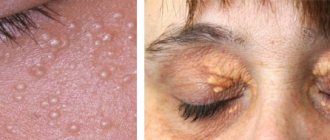
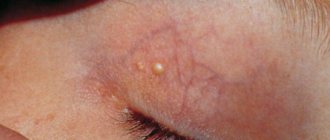
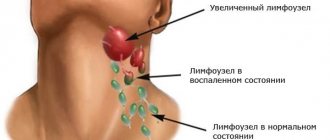
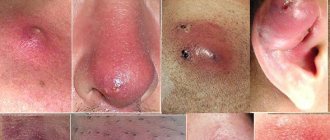
Clinical picture
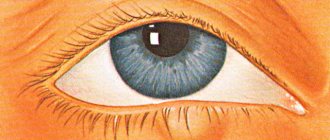
An abscess on the eyelid looks like a reddened, dense swelling, which can be accompanied by drooping of the eyelid and swelling of the conjunctival cavity.
In addition, painful nodes appear and pus is released. With purulent edema, body temperature does not always rise, and in some cases, blood counts do not differ from normal. If, as the disease progresses, the abscess spontaneously opens, then you should immediately consult a doctor, who will recommend how to proceed with treatment.
Main signs of an abscess:
- The area around the eyes and conjunctiva become yellow, and as the abscess develops, a burning sensation occurs.
- Acute pain appears in the area of the infected eye, which can cover the entire head.
- The eyelids swell, enlarge, and the eye opening narrows. The eyelid droops and cannot move due to its own gravity.
The signs of purulent edema are similar to the symptoms of barley, but pathological processes in the first case develop much faster. The painful process of ripening of the abscess is accompanied by redness of the eyelid, swelling and burning pain. In the worst case, the patient may experience intoxication of the body, headache, and loss of appetite.
To stop unpleasant symptoms, doctors recommend opening the capsule, although in most cases the abscess opens spontaneously. After removing the pus from the capsule, the patient's condition improves: the temperature normalizes and the pain disappears.
Treatment
Therapeutic tactics for ulcers in the eye and eyelids involve eliminating bacterial inflammation and preventing complications. The main aspect is the use of medications:
- Antiseptics.
- Antibacterial.
- Anti-inflammatory.
Drug therapy can be local or general. The first is to treat the lesion with antiseptic solutions (diamond green, salicylic alcohol), antimicrobial ointments (tetracycline, erythromycin, Levomekol), and the use of drops (sodium sulfacyl, Cipropharm, Colbiotsin). And in severe cases of the process, systemic measures are indicated: antibiotics (taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen), antipyretics and detoxification agents.
During the infiltration phase, physiotherapy (dry heat, UHF, UV irradiation) is also indicated in a course of 3–5 sessions. And when fluctuations and a necrotic core appear, the pus must be removed in order to prevent its spread. Therefore, mature abscesses require surgical treatment - they are cut, the inflammatory exudate is removed and drained. Subsequently, daily dressings with ointments are carried out until the wound is completely healed.
Purulent-inflammatory processes in the eye area are always dangerous, especially in childhood. Therefore, when the first signs of pathology appear, you should seek medical help. The doctor will conduct an examination, find out the cause of the abscess and its nature, and based on the diagnostic results, prescribe appropriate treatment.
Differential diagnosis
Barley, as a rule, does not present any diagnostic difficulties for a specialist. There are fairly clear criteria for distinguishing barley from, for example, inflammation or a malignant tumor of the lacrimal gland, blepharitis, conjunctivitis.
However, patients often confuse internal stye, especially in the early stages, with its “external” variety - i.e. with typical barley, as well as with chalazion, and all these forms of pathology are directly related, again, to the sebaceous glands. In this case, we are talking about the glands of Meibom, which are located deeper than the glands of Moll and Zeiss, opening with exit tubules at the borders of the skin and conjunctiva, or on the conjunctiva itself - the posterior mucous membrane of the eyelid, directly adjacent to the surface of the eyeball.
Chalazion - “hailstone”, “nodule”, “cold barley” - in fact, is not a barley at all, since it is an encapsulated accumulation of meibomian gland secretion, which, not finding a way out due to its blockage, breaks into the surrounding cartilaginous tissue. Up to this point, symptomatically, and then externally, the chalazion is indeed very similar to the hordeolum that has stopped at the peak of development, differing from it in a significantly longer duration of existence on the eyelid (sometimes up to a year or more), greater density on palpation, painlessness and, in a typical “cold” version , absence of pus.
