Why you shouldn’t stick your finger in your nose and other possibilities of pyoderma infection. We will tell you how you can prevent the development of infection upon contact with a carrier, and what to do in case of this disease is strictly prohibited.
Bacterial skin diseases are extremely unpleasant, and when a patient exhibits characteristic symptoms, of course, it is important for him to know why this happened and whether he can be a source of infection for others.
It is difficult to answer this question unequivocally, so today in the article “Pyoderma: how is it transmitted” we will carefully understand these important issues.
What is pyoderma
Pyoderma is a medical term that combines multiple skin dermatitis with characteristic suppuration, as well as corresponding inflammatory and ulcerative processes that expose the skin to various changes. The cause of this pathological condition is pyogenic organisms that have penetrated into the epidermis - pyococci.
Pyoderma can develop either as an independent disease, when primary damage to the skin occurs, or as a symptom of an existing internal pathology or as a complication.
Most types of pathological condition are contagious. As a rule, transmission of the virus occurs through interaction with a sick person. In some cases, pathogenic bacteria enter a healthy body through airborne droplets (during sneezing or coughing).
Prevention of infection upon contact with a sick person
Bacterial skin infections with an uncomplicated course are treated at home as prescribed by the attending physician. Precautions must be taken to ensure that the disease does not spread to other family members.
- Wash and sanitize your hands frequently.
- Provide the sick person with maximum isolation.
- Use only personal hygiene items and cutlery.
- Since children and the elderly are at particular risk, it is necessary to prevent their interaction with the sick person.
- Bed linen and clothing should be ironed thoroughly, preferably on both sides.
- If the house has a steam generator, it is advisable to use it to treat upholstered furniture and carpets; if not, then the furniture should be cleaned using a disinfectant.
- Wet cleaning and ventilation are of particular preventive value.
- It is optimal to use bactericidal lamps for home use for disinfection purposes; they help to effectively reduce the concentration of bacteria in the patient’s room.
- Pay especially careful attention to the skin of those family members who are not sick. Any scratches or injuries must be treated with an antiseptic.
- The patient must be provided with proper hygienic care and nutrition rich in vitamins.
- Don’t panic because germs surround you and it’s impossible to hide from them; as a rule, sufficient sanitization and following simple instructions help avoid infection.
- When treating purulent lesions, all used consumables: cotton swabs and gauze swabs must be disposed of in a plastic bag: they should not be in the public domain in general trash.
- Observe the skin condition of healthy family members; be sure to immediately treat redness, erosion, and pimples with an antiseptic. Hydrogen peroxide 3%, chlorhexidine, and furatsilin solution are suitable for this.
Classification
The main causative agents of the pathological process are streptococci and staphylococci. Depending on the identified provocateur, pyoderma is divided into two types:
- streptoderma – the development of pathology is facilitated by the penetration of the first type of pathogen;
- staphyloderma - the main aggressor is staphylococcus.
On this topic
- Other
Everything you need to know about hidradenitis
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2021
Streptostaphyloderma can also often be diagnosed when the disease is caused by both types of pathogenic microorganisms.
In addition, bacteria such as:
- Proteus vulgaris;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- enterobacteria;
- other anaerobic fungi and microbes.
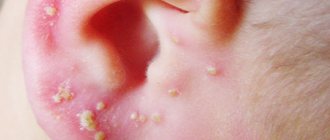
Regardless of the type of aggressor, there is a rapid, in some cases lightning-fast development of pyoderma. It is characterized by a sluggish course with exacerbations. It manifests itself in the formation of pustular formations in a limited area of the skin. When rashes form over a large area, the disease becomes widespread.
Streptoderma is divided into:
- superficial;
- deep.
The first group consists of:
- Lichen. Streptococcal form of infection, which has an acute course. In most cases it is diagnosed in children and adolescents.
- Diaper dermatitis . Develops only in newborns.
- simplex on the face . Characterized by acute manifestations in adolescence.
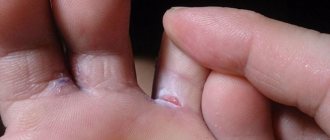
- Impetigo. This is an inflammatory process that affects the tissue of the nail plates.
- Intertriginous. Young children are susceptible to the disease. Formed in the groin, under the arms, behind the ears, on the buttocks.
The second group includes the following pathologies:
- Erysipelas. It is an inflammatory process that affects the lymphatic tissue and dermis. It is diagnosed in most cases in adults over the age of 45 years.
- Vulgar ecthyma is an ulcerative form of streptoderma, characterized by frequent relapses and a long course.
- Absent-minded type . The pathology has a chronic form, accompanied by swelling and the formation of pustular erosive formations.
