If you notice that your scrotum and testicles are itching, then there are reasons for this. Sometimes they are quite harmless, and sometimes they are serious and require medical intervention. Let's figure it out why do men's balls itch??
Itching of the scrotum and testicles in men can sometimes be the first sign of a serious illness, and if you pay attention to it in time, you can avoid many unpleasant consequences. To find out the answer to the question of why men's balls itch, carefully read our article.
Causes
Causes of itching in the scrotum:
- An allergic reaction to the material from which the underwear is made . Sometimes tight pants cause itching. Try wearing looser pants and removing tight underwear;
- In adolescence, intense hair growth in the intimate area can cause itching in the groin . Over time, this discomfort will pass;
- Incorrect or insufficient hygiene of intimate areas. If you take a shower and do not change your underwear, this will cause discomfort in your intimate area. Cleanliness and care will eliminate skin problems and itching;
- If you have long-term stress and have neurological disorders , then you are guaranteed itchy eggs. By eliminating the main cause, you can get rid of unpleasant sensations in the intimate areas;
- When you shave your hair, over time the hairs begin to grow back and the shaved groin causes not only irritation, but also itching;
- Too hard water dries out the skin and can cause itching in the scrotum area;
- Severe skin and urological problems can lead to discomfort in the intimate areas. These include lice, lichen, scabies, and blockage of the sebaceous glands. All of these diseases can lead to itching in the scrotum;
- Metabolic disease;
- Tumors;
- If after examination the dermatologist cannot determine the cause , then it is considered idiopathic itching;
- Fungal infections of the skin . They can cause itching and rashes on the head of the penis and skin. Discomfort may also occur in the urethra. If such symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor and undergo examination and treatment. Otherwise, the pathology will become chronic and will bother the patient, especially in the hot season.
Why does a man feel itchy and dry?
The health of the male reproductive system depends on many factors, ranging from banal hygienic care to contact with all kinds of pathological microorganisms. The skin on the scrotum may become dry and itchy due to:
- Natural factors.
- A variety of diseases - parasitic, infectious, dermatological, etc.
It is quite difficult to independently determine which factor led to the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms in the scrotum area. An experienced urologist or dermatologist can handle this task.
Natural causes of itching in and under the testicles
As a rule, the occurrence of itching in the scrotum area is associated with completely natural factors that can be easily corrected at home. Such a disturbance in well-being can occur when:
- Not wearing the right size underwear or trousers.
- Using underwear made of synthetic fabric.
- Poor-quality underwear, for example, made of rough fabric or with protruding threads, etc.
- Prolonged friction, for example, during certain types of physical activity - running, cycling, etc. Severe abrasions can appear as a red rash and even blisters, involving the skin under and on the scrotum.
- Insufficient or irregular hygiene of the external genitalia. Men need to shower at least once a day, and even more often in hot weather.
- Hair growth after shaving or during adolescence.
- Inaccurate use of the razor, when the blades injure delicate skin.
Sometimes violations of the integrity of the epidermis on the scrotum, caused by natural factors, provoke the occurrence of serious diseases, for example, lead to the development of infection. Therefore, such causes of itching need to be promptly identified and eliminated.
What diseases do they cause?
Itching on or under the scrotum may occur due to:
- Development of various fungal diseases.
- The occurrence of allergic reactions.
- Development of a viral disease - human papillomavirus.
- Development of parasitic infections, in particular, pediculosis or scabies.
- The occurrence of chronic dermatological disease - psoriasis.
- Ingrown hairs.
- Development of cancer.
The list of factors that can provoke itchy skin on the scrotum is quite long. A doctor can make a correct diagnosis based on a number of studies.
