Papilloma on the palate and palatine arch is an unpleasant and sometimes dangerous phenomenon. Moreover, they cause the same problems in both adults and children. The papilloma virus, which provokes this phenomenon, leads to the growth of formations throughout the body. If the infection is not treated, there is a high probability of complications and long, difficult therapy. The longer the virus stays in the human body, the more damage it manages to cause. Therefore, at the first signs of formations in the oral cavity, you should seek qualified help. Only an experienced specialist will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Reasons for appearance
Laryngeal papillomatosis is caused by reasons that have long been known to doctors. The disease begins to spread throughout the body after infection. Because of it, serious changes occur in the structure of epithelial tissues. This is why papillomavirus causes characteristic rashes in the throat.
Over a long period, the human papillomavirus can successfully hide. The patient will not suspect that during one of the past intimate contacts or while using someone else’s thing, he became infected with this disease. A small child can become infected during birth if his mother is sick with papillomavirus.
If the infected person has a strong immune system, then papillomatosis will not bother him for a long time. As soon as the body’s protective properties are weakened, painful rashes will immediately begin to appear on the body. Among them may be squamous cell papilloma of the larynx.
Papilloma in the throat, which can be seen in detail in the photo depicting the area affected by the virus, appears due to the influence of the following factors on the body:
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- Prolonged runny nose;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Avitaminosis;
- Respiratory diseases;
- Failure to comply with oral care rules.
Papillomas in the throat and other places are caused by the human papillomavirus
The risk group for developing papilloma in the larynx includes children under 5 years of age and adults aged 20-40 years. The risk increases several times if a person constantly engages in promiscuity and has bad habits. Due to smoking, a huge amount of harmful substances accumulate in the larynx area. This is fraught for the patient with the development of problems with the evacuation function. Tobacco smoke greatly irritates the mucous membrane, so it becomes defenseless against virus attack.
Additionally, doctors identify risk factors. Papilloma in the throat can grow due to the following reasons:
- Chronic course of tonsillitis;
- Pharyngitis and laryngitis;
- Purulent and acute otitis.
Medical experts who study the nature of the appearance and course of the human papillomavirus are convinced that stressful situations contribute to its development. In this condition, the immune system begins to weaken, allowing the viral infection to freely attack healthy cells.
Drug therapy
With the help of medications, the patient’s oral cavity is thoroughly cleaned, and pockets of infection are eliminated.
A special ointment may be prescribed to treat the oral cavity. With antiviral therapy, the doctor prescribes drugs that neutralize the effect of HPV. With this treatment, a special diet is also prescribed, recommendations are given on proper nutrition and personal hygiene. Additionally, specialists can prescribe vitamins that improve immunity and further help the body fight the virus.
Antiviral drugs
The prescription of drugs of this class is necessary to neutralize the function of HPV. These medications help the immune system restore its normal functioning, and for better effect they are often supplemented with vitamin complexes.
In addition, the doctor can create a unique diet for you if your specific case requires it. You also need to be prepared for the fact that the doctor will demand that you give up bad habits.
Drug treatment of tumors on the tongue is quite complex and requires a complete examination of the patient before choosing a medication. Even making one minor mistake in the process of selecting a drug can aggravate the patient’s condition, allowing the infection to spread to other parts of the body.
After identifying the strain of the virus that caused benign tumors, as well as assessing the patient’s condition and conducting a survey, the doctor will be able to prescribe one or more drugs that will complement antiviral therapy.
Before prescribing medications, the patient’s mouth is sanitized, and then recommendations and a list of procedures necessary to be performed to maintain a healthy oral cavity are drawn up.
Another popular approach is the use of chemical solutions. It is indeed used very often to treat illness caused by the HPV virus, but it cannot be used for the tongue due to the unpredictability of the reaction of the mucous membranes.
Source: coriummed.ru
Why are they dangerous?
The human papillomavirus can survive an incubation period for a long time. Usually this condition is limited to a period of 2 to 5 months. This is one of the reasons that explains the difficult diagnosis of an infectious disease at an early stage.
Laryngeal papillomatosis in children and adults is very dangerous, since the rashes caused by it can degenerate into malignant neoplasms. Such an outcome cannot be avoided if the patient does not follow the doctor’s instructions, refuses treatment and does not dare to quit bad habits.
Another danger of the disease is that papillomas recur. This is well known to thousands of patients who are unsuccessfully trying to get rid of the pathology. A recurrent disease can lead to an increase in the number of papillomas on the uvula, tonsils and throat. And this only increases the chances of cancer cells growing.
Symptoms of growth of papillomas in the throat
Papillomatosis is difficult to recognize, since at the very beginning of its development it does not show any signs. This is due to the immune system, which is able to contain the disease for some time. When the body loses its defenses, viruses accumulate in a certain place. This is how laryngeal papillomatosis develops, which requires mandatory treatment. In the affected area, a failure occurs in the process of cell division, against which growths appear.
Small papillomas do not have any special symptoms. Certain problems are caused by fairly large rashes that are localized in the throat. Their development is usually accompanied by conditions such as dysphagia and dysphonia. Large papillomas prevent a person from eating, drinking, speaking and breathing normally. He begins to complain of wheezing and periodic coughing, which occurs throughout the day. Symptoms of a pathological process in the throat are complemented by swelling and inflammation of the tonsils. Due to the disease, fusion of the palatine arches occurs.
