Medical certificate
Trichophytosis is a dermatological disease of a fungal nature. It affects the hair, skin and nails. Initial signs of infection appear within the first week. With timely treatment, the disease goes away without a trace. Otherwise, a progressive pathological process can lead to disruption of the integrity of the skin and permanent baldness.
Trichophytosis in humans comes in several types: superficial, infiltrative-suppurative (deep), chronic. Each form of the disease is characterized by a specific clinical picture. They will be discussed in more detail below.
Traditional treatment
Since ancient times, our great-grandfathers found salvation from various diseases using the gifts of nature. Trichophytosis can also be treated using traditional methods. Only those recipes that have positive reviews and have been used more than once in the fight against mycoses of the skin and nails will be described here. In addition, healing recipes do not have a negative effect on the human body. However, they must be used with caution, taking into account all the ingredients and the individual tolerance of each of them.
Important addition: How to treat nail fungus with Iodinol?
Let's start getting acquainted with folk remedies for nail trichophytosis. Tea tree oil has proven itself to have antibacterial properties. Its price at a pharmacy is affordable for any category of citizen, and the use of the oil itself is more than simple. You need to take a cotton pad and moisten it generously with oil, then wipe the nail plate and the area around it, previously cleaned with warm water. Manipulations should be carried out twice a day, gradually filing off the affected nail.
Another budget option for treating nail mycosis is garlic compresses. At one time, you will need to chop two large cloves of garlic to a paste-like consistency. Then place the pulp between layers of gauze and wrap it around the sore finger. Place a plastic bag on top. The procedure is carried out at night.
Cutaneous trichophytosis is treated with slightly different recipes; the following “gifts of nature” are usually used:
- apple cider vinegar - treat the skin with a cotton swab every three hours;
- homemade burdock oil (recipe below);
- egg yolks - hard-boiled and crushed yolks are fried over low heat without adding oil for about thirty minutes, wrapped in gauze and used as a compress.
Burdock oil is prepared according to this principle - finely chop the burdock rhizomes (you can use a blender or finely chop them), about three hundred grams, mix with olive oil. Place the mixture in a cool, dark place for one day. After this, boil the oil in a water bath for about twenty minutes and let it cool on its own. Place in the refrigerator. Wipe the affected areas of the skin with burdock oil two to three times a day. By the way, burdock oil is a universal remedy for any type of epidermal trichophytosis.
Traditional recipes are best combined with topical medications. This way the patient will achieve the desired result in a shorter period of time.
Transmission routes
The main carriers of fungi are considered to be street animals, as well as young and middle-aged children. In the first case, the disease will be more severe. The thing is that ringworm can also be caused by other fungi. However, trichophytons are the most common causative agents of the disease.
The fungus tends to persist on household items. Therefore, the main route of transmission of the disease is through household contact. It is not at all necessary to have direct contact with an animal or an infected person. Trichophyton spores easily spread through the air and quickly “take root” in the body.
On the other hand, after direct or indirect contact a person does not always get sick. If the fungus simply gets on the skin, it will be destroyed by the immune system. For infection to occur, predisposing factors must be present. These include traumatic damage to the skin, prolonged exposure to high humidity and a decrease in the body's defenses.
Pathogenesis or picture of the battle with trichophytosis
Dermatophytes have a special affinity for human and animal skin due to the fact that their enzymes can quickly decompose keratin, a protein that is part of the skin, nails and hair and has a protective function.
Penetrating into the surface layers of the skin, trichophyton dissolves the keratin that stands in its way and specifically launches its threads into the space between the cells, where the resistance of the skin is much weaker. The rapid growth of hyphae in the upper layers of the skin is accompanied by massive destruction of skin cells, and this leads to the outpouring of intracellular fluid from the cells and subsequent inflammation of the skin.
Risk group
The likelihood of contracting a fungal infection is the same in almost all age and sex groups. However, trichophytosis in children attending kindergarten or school is detected several times more often. Medical statistics speak about this.
The fungus, which falls off with particles of hair or fur, can live in the soil for up to several months. Therefore, the number of cases of infection increases in the autumn-spring period, when agricultural work begins. Farmers and gardeners are highly likely to develop this disease.
Treatment of cutaneous trichophytosis
Therapy for adults
Regardless of the form of epidermal trichophytosis, an integrated approach is advisable, that is, a combination of topical drugs and tablets. In this case, fungal spores are stopped 100%.
