The appearance of warts on the head in the hair may go unnoticed; they are detected only when the tumor has reached a large size. Their growth may not pose a threat, but during the process of combing, cutting and dyeing, papillomas are often damaged. Then the development of a bacterial infection becomes possible: inflammation of some nodules can give rise to malignancy. That is why it is so important to identify the problem in time and seek help from specialists.
Reasons for appearance
Warts appear on the body after the human papillomavirus enters the human body. It is present in the blood of half of the planet's inhabitants. It can be transmitted through sexual or contact contact. Most often, warts on the head appear after using someone else's comb. The virus is activated and multiplies only when immunity is low. A strong defense system is able to independently recognize the “stranger” and control its numbers, preventing infection. Infection occurs with the development of immunodeficiency states.
They occur after:
- previous colds;
- prolonged mental or physical fatigue;
- hormonal therapy;
- constantly recurring attacks of exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
- the beginning of the development of oncology, HIV.
Excessive sweating, infrequent washing of hair, increased activity of the sebaceous glands, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, unhealthy lifestyle, long-term use of antibiotics - all this contributes to the growth of warts, increasing their size and number. The reason for the appearance of black keratomas is old age.
Causes of human papillomavirus infection
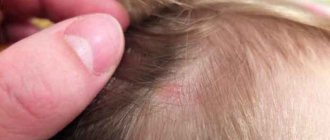
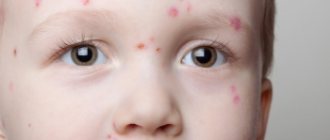
Photo of papilloma on a child’s head
clearly demonstrates the shape and size of the formation. Most often, single growths appear in the head area, arising under the influence of HPV. They are benign in nature and only interfere with their appearance. However, the specific location of the growths is such that during combing, cutting and hygiene procedures, the formations can be damaged, which is fraught with infection and spread of the virus.
The risk group for HPV infection most often includes children attending kindergartens or schools. They can become infected through contact with a carrier of the virus or his personal items. The disease may appear soon after infection or several months after infection with the papilloma virus.
The main causes of infection include:
- malfunction of the body's defense system, vitamin deficiency;
- the child’s stay in poor sanitary conditions (home or educational institution);
- the presence of serious illnesses in a pregnant woman during gestation, as a result of which the baby’s immune system is not able to resist infection;
- late pregnancy in a woman;
- the presence of allergic reactions to foods or other substances.
Any chronic disease, prolonged stress, chronic fatigue can provoke activation of the virus in a child. In newborns, papillomas can appear as a result of infection from the mother during childbirth. In addition to damage to the scalp, growths can occur in the face, neck, upper and lower extremities, and inside the larynx.
Types and diagnosis
In appearance, not all warts on the head are the same. They vary in shape, color, size. Taking these parameters into account, doctors classify neoplasms and distinguish:
- Vulgar warts, externally similar to rounded balls covered with a hard crust.
- Flat papillomas are low growths that grow in width rather than upward.
- Condylomas (hanging) nodules with a stalk. They are soft to the touch.
- Keratomas are dark brown warts with jagged edges. Their growth is often accompanied by itching and burning.
The appearance of the listed papillomas on the head in most cases has a positive prognosis; the risk of degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one is small, but it increases when the warts are injured. Much depends on which serovirus was able to penetrate the deep layers of the skin and begin to actively multiply there. A person can become infected with 40 seroviruses, 27 of them cause the growth of benign tumors, 14 cause tumors that are classified as precancerous. You can find out whether you should worry about the fact that warts have begun to grow on your head by taking a blood test. There are three methods to determine the presence of a virus in a patient’s blood, its concentration, type and oncogenicity. This:
- Enzyme immunoassay blood test. It detects the presence or absence of antibodies to the human papillomavirus in the blood.
- Amplification test. To carry it out, scrapings from the mucous membrane of the vagina or urethra are used.
- PCR. A method based on the detection of viral DNA. For analysis, a smear from the mucous membrane or blood or urine is taken (a pregnant woman has amniotic fluid).
