pharmachologic effect
Antiprotozoal and antimicrobial drug, a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole.
The mechanism of action is the biochemical reduction of the 5-nitro group by intracellular transport proteins of anaerobic microorganisms and protozoa. The reduced 5-nitro group interacts with the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the microbial cell, inhibiting the synthesis of their nucleic acids, which leads to the death of bacteria.
Active against Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica, Gardnerella vaginalis, 2 Giardia intestinalis, Lamblia spp., as well as gram-negative anaerobes Bacteroides spp. (including Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides distasonis, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides vulgatus), Fusobacterium spp., Veillonela spp., Prevotella (P.bivia, P.buccae, P.disiens), and some gram-positive anaerobes ( sensitive strains of Eubacterium spp., Clostridium niger, Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp.). The minimum inhibitory concentration for these strains is 0.125-6.25 μg/ml.
In combination with amoxicillin, it is active against Helicobacter pylori (amoxicillin suppresses the development of resistance to metronidazole).
Aerobic microorganisms and facultative anaerobes are not sensitive to metronidazole, but in the presence of mixed flora (aerobes and anaerobes), metronidazole acts synergistically with antibiotics effective against common aerobes. Increases the sensitivity of tumors to radiation, causes sensitization to alcohol (disulfiram-like effect).
Metronidazole
Active substance:
Metronidazole*
Pharmgroup:
Other synthetic antibacterial agents
Average price in pharmacies
| Name | Manufacturer | average price |
| Metronidazole 0.005/ml 100ml n1 bottle solution d/inf/biosynthesis/ | Biosynthesis of PAO | 85.00 |
| Metronidazole 0.25 n20 tablet /welpharm/ | INDUKERN-RUS | 81.00 |
| Metronidazole 0.25 n20 tablet/Borisov ZMP/ | Borisov Medical Preparations Plant, JSC | 15.99 |
| Metronidazole 0.25 n20 tablet/ozone | OZONE, LLC | 45.99 |
| Metronidazole 0.25 n24 tablet ind/pack | UPDATE | 83.00 |
Analogs for the active substance:Batsimex Deflamon Klion Metrovagin Metrogil Metroxan Metrolacare Metron Metronidazole IV Brown Metronidazole Nycomed Metronidazole-AKOS Metronidazole-Altpharm Metronidazole-LekT Metronidazole-UBF Metronidazole-ESKOM Metronidal Metroseptol Orvagil Rozamet Rosex Cyptrogyl Tricho-PIN Trichobrol Trichopolum Trichosept Flagyl Efloran | Application area:Abdominal infection Abdominal surgery Muscle abscess Bacterial liver abscess Liver abscesses Adenomectomy Adnexit Bacterial septicemia Severe bacterial infections Bacterial bursitis Balloon coronary angioplasty Vaginal hysterectomy Corona bypass Interventions on the vagina and cervix Bladder interventions Intervention in the oral cavity Intraperitoneal infections Intra-abdominal infections Intrauterine infections Inflammation of the ovaries Inflammatory diseases of the female genitalia Inflammatory diseases of the female genitalia Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs Restorative and reconstructive operations Generalized infections Generalized systemic infections Giardiasis Giardiasis Hand hygiene of medical personnel Gynecological surgery Gynecological interventions Gynecological surgeries Hypovolemic shock during surgery Disinfection of purulent wounds Disinfection of wound edges Seborrheic dermatitis Diagnostic interventions Diagnostic procedures Diathermocoagulation of the cervix Diffuse peritonitis Long surgical operations Replacing fistula catheters Infections (opportunistic) Abdominal infections Abdominal infections Generalized infections Soft tissue infections Soft tissue infections Soft tissue infections Soft tissue infections Soft tissue infections Infections due to immunodeficiency Pelvic tissue infections Abdominal infection Gastrointestinal tract infection Genital infection Genital infection Infection during orthopedic surgery Artificial heart valve Cystectomy Intestinal giardiasis Redheads Short-term outpatient surgery Short-term operations Short-term surgical procedures Cricothyroidotomy Blood loss during surgery Bleeding during surgery and in the postoperative period Culdocentesis Laser coagulation Laser coagulation Laser coagulation of the retina Laparoscopy Laparoscopy in gynecology CSF fistula Giardiasis Minor gynecological operations Minor surgical interventions Mastectomy and subsequent plastic surgery Mediastinotomy Microsurgical operations on the ear Infectious myositis