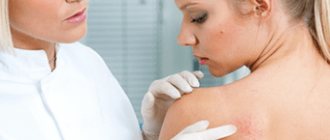
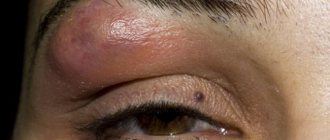
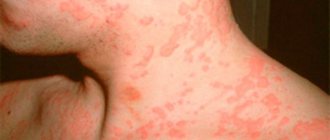
A pustule is the primary element of a rash that appears with the development of a purulent process in the dermis or epidermis. The second name for this pathological element on the skin is abscess. This is the official definition of a pustule.
The pustule has the shape of a small bubble. They mainly appear on the back or face. If pustules appear on the body in large numbers, then this condition in dermatology is called pustulosis. After opening such pustules, scars almost always form.
Papules, like pustules, which can be seen in the photo in this article, are treated by a dermatologist depending on what caused their appearance.
Papule and pustule. Where is the difference
What are papule and pustule on the face? A papule is also an element of a skin rash. But this is the easiest and easiest to treat form of the inflammatory process. Forms only on the surface.
If you look at the papule, you can see a small red ball of small size. Most often it is completely painless. It never appears on its own, but is one of the symptoms of scabies, meningitis, allergies, acne or syphilis.
This is what the pustules look like in the photo:
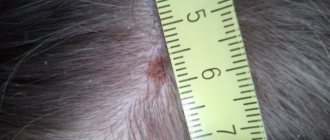
A pustule on the skin is what we used to call a pimple. It has a white purulent head and a red rim, which indicates the development of an inflammatory process. After opening, purulent contents flow out of the abscess and the formation becomes covered with a crust.
Purulent pustules on the body can be present in both minimal and large quantities. When there are several of them, they disappear quite quickly and do not require any treatment. But if the pimples become more and more numerous, they begin to fester, the body temperature rises, the patient is advised to immediately consult a doctor.
A papule and a pustule differ from each other only in the presence of pus. Both elements are treated by a dermatologist and are not an independent disease, but appear on the skin as a result of one or another disease.
Treatment of papulopustular acne
First of all, medical prescriptions are aimed at:
- Reducing sebum production;
- Normalization of keratin deposition in epidermal cells;
- Stabilization of microflora;
- Removing the inflammatory process.
At the initial stage of the disease, drugs are prescribed that reduce the hyperkeratotic process, relieve inflammation and have an antibacterial effect:
- Benzoyl peroxide;
- Tretinoin;
- Resorcinol;
- Azelloic acid;
- Clindamycin;
- Salicylic acid;
- Erythromycin, etc.
- The treatment course may include cryotherapy, cryomassage, mesotherapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment of papulopustular acne in the moderate and severe stages of development involves general therapy, including:
- Antibiotics. Their selection is made only after bacterial inoculation;
- Synthetic derivatives of vitamin A, which effectively neutralizes the bacterial process. However, these medications can negatively affect the liver, so they should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. In addition, synthetic derivatives are prohibited for use by expectant mothers, due to the ability of the drugs to penetrate the placental barrier;
- Medicines that enhance immunity;
- Antiandrogens that reduce sebum production. They are prescribed only after a hormonal examination.
The full treatment course usually lasts more than one month.
In cases of post-acne scar formation, patients are recommended cosmetic procedures, including laser resurfacing, mechanical peeling, etc.
Localization on the body
Superficial pustules, however, like deep ones, can be located on different parts of the body. Based on the location, a preliminary diagnosis can be made.
On the face
External signs : resemble small rings with erosions. Most often, pustules in this area are located on the chin, nose or forehead.
Nature of the lesion : mostly always follicular.
Causes : acne, which happens most often, candidiasis, allergies to medications, aseptic skin lesions called pustulosis.
On the back
External signs : resembles a small ball, in the middle there is a white head. The swelling is small, the redness around is barely noticeable.
Nature of the lesion : most often located under the stratum corneum and are called superficial. Sometimes there may be deep abscesses.
Causes : acne, impetigo, bacterial damage, infections, pustular psoriasis.