For a person, performing all the tests does not cause any particular inconvenience or pain. To obtain an accurate picture, it is necessary to stop taking antibacterial agents and using intimate hygiene products three days before the delivery of biological materials. There is no need to wash your face on the day of donation; it is better to donate blood on an empty stomach. It’s good to go on a light diet a couple of days before the test, eliminating fried and spicy foods and alcohol.
Methods for diagnosing the pathological process
To accurately determine the nature of a growth that has appeared in a person’s hair, a visual examination by a specialist alone is not enough. The main method for diagnosing the nature of the virus that caused the appearance of papilloma is PCR analysis, which provides complete information about viral infection.
The results of a molecular study of a patient’s DNA fragment make it possible to determine whether the virus belongs to a specific strain. This is especially important information because the consequences of infection with some human papillomaviruses can be severe.
Related article:
How to get rid of papillomas in intimate places in men and women?
What other types of examinations will you have to undergo for the treatment of papilloma of the scalp:
Dermatoscopy
- The dermatoscopy method allows you to obtain a many times enlarged image of the wart, which helps identify pathological changes;
- Taking tissue material (particles of growth) for a biopsy is necessary to determine the likelihood of an oncological process.
Attention. The danger of papillomatosis on the head is associated with the threat of suppuration due to involuntary injury to the nodule. Inflammation and suppuration in the lesions leads to the formation of large bald spots, so the tumors must be removed.
How to distinguish a wart from other formations by appearance
Externally, it is difficult to distinguish a harmless wart from a malignant neoplasm. But an experienced doctor can easily do this based on several signs.
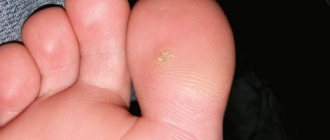
In most cases, simple or flat warts grow on the scalp. They are small in size (5-10 mm), hair can grow through them, and this fact allows the growths to be well camouflaged. They can only be detected when the wart grows to a large size and when a person cuts his hair short. Simple warts have a stalk; frequent combing of hair with a comb leads to injury to it. Constant violation of the integrity of the wart increases the risk of malignancy.
A simple wart is different from genital warts. Condylomas look like multiple growths, shaped like pyramids. They are flesh-colored or brown and grow up to 5 mm in height.
Flat warts are single neoplasms, in their structure they resemble low platforms rising above the skin by 1-2 mm; in structure, flat warts are similar to neoplasms assembled from many lobules.
If a wart grows slowly, if it reaches a certain size and stops growing, if hair grows through it, there is no need to worry. Uniform color and structure, the absence of purulent discharge from the growth allows us to make positive prognoses.
What to do if papillomas appear
You can notice the appearance of papillomas in a child while washing or combing his hair. At first, the formations may be small in size, appear singly and do not tend to grow. If the immune system is weakened, the picture may change radically, so if a growth is detected, it must be shown to a doctor. You will definitely need to take a blood test for HPV to identify the strain of the virus. Further research will help determine the state of the child’s general health and determine the cause of the intensification of the infection.
You cannot self-medicate at home before visiting a specialist, because malignant tumors can be hidden under the guise of benign formations. In addition, a child’s skin is very sensitive and some manipulations can harm it, causing injury or burns.
When your baby develops growths on his scalp, it is important to prevent him from combing and picking them off. In the overgrown cells, particles of the virus are hidden, which, if the formations are damaged, can enter healthy areas of the epithelium, causing its growth. papilloma occurs
(
the photo
shows what this can look like), you need to contact your pediatrician and get recommendations for treatment.
Which ones are dangerous?
Warts that grow quickly and those that produce watery or bloody discharge are considered dangerous. Revealing uneven coloring and an irregularly shaped structure, the presence of additional growths that make the wart look like a head of cauliflower, should force a person to seek help from a dermatologist.