If the papilloma continues to grow, then the person develops a severe cough, which produces sputum mixed with blood. His voice also changes a lot. He becomes more deaf due to the development of hyperkeratosis of the vocal cords.
A large tumor in the throat leads to airway obstruction. Patients have serious difficulties in swallowing water and food. Frequent attacks of suffocation, which can have disastrous consequences, are no exception.
Due to papillomatosis, patients develop psychomotor dysfunction. Dystrophy in the functioning of internal organs and disruption of the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems are often observed.
Patients who have papillomas in the throat develop stenosis of the respiratory tract. It comes in 4 degrees:
- The first degree is called compensatory. The person suffers from hoarseness, there are long exhalations and very noisy inhalations;
- The second degree is called decompensation. Its symptoms resemble a state of hypoxia. The patient is diagnosed with panic attacks, tachypnea, cyanosis and hyperhidrosis;
- Third degree. Accompanied by noticeable pallor of the skin, bradycardia, mydriasis and asphyxia;
- Fourth degree. In this condition, frequent fainting and apnea cannot be ruled out.
Each of these disorders negatively affects the functioning of not only the respiratory system, but also the entire body. If they are detected, you must immediately seek qualified help.
It will not be difficult for an ENT specialist to detect papilloma
Types of growths of the soft palate
Microscopically, oral papilloma is a tumor of highly differentiated stratified squamous epithelium with symptoms of keratinization. The membranes are intact, the polarity of the cells is not changed, but there is an imbalance of the structural elements of the epithelium and connective tissue framework, and a focal infiltrate of inflammation. There are soft papillomas, pinkish doughy in consistency, hard ones - gray dense to the touch. The former often recur, bleed easily when injured, and grow well into nearby tissues. They tend to resolve themselves under a number of conditions. Solid types do not bleed, and no new appearance is observed after removal.
The growths are fixed on:
- amygdala;
- upper soft palate;
- uvula (papilloma of the uvula is rare in practice).
Sometimes papillomas of the soft palate are represented by a single element, but papillomatosis of the throat also occurs, which is characterized by groups of many formations. They (especially in children) can cause obstruction of varying severity - from slight hoarseness of the voice, shortness of breath to asphyxia, which can be fatal.
Treatment methods
A competent specialist can tell you how to treat a viral rash on the mucous membrane of the throat. Depending on the state of health and the severity of the disease, the patient will be offered conservative or radical therapy. As an auxiliary treatment, the use of proven folk remedies may be required.
Medication
For papillomatosis that affects the throat, you will need to take medications. Some of them help cope with the virus itself by suppressing its activity. Others are intended to increase the protective properties of an organism weakened due to illness.
The following medications may be prescribed by your doctor:
- Antiviral - Zovirax, Amiksin, Kagocel, Allokin-Alfa;
- Immunomodulatory - “Interal”, “Viferon”, “Isoprinosine”, “Cycloferon”, “Reaferon”.
The use of several medications that belong to different groups is required at the same time. Due to this, drug therapy becomes more effective.
To avoid the appearance of new papillomas, you need to suppress the activity of the virus and boost immunity
Surgical treatment
Quite often, surgery is mandatory for laryngeal papillomatosis. Removal of viral rashes is carried out using endolaryngeal therapy. Microinstruments are sometimes used to minimize the likelihood of damage to adjacent tissue during surgery. According to patients, they look scary. But they bring excellent results.
To achieve long-term remission, the use of combination therapy is required. It is recommended to combine surgical methods with taking medications that prevent the viral infection from spreading throughout the body.
Cryosurgery and other hardware methods
The cryosurgical method is excellent for removing a single papilloma in the throat. During the procedure, a cooling substance is used, which acts directly on the tissue of the benign tumor. To completely remove the growth, you need to undergo about 5 cryosurgery sessions. An interval of 3 days should be maintained between them to avoid severe swelling of the laryngeal tissues.
There are other hardware methods that help quickly and almost painlessly get rid of tumors that appear on the mucous membrane of the throat. These include:
- Laser therapy;
- Radio wave excision;
- Electrocoagulation;
- Laryngoscopy using high-frequency current.
Traditional methods
Often people who have been found to have papilloma of the throat practice its therapy with folk remedies. As a home remedy, it is recommended to use tinctures and teas made from medicinal herbs and other plant components.
An infusion prepared with buckwheat does a good job of boosting immunity. The following also help improve the patient’s general health:
- Pomegranate juice. Drink 50 ml daily with meals;
- Garlic. Must be added to various dishes;
- Horseradish with honey. Eat the resulting mixture 1 tsp 2 times a day;
- Juniper berries. Must be consumed on an empty stomach every morning;
- Infusion of bay leaves. Drink 1 glass throughout the day.
Don't forget to include fresh vegetables and fruits in your daily diet, which are rich in healthy vitamins and microelements. If a person has papilloma in the throat, then such treatment with folk remedies will help him reduce the severity of painful symptoms. In addition, homemade medicines, prepared with natural ingredients, enhance the effect of the drugs and help consolidate the results achieved through radical therapy.
Folk remedies
Papillomas on the lower and upper parts of the tongue can be treated with folk remedies at home. However, they can only be used as part of the main therapy and after consultation with a doctor. Only in this case will it be possible to achieve an effective result and avoid adverse consequences.