On the arms and hands
External signs: rashes of various sizes with purulent contents inside. Most often appear in women.
Nature of the lesion : can be either follicular or non-follicular, deep or superficial, but more often the middle layer of the epidermis is affected.
Causes : insect bites, bacterial infection, use of household chemicals, vaccinations and vaccinations.
On the legs and buttocks
External signs : can have very different sizes. Inside there is purulent contents.
Nature of the lesion : located in the middle layer of the epidermis.
Causes: insect bites, bacterial damage, increased sweating, neglect of hygiene rules, psoriasis, allergies.
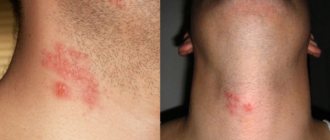
On the shoulders and neck
External signs : similar to small balls. In the center there is a white purulent head. There is a red rim of inflammation around the circumference.
Nature of the lesion : most often superficial, in rare cases it can be deep.
Causes : acne, skin infection, bacterial infection, impetigo.
Pustules on the body can appear for a variety of reasons. The tactics for treating rashes will depend on this.
5.Elements of acne (comedones, papules, pustules, nodes).Severity of acne
Determination of the severity of acne.
It is necessary to determine which elements of the rash are present on your skin.
Elements of acne
There are primary and secondary elements that are formed from the primary ones.
Primary elements include comedones, papules, pustules and nodes.
| Closed comedones | Open comedones |
There are two types of comedones - open and closed. Open comedones look like white dots or nodules and have a white “head”. Closed comedones look like blackheads (“blackheads”). Comedones are most often located on the forehead and chin.
| Papules | Pustules | Nodes |
Papules
These are dense red formations that give the skin a lumpy appearance, with a diameter of no more than 5 mm. They don’t go away long enough and can fester
Pustules
- dense formations that rise above the surrounding tissue and whose cavity contains pus. After opening, scars may remain. Sometimes it is quite difficult to classify a formation as a papule or pustule, so the term papulopustule is used.
Nodes
– larger (more than 5 mm) and deep dense elements, filled with contents of sebum and pus. They are often painful. Purulent decay of the nodes leads to the formation of a cyst. Scars may remain at the site of the nodes.
Secondary elements for acne
1.crust
2.scales
| So, having studied the elements of the rash, you need to count the number of different elements in good lighting; for convenience, you can use a magnifying mirror. |
1st degree – mild course
1.The number of comedones is no more than 12,
2. There are a few papulopustules (hard inflammatory formations with purulent contents), but no more than 11-12.
3. Characteristic is a wave-like course, alternating minor improvements and exacerbations (for example, in women there is a relationship with the menstrual cycle)
2 degree moderate severity
1.Number of comedones 12-30
2.Number of papulopustules 12-22
3. Detection of comedones and papulopusts on the body
4. There are nodes - no more than 4, pigment disorders
5. Characteristic is the absence of spontaneous improvements; there is a constant emergence of new elements.
3 Severe course
1. Number of comedones 30 and above
2. The number of papulopustules is more than 22
3. The number of nodes is more than 4, scars, persistent pigment disorders, keloids.
3. Symptoms such as soreness of the elements are characteristic; acne can merge and form denser lesions. Low effect when using external therapy.
“Geography” of rashes. Some experts are of the opinion that the presence of rashes, mainly located on certain areas of the face, may indirectly indicate problems in the functioning of internal organs.
Acne on the forehead.
Most often, rashes in this area signal a malfunction of the gallbladder, pancreas, or intestines. This may include cholelithiasis, intestinal dysbiosis, dyskinesia, etc.
The skin signals an excess of toxins, this may be due to a disrupted diet (predominance of fatty foods, canned food, confectionery, carbonated drinks).
Also, such rashes are characteristic of an overdose of drugs (large amounts of dietary supplements, hormonal drugs, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs)
Rash on the bridge of the nose.
Most likely, there is liver damage; these can be either mild disorders due to the consumption of heavy food and alcohol, or severe disorders associated with a violation of the cleansing function of the liver. Oriental medicine also associates such rashes with constant nervous tension and the accumulation of negative emotions.
