Papillomas and condylomas in men do not pose a serious health hazard, but you should not delay their removal, as they are very contagious. In addition to the fact that genital warts of the penis are a physiological deviation, they look aesthetically unattractive, which worsens the emotional state of a man.
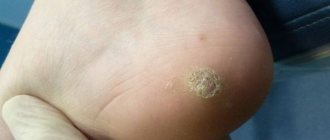
Penile condylomas are benign neoplasms that are somewhat reminiscent of warts. They can have either a scattered structure or be combined into larger clusters, acquiring a red or light pink tint. As a rule, genital warts in men are located in close proximity to the frenulum or coronal beard. They can also be found on the skin of the penis and, in very rare cases, in the external opening of the urethra.
Causes of the disease
The presence of HPV in a man’s body does not necessarily mean the manifestation of external symptoms.
The following factors lead to the activation of the virus:
- Excessive physical activity;
- Presence of sexually transmitted diseases;
- Malfunctions of the immune system;
- Mental fatigue, frequent stress and emotional turmoil;
- Hormonal imbalances in the body;
- The presence of bad habits, such as systematic consumption of alcohol and active smoking;
- Diabetes.
The risk of infection and activation of HPV in men increases significantly in the following cases:
- Homosexual orientation;
- Sexual contacts in the presence of damage to the genitals;
- Having a large number of sexual partners or changing them frequently;
- Beginning of active sexual activity at an early age.
First signs in men and additional symptoms
When HPV activity increases in men, the following symptoms are observed:
- The appearance on the skin or mucous membranes of benign neoplasms in the form of a papilla or small nodule. Papillomas can be located not only on the external parts of the body, but also in the rectum;
- The appearance of bumps , a local change in the structure of the skin without changing its color;
- The localization can be any , often formations appear in the groin area.
Usually, emerging papillomas do not cause physical discomfort.
Sometimes additional symptoms occur, including the following:
- Painful sensations manifested during the act of defecation, urination or sexual intercourse;
- Local bleeding at the sites of papillomas and subsequent formation of ulcers characterized by prolonged healing;
- Itching sensation , leading to scratching of certain areas; this symptom is the most dangerous, since it can lead to mechanical damage to formations and the development of complications;
- The appearance of a specific unpleasant odor.
HPV classification
According to the course of the disease, the following forms are distinguished:
- Latent. The form has no symptoms or external manifestations, the disease occurs latently, and can only be detected through laboratory tests.
- Subclinical. Signs of the disease have been erased.
- Clinical. The infection has classic signs, characterized by the appearance of growths of various types.
The first form of the disease is most often diagnosed.
HPV also has several stages of development, which manifest themselves in formation on the skin:
- Anogenital warts (genital warts, macules, papules, Bowen's disease, giant condylomas of Buschke-Levenshtein, bowenoid papulosis).
- Extragenital papillomas and warts. Lesions appear on the skin in the form of flat, plantar warts, verruciform epidermodysplasia and other neoplasms. Also, growths are found on the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, and larynx.
- Dysplasia and precancerous condition.
- Oncological formations on the anus, penis, anal area.
Features of the course of the disease
The disease usually occurs in men according to the following scheme:
- HPV infection and the absence of visible symptoms , as well as activation of HPV under the influence of provoking factors;
- The appearance of the first papillomas;
- Progression of the disease and the appearance of new formations in various parts of the body in the absence of treatment;
- Deterioration in the quality of life of a man if papillomas are localized on the genital organ, in the bladder or urethra;
- The occurrence of additional symptoms causing physical discomfort. Transformation into malignant neoplasms and the development of other complications with a tendency to damage papillomas.
What will happen if left untreated?
Doctors do not recommend leaving papillomas in the legs and other parts of the body without treatment. Unfortunately, many people seek medical help only because the growth causes them psychological discomfort. And they rarely think about the fact that it can be dangerous to health.
In fact, papillomas are not always harmless. They can lead to tissue infection if they are constantly injured.
Also, a neoplasm, in the presence of appropriate factors, can degenerate into a cancerous tumor. The development of this process is usually indicated by a sudden change in the shape and size of the growth, the appearance of pain and discharge from it. In this case, you need to immediately contact an oncologist.
How does infection occur?
The prevalence of HPV among men of different ages and lifestyles is due to a large number of possible routes of infection.
Typically, the virus enters the human body in the following ways:
- Having unprotected sexual contact and frequently changing partners increases the risk of infection;
- Any contact with the mucous membranes of an infected person , including kissing. The risk of infection increases in the presence of open wounds and other injuries;
- Contact and household route of infection , HPV can be transmitted through ordinary handshakes;
- Using other people's personal hygiene products;
- Infections in childhood during childbirth , if the mother was a carrier of HPV.
The highest probability of infection is when visiting gyms, baths, saunas and swimming pools.