Medicinal herbs help against HPV: lemon balm, rosehip, plantain, chamomile, etc. Infusions and decoctions from these plants strengthen the immune system. You can also consume 100 ml of red potato juice daily.
You can remove formations at home using celandine juice. They need to lubricate the growths. The remedy brings results if the tumors are small. Repeat the procedure three times a day. Duration of therapy is one month.
Prevention
Preventive measures are of great importance in preventing the development of papillomatosis in the throat area. They help prolong remission and reduce the frequency of relapses of viral infection activation.
To avoid the re-formation of papillomas in the throat, you need to ensure a gentle vocal regime, promptly eliminate infectious diseases of the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract, use barrier contraception and regularly strengthen the immune system.
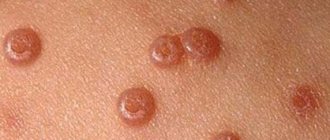
Papillomas on the uvula in the throat are viral growths with a rough surface that affect the mucous membrane. They can be single or grouped, creating a large affected area. Typically painless, but can be dangerous if they grow and block the airways.
Locations
As mentioned above, papillomas can appear in the throat, on the lining of the mouth, and on the tongue. It happens that growths grow in the area of the trachea, upper esophagus, and larynx.
In the throat
In the throat, papillomas most often occur on the arches and tonsils, soft palate, lateral walls of the pharynx, and less often in the larynx and vocal cords. Practically do not appear on the tongue.
In the larynx
Papillomas in the larynx are the most dangerous place. Most often they form on the vocal cords and speech is impaired. The growth of papillomas in the tracheal area is dangerous due to breathing complications (asphyxia).
This is more common in children; in adults, such papillomas are less dangerous.
In the esophagus
Papilloma can grow and affect the upper part of the esophagus, which then impairs the ability to swallow food and clogs the space. Sometimes a benign tumor can develop into a malignant one. If there is papilloma in the esophagus, the following symptoms occur:
- Sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- Difficulty swallowing food;
- Chest pain.
When the growths become damaged, vomiting and bloody stool may occur in the esophagus. A gastroenterologist can give advice and diagnose the result.
Video:
Why do papillomas appear on the tongue in the throat?
The reason for the appearance of papillomas on the human body, including mucous membranes, is the penetration of papillomavirus into tissues and blood. Typically, infection occurs through unprotected sexual contact, as well as in everyday life when sharing objects with an infected person. The easiest way for the virus to enter the body is through damaged skin or mucous membranes. It penetrates into the DNA structure and begins to affect the process of cell division. This is how characteristic benign growths appear.
Most often, neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the mouth, throat, including the tongue, appear due to oral sexual contact in adults or through the use of contaminated hygiene items and utensils among children. Also, sometimes the virus can be transmitted from mother to baby during childbirth. However, it is worth noting that papillomas on the uvula in the throat are quite rare, since this organ is difficult to injure and is well protected. However, with an increase in the viral load on the body and the growth of papillomas in the oral cavity or throat, tonsils, growths can also affect the tongue.
The causes of papillomas on the tongue in the throat are common: decreased immunity, chronic diseases, poor diet, hypothermia, nervous strain, overwork, bad habits. All these factors contribute to the activation of HPV and an increase in the number of viral tumors on the mucous membranes.
Video
Laser removal of papillomas on the tongue.
[youtube.player]
Benign tumors (caused by the human papillomavirus) can appear on any part of the body and mucous membranes, including in the mouth. Papilloma of the palatine arch is a nodule with papillary growths on the palate (uvula, tonsils, tongue, cheek).
Signs of papillomas on the tongue in the throat
Photo of papillomas on the tongue in the throat
For a long time this pathology does not manifest itself. It can be difficult to notice the growths because it is a difficult place to reach. In addition, papillomas on the throat and tongue are painless and often do not cause any discomfort. Also, sometimes they are covered with healthy mucosa, and it is almost impossible to visualize them with the naked eye.
Most papillomas are small growths with a rough, uneven surface. They can blend in color with the healthy mucous membrane or be lighter. Sometimes they are covered with a whitish coating.
Usually, papillomas on the tongue in the throat are discovered during preventive examinations, and also when the patient experiences noticeable discomfort.
Unpleasant sensations in this area can be presented in the form of the following symptoms:
- Difficulty chewing and swallowing;
- Sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- Changing the sound of the voice;
- Difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing for no apparent reason.
In some advanced cases, a cough appears mixed with blood, but without copious sputum. This happens when growths are injured, as well as during malignant degeneration of tumors.
Symptoms
You can see what papillomas look like in the mouth on the tongue of an adult or a child on the Internet on a thematic website. There are different types of growths: thread-like, pointed, etc. The latest type of papillomavirus most often affects the genitals. Sometimes it appears on the frenulum of the tongue. If you type on the Internet: photo of genital papillomas in a person’s mouth, you can see that visually they resemble cauliflower or a cockscomb.