Mucogingival surgeries Stitching Minor surgeries Neurosurgical operation Immobilization of the eyeball in ophthalmic surgery Oophoritis Opportunistic infections Orchiectomy Complications after tooth extraction Acute respiratory infections of the lower respiratory tract Acute adnexitis Acute trichomoniasis Pancreatectomy Parametritis Pericardectomy Rehabilitation period after surgery The period of convalescence after surgical interventions Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty Liver abscess Hepatic giardiasis Pyomyositis Pleural thoracentesis Pneumonia postoperative and post-traumatic Increased sebum secretion Preparing for surgical procedures Preparing for surgery Preparing the surgeon's hands before surgery |
Indications for use
Prevention and treatment of infections caused by metronidazole-sensitive microorganisms (Bacteroides spp., B. fragilis, B. distasonis, B. ovatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. Vulgates, Clostridium, Peptococcus and Peptostreptococcus):
- protozoal infections: extraintestinal amebiasis, including amoebic liver abscess, intestinal amebiasis (amebic dysentery), trichomoniasis, giardiasis, balantidiasis, giardiasis, cutaneous leishmaniasis, trichomonas vaginitis, trichomonas urethritis;
- bone and joint infections;
- central nervous system (CNS) infections;
- abdominal infections;
- pelvic organ infections;
- skin and soft tissue infections;
- sepsis.
- Pseudomembranous colitis (associated with antibiotic use).
- Gastritis or duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori.
- Prevention of anaerobic infection during surgical interventions.
- Radiation therapy for patients with tumors
- as a radiosensitizing agent in cases where tumor resistance is due to hypoxia in tumor cells.
- Crohn's disease.
Instructions:
Clinical and pharmacological groups
29.003 (Antiprotozoal drug with antibacterial activity for external use) 29.051 (Drug for the treatment of acne) 23.017 (Drug with antibacterial, antiprotozoal and antifungal action for topical use in gynecology) 07.001 (Antiprotozoal drug with antibacterial activity) 23.019 (Drug with antibacterial, antiprotozoal, antifungal and anti-inflammatory effect for local use in gynecology) 25.001 (Drug with antimicrobial effect for local use in dentistry) 23.012 (Drug with antiprotozoal and antibacterial effect for local use in gynecology)
pharmachologic effect
Antiprotozoal agent. It is believed that the mechanism of action is associated with a violation of the DNA structure of sensitive microorganisms. Active against Trichomonas vaginalis, Gardnerella vaginalis, Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica, as well as obligate anaerobic bacteria (including Bacteroides spp., Fusobacterium spp.).
Aerobic microorganisms are resistant to metronidazole.
In combination with amoxicillin, it is active against Helicobacter pylori. Amoxicillin is believed to inhibit the development of Helicobacter pylori resistance to metronidazole.
Pharmacokinetics
Well absorbed after oral administration. Bioavailability is 80%. Distributed in tissues and body fluids. Penetrates through the placental barrier and BBB. Binding to blood plasma proteins is 20%. Metabolized in the liver by oxidation and binding to glucuronic acid. T1/2 is 8 hours. Excreted in urine (60-80%) and feces (6-15%).
Dosage
Orally for adults and children over 12 years old - 7.5 mg/kg every 6 hours or 250-750 mg 3-4 times a day. Children under 12 years old - 5-16.7 mg/kg 3 times a day.
When administered intravenously to adults and children over 12 years of age, the initial dose is 15 mg/kg, then 7.5 mg/kg every 6 hours or, depending on the etiology of the disease, 500-750 mg every 8 hours. Duration of treatment courses and their frequency implementation is determined individually.
Intravaginally - 500 mg 1 time per night.
In combination with amoxicillin (2.25 g/day), the daily dose of metronidazole is 1.5 g; frequency of administration - 3 times/day. For patients with severe impairment of renal function (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min) and/or liver, the daily dose of metronidazole is 1 g (amoxicillin - 1.5 g/day); Frequency of administration: 2 times/day.
Apply externally and locally 2 times a day, the dose is set individually.
The maximum daily dose for adults when administered orally and intravenously is 4 g.
Drug interactions
When used simultaneously with antacids containing aluminum hydroxide and cholestyramine, the absorption of metronidazole from the gastrointestinal tract is slightly reduced.