Important addition: Hardware treatment of toenail fungus
All tablets for mycosis belong to the group of antifungal antibiotics, so the dosage and duration of the course of therapy is determined by the dermatologist on an individual basis. It is simply impossible to find the only correct treatment on the Internet.
Antifungal antibiotics include tablets and capsules with trade names: Griseofulvin, Terbinafine, Intraconazole. All of them are sold over-the-counter. But they have a number of contraindications, including pregnancy and age restrictions.
Using only tablets, you can treat trichophytosis for a very long time. Therefore, it is imperative to use ointments or creams, preferably according to this scheme:
- in the morning, Mycoseptin ointment;
- during the daytime, treat the affected area with Lamisil lotion;
- Sulfur ointment is applied at night.
If you are not satisfied with the cost of ointments and lotions, you can purchase their analogues at the pharmacy, which the pharmacist will recommend. Just pay attention to the main active ingredient, it must be identical to the original.
If one of your family members has epidermal or nail trichophytosis, you should definitely reduce the possibility of infection with pathogenic microorganisms.
To do this, you need to take a course of immunomodulators (Polyoxidonium, Lykopid), a vitamin and mineral complex.
Treatment in children
The treatment regimen for epidermal trichophytosis in children is identical to that for adults. The only thing is that the dosage of antifungal antibiotics is reduced. In addition, Griseofulvin is not prescribed to children, as they do not tolerate it well (the drug puts a significant burden on liver function). Usually, pills with the main active ingredient called terbinafine are prescribed. The tablets have the same name.
For children weighing up to twenty kilograms, 95 mg per day is sufficient, up to forty kilograms 190 mg, over forty kilograms 250 mg.
Clinical picture
The incubation period for trichophytosis in humans is 3-4 days. Then its main symptoms begin to form. They depend on the area in which the main focus of the pathological process is localized.
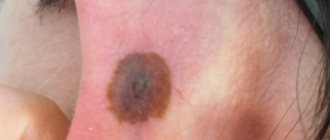
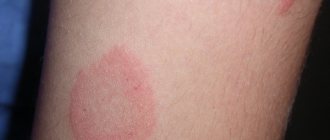
For example, when smooth skin is affected, the disease manifests itself in the form of flaky pinkish spots bordered by a slight thickening. Small bubbles may periodically appear on this peculiar rim. Over time, they burst, dry out and become crusty.
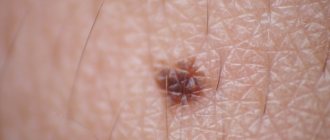
When it comes to damage to the skin under the hair, initially it begins to peel off. In this case, the patient does not experience discomfort. Then the hair in these areas becomes brittle. And after a while they begin to fall out. As for the nail plates, black spots appear on them. They gradually increase in size, spreading over the entire plate. The nail itself becomes brittle.
Prevention
Prevention of trichophytosis consists of observing basic hygiene skills among all segments of the population. This is especially true for children living and studying in closed institutions. Attendants at such establishments should be regularly screened for latent fungal infections to prevent their spread. When cases of trichophytosis are detected, relatives and people close to the patient are subject to mandatory examination.
Alexandr Popov
Author of the article. Practicing doctor
Superficial form of trichophytosis
The incubation period of the disease is 7 days. Depending on the site of localization, superficial trichophytosis can affect both the scalp and smooth skin.
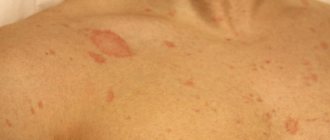
The first case is usually diagnosed in children. This form of pathology occurs much less frequently in newborns and adults. The patient may develop multiple lesions with blurred boundaries. They reach 2 cm in diameter. They are localized mainly in isolation from each other. The dermis around such a lesion is red, slightly swollen, and covered with whitish pityriasis scales. Swelling and redness are sometimes aggravated by blisters and pustules. The hair in this area gradually loses its shine and becomes brittle.
Damage to smooth skin occurs in isolation or in combination with trichophytosis of the scalp. Favorite places of localization are the neck and face, forearms, and torso. The disease occurs in people of different age groups. It begins with the appearance of one or 2-3 edematous spots. They have clear boundaries and may protrude slightly above the surface of the skin. Itching is usually absent or mild.
Forms of infection
There are three forms of pathology, which differ in localization and depth of tissue damage . They affect individual areas of the skin and its appendages: hair and nails .
- Superficial trichophytosis.
- Chronic trichophytosis of smooth skin.
- Infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis.
It’s worth saying right away that the superficial and chronic forms of the disease are caused by the same fungus, which only affects people. This means that infection with these types of pathology is possible only through contact with sick people or things they used: clothes, combs, washcloths, towels, etc.
The infiltrative-suppurative form of the disease is caused by a fungus that can parasitize both humans and animals. Its spread occurs through both direct and indirect contact between a person and a sick pet. The pathogen can be transmitted between animals through soil, feed, hay, etc.
According to statistical data collected over the past 20 years, superficial and infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis occur in people with the same frequency. At the same time, if previously the disease was more often registered in rural areas, in recent years there has been a tendency towards an increase in incidence among city residents. Doctors attribute such changes to insufficient rodent control. The latter leave infected scales on various surfaces in homes. Accordingly, when coming into contact with such things, city residents have a chance of contracting an infiltrative-suppurative form of trichophytosis.
Infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis
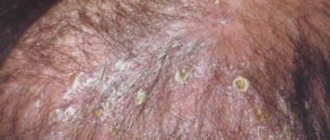
In this case, the incubation period can vary from several weeks to 2 months. The disease begins its development with the appearance of several pinkish spots with pronounced boundaries. Their marginal ridge consists mainly of plaques and blisters, which shrink into crusts over time. In the future, the inflammatory process only worsens. The spots increase in size and may merge together. The favorite places of localization are the scalp. They can also occur in the chin area and above the upper lip.
With infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis, lymph nodes sometimes become enlarged. Patients complain of general malaise. Increased body temperature and severe headaches are possible.
Types of trichophytosis, sources of infection
Based on the type of pathogen, a distinction is made between anthropophilic and zoophilic trichophytosis. Trichophyton fungi spread through flakes of skin, hair, fur, and pieces of nails of a sick person or animal.
Anthropophilic types of trichophytosis
Superficial trichophytosis is caused by fungi that parasitize human skin - the anthropophilic fungi Trichophyton violaceum, Trichophyton tonsurans.
They are located mainly inside the hair and do not cause acute inflammation of the skin. The course of trichophytosis is superficial, not affecting the deep layers of the skin.
The disease is contagious and is easily transmitted from person to person through contact or exchange of personal belongings. Shelled skin flakes and broken hair infected with the fungus are transferred through a common comb, hairpin, or hat to the hair of a healthy person.
Trichophytosis mainly affects the skin and hair on the head, the smooth skin of the torso and limbs (shown in the photo), and very rarely the nails.
Most cases of superficial trichophytosis of the head occur in children. They get sick more often at the age of 5-12 years, which is explained by age-related characteristics of the acid-base balance of the scalp.
Occasionally, anthropophilic trichophytosis is observed in newborns and adults.
In adults, scalp hair is protected from infection by trichophytons by organic acids that have antimycotic activity. Therefore, ringworm, as trichophytosis is also called, is less common among them.
There have been cases of spontaneous resolution of trichophytosis in sick children as they grow older. This mainly applies to boys.
In girls, the disease lasts for years, taking a sluggish chronic course. The lesions are masked by healthy hair, the disease often remains unrecognized until old age, and is detected accidentally when other family members, usually children, are infected with trichophytosis.
Superficial trichophytosis of the smooth skin of the trunk and limbs occurs equally often in children and adults, and does not differ by gender.
Predisposing factors for chronic trichophytosis in adults are diseases of the peripheral blood vessels - acrocyanosis, erythrocyanosis, dysfunction of the gonads.
Zoophilic trichophytosis
Infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis develops as a result of infection with zoophilic fungi that parasitize animals, Trichophyton verrucosum, Trichophyton gypseum.
Zoophilic fungi multiply around the hair, cause profound changes in the skin, lead to suppuration of the hair follicles, and the formation of an extensive focus of inflammation.
A person becomes infected with infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis from wild and domestic animals. The carriers of the disease are mice, rats, sheep, and cows.
The fungus is not only transmitted through direct contact. Much more often, infection occurs through objects contaminated with the fur of a sick animal.
Trichophytosis in humans, caused by zoophilic fungi, is characterized by a severe course.
Risk factors
The risk of trichophytosis increases with fresh cuts, scratches, and skin damage. Endocrine diseases and weak immunity contribute to infection.
The activity of the fungus increases at elevated body temperatures and high ambient humidity.