The risk of life-threatening diseases increases if part of the growth spontaneously falls off, ulcers, erosions, or any other defects form on its surface. Only a doctor, having carried out the necessary tests, will be able to prescribe treatment that will allow you to maintain health and get rid of an unpleasant cosmetic defect.
The danger of papilloma on the head
As long as the skin growth on the scalp is small, it does not cause any particular problems. A person may not even notice its presence or simply not attach any importance to papilloma. But this is a wrong action. Papillomas on the head in the hair must be removed in the initial stages of development. Thanks to this, it will be possible to avoid the possible degeneration of the growth into an oncological tumor. In addition, the papilloma will gradually grow and cause inconvenience.
A large growth will certainly be touched during the process of combing the hair, coloring it and shaping it into a hairstyle. An injured scalp papilloma will begin to become inflamed and painful. All this will lead to an even greater increase in size. In addition, overgrown warts are much more difficult to remove. After them, noticeable marks remain on the skin. Due to the pronounced inflammatory process, serious suppuration can occur, which is extremely undesirable to allow.
Treatment
If the wart is inflamed, it is better to remove it. This can be done in different ways. Medical procedures that have a high percentage of positive results and low rates of possible complications are considered the safest. To remove a benign growth, the doctor may suggest:
- Cryodestruction is a procedure during which the nodule is exposed to liquid nitrogen. The wart cells are frozen, after which the growth turns black, dries and falls off on its own. If the growth is small, one procedure is enough; if the roots of the wart have grown deep into the layers of the skin, to remove it you will need to do a second session in two weeks. After this, there are no traces or scars left on the head. Due to the dosed use of nitrogen, it is possible to preserve the hair follicles on the head.
- Laser removal is a method that is often chosen to remove multiple small papillomas. The use of a laser allows not only to excise the tumor, but also to seal the vessels feeding it, so the risk of bleeding is minimized. After the operation, no marks are left on the head, the laser does not destroy the follicles, so hair growth in the future is not interrupted. Laser is not used to remove large nodules.
- Thermoregulation is a method of removing warts in which they are exposed to high-frequency current. Due to its simplicity of execution, it is used quite widely; it allows for high effectiveness, but after exposure, scars remain on the dermis, and hair no longer grows at the site of resection.
- Surgical excision is an operation performed with a scalpel. During its implementation, not only the papilloma itself is excised, but also the layers of skin underlying it. The wound is then sutured. This method of removal is chosen when you need to get rid of a large wart. After surgery, there is always a scar where hair no longer grows.
There are also pharmaceutical solutions for cauterizing warts. The most popular of them is “Ferezol” - a caustic substance that helps get rid of warts with one cauterization. It can be used if the size of the growth does not exceed 2 mm. This product should not be used to remove warts in young children and pregnant women.
A milder remedy is the drug “Verrukacid”. Using it, you can get rid of a benign neoplasm in two or three cauterization procedures. Iodine solution is the most affordable means for chemical wart removal. They need to cauterize the wart once or twice a day for a week. All chemicals are applied directly to the growth; you must try to prevent the chemical solution from getting into healthy areas of the skin. Before applying the product, hair should be lubricated with Vaseline and covered with film.
Regardless of which method of papilloma removal was chosen, there is always a risk of relapse. This is due to the fact that the virus continues to live in the human body. It cannot be destroyed. For all those who want to minimize the possibility of the appearance of new tumors, doctors recommend constantly increasing the body's defenses. To do this, you need to carry out antiviral therapy, take drugs that have an immunomodulatory effect, lead an active lifestyle, eat right and try to give up bad habits.
About neoplasms
In one of our articles, “Skin growths: benign, malignant and borderline,” we already talked about skin growths and classified them according to their danger to human health. Today we will look at those that are most often found on the head and are sometimes invisible under the hair. Experts recommend regularly palpating and, if possible, examining the head for the presence of tumors, since the proximity of a malignant tumor to the brain can lead to irreparable consequences. If you notice a strange growth on your head, immediately consult a dermatologist or oncologist.