Superficial staphyloderma includes:
- Folliculitis – characterized by suppuration throughout the folliculitis. The inflammatory lesions are large in size, have a thick wall, and the pustules contain green or whitish-yellow pus.
- Vulgar sycosis is pustular skin lesions in areas where hair grows.
- Ostiofolliculitis – the sebaceous ducts and the upper segment of folliculitis are susceptible to inflammation. It is characterized by the formation of small pustules, the location of which is the neck, face, legs, and shoulders. After the maturation process, they have a predisposition to atrophy, without leaving scars on the skin.
- Pemphigus epidemic . It is characterized by multiple ulcers affecting the entire body. Infants are susceptible to the disease. It is considered highly contagious. If mass lesions are observed, the risk of death increases.
- Vesiculopustulosis.
- Acne disease . It has a long-term course. Appears in the face, shoulders, chest.
Among the deep forms there are:
- hidradenitis - a purulent lesion that affects the groin, anus, and sweat glands; manifested by the formation of dense nodules with purulent contents;
- boil - is a formation that penetrates deeply into the layers of the skin, accompanied by pain and purulent discharge; in size reaches up to 50 millimeters, when the abscess is opened, the release of ichor is noted for another 10 days, the healing process continues for 2 - 3 weeks. In the affected areas, noticeable scars remain on the body;
- abscesses are a common skin lesion in childhood;
- carbuncle - characterized by deep suppuration, leads to tissue necrosis, and can affect several hair follicles at once.
The mixed type is characterized by the following forms:
- Gangrenous. It is characterized by a long progressive process. With the disease, gangrene and tissue necrosis develop.
- Chancriformis - diagnosed extremely rarely in the area of the lips, reproductive organs and neck.
- Felon.
- Ulcerative-vegetative.
- Lightning Acne.
What exactly pyoderma looks like will be revealed by the symptoms that appear.
What not to do if you get sick
In previous articles we introduced you to the therapeutic principles of getting rid of pyoderma, today we want to draw your attention to harmful advice and consider in detail what rash actions can cause harm.
- Try not to get the fireplace wet; water helps microorganisms spread.
- Avoid touching your face with your hands. During active illness, nails must be treated with iodine daily and kept short.
- Do not crush pimples, even if you do not have pyoderma, the purulent contents of the pustule can be the cause of the development of this disease in any of its forms.
- This may seem funny, but the habit of clearing dried secretions from the nasal passages with your finger can lead to infection of the mucous membrane and the development of pyoderma. Moreover, the process is sometimes so fascinating that the internal epithelium of the nose is easily injured by nails, and this especially helps microbes develop their vital activity.
- If the outbreak is located on the face, then you should not try to disguise it with decorative cosmetics. In general, using cosmetics during this period is extremely undesirable.
- Hot baths, saunas, steam baths and swimming pools are strictly prohibited until complete recovery.
- Pyoderma cannot be treated with folk remedies. And, for example, hidradenitis and boils are especially often subjected to shamanic methods of influence, since patients are afraid that when they go to see a doctor, they will be prescribed surgical intervention. And it's not always safe. Recommendations such as warming the lesion with a baked onion can lead to the fact that pyococci multiply so quickly that systemic blood poisoning and sepsis can occur.
- It is especially dangerous when active purulent inflammation is localized on the face. Advanced forms of the disease can infect the respiratory tract, conjunctiva of the eyes, and in severe cases cause bacterial inflammation of the membranes of the brain - meningitis, therefore any signs of pyoderma in this area must be urgently treated with proven medical means.
- Don't get carried away with taking antibiotics. They are undoubtedly drugs that save lives, but their unreasonable and frequent use leads to the development of persistent microbial strains and disrupts the natural balance of external and internal microflora, which serves as local protection. It is strictly forbidden to take antibiotics to prevent pyoderma if you are healthy but have contact with a source of infection. In this case, they will not provide protection, but will lead to a weakening of the immune system.
- Do not give in to temptation, alcohol does not disinfect our body from the inside, and certainly does not impart resistance to external infections. You should not drink strong drinks if you have pyoderma; you reduce your already compromised immunity.
Dear readers, in the comments to the article “Pyoderma: how is it transmitted,” you can share your observations about what mistakes can be made with pyoderma, as well as ask your questions.
And in conclusion, we would like to remind you that the healthier a person is, the less he is susceptible to bad habits, takes care of his health, successfully fights stress, approaches his diet rationally, does not forget about vitamins and walks in the fresh air, the lower the likelihood of becoming infected purulent skin infection.
Causes
Pathogenic microorganisms themselves do not pose any danger to human health. During a diagnostic examination, they are detected on the skin of not only the patient, but also a healthy person. In order for them to become provocateurs for the development of any disease, exposure to external or internal factors is necessary.