Rash in the area under the eyes.
This area is associated with the kidneys and adrenal glands. These can be inflammatory processes, genitourinary infections, etc. This condition can also provoke mental and physical exhaustion (strict diet, sleep disturbance).
Rashes on the cheeks, chest, shoulder blades.
Rashes in this area may be associated with pulmonary function disorder, smoking. Mental energy of melancholy, hopelessness, loneliness, feeling of lack of air.
Rashes in the nasal area (tip of the nose and wings).
Disturbances in the area of blood circulation and cardiovascular system. State of fear, anxiety, passivity.
Lip area and shoulders
The gastrointestinal tract suffers, the usual symptoms are heartburn, colic, pain after eating, constipation. Often during examination, worms are found. Mental states of painful thoughts, increased vulnerability, sadness.
Chin and jaw line.
Disruptions in the hormonal sphere, this could be an increased amount of male sex hormones, ovarian dysfunction, ovarian cysts, vaginal dysbiosis.
| Now you can proceed directly to the choice of treatment. Remember, all forms of acne require external therapy. If you choose on your own, you can use one of the proposed schemes. |
Treatment.
Pharmaceutical companies offer a large number of drugs for the treatment of acne; then the most effective drugs for the treatment of acne will be discussed and schemes for their use will be presented.
Source: https://dr.kirov-cosmetic.ru/elementy-ugrevoy-sypi.html
Treatment with medicines and traditional methods
Treatment of pustules is carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist, but in some cases this disease can also be treated by an infectious disease specialist.
How to treat pustules? If there are only a few pustules, then they do not pose any health hazard. They can be easily treated with antibacterial ointments.
Treatment for pustules on the face may involve the use of topical ointments. So, for example, if pustules appear as a result of acne, then you can try using the drugs acnestop, levomekol, solcoseryl, serrata.
Before applying the drug, the abscess must be treated with an antiseptic, for example, chlorhexidine. To improve immunity, vitamin preparations are necessarily prescribed.
Treatment of pustules is carried out with solutions of iodine, 70% alcohol, calendula tincture, salicylic acid. Talkers have a good effect, especially if there are a lot of pustules on the skin and it is not clear how to get rid of them at home.
The mash contains either an antibiotic or a medicine that helps fight fungal skin infections. treating papules and pustules in this way is a good alternative to using expensive ointments.
Acne with pustules is a common occurrence. If the above remedies do not give any result, then it may be necessary to prescribe antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets. If the pustules cover the entire body, antibiotics are best used in the form of an injection solution.
To accurately understand which antibacterial drug to choose, you should culture the contents of the pustule for sensitivity to a particular drug used.
After opening the pustules, the eroded surface is treated with an antibacterial drug, as well as a solution of calendula or any other antiseptic. If the cause is viruses, then the ideal option is acyclovir ointment or cream.
How and with what to treat pustules and papules on the face? The most common cause of their appearance is acne. Acne pustules require the use of special medications - basiron, skinoren, klenzit and many others - the medicine is applied to the abscess twice a day for several weeks.
Salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide - the alpha and omega of acne fighting
It is quite simple to draw a conclusion about which products are most effective in treating acne. If the disease is associated with excessively proliferated bacteria in the pores, then it is necessary to combat the proliferation of microbes. However, bacteria “hide” in the ducts of the sebaceous glands and the canal of the hair follicle under a layer of horny scales mixed with sebum.
Salicylic acid in a concentration of 2–10% counteracts excess accumulation of keratin and improves the exfoliation of dead cells. This substance has moderate anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
Remedies against acne and pimples:
- Stopproblem Salicylic gel, enzyme peeling, pore cleansing mask, day emulsion.
- L'Oreal Pure Zone Against blackheads.
- Clearasil Cream-gel for washing.
- Propeller Salicylic gel.
- Salicylic alcohol 2%.
- Garnier Clear Skin.
Attention! The “gold standard” in the treatment of acne is benzoyl peroxide at a concentration of 1–10%.
