Viral dermatitis is a specific lesion of the skin that appears as a result of various infectious diseases. The viral form of dermatitis is more of a symptomatic factor in diseases than an independent disease.
Viral dermatitis needs treatment, especially in children. Why does dermatitis appear in children, how to correctly determine it and what is the treatment for this disease?
Causes of infectious dermatitis - how does infection occur?
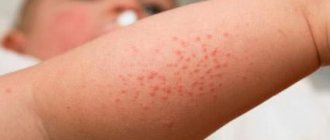
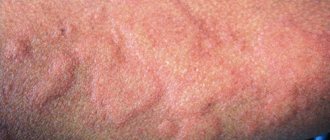
viral dermatitis in children in the photo
It is extremely difficult to identify the specific cause of infectious dermatitis in a completely healthy person, since each case of infection is individual. The incubation period for the development of pathogenic microorganisms affecting the epidermis begins with infection.
It can be external, when bacteria enter directly onto the surface of the skin, or the infection enters the body along with contaminated food and water. Then the pathogenic microflora spreads throughout all tissues along with the bloodstream. Why it is the skin that appears in the affected area, doctors cannot give a definite answer.
In general, there are common causes of viral dermatitis, namely:
- Complications of infectious diseases. In people who have suffered from a severe form of scarlet fever, tonsillitis, pneumonia, or suffering from chronic tonsillitis, viral skin lesions are most often diagnosed. This is due to the fact that due to a prolonged inflammatory process, the immune system becomes weak, and dermatitis is already one of the negative consequences of the underlying disease and the spread of pathogenic bacteria throughout the body.
- Syphilis. This sexually transmitted disease manifests itself on the skin surface in the same way as viral dermatitis caused by any other infection. It is possible to establish that epidermal tissues are systematically destroyed by syphilis bacteria only with the help of a clinical blood test to identify the pathogenic pathogen and the collection of smears from the ulcer formation. It is considered a very severe type of viral dermatitis due to the large number of negative consequences for the health of the patient, as well as complex and lengthy treatment.
- Postoperative period. Surgical intervention involves partial destruction of epithelial tissue at the site of surgical procedures. If an infection enters the wound, the healing dynamics of the surgical suture may be poor and bacteria may spread to healthy areas of the skin. In most cases, the purulent-inflammatory process of the skin of this etiology is localized around the previously operated part of the body.
- Infection with Staphylococcus aureus and streptococcal infection. If these microorganisms get into a wound or scratch, infection occurs and the population of pathogenic bacteria further increases. Viral dermatitis of the streptococcal and staphylococcal type is distinguished by an aggressive clinical picture with the formation of large ulcerative surfaces, which, without adequate drug treatment, tend to increase both in depth and in diameter.
Also, infection of the skin can occur with other types of infections that can parasitize on the surface of epidermal tissues. The most dangerous strains include anthrax and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Causes
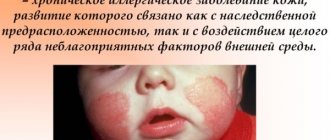
Determining the cause of the disease in children is often difficult. The main (but not specified) reason is the appearance of infectious agents in the bodies of children. In modern medicine, it is customary to identify the following causes of the viral form of dermatitis:
- infectious and viral diseases that are typical for children - chicken pox (chickenpox), scarlet fever, measles or rubella;
- complications arising after surgical interventions;
- entry into open wounds of pyogenic microorganisms (the same streptococci and staphylococci).
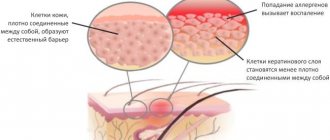
The typology of viral dermatitis is not typical for other skin diseases. The etiology of dermatitis is presented in the form of a symptomatic picture against the background of a previous or existing other disease of viral origin.
The cause of the occurrence and development of the disease are various infectious agents: staphylococci, fungi of the genus Candida, streptococci . Viral dermatitis may not be a simple symptom, but a further cause of the development of skin lesions.
Reasons other than those listed above cannot be considered in the case. Allergic reactions in the form of lesions on the skin do not belong to the category of viral diseases, and the atopic form of the disease occurs exclusively as one of the forms of manifestation of another skin disease.
Symptoms
External signs of the manifestation of a dermatological disease depend on what pathogenic source it was provoked. Let us consider in more detail the characteristic symptoms of viral dermatitis, which manifests itself in connection with the presence of the following infectious diseases, namely:
- Measles. The whole body is covered with a spotty rash, which, like tubercles, rises above the general level of the skin. After some time, the spots begin to merge into one single inflamed formation that resembles a pigment. The skin is very itchy and flaky.
- Rubella. Infectious dermatitis of this origin is characterized by a small rash of bright pink color. The main localization of acne is the surface of the face and neck. Body temperature rises to 39 degrees and above, lymph nodes in the area of the lower jaw and collarbones enlarge.