The scalp is also the most traumatized and exposed area. Many people use combs with hard teeth, which can easily tear off the growth. In addition, we wash our hair, dye it, apply masks that can corrode the tumor and provoke its degeneration into a malignant tumor. Another danger factor is prolonged exposure to the sun without a hat. As you know, many moles tend to become malignant with prolonged and strong exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
That is why, if you feel or feel a growth in your hair that:
You need to urgently contact a specialist.
Types of neoplasms on the head
First, let's look at malignant neoplasms on the scalp.
First of all, malignant neoplasms include melanoma - skin cancer. You can find out more about it in our special article “Skin cancer: melanoma.” The neoplasm looks like a small plaque of light brown or black color with a rough surface. Melanoma is dangerous, it metastasizes and can lead to irreparable consequences. Therefore, if it is detected on the scalp, you should immediately consult a doctor. One of the most effective methods of treating melanoma is laser therapy; it helps skin cells regenerate faster and at the same time kills all harmful cells.
The second reason not to waste time and go for an examination to an oncologist may be a neoplasm that looks like a nodule with a crust, light pink or red in color - this is a basal cell carcinoma. It develops from the cells of the basal layer of the skin and is often accompanied by the formation of ulcers and erosions. More information about this neoplasm can be found in our special article “Basal cell carcinoma. Skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma." An advanced method of treating basal cell carcinoma is photodynamic therapy (for more details, see PDT), this is a gentle method of exposure that gives visible results after just a few sessions.
Skin epithelioma is a tumor that develops on the surface layer of the epidermis. Also distinguished is epithelioma of the sebaceous gland - a neoplasm that occurs on the scalp, with inflammation of the sebaceous glands. Epithelioma looks like a pink or light brown growth and can reach 5 cm in diameter. This tumor is dangerous because it very quickly metastasizes to the lymph nodes. It can occur against the background of previous dermatological diseases, as well as strong UV radiation.
Borderline neoplasms on the scalp
Scalp keratosis is a keratinization of the top layer of skin. Most often found on the face and scalp, it can be located either on a small area of the skin or affect the entire surface of the head. The neoplasm looks like multiple warts, ranging from light to dark brown in color. Experts also identify seborrheic keratosis of the scalp; its appearance indicates pathologies occurring in the body. With this diagnosis, a thorough examination is necessary, since this may be evidence of cancer of the internal organs. Treatment for keratosis of the scalp is prescribed by an oncologist or dermatologist after receiving all the tests. Treatment methods may include medications and peeling procedures, massage, and laser therapy.
Scalp keratoacanthoma is a benign tumor of the hair follicles that most often occurs in older people. It is a spherical dense neoplasm affecting the scalp. Keratoacanthoma and its multiple forms are flesh-colored and can grow quickly, reaching 2-3 cm. In some cases, the neoplasm can become malignant, especially if it is often traumatized. Treatment of keratoacanthoma is possible only with its complete excision using a scalpel, electric current or laser.
Benign neoplasms on the scalp
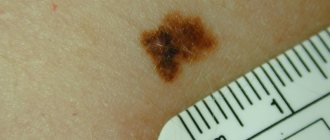
A mole is a small pigmented formation on the skin that can appear at any age and on any part of the skin, even on the head in the hair. Moles can grow in large numbers during puberty, during hormonal imbalance or pregnancy, which you can read more about in our special article. According to statistics, a mole on the scalp is not dangerous, and the likelihood of degeneration into skin cancer is extremely low. However, it is necessary to check moles; RTM diagnostics are the best way to deal with this. Based on the test results, you may be advised to remove the mole.
Perhaps the most common neoplasms on the scalp are warts and papillomas. They appear due to the human papillomavirus, which is most often activated with reduced immunity, severe stress, infectious diseases, and a lack of vitamins in the body. Find out more about what HPV is and how it manifests itself on the body in our article “Human Papilloma Virus”. Warts are classified as benign neoplasms, but if a wart on the head in the hair is often injured, then it must be removed. The most effective method in such cases is laser removal.