With simultaneous use, metronidazole potentiates the effect of indirect anticoagulants.
When used simultaneously with disulfiram, the development of acute psychosis and impaired consciousness is possible.
An increase in the concentration of carbamazepine in the blood plasma and an increase in the risk of developing toxic effects cannot be excluded when used simultaneously with metronidazole.
When used simultaneously with lansoprazole, glossitis, stomatitis and/or the appearance of a dark color of the tongue are possible; with lithium carbonate - it is possible to increase the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma and develop symptoms of intoxication; with prednisone - the excretion of metronidazole from the body increases due to the acceleration of its metabolism in the liver under the influence of prednisone. The effectiveness of metronidazole may be reduced.
When used simultaneously with rifampicin, the clearance of metronidazole from the body increases; with phenytoin - a slight increase in the concentration of phenytoin in the blood plasma is possible; a case of toxic effects has been described.
When used simultaneously with phenobarbital, the excretion of metronidazole from the body increases significantly, apparently due to the acceleration of its metabolism in the liver under the influence of phenobarbital. The effectiveness of metronidazole may be reduced.
When used simultaneously with fluorouracil, the toxic effect, but not the effectiveness of fluorouracil, increases.
A case of the development of acute dystonia after taking a single dose of chloroquine in a patient receiving metronidazole is described.
When used simultaneously with cimetidine, inhibition of the metabolism of metronidazole in the liver is possible, which can lead to a slower elimination and increased concentration in the blood plasma.
With simultaneous use of ethanol in patients receiving metronidazole, disulfiram-like reactions may develop.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Metronidazole quickly penetrates the placental barrier. In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, metronidazole is used only for health reasons.
Metronidazole is excreted in breast milk. If it is necessary to use it during lactation, the issue of stopping breastfeeding should be decided.
Side effects
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, metallic taste in the mouth.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: headache, increased excitability, irritability, insomnia, dizziness, ataxia, weakness, confusion, depression, peripheral neuropathy, convulsions, hallucinations.
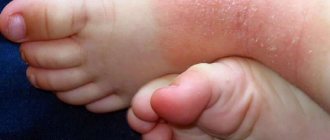
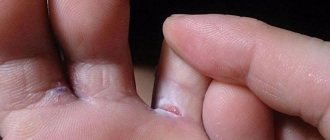
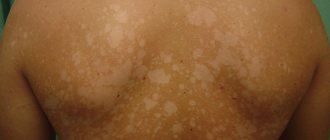
Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, urticaria.
From the hematopoietic system: leukopenia.
Local reactions: irritation.
Other: arthralgia, burning sensation in the urethra.
Indications
Trichomonas vaginitis and urethritis in women, trichomonas urethritis in men, giardiasis, amoebic dysentery, anaerobic infections caused by metronidazole-sensitive microorganisms, combination therapy for severe mixed aerobic-anaerobic infections. Prevention of anaerobic infection during surgical interventions (especially on the abdominal organs, urinary tract). Chronic alcoholism.
In combination with amoxicillin: chronic gastritis in the acute phase, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase, associated with Helicobacter pylori.
For external and local use: treatment of rosacea and vulgar acne, bacterial vaginosis, treatment of long-term non-healing wounds, trophic ulcers.
Contraindications
Organic damage to the central nervous system, blood diseases, liver dysfunction, first trimester of pregnancy, hypersensitivity to metronidazole.
special instructions
Use metronidazole with caution in liver diseases.
It is not recommended for use in combination with amoxicillin in patients under 18 years of age. During treatment, systematic monitoring of peripheral blood patterns is necessary.
During treatment of trichomonas vaginitis in women and trichomonas urethritis in men, it is recommended to abstain from sexual activity; simultaneous treatment of both partners is mandatory.
During the use of metronidazole, darker coloration of urine is observed.
During treatment with metronidazole, you should avoid drinking alcohol, because Due to impaired alcohol oxidation, acetaldehyde may accumulate. As a result, reactions similar to those characteristic of disulfiram may develop (cramping abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, sudden flushing of the face).
