Skin contains melanin, which is the pigment that gives skin its color. With more melanin, the skin becomes darker, and with less melanin, it becomes lighter. Melanin is also responsible for hair and eye color.
Patches of discolored skin are noticeable because they are different from a person's normal skin tone. They may be lighter, darker, or a different color, such as red, gray, or blue.
It is important that people with this symptom understand the cause of the spots on their skin if treatment is necessary.
This article looks at the various causes of discolored patches on the skin and explains which ones require treatment.
What causes spots on the skin?
Discolored areas of skin can have many different causes, including:
- moles
- skin pigmentation disorders
- skin rashes
- skin infections
- skin cancer
- medical indications
Below we will look at each of them in more detail.
Christmas
Christmas spots are discoloration spots that appear on people at birth. Some types of birthmarks disappear over time, while others may be permanent.
Traces of birth are either vascular or pigmented. Vascular moles are red and appear due to abnormal blood vessels in the skin.
Types of vascular birthmarks include:
- Strawberry nevus. Also called a hemangioma, this is a common type of bloody birthmark. Appears as a red spot and is most common on the face, scalp, chest and back. Strawberry nevus usually does not require treatment.
- Salmon patch. Also called nevus simplex, this flat red or pink patch of skin usually appears on the neck or forehead. Up to 40 percent of all babies are born with this type of birthmark.
- Port wine stain. This is a noticeable flat red or purple birthmark. Some port wine stains may require treatment, which may include laser or cosmetic camouflage therapy.
Pigmented birthmarks are usually white, brown, blue or gray. They are the result of a problem with melanin in the skin.
Types of pigmented birthmarks include:
- Mongolian blue spots. These are blue or gray spots that may be present on the back and buttocks at birth. These moles are more common in children with darker skin. Mongolian blue spots often disappear as the child grows.
- Moles. These are black or brown spots that are usually harmless. However, it is best to see a doctor if a mole changes shape, size, or texture.
- Place in an au-light cafe. They appear as light brown spots on light skin or black, coffee-colored spots on dark skin. Ice cream coffee spots are often oval in shape and may disappear as the child grows.
Skin pigmentation disorders
If a person has lighter or darker areas of skin, this may indicate a problem with skin pigmentation. Types of skin pigmentation disorder include the following:
Melasma. This is a common skin condition that usually affects the facial skin and causes brown spots to appear. It affects women more often than men. Melasma triggers may include sun exposure and hormonal changes.
Vitiligo. This disease can affect any part of the body. This causes the cells that produce melanin, known as melanocytes, to stop working properly, resulting in blemishes on fair skin. Sometimes it also changes the color of a person's hair. The exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, but a problem with the immune system may occur.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation. This is a temporary increase or decrease in skin pigment after a skin injury such as a blister or burn.
Albinism. People with albinism do not produce enough melanin. This results in little to no pigment in the skin, hair or eyes. Albinism is a genetic disorder meaning that a person inherits a defective gene from one or both parents.
Skin rash
Some types of skin rashes may also cause patches of discolored skin. These include
- Rosacea. It is a chronic skin condition that can cause increased patches of red skin and pus-filled lesions. It usually affects the forehead, cheeks and nose.
- Contact dermatitis. A rash occurs when the skin reacts to an irritant or allergen.
- Eczema. Also known as atopic dermatitis, this condition can cause itchy, dry, and cracked patches of red skin. Sometimes these areas can ooze juices and form a crust. The cause of eczema is unclear, but it can run in families and is more common in people with asthma, hay fever and other allergies.
Skin infections
Some skin infections can also cause discoloration, such as:
- Pineapple versicolor. This is a fungal infection of the skin that can cause skin patches to become lighter or darker. These patches usually develop slowly and can sometimes coalesce to form larger patches. Pineapple color tends to affect the torso, neck and shoulders.
- Ringed worm. Also known as pineapple, it is a fungal skin infection that causes red or silvery ring-shaped patches to appear on the skin. These areas may be scaly, dry, or itchy. Annelids can appear on most parts of the body, including the scalp, groin, feet, hands and nails.
- Skin candidiasis. It is a fungal skin infection that causes red itching and itching on the skin. Often found in skin folds such as the armpits and groin.
Skin cancer
In rare cases, skin cancer can cause discoloration to appear. Types of skin cancer include:
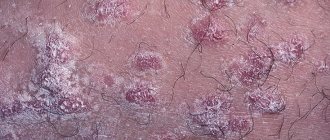
- Actinic keratosis. These are dry, scaly, precancerous spots on the skin. Without treatment, they can progress to squamous cell carcinoma.
- basal cell carcinoma. These are flesh-colored spots or bumps that look like pearls and are pink in color. Basal cell carcinomas are the most common form of skin cancer.
- Squamous cell carcinoma. These are red bumps, sores, or scaly patches that may heal and then open again. Squamous cell carcinomas are the second most common type of skin cancer.
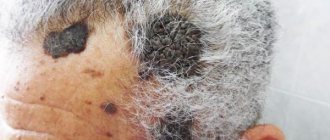
- Melanoma. This cancer can develop in existing moles or appear as new dark spots. Melanomas are the most severe form of skin cancer, so early diagnosis and prompt treatment are critical.
Health status
Certain medical conditions, including the following, can cause skin discoloration:
- Cyanosis. Insufficient oxygen in the blood can cause the skin and lips to appear blue or purple. Sudden onset cyanosis may be a sign of a problem with the heart, lungs, or airways. This is a medical emergency and the person should seek medical attention immediately.