Traditional medicine recipes
In the arsenal of folk treatment there are many recipes that allow you to burn out a benign tumor at home. But their use becomes possible only after diagnostic studies are carried out to prove the absence of malignancy processes. Best suited for these purposes:
- Potato. For preparation, shoots of a young vegetable are taken, half a liter jar is filled with them, the remaining half is filled with thuja shoots and celandine herb. All this is filled with alcohol and left in a dark place for two weeks. After their expiration, a remedy is obtained with which you need to smear the warts three times a day. The wart should turn black.
- Apple vinegar. Two hundred grams of liquid are mixed with fifty grams of salt, the mixture is applied to the wart and fixed with a plaster. Applications are made until the growth turns black.
- Celandine. Juice is extracted from fresh stems and applied directly to the papilloma three times a day. After some time it will turn black and begin to dry out. Then it will definitely disappear.
Cabbage juice extracted from the leaves is considered the safest. The growth is lubricated with it every day three times a day. This method of cauterization will take a lot of time, but there will certainly be results.
Folk remedies for fighting papillomas
At home, you can try to remove a wart on your baby’s head using safe but very effective folk remedies. In this regard, it will help:
- Tea tree oil, which should be used to lubricate the overgrown scalp several times a day. Additionally, a few drops of oil can be added to the water for rinsing your hair.
- Aloe juice (lubricate the wart until it falls off).
- Potato juice.
- Decoction of celandine (used for washing hair).
- Chicken protein.
- Garlic lotions and compresses.
- Castor oil, etc.
All these methods can be used to remove warts in children of primary and high school age. How to treat a viral infection in newborns should be prescribed by a doctor. It is prohibited for infants to undergo therapy with folk remedies in order to avoid the development of complications.
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm. It can appear on any part of the body. Most of all, HPV carriers fear that they will develop papilloma in the hair on their heads. This kind of growth causes a lot of problems. It is the cause of physical and aesthetic discomfort that constantly haunts a person.
Is it possible to dye your hair
In order to answer this question, you need to know whether there is a risk of the wart degenerating into melanoma. If a benign wart has grown on your head, you can dye your hair, but it is not advisable: during the dyeing process, it is easy to accidentally injure the growth, dyeing compounds have aggressive chemical formulas, the effect of which can provoke skin irritation and then inflammation. If, after staining, the wart begins to ooze blood, if it hurts and itches severely, you should immediately consult a dermatologist.
Procedures for removing lesions
Depending on the child’s age, he may be prescribed one of the non-invasive procedures to remove the formations. They are carried out under the strict supervision of an experienced specialist who will remove the growths without harm to health in several sessions.
Recommended procedures for removing scalp lesions are:
- laser therapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryodestruction.
Surgical excision may be used as an alternative to non-invasive procedures. However, this method has its significant drawbacks, so before deciding to undergo surgery, you should weigh the pros and cons. Additionally, antiviral therapy using Interferon may be prescribed. Laferobion and restorative treatment.
Prevention
The papilloma virus, once it enters the human body, does not disappear anywhere. It begins to activate when immunity decreases, so the main prevention of wart growth is strengthening the defenses. This can be achieved by giving up bad habits, competent and timely treatment of viral infections, and regular preventive examination of the scalp. Exercise, proper nutrition, regular walks in the fresh air, and strengthening the nervous system will help strengthen your immune system. A growing papilloma must be removed immediately.
Degeneration of papilloma into cancer
Removal of papillomas on the head in the hair is mandatory for almost all patients. This is the only way they can protect themselves from developing cancer. A benign growth may well degenerate into a malignant one in the presence of accompanying factors, which cannot always be excluded.
As a rule, damage to the scalp by papilloma has a favorable course. It turns into a cancerous tumor in isolated cases. Patients who have noticed the following changes in the structure of papilloma should not hesitate to visit a specialist:
- The growth has acquired an asymmetrical shape;
- The papilloma has changed its natural color to brown, deep red or black;
- From time to time, blood began to flow from the neoplasm. The symptom cannot be ignored unless the bleeding is caused by damage to the wart;
- The growth continues to increase in size.