External reasons include:
- temperature changes - hypothermia or overheating helps to reduce the protective functions of the dermis, which increases its vulnerability;
- excessive sweating - when sweat is released in large quantities, some of the bacteria that affected streptococci and staphylococci are eliminated;
- use of antibacterial agents;
- minor skin injuries - in the absence of therapeutic measures, the risk of penetration of pathogenic bacteria increases;
- negative environmental - dirt, smoke, soot in the air negatively affect the condition of the skin.
Internal causes of the disease:
- decreased immune system as a result of poor nutrition, frequent stress, vitamin deficiency, lack of sleep;
- childhood the epidermis of children is very susceptible to various negative manifestations acting from the outside, and the immune system is not yet sufficiently formed to react and protect the body from negative influences;
- hereditary predisposition – skin problems can be inherited;
- endocrine disorders - for example, the presence of diabetes mellitus, in which the elasticity of the skin is lost, which leads to increased susceptibility to various types of threats;
- chronic pathology .
Excessive consumption of fatty foods and poor hygiene also contribute to the deterioration of skin condition.
Etiological factors
The causative agents of pyoderma are pyogenic cocci. They are part of the opportunistic microflora of the skin. They are grouped mainly at the mouth of the follicles, in the ducts of the sebaceous glands or on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. They can be found in half of the healthy population. Good immunity prevents staphylococci and streptococci from actively multiplying. But in the presence of certain provoking factors and skin injuries, an infection develops with characteristic clinical symptoms.
The main causes of pyoderma can be divided into two large groups: endogenous, depending on processes occurring inside the body, and exogenous, dictated by external circumstances.
Endogenous factors include:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and liver;
- endocrine pathologies;
- hypovitaminosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- immunodeficiency states;
- increased sweating;
- long-term use of cytostatics and immunosuppressants.
Exogenous factors include:
- minor skin injuries (cuts, abrasions, scratches, cracks);
- failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene;
- unbalanced diet;
- bad ecology;
- too much air humidity;
- bad habits.
Treatment of pyoderma should begin with eliminating the cause of the disease.
Symptoms
Among the general signs that are characteristic of any form of pyoderma are:
- redness and swelling of the affected areas of the epidermis;
- painful sensations;
- formation of a purulent-serous lesion;
- pigmentation;
- violation of the structure of the skin;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- general deterioration of health;
- increased body temperature;
- nausea with gag reflex;
- decreased ability to work.
It should also be noted that the manifestation of signs of the pathological process in adults is not as pronounced as the development of the disease in children.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, you must first analyze all the resulting manifestations on the skin and study the general signs of the development of the inflammatory process in the body.
On this topic
- Other
All about hemangioma on the skin in adults
- Irina Nasredinovna Nachoeva
- September 3, 2021
To confirm the presence of the disease and differentiate it from other types of dermatological pathologies that have similar symptoms, a number of instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed. These include:
- histological analysis;
- study of exudate, which is taken from ulcers, pustules;
- microscopy of individual tissue fragments taken from the affected areas;
- blood test for hemoglobin;
- syphilis test;
- polymerase chain reaction.
In addition, in order to identify existing pathological processes that can lead to the formation of pyoderma, additional examinations are prescribed:
- immunogram;
- blood chemistry;
- caprogram;
- Ultrasound of the digestive system.
Only based on the results of all diagnostic measures performed, the specialist makes a final diagnosis and, in accordance with the identified disease, prescribes effective therapy.
Principles of treatment
To make a diagnosis and prescribe a method of therapy, contact a dermatologist. To determine the pathology, the hair in the affected area is cut off. It is prohibited to shave them, as pathogenic microflora will penetrate into areas of healthy skin.
The basis of therapy is the use of drugs. To choose the right disinfectants or antibiotics for the treatment of pyoderma, a bacteriological culture is taken. The laboratory technician takes a smear from the affected area, inoculating it on a nutrient medium. They identify the exact pathogenic microorganisms, as well as substances to which he is sensitive. This is the key to proper therapy that will help the patient.
In addition to taking medications, a person must maintain good hygiene. Hands are treated daily, preventing the infection from spreading from the area of suppuration to other tissues. Adhere to the following principles:
- pre-washing hands with antibacterial soap;
- treatment of the skin of hands and nails with iodine 2%;
- wiping healthy areas of the skin with a damp sponge, avoiding affected areas.
If you are sick, do not take a shower or bath. Otherwise, the infection will spread to many parts of the body. It will penetrate the urinary and genital tract, causing a secondary infection.
Therapeutic measures
The treatment regimen will depend on many factors:
- type of pyoderma;
- severity of the process;
- age category of the patient;
- the presence of internal pathology.
On this topic
- Other
How to prevent the occurrence of a carbuncle in time
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 17, 2021
In any case, treatment should include a set of procedures and be carried out by specialists such as a dermatologist and surgeon.