Redness and severe itching due to fungus
The delicate skin of the scrotum and groin often becomes a target for pathogenic fungi. Some of them are constantly present on the human body and begin to actively reproduce due to decreased immunity, insufficient hygiene, excessive sweating and other factors. It is quite possible to become infected with other fungi through contact with other unhealthy people or even animals. In this case, doctors can talk about the occurrence of lichen. Possible signs of fungal diseases include:
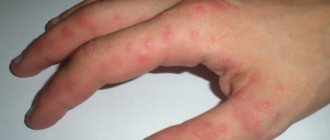
- The appearance in the fold under the scrotum of a small scaly red spot (one or several), no more than 0.5 mm in size. Over time, the spot increases in size and bubbles and crusts form on it. The skin swells and itches, and it seems as if the blood is not draining from it at all. A ridge is visible along the edges of the lesion. The spots may spread to the skin of the groin.
- The appearance of dry, scaly areas that are round in shape and itchy a lot.
- The appearance of red unformed spots with a white coating. This is how thrush can manifest itself - candidiasis. But with this disease, the lesion is first observed on the penis and only later, in the absence of adequate therapy, does it spread to the scrotum.
Unobtrusive itching in the scrotum area may be the first manifestation of a fungus. In the absence of timely diagnosis, the disease spreads and causes more obvious health problems.
Allergic reactions in the intimate area
As a rule, allergies in the intimate area manifest themselves primarily on the glans penis, which is particularly sensitive to a variety of external influences. But sometimes the scrotum can also suffer from such a problem. Allergies can manifest themselves:
- The appearance of itchy red spots.
- Increased dryness and flaking of the skin. Sometimes the epidermis cracks and even peels off.
- The appearance of a small red rash that itches noticeably.
- Crusts and weeping in the folds under the scrotum.
Allergies in the scrotum area are most often of a contact nature and can occur due to the body’s sensitivity to detergents (soap, shower gel, washing powder, etc.) or locally used medications (in the presence of concomitant diseases). It is extremely rare that other types of allergies appear in the scrotum area - to food, systemic medications, etc. In such a situation, the patient is usually bothered by dermatitis in other parts of the body.
Distinguishing allergies from infections and other health problems is quite difficult. This may require skin scrapings, blood tests, and other tests.
Severe itching due to pediculosis
Even in the modern world, doctors quite often have to deal with phthiriasis - pubic lice or pubic lice. You can catch such parasites in a bathhouse or swimming pool, as well as during sexual intercourse, on the beach or on a train. You can suspect the presence of pubic lice by:
- Severe itching.
- The appearance of bluish or dark spots up to 1 cm in diameter on the affected skin, which quickly disappear. This is what hemorrhages or sites of injection of secretion from the salivary glands of parasites look like.
- Dark spots on underwear are waste products of parasites.
- Blisters - red bumps, blisters and eczema. Such skin manifestations occur on the skin due to constant scratching.
It is almost impossible to see pubic lice with the naked eye. But the doctor will cope with this task very simply.
Genital warts in humans
The appearance of genital warts on the body is associated with infection with the human papillomavirus. It can be picked up during sexual contact, including protected sex - by simply touching the infected skin of a partner. Sometimes such contacts do not lead to the appearance of growths on the intimate organs, but with a decrease in immunity, condylomas - flesh-colored or dark-colored growths - may appear on the skin of the groin and scrotum, as well as on the penis and near the anus. At the very beginning of their appearance, they may itch noticeably, but over time this discomfort disappears.
Growths on the body are dangerous in terms of cancer development and potential danger to other people - they are contagious. The only method of getting rid of them is removal using different methods.
Causes of progressive hardness and itching
The appearance of a dense nodule or subcutaneous formation on the scrotum, which itches noticeably, can be associated with both completely harmless conditions and life-threatening diseases. This symptom may be explained by:
- A banal ingrown hair. Sometimes the hairs cannot break through the skin and begin to grow under it, twisting into a spiral. This problem most often occurs when wearing tight underwear and tight, tight trousers. An ingrown hair does not always hurt, but it feels like a subcutaneous lump and itches. It can become inflamed, and in such a situation cause more obvious discomfort.
- Benign tumors. Often, such neoplasms do not itch and do not manifest themselves in any way, but itching can appear as a result of their constant compression or injury.
- Cancerous tumors. Unexplained lumps on the scrotum that cause discomfort may be a sign of cancer. Of course, this situation occurs very rarely, but it is better not to leave tumors without medical supervision.