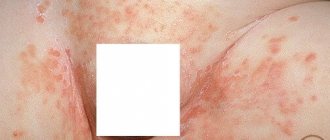
- Scarlet fever. Viral dermatitis, which occurs against the background of this infectious disease, manifests itself in the form of multiple rashes in the groin area, causing swelling of the mucous membrane of the genital organs in men and women. From the groin area, skin damage spreads to the abdomen, back and armpits. After 5 days from the onset of the disease, profuse peeling of the skin begins. The rash is very itchy, and the patient suffers from fever and fever.
- Enterovirus infection. The rash spreads completely over the entire surface of the body. They look like voluminous spots that resemble in appearance an allergic reaction like urticaria. The more successful the fight against enterovirus infection is, the dermatological symptoms will fade proportionally.
- Chicken pox. This type of infectious dermatitis manifests itself in the form of large large pink pimples that concentrate on the surface of the head and facial disc. After 3 days, the inflammatory formations transform into blisters with sanguineous fluid, which burst and turn into a weeping ulcer. As the ichor is released, a pink crust forms on the wound.
- Typhus. Viral dermatitis of this type begins with the formation of a small red rash on the elbows, spreads over the entire surface of the arm, and moves to the chest and abdomen. The disease is characterized by severe itching of the skin and a temperature that rises to 40 degrees.
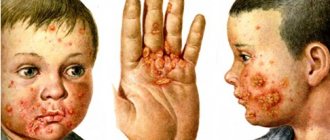
- Syphilis. Red spots appear on the epidermal tissues, which feel like nodules to the touch. As they mature, they increase in volume, and the inflammatory process becomes more acute. The final stage of the development of infectious dermatitis is the destruction of the surface of the epithelium over the inflamed node and the appearance of an extensive wound, the edges of which are inflamed, the epidermal tissue disintegrates, and the ulcer itself constantly increases in diameter. The patient experiences severe pain, and the body temperature is elevated to 40 degrees and lasts for several days.
- Staphylococcus aureus or streptococcal infection. It is characterized by the formation of small watery blisters that originate in the circumference of the oral cavity and in the navel area and spread throughout the body. After 3 days from the moment of appearance, the bubbles burst, leaving behind wound surfaces. The ulcerative formations are so deep and voluminous that they resemble a 2nd degree thermal burn. In addition to dermatological damage, the patient also encounters symptoms such as swelling of the mucous membrane of the genital organs and wounds in the oral cavity.
These are the most common types of viral dermatitis that occur against the background of infection with certain strains of bacterial infections. There are also other more severe dermatological diseases that are practically never encountered in medical practice. This category includes epidemiological outbreaks of anthrax and other mass destruction infections.
Causes of dermatitis in adults and their symptoms
Let's look at the main characteristics and causes of each type of disease.
Atopic dermatitis
It is chronic and transmitted genetically.
A common cause of atopic dermatitis is an allergic reaction to food or a contact irritant. Locations include: subcutaneous folds, forehead, around the eyes, face and neck. The disease can also affect the skin on the shoulders, feet and arms. In an adult, this type of disease causes scaly papules and plaques. The skin becomes dry, and in severe cases of the disease, erythematosis occurs.
In addition, atopic dermatitis in children and adults is accompanied by severe itching. The epidermis begins to thicken and blisters may appear. Such bubbles can open on their own, the area begins to get wet, then gradually dries out and a yellow-rough crust forms.
Seborrheic dermatitis
The second name of the disease is seborrheic eczema. Most often it occurs in people over 40 years of age. Damage to the skin occurs on the head, nose, and sternum. The frontal part and interscapular area may be affected.
Oral dermatitis
Irritation appears in the area around the mouth.
Therefore, the disease brings not only discomfort, but also psychological distress. Occurs mainly in childhood and in men over 30 years of age. The causes of this illness can be hygiene products, lotion, wash, tonic or moisturizer. It was also noted that the disease occurs against the background of contact of the skin on the face with corticosteroids. For example, some hormonal medications may be included in inhalers that a person can use to relieve asthma attacks or allergies.
Varicose dermatitis
It occurs in an adult due to stagnation of venous blood directly in the lower extremities. Against this background, the patient experiences inflammation, severe itching, and swelling of the lower extremities. The skin is damaged and severe peeling may occur.
Ear dermatitis
The causes of dermatitis are exposure to chemicals, decreased immunity, and symptoms of general intoxication. The disease also occurs against the background of passing dermatosis, as well as when metabolic processes are disrupted.
Staphylococcal dermatitis
The causes of occurrence are various injuries to the skin, hypothermia, impaired immunity and hydrocarbon metabolism. The patient experiences severe symptoms, and treatment must be comprehensive. Red nodules and hemispherical pustules begin to appear on the skin.
Now you know what types there are and what symptoms of dermatitis occur. Before the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment, a thorough diagnosis and a complete examination are carried out first. Only after this, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment.