The therapeutic method includes the following procedures:
- UHF;
- exposure to dry heat;
- irradiation with ultraviolet light;
- dietary nutrition;
- drugs to strengthen the immune system;
- taking vitamin complexes;
- in case of severe forms - blood transfusion.
Drug therapy
External agents are prescribed for the purpose of washing and applying if a superficial type of disease is diagnosed. These can be antimicrobial, antiseptic gels and ointments that help suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, also aimed at reducing pain and inflammation.
The most common ones include:
- Fukortsin, Betadine, Pyolysin, Gentamicin, erythromycin and syntomycin ointments and others;
- corticosteroids - Belogent, Hyoxysone, Triamcinolone, Triderm.
In addition, other means are used:
- Hydrocoloid sealant dressings - if extensive ulcers and ulcerations are noted.
- Soft sanitation. For these purposes, Furacilin, a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and Burov's liquid are used.
On this topic
- Other
What is skin ichthyosis
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 17, 2021
Before prescribing antibacterial drugs, an antibiogram must be performed. This procedure is necessary to determine the sensitivity of the detected pathogenic microorganism to this group of drugs. After receiving the results, the most effective drug for therapy is selected.
The use of antibacterial drugs is possible if:
- local remedies do not have the desired effect;
- pyoderma is complicated by concomitant diseases or its intensive progression is noted;
- in the presence of a boil, hidradenitis or carbuncle.
At a mild stage of the disease, the drugs are prescribed for internal use. In case of severe form, the drugs are administered intravenously or intramuscularly for 6-10 days.
Basic medications:
- Cefotaxime;
- Clarithromycin;
- Erythromycin;
- Gentamicin;
- Doxycycline and others.
For the treatment of gangrenous pyoderma, Dapsone, Cefuroxime, and Clofazimine are used.
Prednisolone is prescribed among hormonal drugs.
Immunotherapy
This method involves the use, simultaneously with antibiotics, of agents that neutralize the activity of pyococci, as well as their toxic substances. Helps strengthen resistance to pathogenic agents.
It is recommended to use during the process over a long period of time, in which relapses occur at least once every three months.
Surgery
Surgery is used only if pyoderma is severe and is accompanied by purulent inflammation that penetrates deep into the layers of the skin. In this case, there is the formation of a large amount of purulent contents and necrosis of some areas of the dermis that require removal.
The operation is performed with the administration of a local anesthetic.
Immune stimulation
If the pathology becomes chronic, antiseptics and antibiotics do not help well, this means that the patient has reduced immune function. He is not able to cope with the disease on his own, so it becomes sluggish. Use procedures and drugs to boost immunity indicated in the table.
| Method | Influence |
| Subcutaneous administration of toxoid, antigens | Sensitizing therapy, a person is injected with a small amount of bacterial particles so that the immune system produces a sufficient amount of antibodies |
| Autohemotransfusion | Transfusion of own blood components that have been exposed to ultraviolet irradiation |
| Methyluracil, Eleutherococcus, Schisandra tincture | Stimulation of immune function |
| Immunostimulants | Corrective function of the thymus for greater release of leukocytes and antibodies |
| Preparations based on gamma globulins, interferon stimulators | Increase in antibodies |
| Administration of large doses of vitamins | Stimulate immunity and metabolism, increase tissue regeneration |
During therapy, a CBC and a complete leukocyte count are taken. To understand whether it is effective, tests are repeated in the middle and end of treatment with immunomodulators. The number of antibodies and leukocytes should gradually increase.
Methyluracil for immunity
Methyluracil - tablets based on the active substance of the same name. These are immunostimulating agents. Its action is based on the following processes:
- normalization of metabolism;
- acceleration of tissue regeneration;
- stimulation of the production of cells of the hematopoietic and immune system;
- strengthening the production of humoral immunity factors.
The drug is indicated for use in chronic infections that are difficult to treat with antibacterial and antiseptic agents. Often used for severe lesions of the skin, soft tissues, and bones. The only adverse reactions include allergies, headache, and dizziness. The medicine is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance, cancer of the blood and immune system.
The drugs must not be used independently. An inappropriate immune system response may occur. Therefore, consult a dermatologist or immunologist about its use.
Complications
Skin pathologies accompanied by pustular lesions tend to spread. Therefore, if measures are not taken in a timely manner to eliminate the pathological process, then there is a high probability of complications developing. It can be:
- pneumonia;
- inflammatory processes affecting bone tissue;
- abscesses;
- meningitis;
- thrombosis of the brain and blood vessels;
- sepsis;
- lymphadenitis.
If you are inattentive to seemingly harmless rashes, the simplest thing that can happen is cosmetic defects of the skin. In more severe cases, the manifested diseases pose a serious threat to human life.