An increase in papilloma may indicate its degeneration!
These signs indicate the degeneration of a benign growth into a malignant tumor. If you notice these symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. If you treat papilloma at an early stage of its growth, you can avoid such a sad outcome.
Treatment methods
Doctors are unanimous in their opinion that treatment of papilloma on the head should be comprehensive. It is not enough to remove the consequence - a neoplasm that has become a cosmetic defect. It is important to “put to sleep” the virus that caused its appearance, to increase immunity so that this does not happen in the future.
Treatment of papillomas includes the following methods of treatment:
- removal of growth;
- taking medications;
- vitamin therapy;
- the use of folk remedies as a supplement to the listed activities.
It is strictly forbidden to remove papillomas on the head yourself, for example, using threads or scissors.
Such home treatment leads to sad consequences: inflammation of surrounding tissues, spread of infection, bleeding, and degeneration of the tumor into a malignant tumor.
Drug therapy
Treatment of papilloma on the head with medications is intended to “put to sleep” the virus that has entered the body. The following groups of drugs are used for this purpose:
- Antiviral agents - used in the form of tablets, injections, vaginal or rectal suppositories. Their task is to suppress the activity of HPV. This category of drugs includes Isoprinosine (used in courses of two times for two weeks with a ten-day break), Panavir (used in a course of 5-10 doses).
- Immunomodulators - used in the form of tablets or injections. The most well-known products in this category are Polyoxidonium and Lykopid.
- Vitamins – used as an adjunct to drug therapy.
- Pharmacy external remedies - to combat papillomas on the head, burning ointments (Verrukacid, Collomac, etc.), local antiviral drugs are used (the most famous is Epigen Intim Spray, which is applied to growths).
The combination of medications is selected by the doctor based on the diagnostic results. Treatment is not specific for different types of HPV.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are used as an addition to drug treatment for scalp papillomatosis. Many of them are controversial, so their use is possible only after consultation with a dermatologist.
There are the following recipes for removing papilloma on the head at home:
- Celandine juice
The juice is squeezed out of the stem of a freshly picked plant and applied to the new growth. The procedure is repeated until it turns black.
- Super clean
This is a pharmacy analogue of freshly squeezed juice of a medicinal plant. The papilloma is steamed, the area around it is smeared with cream, and the product is applied pointwise to the growth. The number of repetitions of the procedure is until the tumor blackens.
- Laundry soap
The original product is grated and mixed with water until a thick paste is formed. Next, it is applied to the papilloma, covered with a gauze bandage, and left overnight.
- Castor oil
This product is known for its ability to increase local immunity and stimulate metabolic processes. The papilloma is smeared with it every morning and evening until it disappears completely.
- Tea tree oil
This product is credited with disinfecting properties. A small amount of it is applied to the tumor and is not washed off.
After regular procedures, the papilloma should turn black and disappear.
Surgical intervention
To decide on the method of removing papillomas on the head in the hair, you need to consult a specialist. The following methods of resection are possible:
- use of pharmaceutical burning agents;
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryotherapy;
- classical resection with a scalpel.
Laser removal is recognized as the most progressive technique, because it allows you to shorten the healing period of a wound on the head to 10 days, reducing to zero the likelihood of scars, cicatrices and relapses. This method is not used for neoplasms, the benign nature of which is doubtful, because the growth is “evaporated”, i.e. There is no papilloma tissue left for histology.
Electrocoagulation is exposure to an electrical impulse. It destroys the tissue of the neoplasm, in its place a crust forms, which disappears after a week. The healing time for the operated area is about 14 days. After surgery, the wound must be treated with disinfectants; a patch or bandage is worn for 1-2 days.
Cryotherapy is recognized as a modern and effective way to combat papillomas. She assumes that resection occurs with liquid nitrogen. The tumor turns white and then disappears spontaneously. The technique is used mainly for small papilloma sizes. Healing time is up to 14 days. The procedure is contraindicated for persons with individual intolerance to cold.
