If you do not consult a doctor in time, serious consequences may arise, since the cause of noise and crackling in the ear canal can be very different. This sound occurs due to various diseases caused by inflammation of the inner lining of the ear, due to the occurrence of wax plugs, the presence of a foreign object in the ear canal and other disorders.
Causes of a sensation in the ear as if bubbles are bursting:
- inflammatory processes in the ear canal (manifestation of diseases such as otitis media and otosclerosis);
- foreign body in the ear;
- formation of sulfur plugs;
- problems in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system (heart and vascular diseases);
- head and jaw injuries;
- human allergic reaction;
- atrophy of the ear nerve;
- Eustachian tube congestion.
If you hear gurgling sounds in your ear, then you should immediately consult an otolaryngologist who will identify the cause of the sounds and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Associated symptoms
Depending on the cause of this symptom, the following accompanying symptoms may be observed:
- Pain in the ear of varying intensity;
- Discharge from the ear of various types;
- Dizziness and darkening of the eyes;
- Humming and other foreign sounds in the ears.
This is important: Based on complementary symptoms, the doctor can judge the presence of any disease. When you visit your doctor, be sure to tell him about all the signs that appear.
What to do to get rid of the symptom
First of all, it is worth noting that you definitely need to visit a doctor who will examine your ear canals. Depending on the cause of the symptom, different treatments will be needed.
- If the cause is a sulfur plug, to remove the symptom it is enough just to dissolve the plug. This can be done using special drops or using phytosuppositories. You can also use ear rinsing, but it is advisable to carry out such a measure only in stationary conditions;
- If a symptom occurs due to developing purulent otitis media, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents for oral use are mandatory. As an additional therapy, ear drops with an anesthetic and anti-inflammatory effect are needed;
- If the cause is a foreign body, it is necessary to remove it, only in stationary conditions. Using special forceps, the doctor will remove the object and treat the ear with an antiseptic.
For other reasons with blood vessels, treatment and recommendations can only be given by a specialized specialist - a neurologist.
What not to do
In order not to aggravate the situation and not cause harm to the body, experts advise taking precautions and under no circumstances self-medicating, including not doing the following:
- If you suspect the presence of a foreign body, under no circumstances try to remove the object yourself;
- You should not try to remove fluid from the ear on your own;
- You cannot take any medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- Do not under any circumstances try to clean your ears with cotton swabs if you have this symptom. If we are talking about the presence of a foreign body or wax plug, you can only aggravate the situation by pushing the object even further.
Treatment
Diagnosis of bullous otitis is quite simple, since characteristic symptoms allow a quick diagnosis. To do this, just consult an otolaryngologist. By the appearance and contents of the bullae, the doctor can easily determine the virus that caused the inflammatory process in the ear.
A visual examination of the bullae will allow the otolaryngologist to often determine the cause of the disease without additional research.
In complex cases, research methods such as:
- General (clinical) blood test;
- Serological blood test;
- Tank. culture of fluid from the ear (contents of bullae);
- Oto microscopy;
- Tuning fork test;
- Tympanometry;
- Audiometry.
Video: diagnosing the disease
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor decides whether treatment at home is possible or whether hospitalization will be required.
If we are talking about hemorrhagic otitis in a child, especially under the age of 6 years, then hospital treatment is necessary. This will help reduce the risk of serious complications.
The general principles of treatment of bullous otitis include the following principles:
- Bed or semi-bed rest;
- Limiting physical activity;
- A complete diet rich in vitamins.
It's like bubbles are bursting in my ears
Tinnitus is a symptom characteristic of both pathological processes occurring in the ear and diseases not related to this organ. At the same time, the nature of the noise can be described by patients in different ways. This could be the rumbling of a motor, the buzzing of a saw, crackling, gurgling, or humming. Some patients describe this symptom in such a way that it is as if bubbles are bursting in the ear, or there is a feeling that the sea is splashing.
The content of the article
The most common diseases that may be accompanied by such symptoms are
Among diseases of the ENT organs, the presence of noise in the ear is most often caused by the development of eustachitis, inflammation of the auditory tube.
In this case, this symptom occurs quite acutely and is permanent, which distinguishes it from noise caused by vascular disorders. The pulsating character is atypical for him. There is an increase in noise in a horizontal position, especially with a lowered head edge, which is due to the anatomical structure of the auditory tube and its angle of inclination. When moving to a vertical position, the noise intensity decreases.
Most often, eustachitis is a consequence of acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis, or laryngitis. An important factor contributing to the diagnosis of this condition is the presence of catarrhal symptoms, nasal congestion, and runny nose, which appeared several hours before the development of noise in the ear.
The diagnosis can be reliably clarified using otoscopy, which allows one to identify a retracted eardrum.
Such changes are caused by a decrease in pressure in the tympanic cavity, resulting from a violation of the drainage function of the auditory tube.
An effective method of treating eustachitis is the use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops. Their use helps reduce swelling of the auditory tube, as well as reduce the amount of mucus formed. This effect leads to improved patency of the Eustachian tube and, therefore, reduces symptoms.