You should not scratch the itchy areas on the scrotum, this can lead to the development of an inflammatory process. It is better to provide the problem area with maximum rest before visiting the doctor.
Peeling with genital psoriasis
Psoriasis is considered a chronic dermatological disease; it can be localized in different parts of the body, including the external genitalia. You can suspect the development of the disease by:
- The appearance of a small reddish-pink rash.
- Peeling, itching and a visible white or silvery coating.
- The formation of psoriatic plaques - spots protruding above the skin, covered with many white scales. Sometimes the rash remains demarcated and does not merge into spots. If you pick off the scales, you will see inflamed skin underneath, which cracks and bleeds.
Psoriasis can be accompanied by very severe itching, but many men mistake its primary symptoms for sexually transmitted diseases and self-medicate instead of consulting a doctor in a timely manner. In this case, the disease can develop into a widespread advanced form.
Red and itchy due to scabies
Scabies is a parasitic infection caused by the scabies mite. Most often, the first signs of the disease appear on the hands, and in men the parasite can easily get on the penis, as well as on the scrotum, which is accompanied by:
- Severe itching, which intensifies at night and disrupts night rest.
- The appearance of scabies on the skin, similar to lines up to 5 mm in length. Pinkish stripes - scratches - may also be detected.
- Pimples-nodules.
- Redness.
- Scratching, secondary pustular rashes, crusts.
Scabies is often complicated by a bacterial infection, which in turn can cause other serious complications. Fortunately, this disease can be successfully treated if you seek medical help in a timely manner.
Pubic lice: symptoms
Quite often, the cause of itching in the area of the eggs is pubic lice . They appear in pubic hair. Not only the scrotum, but also the anus can itch. Lice can also appear on the chest and abdomen, where there is hair. Here you can read more about how to shave your penis and pubis.
Transmission factors:
- Lice move along the hair from one sexual partner to another;
- You can become infected through contact with underwear and bedding;
- When visiting baths, saunas.
Symptoms:
- Itching. When lice bite, they inject a special substance that thins the blood and causes itching;
- The appearance of blue shadow spots with a diameter of about 1 cm;
- Dark spots appear on the laundry. Such spots are a process of vital activity of pubic lice;
- Blisters and even eczema may appear at the site of scratching the skin;
- When the lice grows, it can be seen on the surface of the pubic hair. By their height, you can diagnose how long lice have been parasitizing on the skin.
Non-dermatological causes of itching of the groin and scrotum
Sometimes the scrotum, penis and groin area begin to itch due to factors not directly related to skin pathology. Thus, itchy skin is a frequent companion to diabetes mellitus and diseases of the liver and thyroid gland. When the whole body itches, both the scrotum and groin begin to itch. Similar symptoms are also typical for hypovitaminosis and some other problems. Separately, it is worth paying attention to the damage to the testicles themselves. Orchitis, orchiepididymitis, varicocele, testicular cysts and dropsy are almost never accompanied by itching of the scrotum.
In such cases, pain comes first in the groin, on one or both sides above the pubis. Alternatively, when the scrotum swells against the background of dropsy (hydrocele), it begins to rub harder against the thighs when walking. Then itching appears as a symptom of chafing or diaper rash.
Common diseases: symptoms
If a man experiences severe itching in the scrotum, this can be caused by several reasons. Most often this provokes the development of allergic contact dermatitis. More often, this pathology is typical for males from 20 to 40 years old.
This disease is caused by:
- Wearing low-quality underwear and trousers. Especially when harmful dyes with chromium were used in their production;
- Latex can also cause irritation and itching;
- The main allergy symptoms may occur two weeks after exposure. This is called a delayed-onset allergic reaction;
- A feeling of itching can also provoke inflammatory contact dermatitis;
- Another cause of itching can be mechanical urticaria;
- The appearance of blisters;
- Discomfort;
- White coating on the base of the foreskin;
- Burning sensation.
Itching of the scrotum with erythrasma
A fairly common pathology among men.
It is caused by specific corynebacteria, which are infected through the soil (the pathogen penetrates the lymph and spreads throughout the body).