The tongue is most susceptible to flat growths. If they are extensive, the pathological condition is called papillomatosis. Such growths do not grow more than 3 mm. After some time, they provoke keratinization of the epidermis and non-healing ulcers. Symptoms in children and adults include the following:
Papillomas are often damaged by eating food
- swelling of nearby tissues;
- itching and burning sensation;
- soreness;
- difficulty breathing reflex;
- difficulty swallowing;
- sensation of a foreign object in the oral cavity;
- increased salivation;
- problems with pronunciation;
- bad breath;
- feeling of nausea;
- belching;
- swelling of the tongue.
Papillomas are often damaged by eating food. Sores appear that cause pain when chewing. If no measures are taken, bleeding ulcers will soon appear in their place. Over time, the tongue will lose motor function. The blood spreads the infection throughout the body, which contributes to the appearance of growths in other places. If you notice symptoms of papillomavirus, you need to consult a doctor.
Methods for diagnosing papillomas on the tongue in the throat
The throat and uvula area can be examined without special equipment. This is done by otolaryngologists at the appointment. A laryngeal mirror can also be used to visualize papillomas. If the neoplasms are covered with healthy mucosa, then diagnosis can be complicated.
Indirect laryngoscopy can detect a group of papillomas in the throat. Also, if cancer is suspected, the doctor will prescribe a biopsy of the growth. The seized biological material will be sent for histological examination. This analysis will determine the benignity of the papilloma on the uvula in the throat.
Modern autofluorescence research allows us to determine the boundaries of the throat and larynx affected by papillomas. The doctor may also prescribe computed tomography and macrolaryngostroboscopy to clarify the diagnosis.
In addition, a blood test - PCR - will help determine the presence of papillomavirus in the body. This is a labor-intensive test that detects the nucleic acids of the pathogen. However, despite the fact that this study reveals the presence of the virus in the blood, this is not proof that the tumors in the throat are papillomas.
Treatment methods for papillomas on the tongue in the throat
Treatment of papillomas on the tongue in the throat should be carried out exclusively by a specialist. This is a difficult-to-reach area; in addition, the growths can grow deep into the esophagus or larynx, and it is not possible to remove them yourself without risk to health. The main method of treatment is the physical destruction of papillomas on the tongue in the throat. Doctors can also include antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy.
Removal of papillomas on the tongue
The localization features of the growths do not allow the use of all existing methods of physical removal of papillomas. The cryodestruction and electrocoagulation techniques are practically not used. Firstly, in these cases it is quite difficult to control the depth of penetration of liquid nitrogen or electric current, and therefore there is a risk of causing serious damage to the reed. Secondly, after such removal it is impossible to remove biological material for a biopsy to determine the malignancy of the growth.
If you are interested in how to remove papilloma on the uvula of the larynx, then pay attention to laser coagulation. This is the optimal way to destroy a tumor. The laser allows you to accurately measure the depth of penetration into tissue. In addition, during the removal process there is no severe bleeding, since the laser beam cauterizes the vessels. The risk of relapse after such treatment is minimal, and the recovery period is short. The price of laser removal of papillomas on the tongue in the throat is 1200-2600 rubles in Russia and 340-670 hryvnia in Ukraine.
Radiosurgical removal of growths is also often prescribed for the treatment of papillomatosis in the throat. This is the most modern and low-traumatic method of destroying tumors. A radio knife or radio loop affects only diseased tissues without affecting adjacent healthy ones. This method of destruction also does not cause blood loss and does not leave scars. The mucous membrane is quickly restored. The price of radiosurgical removal of papillomas on the throat and tongue is 1900-3100 rubles in Russia and 600-1200 hryvnia in Ukraine.
In some cases, papillomas in the throat and mouth can be removed using a regular scalpel or surgical loop. However, this technique is used less and less often, since this operation is traumatic and requires high skill of the surgeon. After such a surgical intervention, complications often develop in the form of severe bleeding, scar formation, and a long rehabilitation period. The cost of surgical excision of papillomas in the throat is 650-1450 rubles in Russia and 180-470 hryvnia in Ukraine.
Treatment of papillomas in the throat on the tongue with medications
Photos of medications for papillomas on the tongue in the throat
In the treatment of papillomatosis, medications are often prescribed. The main groups of medications used in this case are antiviral and immunomodulatory. The main goal of such drug therapy is to strengthen the body’s protective functions and force the immune system to fight the pathogen that causes papillomas on the uvula in the throat.
Immunomodulators increase the production of interferon in the body, which fights pathogens. In most cases, doctors prescribe immunomodulators in tablet form. Sometimes injections of drugs may be prescribed. There are also immunomodulatory medications in the form of sprays for irrigating the mouth and throat. Amiksin (from 600 rubles), Likopid (from 400 rubles) and their analogues - IRS-19 (about 600 rubles), Derinat (from 400 rubles) are popular.
For papillomas on the throat and tongue, antiviral drugs that suppress HPV in the body can also be prescribed. They block the activity of the pathogen, reduce the viral load on the body and help avoid relapses after the destruction of tumors on the uvula in the throat. The following medications showed positive results: Panavir (1600-2100 rubles), Allokin-Alpha (3400-4000 rubles) and their analogs - Cycloferon (from 300 rubles) and Viferon (from 400 rubles).
Treatment of papillomas on the tongue in the throat with folk remedies
It is worth remembering that self-medication of papillomas on the tongue in the throat is contraindicated. You will not be able to completely remove the growth on your own. In addition, improper treatment can lead to malignancy of the tumor.