Chronic form of trichophytosis
The disease is most often diagnosed among adolescents and adult women. In boys infected in childhood, spontaneous self-healing is observed during puberty. In girls, the pathology becomes chronic. The disease is characterized by a poor clinical picture. In most cases, it is detected during an “epidemiological chain” in order to identify the carrier of a fungal infection within the same family.
Pathological foci of chronic trichophytosis occur both on the scalp and in the area of the buttocks, legs, and forearms. Rarely, symptoms of the disease appear on the torso or face. First, the patient develops pinkish-bluish spots with a flaky surface. In this case, there are no pustules or blisters.
Against the background of a chronic form of the disease, sometimes the nail plates are involved in the pathological process. First, gray spots appear on them, which gradually increase. Then they change color to yellow, and the entire surface becomes lumpy. Next, the nail plates thicken and become noticeably deformed.
Treatment
For local treatment of trichophytosis, various combinations of antiseptics and antifungal drugs are used. Antiseptics allow you to dry the affected area, and the antimicrobial drug destroys the pathogen on the spot. For this purpose, antifungal ointments such as:
- Clotrimazole;
- Mycosporus;
- Exoderil.
When treating severe clinical forms of trichophytosis, systemic therapy is used to combat the pathogen in the internal environments of the body. One of the drugs for this protocol is Griseofulvin. The course of treatment with Griseofulvin is quite long and can last up to two months, depending on the progression of the clinical symptoms of trichophytosis.
To achieve the best treatment result, the hair for ringworm is shaved, this provides direct access to the affected areas of the skin, which are especially difficult to access in women with trichophytosis. The same applies to inguinal trichophytosis.
In young children with chronic diseases, as well as in patients with varying degrees of immune deficiency, the following vitamins are added to the treatment protocol:
- ascorbic acid;
- vitamin E.
The purpose of microelements, primarily zinc, is also indicated.
Diagnostic methods
Trichophytosis in humans is a dermatological disease. Therefore, if you suspect an illness, you should contact a dermatologist for help. There is also another specialist working in this area - a mycologist.
Diagnosis of a fungal infection is quite simple. First, the doctor performs a physical examination, sometimes supplemented by a Wood's lamp examination. It is necessary for differentiation from microsporia, which gives a green glow in the light of this device.
The next stage of diagnosis is microscopic and cultural examination of scrapings from the affected areas. This approach allows you to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. During the procedure, the doctor scrapes off flakes of skin or fragments of hair with a scalpel, and then examines them under a microscope and sows them into Sabouraud's nutrient medium.
In practice, microscopic and cultural examinations are not always prescribed. An urgent need arises only when it is necessary to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antifungal drugs. Inexpensive but effective remedies against trichophytosis will be mentioned below.
How to identify trichophytosis
To make a diagnosis, you must consult a dermatologist. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe laboratory tests. A small amount of affected skin is removed from the patient using a blunt scalpel. For nail trichophytosis, a small piece of the plate is examined. When examining the scales under a microscope, it is possible to identify fungal spores and their resistance to drugs. Additionally, the doctor can examine the affected areas under a Wood's lamp. In this case, the lichen will be highlighted in a characteristic green color.
Often, it is enough for a doctor to examine a patient to make a diagnosis and prescribe therapy. Laboratory tests are carried out to identify the type of pathogen and determine the sensitivity of mycosis to drugs when treatment does not bring results.
Drug treatment
Treatment of the disease depends on where the focus of the pathological process is located.
The infiltrative-suppurative form of trichophytosis can be stopped with the help of lotions prepared from Burov's liquid. In a hospital setting, the abscesses must be opened, then the cavities are washed with a special solution. The sanitized lesion is treated with tincture of iodine and sulfur ointment is applied.
Therapy for trichophytosis of smooth skin involves the external use of antifungal drugs. Inexpensive but effective remedies are the well-known ointments: salicylic, sulfur and sulfur-tar. Any drug can be used to treat the affected areas. Isoconazole and Clotrimazole have a positive therapeutic effect. The pronounced inflammatory process can be eliminated with the help of combination medications that contain hormones (Mikozolon, Travocort). If the underlying illness is accompanied by a bacterial infection, the doctor may recommend Triderm cream.
When the scalp is infected, systemic antifungal therapy is used. The main drug to eliminate pathology is the antibiotic Griseofulvin. It comes in tablet form and is a derivative of a mold fungus.
