What is weeping dermatitis in children?
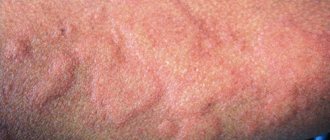
A distinctive feature of this type of dermatitis is the fact that the site of inflammation is constantly moist, cracks or ulcers that appear are filled with pus, which complicates the course of the disease and its treatment.
There are several types of weeping dermatitis in children. The localization sites are different for each age group.
By age, weeping dermatitis is divided into:
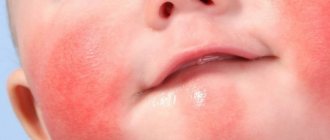
- Infants and children under 2 years of age. Affected areas are the face, elbow and knee bends, and occasionally the body.
- Children from 3 to 12 years old - neck, bends of limbs, hands from the back.
- Teenagers from 13 to 18 years old - face, neck, natural folds.
This type of dermatitis should not be confused with eczema, which affects only the surface of the skin. Weeping dermatitis (see photo below) causes swelling due to inflammation of the skin in the deep layers.
Dermatitis on hands photo
Palm dermatitis. Photo 1.
Dermatitis of the dorsum of the hand. Photo 2.
Dermatitis on the hands. Photo 3.
Dermatitis on the hands. Photo 4.
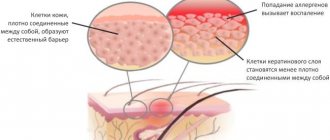
Causes of dermatitis: contact with an aggressive chemical environment.
Prolonged exposure to low temperatures
Dermatitis on the hands is not only a physical problem, but also a cosmetic one. Most of the time, hands are seen by strangers, who may react to rashes, papules and scratching in completely different ways. The patient’s experiences and psychological discomfort aggravate the course of the disease. According to statistics, the risk group consists of women living in big cities, but dermatitis on the hands can appear in anyone, regardless of gender, age, and lifestyle.
In addition to mental factors, the treatment of dermatitis on the hands is complicated even by hygiene and contact with the environment: with air (which can be dusty, dry, etc.), cleaning products, water, and various surfaces, sometimes contaminated. That is why dermatitis is called a disease of civilization: the development of industry and the emergence of new household chemicals have led to the fact that people are constantly faced with new types of cleaning, washing, dyeing, and adhesive products. Even the rules of hygiene, so necessary in a modern city, can do a disservice to a patient with dermatitis on the hands. Public and home toilets, money, door handles and handrails - contact with these objects, firstly, increases the risk of infection of diseased skin, and secondly, makes frequent hand washing necessary, which leads to drying, peeling, and cracking of the skin.
Through wounds formed at the site of scratching or bursting dry skin, infection can enter the bloodstream. In turn, this can lead to serious consequences for the body, including a general decline in immunity and the spread of dermatitis to other parts of the body.
Causes of the disease
The appearance of weeping dermatitis in children can be caused by external and internal reasons. These include:
- Problems in the gastrointestinal tract. The disease occurs due to insufficient breakdown of food fragments. This type of weeping dermatitis occurs most often in infants, which is associated with imperfect development of the digestive system.
- Allergies to food or chemicals and medications. For example, weeping atopic dermatitis occurs more often in young children who are fed breast milk.
- The presence of a bacterial infection in the body provokes the appearance of dermatitis with the formation of blisters with pus.
- Pathologies of the kidneys and liver, as well as malfunctions of the pancreas, are the least common cause of dermatitis in children.
Children's immunity, weakened by any disease or teething, can cause the development of weeping dermatitis.
Antipruritic ointments
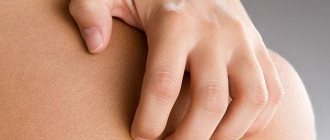
Dermatitis is always accompanied by itching. It can be of varying degrees of severity. With intense itching, patients become nervous, lose peace and sleep. Stress only makes dermatitis worse
Therefore, in such situations, it is important to alleviate the condition of patients with the help of antipruritic drugs.