Medicines containing METRONIDAZOLE
• METRONIDAZOLE-ROS tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE NYCOMED (METRONIDAZOLE NYCOMED) solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10,20, 50 or 12000 pcs. • FLAGYL® vaginal suppositories. 500 mg: 10 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE NYCOMED tab. 500 mg: 200 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: bottle. • CLOMEGEL vaginal gel 10 mg+20 mg/1 g: tubes 30 g • ROZAMET ◊ cream for external use. approx. 1%: tube 25 g • METROVIT vaginal suppositories 500 mg: 5 or 10 pcs. • METROGYL® ◊ gel for external use. approx. 10 mg/1 g: 30 g tube • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 5000 or 10000 pcs. • METROGYL® vaginal gel 10 mg/1 g: tube 30 g 1 pc. included with applicator • ORNIDAZOL (ORNIDAZOL) solution for inf. 5 mg/ml: vial. 1 PC. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for injection. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • METROGYL® tab., coated. film-coated, 400 mg: 20, 100, 1000 or 5000 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 90, 100, 200, 300, 4000, 8000 or 12000 pcs. • METROZOL tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 or 100 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • TRICHOPOL® solution for inf. 100 mg/20 ml: amp. 10 pieces. • METROLACARE solution d/inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. • METROVAGIN vaginal suppositories 500 mg: 10 pcs. • METROSEPTOL ◊ gel for external use. approx. 10 mg/1 g: tube 15 g • EFLORAN solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 10 pieces. • Tricho-PIN tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • TRICHOPOL® tab. 250 mg: 10 pcs. • METROGYL DENTA® (METROGYL DENTA®) ◊ dental gel 10 mg + 500 mcg/1 g: tubes 5 g, 10 g or 20 g • TRICHOPOL® solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • TRICHOSEPT vaginal suppositories 500 mg: 10 pcs. • BACIMEX (BACIMEX) solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METROSEPTOL ◊ cream for external use. approx. 10 mg/1 g: 15 g tube • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE vaginal suppositories 100 mg: 10 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METROGYL® solution for intravenous administration 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE vaginal suppositories 500 mg: 10 pcs. • GYNALGIN tab. vagina. 250 mg+100 mg: 10 pcs. • KLION (KLION) solution for inf. 5 mg/1 ml: vial. 100 ml 1 pc. • NEO-PENOTRAN® (NEO-PENOTRAN®) vaginal suppositories. 500 mg+100 mg: 7 or 14 pcs. included with fingertips • METRON (METRON) solution d/inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • NEO-PENOTRAN® FORTE (NEO-PENOTRAN® FORTE) vaginal suppositories. 750 mg+200 mg: 7 pcs. included with fingertips • METRONIDAZOLE vaginal suppositories 100 mg: 10 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 30, 50 or 100 pcs. • KLION-D 100 (KLION-D 100) tab. vagina. 100 mg+100 mg: 10 pcs. • METROHEX® (METROHEX) ◊ dental gel 10 mg+500 mcg/1 g: tubes 10 g 1 pc. • CIPTROGIL solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40 or 50 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10, 20 or 700 pcs. • ROZEX ◊ cream for external use. approx. 0.75%: tubes 5 g, 15 g, 30 g or 50 g • METROGYL® tab., coat. film-coated, 200 mg: 20, 100, 1000 or 5000 pcs. • EFLORAN solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1, 10 or 70 pcs. • TRICHOPOL® tab. vaginal 500 mg: 10 pcs. • ROZEX ◊ gel for external use. approx. 0.75%: tubes of 5 g, 15 g, 30 g or 50 g • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 or 48 pcs. • FLAGYL® tab., coated. film-coated, 250 mg: 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 or 24 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE-AKOS (METRONIDAZOLE-AKOS) tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE-UBF tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80 or 100 pcs. • GYTERNA tab. vaginas: 6 or 10 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • METROGYL® solution for intravenous administration 100 mg/20 ml: amp. 5 pieces. • METRONIDAZOLE VATCHEM tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • EFLORAN tab. 400 mg: 10 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: containers of 1, 3 or 70 pcs. • DENTAMET ◊ dental gel 250 mg+1 mg/1 g: tubes 10 g or 25 g • METRONIDAZOLE ◊ vaginal gel 1%: tube 30 g included. with applicator • METROZOL (METROZOL) solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC. • METROGYL® PLUS vaginal gel 10 mg+20 mg/1 g: tubes 30 g included. with applicator • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 20 or 50 pcs. • NEO-PENOTRAN® FORTE L (NEO-PENOTRAN® FORTE L) vaginal suppositories. 100 mg+750 mg+200 mg: 7 pcs. included with fingertips • METRONIDAZOLE tab. 250 mg: 10, 20 or 40 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 5 mg/1 ml: vial. 100 ml • METRONIDAZOLE-AKOS (METRONIDAZOLE-AKOS) solution for inf. 0.5%: fl. 20 ml and 100 ml, 100 ml bottles • KLION tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • TRICHOBROL tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 40 or 60 pcs. • METRONIDAZOLE solution for inf. 500 mg/100 ml: vial. 1 PC.