The solution counteracts excessive keratinization at the mouths of the pilosebaceous follicles and dissolves dead epidermal cells. In addition, benzoyl peroxide has a significant antibacterial effect. The active substance inhibits the development of bacterial cells, thereby eliminating the initial link of the inflammatory process.
Gels for the treatment of papulopustular acne with benzoyl peroxide:
- Duac (clindamycin + benzoyl peroxide).
- Effesel (benzoyl peroxide + adapalene).
- Baziron AS.
Prices for pharmaceutical alcohol solutions and ointments with salicylic acid are low (from 14 rubles). The average price of Baziron AS gel is 600 rubles. You have to spend from 300 to 2000 rubles to purchase gels and lotions from well-known companies.
Traditional medicine recipes
Pustules on the head, as well as on other parts of the body, can be lubricated with an alcoholic infusion of calendula, which should be purchased at the pharmacy. the same treatment is carried out when a vesicle or papule appears.
You can also use an infusion of calendula flowers. Brew a tablespoon of flowers with a glass of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, strain and use as a cleanser.
Another treatment option for red pustules is aloe. Chop the leaf, add 5 times more water, boil over heat for 3 minutes, strain and also use for washing.
With proper and timely treatment, pustules can be eliminated within a few weeks. In severe cases, treatment can be carried out in a hospital setting.
Author - Anna Mikhailova, dermatologist-cosmetologist of the first category, specialist at the Academy of Scientific Beauty. Especially for the site “Treating Acne”.
Diseases with papules
Rashes are characteristic of the following pathologies: psoriasis, measles, scabies, anthrax, syphilis, atopic dermatitis, herpes, typhus, eczema, Kaposi's sarcoma, streptococcal impetigo.
READ ALSO: All about blackheads: where they come from and how to get rid of them
The diseases differ in the appearance of the papules, their location and other associated symptoms:
. It is an autoimmune chronic disease that affects the skin. Manifested by weakness, fatigue, depression. The main symptom is spots that rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Red psoriasis papules vary in size and shape: teardrop-shaped, coin-shaped, and dotted. Initially, the size of the formation is 3-4 mm, but as the disease progresses, the papules increase to 10 or more centimeters. Morphological elements affect the entire body and can merge;
psoriasis- eczema _ This is a neuro-allergic recurrent pathology that manifests itself in the upper layers of the dermis. This disease is characterized by a rash that causes itching and burning. At first the skin turns red. Then small pink-red papules form. As inflammation progresses, they transform into vesicles and pustules. After opening the formation, weeping eczema occurs. When the inflammatory process subsides, the skin turns pale, erosion becomes crusty;
- scabies _ The disease is contagious and is caused by parasitic scabies mites on the skin. Elements of the rash are represented by scabies. They look like dirty gray lines of a straight or curved shape. Elongated papules and pustules can form under them. The formations cause severe itching. When scratching, erosions occur;
- Kaposi's sarcoma . These are multiple malignant neoplasms on the skin. First, papules form, similar to rashes caused by lichen ruber. Places of localization are the arms, legs, and feet. Papules peel, increase in size (can reach 5 cm), and are painful. After resorption, the nodules leave pigmented impressions. Kaposi's sarcomatosis can metastasize to the lungs, bones, and liver. In this case, the person experiences a bloody cough and diarrhea, and a high fever;
How to get rid of spots on a child's skin?
It is prohibited to independently fight epidermal diseases in a child. The problem should be solved by a specialist, based on the results of the examination.
To treat spots on a baby’s skin, medications of different effects are used, depending on the cause of the development of the pathological process.
To relieve redness and itching, ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory, softening and drying properties are used.
Diagnostic methods
If papules, pustules, or vesicles appear, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist, consult with an infectious disease specialist, venereologist or allergist. At the appointment, the doctor interviews the patient, examines the skin using a dermatoscope, and prescribes a series of examinations.
The following diagnostic techniques are used:
- liver tests;
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
- skin allergy tests;
- bacterial sowing;
- biopsy;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- chest x-ray;
- HIV test;
- plasma analysis for hormone levels;
- skin scraping microscopy;
- urine test.