General characteristics
So, HPV type 51 in women - what is it and what are the distinctive features of this type of viral organism? One of the main criteria that distinguishes the virus of oncogenic type 51 from pathogens of an infectious nature is its small size. The virus is so small that even close bodily contact, such as shaking hands with a sick person, can lead to infection. Pathogenic flora enters the body through microscopic damage.
Once in the structure of healthy cells, HPV type 51 gradually destroys them and changes the original DNA. With a long course of the disease, uncontrolled cell growth occurs in the affected area and further transformation of the tissue into a malignant tumor.
Types of HPV in men
The HPV group is quite extensive and includes more than 150 viral types, but less than 10% of genotypes that can lead to the development of cancer are dangerous.
Depending on the clinical manifestations, the main varieties are distinguished:
- Papillary growths are the most common type and are common warts. They do not stand out in color or have a darker shade, the main localization is the skin of the face, torso and feet;
- Inferted papillomas are also known as intraepithelial formations. Their main feature is their special flat shape and deep ingrowth into the epidermis; localization can be any;
- Genital warts are another common type; They are small formations attached to the skin or mucous membranes on low stalks. There is an external resemblance to cauliflower; individual formations or groups of pink or brown papillomas may be found. The most common sites of localization: the area around the genitals and anus, oral cavity, rectum and urethra;
- Flat condylomas are considered the most dangerous to human health; their appearance is often accompanied by physical discomfort in the form of itching and burning. This type has a tendency to progress and gradually grow, which leads to tissue deformation. Localization can be any.
Symptoms
If a man’s immune system is strong and he leads a healthy lifestyle, then the disease can go away on its own without manifesting itself in the form of papillomas. The young man becomes a carrier of the virus, the disease does not bother him, but he can still infect other people.
The development of HPV can be suspected by the appearance of growths and neoplasms on various areas of the skin and mucous membranes.
Condylomas acuminata
Papillomatosis often manifests itself in men in the form of genital warts, which have a light pink or pale brown tint. Externally, the growths resemble cauliflower inflorescences.
Condylomas grow in the anus, glans penis, foreskin, frenulum, and less commonly form on the inner thighs and pubis. They cause unpleasant symptoms such as:
- pain during the process of defecation, sexual intercourse;
- pain, itching;
- discomfort during ejaculation or urination.
New growths have a rough surface and are often subject to injury, which is why a secondary infection is added to HPV.
Warts
The appearance of warts of various types can also signal papillomatosis. The growths affect not only the male genitals, but also grow on the feet, skin of the upper and lower extremities, face, neck, and body. Doctors distinguish three main types of warts that arise due to the activity of the virus:
- flat or vulgar (formed on the back of the hands, measuring up to 0.5 cm in diameter);
- thread-like or “hanging” nevi (grow in the armpits, eyelids, back, neck, chest);
- cystic or mosaic (localized on the feet).
Papillomas on the penis and groin
Genital warts are most often diagnosed on the penis; in the groin, doctors note such manifestations of HPV as bowenoid papulosis.
The growths with it have a dense structure, slightly rise above the surface of the dermis, are pinkish, yellowish or white, and do not cause discomfort. They grow in the area of the anus and urethra.
Why is HPV dangerous in men?
The degree of danger is determined by the type of virus, the location of the papillomas and the likelihood of their accidental damage due to systematic exposure.
Adverse factors can provoke the following consequences and complications:
- The occurrence of malignant neoplasms;
- Deterioration of potency;
- Blocking the lumen in the urethra;
- Infertility.
Complications most often develop when mechanical injuries and damage to papillomas are caused or in the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
Which type of HPV is considered the most dangerous?
The main criterion for HPV classification is differences in DNA structure.
The most dangerous viruses for men are the following types:
- HPV types 6 and 11 - lead to the formation of genital warts; these viruses can cause the development of respiratory papillomatosis. In rare cases, the disease is fatal;
- HPV type 70 is considered a precancerous condition; the high activity of this virus requires treatment under the supervision of a specialist;
- HPV group a9 - includes more than a dozen types of the virus, increases the risk of developing cancer.
Diagnosis of the disease in men
Increased activity of human papillomaviruses in men is the main evidence of deterioration of the immune system, so first of all you will need to get tested to make sure there are no sexually transmitted diseases.
Considering that some types of the virus provoke the development of cancer, especially when papillomas appear on the genitals, you need to contact a specialist for diagnosis.
It includes the following set of activities:
- Conducting a survey and examining emerging tumors are the primary measures that are carried out at the first visit to the doctor;
- Taking a blood test to confirm the presence of human papillomavirus in the body;
- Taking a urine test and, in rare cases, stool tests;
- Smears from the urethra are taken only when genital warts occur. Before taking the test, you should not go to the toilet for 2 hours;
- Taking a piece of papilloma for detailed examination is required to exclude the presence of cancer cells
The day before taking any tests, you must completely avoid drinking alcohol, having sexual intercourse, and taking pharmacological medications.