Erythrasma is rare in children.
Weeks or months pass between the moment of infection and the beginning of the active phase of the disease. Symptoms occur when conditions favorable for the proliferation of corynebacteria appear - humidity, heat, changes in pH.
The manifestations are as follows:
- the appearance on the lateral surfaces of the scrotum and the inner skin of the thighs of several pinpoint red spots with a smooth or flaky surface;
- the spots merge, forming large lesions with a clear, uneven border;
- the process is painless, erythrasma gives men only slight discomfort in the form of itching, and even then not for everyone, however, due to damage to the surface layer of the skin, a secondary infection quickly occurs in these places, then pain, weeping, and burning appear.
If the pathology is ignored, diaper rash occurs, and skin lesions become deeper. Neglected forms can lead to the formation of extensive eroded surfaces. It is not easy to treat erythrasma; the disease is prone to relapses and exacerbations.
Diagnostics
Before the doctor makes a diagnosis, he will examine the patient and take a medical history. He will also additionally prescribe a number of tests. Skin samples are taken and sent for analysis. Often these indicators are enough to clarify the diagnosis.
If scabies is suspected, the doctor performs the following algorithm:
- Conducts tests using iodine;
- Carefully examines the patient's skin;
- Takes skin tests.
Diagnostic plan:
- If the doctor suspects the patient has chlamydia, trichomoniasis and gonorrhea, the patient is prescribed a microscopic examination of the discharge;
- In case of allergic pathology, it is enough to carry out skin tests;
- Dermographic urticaria is easily diagnosed. If you touch the patient's inflamed skin, this will lead to pain and the appearance of itchy blisters;
- Candidiasis is diagnosed by visual examination and microscopic examination of a smear;
- When diagnosing erythrasma, the patient must be carefully examined and examined using a lamp and a smear taken for microscopic examination.
Which doctor should I go to if I have itching after intercourse?
If you are concerned about itching after sexual intercourse, you should consult a dermatologist. Men will also be helped by a urologist who will examine the external genitalia, as well as palpate the prostate gland through the rectum. A gynecologist examines women in a gynecological chair, drawing conclusions about the condition of the genital organs: the presence or absence of hyperemia, swelling, pathological discharge. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on examination alone, so laboratory and instrumental tests are prescribed:
- clinical blood test,
- general urine analysis,
- a smear from the urethra, cervix, vagina, followed by examination using PCR, microscopy, bacteriological culture on media with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics. This study allows us to detect inflammation of the urethra in men, colpitis and cervicitis in women.
In order for the examination data to be as accurate as possible, it is not recommended to urinate two hours before taking a smear; you should abstain from sexual intercourse for two to three days.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women, ultrasound of the scrotum and prostate gland in men: this allows us to identify inflammatory diseases of the uterus and its appendages, orchitis and prostatitis in men.
- MRI and CT are more accurate methods and, as a rule, are prescribed in controversial cases.
Treatment
If itching in the scrotum is associated with allergic reactions, then you need to consult an allergist.
He prescribes the following treatment regimen:
- The patient is prescribed to take general and local antihistamines;
- Also, thanks to modern techniques, desensitizing therapy now helps to cope with allergy symptoms. It will help reduce the risk of susceptibility to allergens;
- To eliminate the symptoms of scabies, the patient is prescribed a variety of ointments, where the main substance is sulfur and aerosols. To relieve severe itching, hydrocortisone-based ointments are used;
- For bacterial infections, the patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy;
- During candidiasis, in addition to antihistamines, antifungal agents are added to treatment;
- For herpes, antiviral therapy is prescribed.
Lichen planus and scrotal itching
This pathology cannot be classified into any of the above categories, because it is still not known for certain why it appears. It is believed that provoking factors are stress, diabetes, gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer), hepatitis, and allergic reactions.
There are several clinical forms of the disease.