You can use traditional medicine recipes as additional therapy. They will help boost immunity and strengthen the body's defenses. This will be a good prevention of HPV relapses. But traditional methods cannot be used as the main methods for treating papillomas.
The following recipes for papillomas on the tongue and throat have proven themselves to be effective:
- Dilute a teaspoon of honey in a cup of clean warm water and drink once a day on an empty stomach (if you are not allergic to bee products).
- Grind the horseradish root and mix 1 tablespoon with a teaspoon of honey. Use this mixture once a day.
- Mix crushed leaves of oregano, coltsfoot, raspberry, plantain, thyme, black currant, and licorice root. Pour the collection with hot water and leave in a thermos for several hours. Take the infusion several times a day for 30 days.
The above remedies will help strengthen the immune system and give the body the strength to fight infection. These recipes are effective if used regularly.
Malignant tumors
Clinical picture
Malignant tumors of the middle part of the pharynx grow quickly. They may remain unnoticed for some time, usually several weeks, much less often months. The first symptoms of malignant tumors depend on their primary location. Subsequently, as the tumor grows, the number of symptoms increases rapidly. One of the early signs of a tumor is the sensation of a foreign body in the throat. Soon it is accompanied by pain in the throat, which, like the sensation of a foreign body, is strictly localized. Epithelial tumors are prone to ulceration and decay, as a result of which the patient develops bad breath and blood in the saliva and sputum. When the tumor process spreads to the soft palate, its mobility is impaired and a nasal sound develops; liquid food may get into the nose. Since swallowing disorders occur quite early and the passage of food is disrupted, patients begin to lose weight early. In addition to local symptoms, due to intoxication and inflammation accompanying the tumor, general symptoms also develop, such as malaise, weakness, and headache. When the lateral wall of the pharynx is affected, the tumor quickly penetrates deep into the tissues towards the neurovascular bundle of the neck, and therefore there is a danger of profuse bleeding.
Among malignant tumors of the oropharynx, neoplasms of epithelial origin predominate. Epithelial exophytically growing tumors have a wide base, their surface is bumpy, in places with foci of decay; pink color with a grayish tint. There is an inflammatory infiltrate around the tumor. The tumor bleeds easily when touched.
A tumor ulcer is quite often localized on the palatine tonsil. The affected tonsil is enlarged compared to the healthy one. A deep ulcer with uneven edges, the bottom of which is covered with a dirty gray coating, is surrounded by an inflammatory infiltrate.
Diagnostics
Laboratory research
Cytological examination of smears-imprints or reprints. The final diagnosis of a tumor, determining its type, is established by studying its histological structure.
Instrumental studies
Biopsy - excision of a piece of tissue for histological examination - is one of the important diagnostic methods in oncology. It is well known that a piece of tissue should be taken at the border of the tumor process, but it is not always possible to determine this border, especially with tumors of the ENT organs. Neoplasms of the palatine, pharyngeal and lingual tonsils, especially connective tissue ones, arise deep in the tonsil tissue. The amygdala enlarges. An enlarged tonsil should be alarming and requires targeted research, including a biopsy. In case of asymmetry of the palatine tonsils, if a tumor process is suspected, if there are no contraindications, it is necessary to perform a unilateral tonsillectomy or tonsillotomy as a biopsy. Sometimes such a tonsillectomy can be a radical surgical intervention in relation to the tumor.
Differential diagnosis
An ulcerated tumor of the tonsil must be differentiated from ulcerative membranous tonsillitis Simanovsky-Vincent, syphilis and Wegener's disease. For this purpose, it is necessary to examine smears taken from the edges of the ulcer and perform the Wasserman reaction.
Treatment of patients with oropharyngeal tumors
The main treatment method for patients with benign tumors of the middle part of the pharynx is surgical. The extent of surgical intervention depends on the extent, histological structure and location of the tumor. Limited tumors, such as palatine papilloma, can be removed in the clinic using a loop, scissors or forceps. After its removal, the original site of the tumor is treated with galvanocauter or a laser beam. In a similar way, you can remove a pedunculated fibroma, a small, superficial cyst of the tonsil or palatine arch. A small mixed tumor of the soft palate can be removed through the mouth under local anesthesia. More often, when removing tumors of the oropharynx, anesthesia is used, using a sublingual pharyngotomy as access, which is often supplemented by a lateral one.