For this purpose, external antihistamines (Fenistil gel for dermatitis) and calcineurin inhibitors (Protopic, Elidel) are used. These drugs stop inflammation and have an anesthetic effect, thereby reducing skin itching. A menthol-based ointment for dermatitis on the skin (Boromenthol, Menovazan) has a similar effect. It cools and soothes inflamed skin, reduces the sensitivity of receptors, as a result of which the affected area stops itching for some time.
As mentioned above, hormonal antipruritic ointment for dermatitis has a faster and more effective effect. But it is still better to start treatment with non-hormonal ointments due to the low risk of side effects and a small list of contraindications.
Treatment of seborrheic skin lesions
The main ointment for seborrheic dermatitis is antifungal: Ketoconazole, Nizoral, Sebozol, Nizorex, Mycozoral.
It is recommended to treat the affected skin with keratoregulating agents (for example, Mustela Stelaker). In special cases, Sulsena paste and hydrocortisone ointment are added, but preference in the treatment of this type of dermatitis is given to physiotherapeutic methods.
Remedies for atopic dermatitis
Therapy for atopic dermatitis begins with the use of non-hormonal agents. These are Gistan, Fenistil, Eplan, Radevit. If the severity of clinical manifestations does not decrease within several days, the therapeutic regimen is adjusted.
It is replenished with hormonal agents:
- Cutivate;
- Akriderm;
- Momatom;
- Beloderm;
- Celestodermos.
Cheap ointments for dermatitis (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone) are effective only for minor rashes. Papules, vesicles, blisters can usually be eliminated with expensive means, for example, Cutivate.
After the rash disappears, patients are prescribed products with dexpanthenol to accelerate skin regeneration. If the course of the pathology is complicated by infection, the use of drugs with a combined composition is recommended - Akriderm GK, Triderm.
Symptoms
The manifestation of the disease is also associated with the age groups of children:
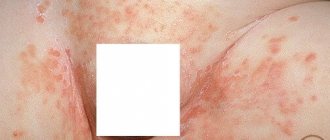
- In infants and children under 3 years of age, the disease begins with the appearance of wet spots, which then dry out to a crust. This group is characterized by dry skin, flaking and severe itching. If bubbles form, they most often burst.
- Children 3-12 years old get sick longer than toddlers, even despite treatment. Dermatitis is characterized by swelling of the skin, peeling and hyperemia. Very painful cracks may appear at the site of the lesion. After recovery, dark spots often remain on the skin, which disappear without a trace after a few months.
- Teenagers 13-18 years old. The disease can begin suddenly and also end unexpectedly. In the acute stage, large areas of the body are affected.
If you have one or more symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis, especially for infants.
Simple contact dermatitis
Simple contact dermatitis is an inflammatory reaction of the skin that occurs in response to direct exposure to irritating substances (alkalies, acids, detergents, solvents, bleach, etc.). Symptoms of the disease depend on the strength and nature of the exposure.
This may include skin redness, dryness and cracking, swelling, blistering or scabby ulceration. Diagnosis of simple contact dermatitis and its differentiation from other dermatitis is based on identifying the connection between the occurrence of the disease and exposure of the skin of the affected area to a chemical substance.
Treatment consists of eliminating the causative factor, local application of glucocorticoids, anti-inflammatory, healing and antibacterial agents.
Along with simple contact dermatitis, the group of contact dermatitis includes allergic contact dermatitis. However, in dermatological practice it is less common.
Simple contact dermatitis is a reaction to direct exposure to an irritant and occurs upon first contact with it.
The allergic variant of contact dermatitis is caused by a delayed-type allergic reaction and develops with repeated exposure to an allergen.
Simple contact dermatitis
Clinical dermatology distinguishes acute and chronic forms of simple contact dermatitis. Depending on the nature of the substance affecting the skin and the individual characteristics of the permeability of the epidermis, one of three types of acute contact dermatitis may develop: erythematous, bullous or necrotic.