special instructions
Regionally approved standards for antibiotic use should be followed.
It is not recommended to use metronidazole in combination with amoxicillin in patients under 18 years of age.
With long-term therapy, it is necessary to monitor the blood picture. With leukopenia, the possibility of continuing treatment depends on the risk of developing an infectious process.
The appearance of ataxia, dizziness and any other deterioration in the neurological status of patients requires cessation of treatment. May immobilize treponemes and lead to a false-positive Nelson test.
Colors urine dark.
When treating trichomonas vaginitis in women and trichomonas urethritis in men, 10 it is necessary to abstain from sexual activity. Simultaneous treatment of sexual partners is mandatory. Treatment does not stop during menstruation.
After treatment for trichomoniasis, control tests should be carried out during three consecutive cycles before and after menstruation.
After treatment of giardiasis, if symptoms persist, after 3-4 weeks, carry out 3 stool tests at intervals of several days (in some successfully treated patients, lactose intolerance caused by infestation may persist for several weeks or months, resembling the symptoms of giardiasis).
Directions for use and doses
The drug is taken orally during or after meals (with milk), without chewing.
- Trichomoniasis: adults are prescribed 250 mg 2 times a day for 10 days or 400 mg 2 times a day for 5-8 days. Women must additionally be prescribed metronidazole in the form of vaginal suppositories or tablets. If necessary, you can repeat the course of treatment or increase the dose to 0.75-1 g/day. Between courses you should take a break of 3-4 weeks with repeated control laboratory tests.
An alternative treatment regimen is to prescribe 2 g once to the patient and his sexual partner.
For children aged 2-5 years, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 250 mg/day, for children aged 5-10 years - 250-375 mg/day; over 10 years - 500 mg/day. The daily dose should be divided into 2 doses. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Giardiasis: adults are prescribed 500 mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days.
Children over 8 years old - 500 mg/day (in 2 doses), aged 5 to 8 years - 375 mg/day, aged 3 years and older - 250 mg/day; the daily dose should be divided into 2 doses; course of treatment - 5 days. The dose of the drug can be 15 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses for 5 days.
- Asymptomatic amebiasis (if a cyst is detected): adults are prescribed a daily dose of 1-1.5 g (500 mg 2-3 times a day) for 5-7 days.
- Chronic amebiasis: 1.5 g/day in 3 divided doses for 5-10 days.
- Acute amoebic dysentery: 2.25 g/day in 3 divided doses until symptoms stop.
- Liver abscess: the maximum daily dose is 2.5 g in 1 or 2-3 doses over 3-5 days, in combination with antibiotics (tetracyclines) and as part of complex therapy.
Children from 3 years old - 1/4 adult dose, at the age of 3-7 years - 1/3 adult dose, at the age of 7-10 years - 1/2 adult dose.
- Balantidiasis: 750 mg 3 times a day for 5-6 days.
- Ulcerative stomatitis: adults are prescribed 500 mg 2 times a day for 3-5 days. In this case, the drug is not indicated for children.
- Pseudomebranous colitis: 500 mg 3-4 times a day.
- For eradication of Helicobacter pylori: 500 mg 3 times/day for 7 days (as part of combination therapy, for example, in combination with amoxicillin 2.25 g/day).
- Treatment of anaerobic infection: maximum daily dose - 1.5-2 g.
- Treatment of chronic alcoholism: prescribed at a dose of 500 mg/day for a period of up to 6 (not more than) months.
- For the prevention of infectious complications: 750-1500 mg/day in 3 divided doses 3-4 days before surgery, or a single dose of 1 g on the first day after surgery. 1-2 days after surgery (when oral administration is already allowed) - 750 mg/day for 7 days.