A wide external approach allows complete removal of the tumor and ensures good hemostasis. External access is also required when removing vascular tumors of the pharynx. Before removing hemangiomas, the external carotid artery is first ligated or embolization of the afferent vessels is performed. Intervention for these tumors is always associated with the risk of severe intraoperative bleeding, which may require ligation of not only the external, but also the internal or common carotid artery to stop. Considering the possibility of intraoperative bleeding and the severity of the consequences of ligation of the internal or common carotid artery, in patients with parapharyngeal chemodectomas and hemangiomas, “training” of intracerebral anastomoses is carried out 2-3 weeks before surgery. It consists of pinching the common carotid artery on the side of the tumor localization with a finger 2-3 times a day for 1-2 minutes. Gradually, the duration of clamping is increased to 25-30 minutes. At the beginning of the “training” and then when the duration of clamping of the common carotid artery is increased, the patient feels dizzy. This sensation serves as the criterion by which the duration of clamping of the artery is determined, as well as the duration of the “training” course. If clamping the artery for 30 minutes does not cause a feeling of dizziness, then after repeated clamping for another 3-4 days, you can begin the operation. Cryotherapy as an independent method of treating patients with benign tumors is indicated mainly for superficial (located under the mucous membrane) diffuse hemangiomas. o can be used in the treatment of deep hemangiomas in combination with surgery. The main methods of treatment for malignant tumors of the oropharynx, as well as for neoplasms of other localizations, are surgical and radiation. The effectiveness of surgical treatment is higher than the effectiveness of radiation and combined treatment, the first stage of which is radiation. Through the mouth, it is possible to remove only limited tumors that do not extend beyond one of the fragments of this area (soft palate, palatoglossal arch, palatine tonsil). In all other cases, external approaches are indicated - transhyoid or sublingual pharyngotomy in combination with a lateral one; sometimes, to gain wider access to the root of the tongue, in addition to pharyngotomy, resection of the lower jaw is performed. Surgeries for malignant tumors are performed under anesthesia, after ligating the external carotid artery and performing a tracheotomy. Tracheotomy is performed under local anesthesia, and subsequent stages of the intervention are performed under intratracheal anesthesia (intubation through a tracheostomy). If the palatine tonsil is affected by a tumor that does not extend beyond its limits, they are limited to removing the tonsil, palatine arches, paratonsillar tissue and part of the root of the tongue adjacent to the lower pole of the tonsil. The gap of unaffected tissue around the tumor focus should not be less than 1 cm. This rule is also followed when removing common tumors using external access. Radiation treatment of patients with pharyngeal tumors should be carried out according to strict indications. This therapeutic effect can only be used for malignant tumors. As an independent method of treatment, irradiation can be recommended only in cases where surgery is contraindicated or the patient refuses surgery. We recommend combined treatment, the first stage of which is surgery, for patients with stage III tumors. In other cases, you can limit yourself only to surgery. For tumors occupying the middle and lower parts of the pharynx, spreading to the larynx, a circular resection of the pharynx is performed with removal of the larynx. After such extensive intervention, an orostoma, tracheostomy and esophagostomy are formed. After 2-3 months, plastic surgery of the lateral and anterior walls of the pharynx is performed, thereby restoring the path of food passage. The five-year survival rate of patients after surgical treatment is 65+10.9%, after combined treatment (surgery + radiation) - 64.7±11.9%, after radiation therapy - 23+4.2% [Nasyrov V.A., 1982 ].
Source: vse-zabolevaniya.ru
Common symptoms that can be observed to varying degrees with any of the benign tumors of the pharynx are: sore throat, sensation of a foreign body in the throat, difficulty in nasal breathing and a nasal tone of voice. With benign tumors of the pharynx, catarrhal symptoms may appear: redness and some swelling of the palatine arches and the posterior wall of the pharynx. The clinical picture of a benign tumor of the pharynx has its own characteristics depending on the type of tumor.
Papillomas
Benign tumors of the pharynx, which may be caused by the human papillomavirus, which also causes the appearance of warts, genital warts and papillomas in other areas. Papillomas are nodules covered with papillary outgrowths. These benign tumors of the pharynx are located on a narrow or wide stalk, can be multiple and combined with laryngeal papillomas.
There are soft papillomas, which have a loose consistency, and hard papillomas, which are dense formations of a grayish color. Soft papillomas tend to recur, can bleed and grow into nearby tissues, and sometimes disappear on their own. Hard papillomas usually do not recur and do not bleed. Separately, pharynx papillomatosis is distinguished - damage to entire areas of the mucous membrane by papillomas.
Fibroids
They are usually round in shape, pink or red in color and located on a wide base. Their surface can be smooth or bumpy, and it bleeds easily when touched. The density of this type of benign pharyngeal tumors can reach the consistency of cartilage. In this case, the densest part of the tumor is its base. Microscopically, fibroids are connective tissue with many elastic fibers and blood vessels.
Although fibromas are benign tumors of the pharynx, they are characterized by a malignant course, since they often grow rapidly and invade surrounding tissues. A significant increase in tumor size can cause disruption of nasal breathing, difficulty swallowing, and the appearance of stenotic breathing. Invasive growth of fibroma with destruction of adjacent tissues can lead to the development of massive bleeding. A tumor growing into the nasal cavity causes a disturbance of the sense of smell, into the orbital cavity - displacement of the eyeball and exophthalmos, into the auditory tube - hearing loss.
Tumor infiltration of bone structures leads to facial deformation. The most dangerous complication of these benign tumors of the pharynx is germination into the brain structures, which leads to meningitis, cerebrovascular accident, damage to the cranial nerves and other pathological changes.
Teratomas
Congenital benign tumors of the pharynx that appear as a result of disturbances in the development of the embryo. The most common teratoma is a hairy pharyngeal polyp, which looks like a rounded growth on a stalk, covered with vellus hairs.
Angiomas
Benign tumors of the pharynx, originating from lymphatic (lymphangiomas) or blood vessels (hemangiomas). They occur on the tonsils, soft palate, at the root of the tongue, on the side or back of the pharynx. Pharyngeal angiomas are often characterized by rapid growth with invasion into surrounding tissues. Lymphangiomas are yellowish in color and filled with lymph, and can be multilocular. Hemangiomas are red or bluish in color and are prone to bleeding.