After diagnostic measures are carried out, treatment is prescribed if necessary.
How to treat HPV in men?
If papillomas appear, especially those causing physical discomfort, you should immediately seek professional advice, since treatment in the initial stages is much easier and eliminates the risk of developing dangerous complications.
In total, there are 3 directions to solve the problem:
- Completing a course of drug therapy , which involves the use of pharmacological drugs;
- Undergoing treatment using modern medical equipment or treatment using a hardware method;
- The use of traditional methods for eliminating such formations.
Drug therapy
The basis of drug therapy is immunostimulating drugs with antiviral effects.
They are designed to suppress the activity of HPV, inhibit the spread and occurrence of new papillomas, as well as normalize the functioning of the immune system.
Completing the course allows you not only to get rid of emerging signs of the disease, but also to prevent possible relapses in the future by activating the body’s natural defenses.
Drugs that perform such functions include:
- Cycloferon - has a complex effect, a drug based on meglumine acridone acetate allows you to suppress viral activity, strengthen the immune system and reduce inflammation that can occur if the papilloma is accidentally damaged. The daily dose is 3-4 tablets, the course includes taking up to 40 tablets. A month after completion of treatment, a repeat course is recommended. A package of tablets, depending on its volume, costs from 350 to 850 rubles ;
- Amiksin is an antiviral drug with immunomodulator functions, the release form is tilorone-based tablets. The basic treatment regimen involves taking 1 tablet per day, starting from the third day, taken every other day. The course dose is 10 tablets; if necessary, the doctor can make adjustments to this regimen. The cost ranges from 600 to 900 rubles .
Cycloferon Amiksin
Antitumor drugs based on podophyllotoxin have a cauterizing effect; they are included in complex therapy to eliminate existing formations.
The cream is intended mainly for the treatment of papillomas on the female genital organs; for men, the product in the form of a solution is more suitable.
Similar drugs are also prescribed after surgical removal of formations to prevent their reappearance.
Below are some types of funds:
- Condilin - after application it causes necrosis of the outer parts of papillomas and their subsequent elimination. The bottle is equipped with an applicator for spot treatment; no more than 50 formations can be treated in one procedure. Application is carried out 2 times a day for 3 days, after which you should pause for 4 days and repeat the course. The total course of therapy should not exceed a month. You can purchase the drug at a price of 600 rubles ;
- Podophyllin - in the form of a solution is intended for 10 treatments of papillomas and 20 treatments of the places where they were located after their removal. The procedure is repeated daily, if local inflammation occurs, with a break of several days. The cost starts from 900 rubles .
Condilin Podophyllin
Drugs with a pronounced antiviral effect are also an important part of therapy; they are prescribed to stimulate the production of the body's own antibodies.
Local preparations
After the tumor is removed, antiviral ointments and creams must be applied to problem areas for several weeks. They are also used before removal of condylomas to prevent infection of healthy tissues. Prescribed drugs include:
- Panavir;
- Epigen;
- Acyclovir;
- Oxolinic ointment;
- Viferon;
- Malavit.
Aldara cream is considered one of the most effective local remedies for genital warts. Its use is contraindicated in children under 18 years of age. The drug is applied to the problem area 3 times a week and left for 10 hours. After the specified period of time, it is washed off with warm water and soap. The course of treatment is calculated individually and does not exceed 4 months.
Antiviral ointments may cause itching, burning and pain at the site of application. If such side effects occur, it is necessary to stop treatment and replace the drug. Medicines should be applied to clean, dry skin without damage. You cannot smear papillomas with several products at the same time.
Recommendations for treatment
The following recommendations can speed up the treatment process and minimize the risk of spreading the virus:
- Refusal of sexual intercourse for the entire period of treatment, regardless of its methods;
- Ensuring moderate physical activity and maintaining a daily routine;
- Ensuring a healthy diet and additional intake of vitamin and mineral complexes during treatment to increase the body's natural resistance.
It is not allowed to try to remove papillomas yourself at home, since this is associated with the risk of secondary infection, the appearance of scars and cicatrices, and transformation into malignant neoplasms.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from HPV, but there are a number of preventive measures aimed at reducing the risk of infection and the manifestation of virus activity.
Basic Rules:
- Maintaining an orderly sex life and having sexual contacts only with trusted partners.
- Use of high-quality protective equipment during sexual intercourse.
- Active sports , ensuring a normal daily routine, proper rest after physical activity, preventive intake of vitamins, ensuring a healthy diet, hardening and other measures aimed at strengthening the immune system.
- Getting vaccinated against HPV . A total of 3 injections are made into the brachial muscle, which minimizes the risk of infection; Vaccination is possible only if there is no HPV in the body and permission has been obtained from a specialist.
- Annual preventive examination by a urologist and other specialists.