- Lupus. It is a complex autoimmune disease that can cause a butterfly-shaped rash on the cheeks.
Undiagnosed or untreated diabetes can also cause skin changes such as
- yellow, reddish, or brown patches of skin.
- dark, velvety areas of skin.
- thick, hard patches of skin.
- blisters
- shin spots
Other reasons
If discolored patches of skin appear suddenly and then disappear, there may be a simple explanation for this.
Causes of temporary spots or spots on red skin:
Causes of temporary patches of pale skin include:
Yellow and dry spots on the body
Yellow and dry spots on the body appear in case of hypothyroidism. As a result of liver dysfunction and the deposition of carotene in the skin, it takes on a yellowish tint, becomes cold, pale, dry and loses vitality. Numerous freckles, brown moles and warts can cause anxiety.
Yellow-brown spots are a symptom typical of yeast dandruff, i.e. superficial skin infection. The disease usually develops after puberty. Skin changes are located mainly on the chest, neck, trunk and scalp. They reach a size of about 4 mm and tend to mix with each other. They have an irregular shape. Well demarcated. When exposed to sunlight, the changed areas do not tan.
diagnosing
To diagnose discolored areas of skin, the doctor may ask the patient:
- pre-existing medical conditions
- when and how quickly the discolored spot on the skin appeared.
- Has the color of the skin patch changed since it first appeared?
- any associated symptoms
The doctor may examine the affected skin under a lamp. They may also need to do additional tests such as blood tests and skin biopsies. For a skin biopsy, the doctor takes a small sample of skin and examines it under a microscope.
White spots on the body
White spots on the body are a characteristic symptom of acquired vitiligo. This is a chronic and progressive disease that involves depigmentation of areas of the skin (local discoloration of the skin).
The exact factors determining its development are unknown. It is assumed that the disappearance of melanocytes, that is, the cells responsible for skin color, is a consequence of dysfunction of the immune system. In addition, it may be genetically and environmentally determined.
Vitiligo most often begins in childhood. At first it is one or more colorless spots. Skin changes are localized mainly on the face, legs, elbows, forearms, knees or hands. The skin becomes warm, moist, smooth, more sensitive to sunlight and symptoms of seborrhea often occur.
Pibaldism is another disease characterized by the appearance of white spots on the skin. This is a rare developmental disorder caused by dysfunction of melanocytes. Its characteristic symptoms are a white strand of hair above the forehead, white patches of skin located mainly on the forehead, chin, chest, limbs and abdomen. Discolored, white patches on the skin may appear during eczema. The skin is initially red and rough, then becomes white.
White spots on the body are common in patients with pernicious anemia, hyperthyroidism, Addison's disease and Hashimoto's disease. Other diseases that can cause skin changes include: Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome (choroidal meningitis), Waardenburg syndrome, Alezzandrini syndrome, and scleroderma fungus.
Treatment
Treatment for discolored skin depends on the cause.
If a person is suffering from any disease, the doctor will recommend the best course of treatment for that disease. Treatment of the underlying disease often resolves all associated skin problems.
If the underlying cause is skin cancer, it is very important that the person receives treatment as soon as possible.
Birth and skin pigmentation disorders usually do not require treatment. However, some people may wish to undergo treatment for cosmetic reasons. Treatment options include laser treatment, chemical peels, and topical creams.
Lemon juice or castor oil can also help reduce the appearance of discolored spots on the skin. Alternatively, people can use cosmetics to camouflage affected skin.
Brown spots on the body
Brown spots on the body are typical of dark keratosis. It is a skin disorder that occurs in, among others, type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, gastrointestinal malignancies (especially gastric cancer), Addison's disease, acromegaly, Cushing's syndrome, and hypogonadism.
Actinic keratosis can be a side effect of taking certain medications, such as insulin, oral contraceptives, niacin, and glucocorticoids. Typical for this disease is hyperkeratosis, that is, thickening of the stratum corneum. Numerous warts and brown spots appear on the skin, often localized in the armpits, around the nipples, navel, on the neck, arms, oral mucosa, and nose.
Brown spots on the skin are called age spots. They most often occur in women over 50 years of age. They are often caused by excessive tanning of unprotected skin, hyperthyroidism, hypoadrenalism and hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause. They often appear on the face - cheeks, nose, forehead, décolleté, arms and hands.
Numerous coffee and milk spots on the body are caused by diseases of genetic origin, which are classified as so-called phakomatoses. Light brown spots are typical of neurofibromatosis type 1 and tuberous sclerosis (Bournville-Pringle disease).
Red spots on the body - causes
Red spots on a child's body are associated with many diseases typical of childhood, such as scarlet fever, rubella, measles, chicken pox, fever, allergic urticaria, atopic dermatitis, mononucleosis or erythema infectiosum.
Red spots on the body in adults may appear as a result of fungal mycosis - cutaneous lymphoma. The disease is characterized by erythematous-exfoliative, psoriatic, eczematous lesions and severe itching.
Bright red spots on the skin are a sign of Gibert's pink dandruff. Characteristic signs of the disease are erythematous-exfoliative lesions located on the trunk and proximal parts of the extremities. Symptoms last 4-6 weeks. Skin changes are often accompanied by slight itching.
Another disease that appears as red spots is stellate hemangiomas. Nevi look like red spots with radiating branches. They are often located on the face and upper body. They appear in women during pregnancy and the postpartum period. They may be evidence of circulatory disorders and liver cirrhosis.