For large papillomas on the head and formations that have developed into a malignant form, resection with a surgical scalpel is used. It is performed under local anesthesia and leaves the possibility of scarring. If studies of the taken material are necessary, the tissues are sent for histology.
How can you become infected with HPV?
Papilloma on the head is an external manifestation of an internal problem - the HPV virus. According to statistics, 70% of the world's inhabitants are its carriers, regardless of age and gender.
It is believed that the most common way of contracting the virus is sexually. It is also possible to transmit HPV through everyday contact, from mother to child during fetal development, childbirth or breastfeeding.
Once in the human body, the virus “dormants” for a long time, i.e. does not give any external signs. When the patient’s immunity decreases due to the negative impact of internal or external factors, manifestations of HPV occur - genital warts located on the skin and mucous membranes.
In utero
According to statistics, intrauterine infection of a child is a rare occurrence. It is possible if there are changes in the structure of the placenta, for example, its damage. In a child in the womb, the alveoli and bronchi are not formed, so the penetration of HPV into his body leads to the development of respiratory papillomatosis. Less commonly, it becomes the cause of scalp papillomas.
The consequences of intrauterine infection are congenital breathing disorders, which require surgical intervention to eliminate. To avoid adverse consequences, when planning a pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to undergo an HPV diagnosis, and if it is detected, treatment.
At birth
Why do newborn children have papillomas on the head, skin, and mucous membranes? The reason is vertical infection, i.e. penetration of the virus during childbirth. As a result, the baby develops genital warts in the mouth and larynx. In the future, problems associated with breathing problems and low immunity are possible.
If there are papillomas on a woman’s genitals, doctors recommend that she refuse natural childbirth, which means a high probability of infection, and give preference to a cesarean section. Breastfeeding becomes an additional risk factor.
By everyday means
Papillomas of the scalp are a consequence of the HPV virus that entered the body through household means, i.e. through microcracks, small wounds, scratches of the skin and mucous membranes. This happens at home in the following ways:
- Use one towel, bed linen, soap or washcloth.
- Wearing only clothes, especially underwear.
- Food from one plate, with one cutlery, poor washing of common dishes.
- Walking barefoot in public baths, saunas, swimming pools: a humid, warm environment is favorable conditions for the spread of the virus that causes the appearance of papillomas on the head.
- Handshakes, kisses if there are microcracks on the lips or hands.
In addition to the listed methods, doctors identify a special way - self-infection. When shaving the bikini area, a person damages one papilloma, which contributes to the spread of the virus further.
A similar situation can occur when scratching the head.
Sexually
Papillomas on the head in the hair are a consequence of HPV infection, the most common route of penetration of which is considered to be sexual. For transmission of a dangerous strain to occur, one intimate contact of any type is sufficient: vaginal, anal or oral.
The likelihood of infection increases significantly if the partner has microcracks in the genitals. If anal sex is practiced, genital warts may form in the anal area.
Factors that increase the likelihood of infection include:
- early onset of intimate life;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- the partner has papillomas and warts on the head and in other places.
You can use a condom to reduce the chance of transmitting the virus, but it does not guarantee 100% protection. Its effectiveness will be especially low if the partner has papillomas throughout the groin area.
Poor health
Papillomaviruses of the pilar part, once entering the body, can lie dormant for a long time, i.e. do not give outward signs. Their rapid life activity begins if a provoking factor appears - a decrease in immunity. The triggers for it can be:
- colds;
- exacerbation of chronic ailments;
- constant nervous tension, stressful situations;
- advanced age of the patient;
- hormonal disorders;
- uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives;
- dysbiosis of the vagina or intestines;
- bad habits (smoking, love of alcohol), etc.
When one or more of these factors appears, external manifestations of the virus occur. One of them is papillomas on the head, which become a cosmetic defect, and in some cases can degenerate into malignant tumors.