Adenomas
Rarely occurring benign tumors of the pharynx, located in various areas of the pharynx. They are nodes of a gelatinous consistency, covered with a capsule. The nodes have a wide base. Their size varies from 0.5 to 2 cm. Adenomas are pink, gray or brown. Microscopically, these benign tumors of the pharynx consist of atypical mucosal glands, in the lumen of which mucus, pus and desquamated cells are detected.
Cylinders
A separate type of pharyngeal adenoma, originating from the epithelium of the salivary glands. Macroscopically, these benign pharyngeal tumors resemble a node. They do not always have the correct shape and are often not clearly demarcated from neighboring tissues. The size of the cylinder rarely exceeds 3 cm. Microscopic examination reveals lobules consisting of lamellar cells and layers of fibrous tissue separating them.
Neurogenic formations
Neuroma and neurofibroma are quite rare benign tumors of the pharynx, usually localized in the area of its lateral or posterior wall. Pharyngeal neuromas are represented by encapsulated nodes of a fusiform or oval shape. They have a smooth surface and are covered with an unchanged mucous membrane. There is no ulceration or bleeding.
Pharynx cysts
They are divided into retention and dermoid. Retention cysts are benign tumors of the pharynx that manifest themselves clinically only when they reach a significant size, when they can lead to asphyxia. They are distinguished by their spherical shape and pliable thin walls. Dermoid cysts are congenital benign tumors of the pharynx.
Extramedullary plasmacytoma
It is a borderline tumor of the pharynx, since cases of its malignant course with metastasis to the lymph nodes have been observed. It looks like single or multiple elastic knots with wide bases. As it grows, it reaches more than 3 cm in diameter. Microscopically, this benign tumor of the pharynx consists of a polymorphic cellular infiltrate, which includes a large number of plasma cells.
Source: www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru
What it is
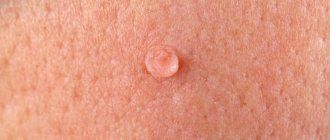
Papilloma in the mouth is a widespread phenomenon. When the soft palate is damaged, a simple condyloma is formed, resembling a lump. If you press on the wart, you feel softness and mobility.
Unlike pointed nodules, flat growths in the oral cavity with a wide base are more difficult to injury.
Neoplasms of the palatal arch almost always bring discomfort, as they interfere with normal chewing of food.
Due to regular contact with food, warts are often damaged, causing bleeding and other complications. The disease can affect both children and adults. Moreover, women suffer from oral papillomatosis several times more often than males.
Causes
The main reason for the formation of papillomas is damage to the body by HPV. The virus is transmitted during sexual intercourse or through household contact.
On this topic
Signs and consequences of granuloma migrans
- Alena Kostrova
- May 27, 2021
Most people have the infection, but not everyone gets warts. In the initial stage, a single growth appears on the palatine arch, but if you do not contact a specialist, then over time the number of tumors increases significantly.
The following provoking factors should also be highlighted:
- Permanent injuries to the mucous membrane of the soft palate.
- Weakening of the body's protective functions due to the presence of chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx and infectious diseases.
- Frequent visits to saunas , baths or swimming pools.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Constant stress , poor nutrition, systematic overwork.
- Natural aging of the body.
- Poor oral hygiene
Children become infected with the human papillomavirus before birth, as the infection is transmitted from the mother. In this case, the risk of developing papillomatosis significantly increases.
Warts do not always appear immediately after HPV penetration. The carrier may not even be aware of the presence of the virus in his or her body for many years until the immune system weakens.
Diseases associated with papillomas
Let's look at the main diseases caused by the papilloma virus:
- Warts are the most common type of papillomas. They appear in the form of round and dense skin formations. Painless and safe. They are purely an aesthetic defect.
- Genital condylomas are papillomas that occur on the genital organs: on the male penis and on the female labia.
- Bowenoid papulosis - the disease is a rash on the genitals. It occurs in both men and women. This type of papillomas is unsafe - cases of development into skin cancer have been reported.
- Bowen's disease develops only in men. The formation is localized on the head of the penis in the form of a bright plaque. Often people do not give due importance to this education, but in vain: malignancy is possible.
- Precancerous condition of the cervix. There are three stages of this disease. Moreover, the latter is the initial stage of cancer. It is practically asymptomatic. The causative agent is HPV type 18 or 16.
- Cervical cancer is the main danger of papillomas! Caused by HPV types 16, 18, 33, 35 and 39. Unfortunately, it is asymptomatic for quite a long time, complaints arise at serious stages. This once again indicates the need to visit a gynecologist 2 times a year.
Papillomas are not the harmless skin diseases that they seem at first glance. It is necessary to monitor the condition of your skin and mucous membranes, and incomprehensible formations must be shown to a doctor.
Source: ladycleo.ru
Clinical picture
Growths on the arch of the palate constantly cause unpleasant sensations in the form of a sore throat, a feeling of the presence of a foreign object. As the pathology progresses, hoarseness, muffled voice occurs, and speech is impaired. The patient still experiences difficulty chewing food, swallowing, and talking.
In advanced cases, large papillomas complicate breathing . During contact with pieces of food, papillomas are often injured. As a result of a violation of their integrity, bleeding develops, which can lead to extensive blood loss.
Can it develop into cancer?