In the chronic form of the disease, black spots on the head are removed using the Arievich method. First, milk-salicylic ointment is applied under a compress for two days. Then the bandage is removed and 2-5% salicylic ointment is reapplied. After this, the keratinized layer of skin is removed with a blunt scalpel, and the points themselves are removed with tweezers.
Treatment of trichophytosis is not stopped until the tests show a negative result. The standard course of therapy is from 1.5 to 2 months.
Trichophytosis
Trichophytosis (ringworm) is a mycotic infection of smooth skin, hair, and nails by fungi of the genus Trichophyton. It is characterized by the formation of inflammatory foci with clear boundaries and peeling. The affected hair becomes brittle, breaks off above the skin level and sticks out in the form of stumps. The disease is highly contagious. Deep skin lesions lead to deterioration of the general condition and the formation of abscesses. In advanced cases, persistent baldness may remain in place of the hair. Trichophytosis is caused by various types of fungi of this genus. It can affect any part of the skin, including nails. Left to its own course, the disease can exist for many years, but usually goes away spontaneously by puberty. Clinically, two forms are distinguished:
Superficial trichophytosis is caused by anthropophilic fungi, i.e. parasitic only in humans. Children usually get sick. The infection is transmitted by direct contact, less often through objects (underwear, combs, brushes, hats, etc.). The disease is very contagious, which is why it is often observed in the form of family and school epidemics.
Symptoms and course:
Round or oval, slightly swollen spots appear on smooth skin, bordered by a border of small bubbles, nodules, and crusts; in the center there is slight pityriasis-like peeling. When the process is localized on the scalp, numerous, random bald patches the size of a pea to a fingernail, covered with grayish-white scales, form.
Diseased hair has extremely characteristic changes: most of it does not fall out, but is only shortened and broken off. Due to the development of fungi inside, some of the hair breaks off at the point where it exits the skin and looks like dark dots. Others are dull, grayish, curved, and break off at a height of 2-3 mm. Superficial trichophytosis, which begins in childhood, can become chronic.
The disease mainly affects women (about 80% of patients) who have dysfunction of the endocrine glands (usually the sex glands), hypovitaminosis A and E. Most often, in the occipital and temporal regions there is a barely noticeable finely focal peeling of the type of dry seborrhea. In these same places you can find small scars and “black dots” - stumps of broken hair. The favorite localization of the process on the skin is the area of the buttocks, thighs, palms (back side) and fingers
Infiltrative-suppurative (or deep) trichophytosis is caused by zoophilic fungi, infection of which occurs from domestic animals (horses, cattle, etc.). Less commonly, the source of infection is a person. Both adults and children are susceptible to the disease. In adults, the process is most often localized in the area of the beard and mustache and is called parasitic sycosis, in children - on the head and is called “honeycomb”.
Treatment:
Therapeutic tactics depend on the type of trichophytosis and, if possible, then it is necessary to limit ourselves to local drugs only.
When treating trichophytosis of smooth skin without involving vellus hair in the process, it is advisable to use alternating antifungal ointments and iodine-containing solutions to treat the skin. So, in the morning the affected areas are lubricated with an iodine solution, and in the evening an application is made with ointments such as Lamisil, Microspor, Exoderil. If the inflammatory phenomena of the skin are more pronounced, then combined hormone-containing drugs are indicated for the local treatment of trichophytosis.
If trichophytosis of smooth skin has a large number of foci and vellus hair is involved in the process, then in addition to local therapy, a course of treatment by taking antifungal drugs orally, for example Irunin, Itrazil and other triazole derivatives, is indicated. It is recommended to shave or cut the hair in the lesions.
Infiltrative-suppurative forms of trichophytosis, in addition to taking a systemic drug and local antifungal therapy, also require therapy for the suppurating infiltrate, the crusts are softened with Salicylic ointment or a solution of potassium permanganate, and then carefully removed; at the stage of resolution of the infiltrate, absorbable ointments are indicated, such as Ichthyol and liniment according to Vishnevsky.
Prevention of trichophytosis consists of timely identification of foci of the disease with isolation of patients and quarantine of contact persons. Systematic examinations in kindergartens make it possible to identify children with trichophytosis and prevent the spread of infection. Avoiding contact with stray animals, examining domestic animals, including those that do not come into contact with wild ones, reduce the risk of infiltrative-suppurative forms of trichophytosis.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital and on an outpatient basis. If only smooth skin is affected, the lesions are lubricated with 2-20% iodine tincture in the morning and 5-10% sulfur-salicylic ointment in the evening for several weeks, i.e. until the lesions completely disappear. If the scalp is affected, the hair in the lesions is shaved off once a week and the lesions are lubricated in the morning with a 2-5% alcohol solution of iodine, at night - 5% sulfur-salicylic or 5-10% sulfur-tar ointment.