Treatment of infectious dermatitis
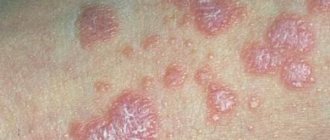
infectious dermatitis in the photo
Treatment of symptoms of viral dermatitis is based on an integrated approach to the treatment of this disease. An individual therapeutic protocol is developed for adults and children, consisting of medications of various spectrums of action.
In children
The following group of medications are used to treat a child:
- ointments with antiseptic properties that suppress the bacterial activity of pathogenic microflora;
- glucocorticosteroids, which eliminate itching of the skin, relieve swelling and inflammation;
- antibacterial drugs depending on what type of infectious pathogen was identified based on the results of taking smears from the skin surface for bacterial culture.
In adults
Patients of the adult age category have the opportunity to receive more extensive drug therapy due to the fact that they do not have such a large number of contraindications. Adults are treated with the following medications:
- tablets and injection antibiotics, which are taken orally or administered intramuscularly;
- antiseptic solutions for external wiping of affected skin areas;
- ointments, gels and creams that relieve itching, swelling and reduce the severity of the inflammatory process;
If necessary, the patient is treated not only with external areas of inflamed skin, but also with the drug administered intramuscularly or by installing a drip system.
If infectious dermatitis is a consequence of an underlying skin disease, then for complete recovery the primary disease must be eliminated.
The most common types of viral dermatitis
Do not forget that this type of dermatitis begins to develop as a secondary sign of any infectious disease. However, it is also possible that this disease appears as a completely independent disease. Let's consider its main forms of manifestation:
- chickenpox;
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- rubella;
- an illness caused by an enterovirus infection.
It is very important to correctly establish the cause of this disease, because further treatment will depend on this.
Possible complications
The negative consequences of viral dermatitis in adults and children are rarely recorded, but it still happens that the disease is too acute and provokes the occurrence of secondary health complications. These include the following:
- meningitis, which is provoked as a result of infection penetration into the tissue of the cerebral cortex with further spread of the inflammatory focus;
- sepsis that arose due to the lack of any drug therapy (observed most often in case of infection of the body with Staphylococcus aureus or streptococcal infection);
- loss of the affected area of skin's functional abilities;
- necrosis of epidermal tissues.
These complications will never arise if treatment for a dermatological disease begins immediately after the appearance of its first symptoms. The longer the infection parasitizes on the surface of the skin without affecting it with medication, the longer the subsequent course of therapy will be.
Traditional methods of treatment
You should not expect that with the help of folk remedies you will get an incredible healing effect. It is best to use traditional medicine not as the main method of treatment, but as an auxiliary one, and then the healing process will be significantly accelerated. However, even in this case, be sure to consult a specialist to avoid various side effects.
So, grated raw potatoes relieve itching and swelling very well. You can apply it directly to damaged skin, or start by laying it on a clean napkin. Such compresses should be done daily, leaving them on the epidermis for about twenty minutes. After which this mixture must be thoroughly rinsed and the skin dried.
Homemade cream, which should contain butter and St. John's wort, has a very good antibacterial effect. To prepare this composition, take one tablespoon of crushed St. John's wort leaves and pour half a glass of boiling water over it. Leave the liquid to infuse for ten minutes, then strain it and add 50 grams of a little warm butter to it.
Homemade cream should be applied to the skin daily and left there for ten minutes.
Routes of infection
There are a number of ways of contracting viral dermatitis, in which each type of disease is transmitted in its own way.
Transfer methods:
- Airborne droplets (when communicating with a patient, kissing) – enterovirus, measles, rubella infections, chickenpox, mononucleosis are transmitted.
- Through dirty hands, penetration of feces particles onto the limbs, and then into food: in the case of enterovirus infection.
- Contact (from penetration to rash sites) – infectious agents caused by herpes viruses are transmitted.
Dermatitis caused by fungi, bacteria or parasites is transmitted:
- by airborne droplets after infection with scarlet fever, meningococci,
- not washed hands after contact with a patient with yersiniosis, pseudotuberculosis, typhoid fever,
- when touching scabies rashes.
When there are even minor injuries on the hands, fungal and bacterial infections can be transmitted through them. If the skin areas are intact and clean, then even contact with the exudate of the boil and other pustular formations will not bring consequences.
Prevention
Preventive measures can prevent dermatitis, but not 100%. Doctors advise following these rules:
- maintain hygiene, carry out water procedures every day, have your own personal towel,
- lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid smoking, alcohol,
- exercise regularly, increase immunity through hardening,
- during virus outbreaks, wear protective masks, avoid contact with sick people,
- carry out vaccinations against infectious diseases,
- at the first suspicion of dermatitis, immediately consult a doctor,
- arrange fasting days for the body.
With strong protective properties, the chances of contracting viral dermatitis are almost zero.