The most common one appears in the form of small compactions (papules) with a diameter of several millimeters. Such rashes rarely appear on the scrotum; they can be found much more often on the head of the penis. One of the leading symptoms of lichen planus is itching. However, the severity of this feeling varies. From unbearable, accompanied by scratching of the affected areas, to a completely indifferent, asymptomatic process. The disease is not contagious. But there are observations that in 0.5-5% of cases, lichen planus rashes can develop into skin cancer. Therefore, if within a couple of months the papules do not disappear, grow, merge with the formation of a navel-like depression in the center, you need to see a dermatologist.
Prevention
As preventive measures, the patient is prescribed to avoid the following factors:
- Do not change sexual partners frequently;
- Monitor the hygiene of the intimate area;
- Try to avoid contact with the allergen;
- Fight against excessive sweating;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Exercise;
- Reduce alcohol intake;
- Eliminate fatty, spicy, salty foods from the diet;
- Strengthen immunity;
- Temper yourself;
- After visiting the street and the toilet, wash your hands.
Treatment of itching after intercourse
Treatment for a symptom such as itching after sexual intercourse is prescribed by a doctor based on examination data and the cause of the disease or condition that caused it. For example, with menopausal syndrome in women, estrogen deficiency is compensated, which negatively affects the vaginal mucosa. If you are allergic to contraceptives or hygiene products, you must choose hypoallergenic products that will not cause a pathological reaction. Of course, you need to carefully monitor intimate hygiene and wear underwear made from natural fabrics.
If the cause of itching after sexual intercourse is candidiasis, local and systemic antifungal agents are prescribed; Most STDs and bacterial infections of the genitourinary system require antibiotic therapy. At the same time, the immune system is strengthened and vitamin therapy is prescribed.
Due to the availability and accuracy of diagnostic methods, identifying the cause of itching after sexual intercourse is not difficult. To increase the chances of a successful recovery and the absence of dangerous consequences, you should follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Doctor of the Private Practice clinic, dermatovenerologist, urologist Volokhov E.A. talks about itching after intercourse.
Many men are constantly interested in the question of why itching appears in the eggs. Some men believe that the intimate area itches when there is sexual abstinence. But this is a mistaken opinion. It's not the balls that itch, it's the scrotum.
Only a dermatologist can determine the cause of such discomfort. Before a diagnosis is made, the patient is prescribed to undergo an examination, usually this means taking tests. Before you see a doctor, you need to find out the cause of the itching yourself. In most cases, the reasons are harmless and can be easily eliminated.
Scabies: symptoms
Scabies is caused by the scabies mite. Infection occurs through close contact with an infected person. To reduce the risk of contracting scabies, you must follow all hyena precautions and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms of scabies:
- The appearance of a nonspecific rash;
- Skin itching worsens at night, after a bath;
- Scabies are noticeable on the skin. They are strips of about 15 mm with a small visicle at the end;
- Also on the skin there are characteristic papules and weeping plaques;
- Usually the thinnest areas of the skin suffer from mites: the radial joint, the forearm area, the elbow joints, the external genitalia, the skin under the breast, the surface between the fingers;
- The appearance of severe itching, which is caused by the development of an allergy to the excrement of mites;
- Itching can lead to scratching and excoriation;
- Also, if the skin is damaged, bacterial infections can occur;
- Scabies can be complicated by pustular diseases.
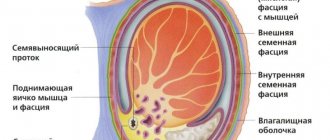
The structure of male testicles
To understand the reasons why men scratch their testicles, as well as why the eggs could turn red, begin to itch constantly, or even become covered with white spots, boils or peeling appear on them, it is necessary to study in more detail the structure of the testicles and scrotum.
The scrotum is the genital organ of the anterior abdominal cavity, which protrudes outward. Inside the scrotum there are two chambers in which the male eggs are located. The scrotum also contains the appendages and spermatic cord.
The scrotum with testicles is located between the anus and the penis. It is in this genital organ that the temperature required for the testicles is maintained - 34.4 degrees. For sperm, human body temperature is destructive. It is for this reason that nature created the external genital organ, taking care of the continuation of humanity.
If a boy or man is cold, then his scrotum and balls are pulled up - closer to the body. And at normal temperatures they lower and relax.