It is also recommended to wash your hair with hot water and soap every other day. At the same time, griseofulvin is prescribed orally in tablets at the rate of 22 mg per 1 kg of body daily (for 20-25 days). After receiving the first negative fungal test, griseofulvin is prescribed every other day for 2 weeks, and then every 3 days for another 2 weeks until complete recovery.
In children with contraindications to griseofulvinotherapy, it is recommended to remove hair with a 4% aniline patch. First, the hair is shaved off and the patch is applied in a thin layer to the lesions. For children under 6 years of age, the patch is applied once for 15-18 days, and for older children - twice, changing the bandage after 8-10 days. Hair usually falls out after 21-24 days.
Then fungicidal agents are prescribed. For infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis, treatment begins with removing the crusts present in the lesions using bandages with 2% salicylic petroleum jelly. Then manual epilation (removal) of hair is performed using tweezers both in the lesions and 1 cm in their circumference.
Subsequently, wet-dry dressings are prescribed from a solution of ethacridine lactate, a 10% aqueous solution of ichthyol, or drilling fluid. After the elimination of acute inflammation, 10-15% sulfur-tar, 10% sulfur-salicylic ointment, Wilkinson's ointment are used. This treatment can be combined with oral griseofulvin.
Help from traditional medicine
Traditional therapy for trichophytosis in humans can be successfully supplemented with the use of non-traditional means. For example, traditional healers recommend rubbing an ointment prepared with garlic into the affected areas. The crushed mass must be supplemented with plantain juice and birch charcoal. All ingredients are taken in equal proportions.
You can also wash the infected areas of the skin with an aqueous infusion of string, celandine and horsetail. For this recipe, herbs are taken in an approximate ratio of 4:2:1. Dry ingredients should be poured with water and left to brew for 50 minutes. It is recommended to use the resulting product several times a day.
Treatment of nail trichophytosis
If a patient is diagnosed with nail trichophytosis, the dermatologist can offer several treatment options, from the use of topical medications to more radical methods - nail removal under local anesthesia (laser removal).
By the way, the latter method helps to quickly get rid of pathogenic fungal spores, but the disadvantages should also be taken into account - a person will need at least a week for rehabilitation (dressing, wound treatment). In addition, if onychomycosis is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, such a radical approach will be prohibited due to contraindications for the use of painkillers.
Still, patients prefer to be treated conservatively - with ointments and creams, as well as protective varnishes:
- “Batrafen”, “Loceryl”, “Mikozan” - varnishes against fungus.
- "Lamisil", "Resorcinol" - ointments.
- "Terbix" - spray.
- "Exoderil" - drops.
Ointments and creams stop the source of the disease itself, that is, fungal spores. The current pharmaceutical market offers many topical drugs with proven effectiveness and at an affordable price. Resorcinol ointment has shown good results in the fight against nail trichophytosis; it must be applied to the painful area only once a day. Available without a prescription.
Drops and sprays, in principle, have the same effect as ointments. You can buy the same “Resorcinol” (it has two release forms) or “Exoderil”. But keep in mind that Exoderil drops have a more pronounced effect than the cream of the same name. Now about the varnishes. Their purpose is to prevent further spread of infection. All nails need to be coated with varnish, not just the affected nail.
If the therapeutic effect cannot be achieved only with topical drugs, the dermatologist prescribes tablets to the patient that have a prolonged effect on the fungus, accumulating in the body. It is important to understand that all pills for trichophytosis are antifungal antibiotics, so they should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor, following the instructions. These include the drugs Griseofulvin, Ketonazole, etc.
To improve microcirculation in the area of the nail plate and ensure its speedy recovery, you should attend physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, UHF (exposure to a high-frequency electromagnetic field) for seven days.
Diagnostics
Only a highly qualified doctor can diagnose and prescribe treatment, for whom it will not be difficult to make the correct diagnosis based on the external specific manifestations of trichophytosis on the skin or hair of a person. After this, if possible, it is necessary to find out the causes of the disease and the intensity of the symptoms.
For additional confirmation, the hairline is examined using special lighting, as well as a determination of how deep the ulcers are on the skin. In some cases, laboratory testing of hair or scrapings from damaged skin may be necessary for diagnosis.