Growths in the oral cavity are benign neoplasms. However, these defects are considered oncogenic.
If you do not consult a specialist in time, the likelihood of malignant degeneration of small papilloma into a cancerous tumor increases significantly.
Most often, malignancy occurs when the defect is frequently damaged while eating food or palpating the growth with the hands or tongue. To protect yourself from cancer, you should immediately visit an otolaryngologist if you experience discomfort in your mouth or throat.
Papillomas in the mouth, larynx
Their appearance is associated with the activity of papillomavirus types 6, 7, 11, 72, 73, 57, 32. The formations are rounded formations on a thin or wide base. The mucous membrane around them is pale pink, without any visible pathological changes. The surface of the growths is pale pink, whitish.
Neoplasms can be single, multiple, and painless when palpated. They are located on the floor of the oral cavity, the back surface of the tongue, the hard and soft palate, the mucous membrane of the larynx, the size ranges from 2 mm to 2 cm,
When biting, the growth of the oral mucosa bleeds and darkens as a result of the outpouring of blood into it. The state of health in the presence of such a disease does not worsen, the oral cavity opens freely.
When in an adult, single growths are located on the soft palate, tonsils, or in the glottis, there is a feeling of the presence of a foreign body, coughing, and the voice becomes hoarse. If the tumors become multiple, these symptoms intensify.
In children, pathological growths are often bilateral, their occurrence is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Difficulty in inhaling and exhaling, which occurs after physical exertion, then during complete rest.
- Cough after running, excessively active games.
- Attacks of suffocation due to laryngeal stenosis (pathological narrowing that prevents the flow of air into the lower respiratory tract).
The appearance of externally different papillomas is associated with infection with various types of HPV. To remove tumors, you must consult a doctor. This should be done as quickly as possible if the papillomas are multiple, quickly increase in size, cause discomfort, or are constantly injured.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor must study the history of the pathological process based on the patient’s complaints and conduct a visual examination of the oral cavity. An accurate diagnosis is established after a histological examination.
To obtain a biological sample, a biopsy must be performed. Thanks to this method, it is possible to identify or exclude a malignant tumor, determine the type and structure of papilloma.
PCR diagnostics allows you to detect HPV in the patient’s body, the type and amount of infection. It is also important to carry out a differential diagnosis in order to separate papillomatosis from fibroma, hyperplasia of the mucous membrane due to a somatic disease, or the Serre glands.
To do this, you need to visit a dental surgeon or otolaryngologist. If there is a suspicion of cancer, a consultation with an oncologist is required.
How to distinguish from other formations
Palatal papilloma must be differentiated from other formations of the oral cavity. Diagnosis is based on complaints, pathological history, and examination. The doctor notes that the nodule has no signs of inflammation, no pain, and no disturbance in the patient’s general condition. The mouth is not limited in opening, and nearby lymph nodes are not enlarged. Proof of the viral etiology of formations is the DNA hybridization method, which identifies the human papillomavirus, its type, and quantity. The diagnosis is confirmed by histological examination after destruction of the outgrowths. It is necessary to distinguish them from hyperplasia in somatic diseases, fibroids, and Serre glands.
Who to contact for examination and treatment:
- dental surgeon;
- otorhinolaryngologist;
- oncologist if malignancy is suspected.
Treatment
Papillomas of the palatal arch are treated using two methods. The main thing is to visit a specialist who will select the right treatment option.
Use of medications
Antiviral drugs, drugs to strengthen the immune system, and vitamin complexes are prescribed as conservative therapy. To avoid relapses, it is important to sanitize the oral cavity. To do this, the dentist removes tartar and eliminates carious processes.
After this, medications are prescribed to maintain the body's protective functions. It is important to pay special attention to your diet. General weakening of the immune system is eliminated by immunomodulators.
Surgical intervention
Before excision of a wart, you must consult an oncologist. Removal of growth is done in several ways.
If there are no contraindications, the defect is cut out with a scalpel . This method is used to remove large tumors. In addition, a standard operation allows subsequent histological examination.
Laser therapy is considered painless and less traumatic . Laser beams are aimed directly at the wart, so nearby healthy tissue is not affected or damaged. This procedure is also highly effective.
Cryodestruction – removal of papilloma using liquid nitrogen. However, with such manipulation it is difficult to control the direction of the cold substance, so cryotherapy is fraught with burns. If there is no suspicion of a cancerous tumor, then the growth is still removed with a radio wave knife.
Possible complications
Papillomatosis of the soft palate is difficult to determine at the initial stage. Small single warts cause only minor discomfort, so people often do not pay attention to the symptoms. As the pathology develops, the number of tumors increases, which is dangerous due to various complications.
If the defect has formed on the soft palate, then the growth is constantly in contact with food. Chewing food is dangerous due to rupture of the papilloma, as injury leads to bleeding or infection.
The lack of timely treatment sometimes ends with the degeneration of a minor pathology into a malignant tumor that threatens the patient’s life.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the severity of symptoms and the presence of complications. It is easy to get rid of a small single growth through surgery, while infection due to damage to the tumor requires additional therapy.
The malignant process is dangerous due to metastasis and intense enlargement, so it is important to get rid of the wart before malignancy. Even after complete removal of the papilloma, the possibility of relapse exists, since HPV remains in the body, and antiviral drugs only stop its activity.