Erythematous dermatitis is manifested by redness and swelling of the skin area in contact with the irritant. Soreness and itching are mild. The skin may become dry and cracked.
The bullous version of simple contact dermatitis is represented by blisters of various sizes filled with clear liquid. Bubbles appear on a hyperemic background and burst with the formation of erosions.
Characterized by soreness, a feeling of heat or burning.
The chronic form of simple contact dermatitis develops with repeated exposure to a weak irritant. The skin of the hands is most often affected. The disease is usually associated with the use of household chemicals or professional activities.
Chronic dermatitis is characterized by increased skin pattern, congestive hyperemia, infiltration, dry skin and hyperkeratosis. In some cases, atrophic processes in the skin are observed. Subjective sensations are mild and do not bother the patient much.
The diagnosis of simple contact dermatitis is established by a dermatologist based on characteristic clinical manifestations and a clearly visible connection between the occurrence of symptoms and exposure to an irritating substance on the skin.
The appearance of signs of purulent inflammation indicates infection of the affected area and is an indication for bacterial culture of the discharge with the obligatory preparation of an antibiogram.
Histological examination of a sample of affected skin reveals blisters containing accumulations of neutrophils inside the upper layers of the epidermis. In chronic simple contact dermatitis, acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, dilation and elongation of the dermal papillae are observed.
The main principle of treatment is to identify and eliminate the cause of simple contact dermatitis. Erythematous dermatitis usually does not require treatment and goes away on its own when the causative factor is eliminated.
To prevent secondary infection, lubricate the area of the blisters with a solution of potassium permanganate or aniline dyes. Healing ointments are used in the treatment of necrotizing dermatitis.
In severe cases of acute simple contact dermatitis, local application of glucocorticoid ointments and systemic administration of small doses of corticosteroids are possible.
The addition of a secondary infection is an indication for antibiotic therapy.
Diagnostics
At the initial stage of the disease, diagnosis is very important. It is necessary to immediately show the child to a pediatrician, who will advise any measures to alleviate the symptoms of dermatitis and refer him to an appointment with an allergist.
An allergist will prescribe the necessary tests to determine the cause of dermatitis. Most often, this is a blood test to determine the level of eosinophils and the presence of IgE. These two indicators are basic for establishing the allergic origin of dermatitis.
After this, the child should be examined by a pediatric dermatologist and scrapings taken from the wounds for mycotic lesions.
When the results of all tests are known, the pediatrician will determine the type of disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Dermatitis on the legs. Treatment
You have discovered dermatitis on your feet. Treatment should begin right now, and we do not suggest immediately starting self-medication, armed with theses and recommendations from our article.
This article is for informational purposes only, so that you understand how you can notice the disease on your feet at the inception stage and do not faint, realizing that they will not cut off your foot.
But to try to treat on your own, without consulting a professional, we not only do not advise, we forbid you to do this! After examining the foot, the doctor will be able to make a diagnosis and only after that will prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
You should also not listen to friends and relatives who will tell you that they have already had this and were treated with such and such drugs. The treatment was short and easy.
Remember, each patient is individual, and the course of treatment must be individualized. What helped your friend can only hurt you. Conversely, what did not help your relative may be an excellent cure for you.
For the most part, diagnostics are used:
- Blood tests: biochemical and general;
- Skin scrapings from the affected areas;
- An immunological test to determine allergens, in the case of allergic rashes.
After the results are obtained and processed in the laboratory, the doctor can begin prescribing a course of treatment, which may consist of more than just medications. Typically treatment consists of:
- Diets. The patient should refrain from eating cereals, tomatoes, spices, chocolate-containing foods, honey, smoked products, and seafood.
- Stopping contact with the allergen. You may not be able to wear certain shoes, synthetics, or jewelry. If the irritant is a chemical substance, it must be replaced by another.
- Prescribing salicylic petroleum jelly to eliminate inflammation and dryness. It is applied 2 times a day (a light layer for inflammation). Treatment of dermatitis on the legs with ointments is also used.