The testicles are located on the spermatic cords and are in a suspended position, and the appendages are located on their back walls. The testicles and epididymis are covered on top with the tunica vaginalis, which is a closed serous cavity. Inside the scrotum, in addition, it is assumed that the testicles are covered with a parietal and visceral plate. Vessels and nerve endings are located in the part where there is no visceral covering. Between the tubules in the structure of a man's eggs there are Leydig cells, which are responsible for the production of testosterone.
STD: symptoms
STDs are diseases that are transmitted sexually. The incubation period for STDs ranges from one to seven days. After this time, the patient experiences the first symptoms of the disease. All disease symptoms vary and may resemble a common cold.
There are several characteristic causes that occur equally in all sexually transmitted pathologies:
- Frequent urination;
- Pain during urination;
- White and foamy discharge appears from the penis;
- Temperature may rise;
- Pain in the epididymis and testicles; The article about pain in the right testicle addressed a similar issue.
- Pain in the lumbar region and sacrum;
- Ulcer in the genital area;
- Rashes on the body.
If you find yourself with the above symptoms, you need to contact a venereologist and undergo an examination. When the disease becomes chronic, it is difficult to treat. Modern treatment methods make it possible to get rid of STD symptoms in a short period of time.
How to avoid what is predicted in omens
If the egg itches is a sign of trouble, a man can do the following:
- In the morning, swim in cool water and then go to church. After church, sprinkle the house with holy water.
- Pour a glass of salt onto the intersection.
- Destroy the omen. From the existing options for the development of events, choose the most likely one. Draw this scenario in your imagination and then erase it with an imaginary eraser. You can also describe the script on a piece of paper and then burn it. Both methods are equally effective.
- Make a talisman. Pour 1 tbsp into a cotton bag. l. peppermint, 2 tbsp. l. hawthorn berries, 5 viburnum berries and 4 tbsp. l. St. John's wort flowers. Tie the bag and draw 3 triangles on it. Place the finished talisman under the pillow.
- Attach a pin to your clothing.
- Donate a small amount of money to the homeless.
- Spit over your left shoulder three times and knock on wood (contrary to popular belief, this helps not only against the evil eye).
- From all the options for the development of events, choose the one that is most likely to happen, and compose a phrase denoting the opposite. So, if the sign indicates that betrayal will soon be exposed, you can say: “my love affair will remain a secret” or “they won’t find out about my affair on the side.” A man needs to repeat this phrase periodically throughout the day. In the evening, it should be written on paper and burned over the flame of a candle (yellow, white or green).
Important! In practice, predictions come true within 2-3 days. If during this time what was predicted did not come true, then you should no longer wait for it.
Common Factors for Itching in Eggs
First factor
Itching of the scrotum is a fairly common pathology that causes discomfort and discomfort.
The first factor in the development of itching includes:
Allergy to underwear material;- Shaving the groin; Here you can read more about how to shave a man's groin.
- During adolescence, abundant growth of hair on the scrotum and pubis;
- Poor genital hygiene;
- Allergic reaction to the use of hygiene products;
- Neurasthenia, stress and depression;
- Hard water;
- The skin on the scrotum becomes dry and peels.
- Visiting saunas and baths.
Second factor
The second factor is the presence of serious diseases or tumors. They are also accompanied by itching, pain and discomfort.
This includes the following pathologies:
- Herpes genital;
- Pubic lice;
- Scabies;
- STD;
- Lichen;
- Candidiasis.
These diseases are characterized by various symptoms and manifestations. You can become infected with sexually transmitted diseases from another partner, as well as through hygiene items, bedding and underwear.
Itching of the scrotum in infectious and parasitic diseases
The skin of the groin is sufficiently unsterile to be at risk of being damaged by various microscopic and not very microscopic pathogenic organisms. In dermatological practice, we most often encounter damage to the scrotum by fungi, pubic lice, streptococci and other flora. Both adult men and children suffer from such causes. Separately, in sexually mature patients, itching of the scrotum can be caused by sexually transmitted infections - Trichomonas, chlamydia.