Reduction of noise in the ear can also be achieved by applying warming procedures to the parotid area. These can be physiotherapeutic procedures, UHF, electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory solutions, wet and dry compresses. A similar effect can be expected from the use of heated ear drops containing boric or camphor alcohol, solutions with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory component. Improvement should occur within the next few hours.
Untimely implementation of therapeutic measures can lead to the spread of infection to the middle ear and the development of first catarrhal, and possibly exudative otitis media.
In this case, an increase in symptoms and a deterioration in general condition are characteristic. Added to the unpleasant sensations in the ear is severe pain. Otitis media often occurs with an increase in temperature to 38 -39 degrees. The development of this condition requires immediate consultation with an otolaryngologist, whose task is to clarify the nature of the inflammation and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Causes of extraneous sounds in the ears
Let's look at the most common conditions that can cause this symptom.
- Inflammation of the Eustachian tube . The most common causes of this disease are complications after ARVI, laryngitis or tonsillitis. Diagnosis is helped by catarrhal phenomena visible upon examination or symptoms characteristic of a cold that arose several days before the onset of noise. With eustachitis, extraneous sounds in the ear develop acutely and are permanent. This feature is a differential diagnostic feature that distinguishes this symptom of inflammation of the auditory tube from noise of vascular origin. Features of noise with eustachitis are its intensification when taking a horizontal position, intensification when taking a vertical position of the body and the absence of pulsation. A reliable diagnostic sign is a retracted eardrum visualized by otoscopy. If symptoms of eustachitis appear, the patient should consult a doctor, as attempts at self-treatment can lead to complications.
- Vascular disorders resulting from vascular atherosclerosis, cervical osteochondrosis or congenital features of the development of head vessels . In some cases, when there are no signs of inflammation of the auditory tube, but the patient still complains of a sound in the ear, as if bubbles are bursting, a therapist, neurologist and angioneurologist search for the causes of this condition. Vascular pathology (such as vascular atherosclerosis, aneurysm, can lead to insufficient blood supply to the hearing organ, which causes various symptoms, including tinnitus.
- Rheumatism . Arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint is important. The diagnosis must be clarified and confirmed by specialized specialists.
- Neuritis of the auditory nerve . The diagnosis is established based on the characteristic clinical picture and the results of additional studies.
- Head injuries . To clarify the nature of the disorders, a series of examinations will be required, the results of which will tell the specialist the correct treatment tactics.
- Sulfur plug . As a rule, there is no deterioration in the general condition of the patient with sulfur plugs; however, this condition can still cause serious concern. In addition to extraneous sounds in the ear, wax plug can cause hearing loss and local pain of varying severity.
- Otitis . The disease is characterized by severe pain in the area of the auricle and external auditory canal against the background of a deterioration in general condition and an increase in body temperature. The diagnosis is made by an otorhinolaryngologist, and a doctor of the same specialty prescribes the necessary therapy.
- Cicatricial changes in the eardrum . This condition may be a consequence of inflammatory processes or mechanical trauma. The noise in the affected ear in this case resembles clicking.
- Fluctuations in blood pressure . Regular measurement of blood pressure will help to reliably determine whether instability of blood pressure is the cause of the appearance of extraneous sounds in the ears in order to establish a connection between the appearance of a symptom and changes in this parameter.
- If tinnitus is a consequence of taking pharmaceutical drugs , then the problem can be solved by changing treatment, selecting a similar remedy that does not have side effects that cause discomfort. You should not do this yourself; only the attending physician should make any changes to the treatment regimen.
Neurological and vascular disorders
In cases where there is no inflammation of the auditory tube and middle ear, but the sound in the ear persists, as if bubbles are bursting, it is necessary to consult a specialist to clarify the diagnosis. A neurologist and an angioneurologist are involved in the study of this pathology.
The presence of noise in the ear may be due to dysfunction of the auditory nerve. Infectious or traumatic damage to it leads to insufficient blood supply to the auditory artery, which is manifested by the development of this symptom. Similar symptoms occur with cerebral aneurysm. Rheumatic and atherosclerotic vascular damage can also be manifested by the presence of a sensation as if bubbles are bursting in the ears.
Temper of tinnitus
Tinnitus can have a completely different character , so patients who come with similar problems constantly describe the illness in their own way. Someone complains of periodic “gurgling”, bubbles burst in the ear, a crackling noise is heard.
Others say that it is as if a bee is buzzing near the ear, the sound of a chainsaw is heard, and a machine is humming.
Someone hears the splash of a wave or the sound of raindrops falling on the asphalt.
Reference. Noises may be constant or occur in certain situations.
The duration of the phenomenon also varies:
- For some people, tinnitus goes away in one moment, just as it started.
- Others hear outside sounds throughout the day.
In this case, there may be no additional symptoms of irritants at all, or, on the contrary, together with extraneous sounds (a physical phenomenon that represents the propagation of mechanical vibrations in the form of elastic waves in a solid, liquid or gaseous medium), a headache begins to ache, hearing disappears completely or partially, it is felt general malaise or irritation caused by general discomfort.
When lying down, standing or sitting, the nature of the noise may change . Pulsating sounds become monotonous, quiet sounds become loud and vice versa.