- Taking antihistamines tablets as the main therapy (Erius, Tavegil, Zodak, etc.). Typically, a two-time dose is prescribed.
- Prescribing a hormone-based ointment (corticosteroid), which is prescribed exclusively for severe itching of the feet and the appearance of blisters. It is possible to prescribe Elidel or Advantan, which are also applied very thinly and only to itchy areas. The duration of the course is no more than 5 days.
- Autohemotherapy and taking vitamins to restore the immune system.
We remind you once again that this article is just an introductory review. Value your health and do not try to heal yourself!!!
Therapeutic treatments
Weeping dermatitis, treatment of which must be started immediately, requires a whole range of therapeutic procedures. These include:
- isolation of the allergen from the child;
- careful hygiene of affected skin areas;
- environmental control;
- lubrication of lesions with anti-inflammatory ointments;
- diet.
If the doctor determines that the disease occurred due to the presence of any allergen in the house where the child is, this cause must be eliminated. Such pathogens can be washing powder, dust, various chemicals that affect the child’s skin.
A prerequisite is compliance with the diet. If a diagnosis of “wetting dermatitis” is made in an infant, treatment should begin with the diet of the nursing mother or a review of the complementary feeding regimen.
Older children should not eat red or yellow foods or a specific allergen.
Foci of dermatitis should be washed with saline solution and a weak solution of manganese should be applied. Also, as prescribed by a doctor, you need to use external anti-inflammatory and antibacterial ointments, creams or sprays. It could be “Bepanten”, “Solcoseryl”.
If a secondary infection occurs, combination and antibacterial drugs should be used - Triderm, Pimafucort.
When treating weeping dermatitis, it is necessary to maintain a comfortable air temperature for the child, ventilate the room and prevent the mucous membrane from drying out. These measures will help prevent the occurrence of other diseases against the background of a weakened immune system due to dermatitis.
Medicines and traditional medicine
The most effective treatment is to eliminate the underlying cause of the disease. By curing or localizing chronic diseases of the body that lead to inflammation of the skin, it will be much easier to defeat dermatitis.
All types of skin diseases are treated with regular consultations with a dermatologist. Only a specialist, having examined the tests, will be able to prescribe correct and effective treatment. Modern pharmaceuticals are constantly developing new treatments for skin diseases with the least side effects. But there are already proven effective remedies, such as Advantan.
In the acute stage: in the presence of edema, blisters and erosions, lotions are prescribed, then indifferent creams, ointments and pastes. If the wound becomes infected, antibiotics are used and the lesion is smeared with bactericidal preparations. A constant food and hygiene regime is required. Many medications have contraindications for use, for example, Advantan ointments cannot be used to treat perioral dermatitis and chickenpox.
To relieve external symptoms of dermatitis, especially in children, it is recommended to take baths and make lotions based on celandine, sage, calendula and viburnum roots.
Recipes based on strings and hop cones have proven themselves well. The mixture of herbs poured with boiling water is infused for 20 minutes in a water bath, cooled and the affected areas are treated. In the early stages, you can treat uninfected lesions with self-made creams based on these medicinal herbs: you need to choose a base - neutral ointments, add the essential oil of the desired plant. You can apply a bandage with the resulting cream for one hour a day, or smear it two or three times a day.
For the treatment and prevention of DERMATITIS and other skin diseases, our readers successfully use the method from Elena Malysheva. Having carefully studied this method, we decided to bring it to your attention.
If an infant has such a disease, then frequent bathing should be avoided; it would be correct to alternate baths with treating the lesions with Advantan emulsion. After water procedures, the child’s body should be treated with cream to restore the water balance of the skin.
Maintaining a strong immune system, hardening, a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and moderate exercise will help you avoid frequent visits to specialists at the clinic.
Preventive measures for people prone to allergic reactions of the body consist of maintaining a hygienic and dietary regime, especially when the season changes, and avoiding hypothermia of the body and drying out of the skin.
It’s worth knowing: only a dermatologist can diagnose weeping dermatitis. Children can be treated only after consulting a pediatrician.
Feedback from our reader - Irina Chernova
I recently read an article that talks about the natural remedy “Zdorov” Cream-Wax for dermatitis. Using this cream you can get rid of DERMATITIS at home in a short time.
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered one package. I noticed changes within a week: itching, rashes, and swelling decreased. After 2 weeks of use, the dermatitis almost completely disappeared, and the skin became soft after the cream. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
Drug treatment
If complex therapy methods do not bring the desired result, the doctor prescribes the use of medications orally.
These drugs include medications from the following groups:
- antihistamines;
- probiotics;
- sedatives;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- systemic enzymes;
- immunomodulators.
First of all, antihistamines are prescribed that will relieve itching (Claritin, Loratadine).
For children, such skin problems cause great discomfort. They begin to be capricious and have difficulty sleeping. In such cases, taking mild sedatives (valerian, motherwort) is quite justified. It is important to follow the dosage exactly.
Probiotics (Dextrin, Lactulose) will help restore the microflora of the stomach and intestines after taking medications.
If the degree of damage to the skin is large, the doctor will prescribe hormonal ointments - glucocorticosteroids. These include Hydrocortisone and Prednisolone.
Immunomodulators will support the weakened strength of the child’s body and help fight the disease naturally.
In some cases, a large blister may form at the site where small papules appear. Doctors recommend performing an autopsy, but this should only be done in a hospital setting, where all sterility rules are observed.
How to treat a weeping burn?
In order for the skin to recover faster after a thermal injury, it is necessary to properly organize care for the patient. How to treat weeping wounds after a burn in a child and an adult? First of all, you need to purchase a sterile bandage. A loose bandage will allow the wound to breathe, which means that the outflow of fluid will soon stop. For second and third degree burns, special ointments with an antibacterial effect are used. If the wound is large enough, therapy takes place in a hospital setting.
Before treating weeping wounds on your feet, you should completely get rid of your shoes and clothes. Therapy at home can also be carried out openly, without applying a sterile bandage. But for this, the patient must be provided with bed rest, regularly ventilate the room, and limit physical activity. It is worth noting that with the open method, burn wounds dry out much faster. But not everyone can ensure complete sterility in the room.
If you take the right approach to treatment, a weeping burn will heal in just a week. Therapy of deep lesions is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting.
Other means
Weeping dermatitis can also be treated with traditional medicine. Only they must be combined with medications and with the permission of the attending physician.
Children under one year old from this complex are only allowed to use a decoction of the string. For children over one year old, a compress of grated potatoes is recommended. Only the pulp must first be wrapped in clean gauze.
After 5 years, you can use lotions from a decoction of chamomile or celandine.
Physiotherapy also has a good effect. These include:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- medicinal baths;
- laser and mud therapy.
The use of all these methods will allow you to get rid of the disease in a short time and without any special consequences.
Disease prevention
Measures to prevent weeping dermatitis in children are aimed at following a set of rules:
- maintaining the child’s personal hygiene daily;
- monitoring the nutrition of mother and child, if he is no longer breastfed;
- avoiding contact with the irritant if you already have an allergy;
- treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas;
- timely consultation with a doctor.
Following these simple recommendations will help children and their parents avoid such an unpleasant disease as weeping dermatitis. Even if the disease is in its early stages, you should try to take preventive measures. This will avoid complications, and the child will suffer from itching much less.
Providing treatment with medications
Many people wonder how to treat weeping dermatitis. There's nothing special here. Doctors advise their patients to use drugs that are classified as antiallergic. Drugs called “Claretin” and “Telfast” help a lot. These types of drugs have virtually no negative effects. The effects that the above drugs provide will not have a positive effect on a certain area of the skin unless additional hormonal drugs are taken. As a rule, it is topical medications that can be used by patients in this case. They contain a substance such as zinc. It is also important to remember that you should not use medications that have not been approved by your doctor.