At the same time, chalazion can be either a consequence of a true infectious-inflammatory barley, or its cause - due to secondary bacterial infection of the capsule.
As for the “internal stye,” it is initially caused by the introduction and introduction of an infectious pathogen into the meibomian (and not the Zeiss) sebaceous gland.
Non-standard methods of treatment
In addition to the usual compresses and lotions, there are also unusual ways to eliminate the disease. In ancient times, the appearance of inflammation on the eyelid was considered a sign of damage. There were special conspiracies and manipulations against barley, designed to stop the spread of negative energy throughout the body. Currently, such methods seem ridiculous, but numerous reviews often confirm their effectiveness. Here are a few of these non-standard techniques for breeding barley.
You need to take a red woolen thread and tie a figure of eight around two fingers – the ring and middle fingers on the hand on which the abscess appeared.
It is believed that barley can be “driven away” by properly “scaring” it. To do this, they twist cookies in front of the patient’s eyes, show the ring finger, cross the inflamed area, telling him to let the stye go away, otherwise he will have a bad time.
Whether or not to use such unusual methods is up to everyone to decide for themselves. Obviously, they cannot cause severe harm to the body, which means you can experience their effects on yourself without fear of consequences.
Navaga during pregnancy
Omega-3 fatty acids contained in this fish make a major contribution to the development of the visual apparatus and brain of the fetus. They also help the development of the unborn child's central nervous system. Fatty acids accumulate in the body from the 27th week of pregnancy to the first 1.5 months of the baby’s life.
Therefore, it is recommended to add this product to the diet during pregnancy and in the first months of breastfeeding. In addition, such fish has a low calorie content, which makes it possible to use it when losing weight, after childbirth. Including navaga in the diet will help improve the condition of the skin and skeletal system, strengthen the immune system, maintain healthy eyes and a youthful body.
Pain when moving for centuries
In some diseases, pain under the lower eyelid intensifies when blinking or moving the eyeballs. This symptom should alert you, as it may be associated with damage to the internal structures of the eye. Such pain is observed in the following diseases:
- Endophthalmitis. This is an inflammation of the vitreous body of the eye. The disease occurs after eye injury, infection during surgery, or as a complication of corneal ulcers. The pathology is dangerous, as in advanced cases it leads to loss of vision. At the same time, it hurts to press on the eye, but the pain is felt not in the skin, but in the sclera. With endophthalmitis, intraocular pressure drops, the eyelids swell, and vision deteriorates. Treatment is carried out in a hospital.
- Blepharitis. This is inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. It may occur with the formation of ulcers or scales on the affected area. With this pathology, the eyelids swell, turn red and hurt. When a person closes his eyes, the pain increases significantly. The edges of the eyelids thicken and discharge comes from the eyes. Blepharitis often affects children because their immune system is weak. The disease is difficult to treat, and relapses often occur. This pathology requires long-term treatment.
- Corneal ulcer. Ulcers occur due to injury, improperly fitted contact lenses, or infection. The eyelids swell and hurt, especially when blinking, there is an increased secretion of tear fluid, and blurred vision. The sclera of the eyes turn red, the pupils are reduced. Treatment is carried out with antibiotics and special eye drops to rest the eyes.
- Molluscum contagiosum. This is a viral disease that most often affects children. Small yellowish-white nodules form on the skin of the face and eyelids. These growths usually do not cause severe pain, but discomfort may be felt when pressing or blinking. The nodules are removed or cauterized with iodine. Without treatment, molluscum contagiosum goes away on its own within 6 months.
Types of blepharitis
Corneal ulcer
Blepharoconjunctivitis treatment
If you discover the first signs of this disease, there is no need to delay treatment; you must immediately contact a competent doctor for help. Initially, experts recommend proven folk remedies if the disease is mild.
In more severe cases, drugs of the antihistamine, antiviral or corticosteroid spectrum are prescribed, namely:
- "Khilozar-Komod";
- "Voltaren Ofta";
- "Floxal";
- "Tobrex".
The course of treatment is determined by the doctor himself, depending on the complexity of the disease.
ethnoscience
Before starting treatment with folk remedies, consult a specialized doctor for advice so as not to harm your health in the future and prevent the disease from fully developing.
Let's get acquainted with the main traditional medicines that will help cope with the disease:
- Echinacea decoction. Take one spoon of crushed echinacea root and pour boiling water (200 ml). Boil the resulting mass over low heat for fifteen minutes. After boiling, let it brew for 50-60 minutes and take 20 ml orally. four times a day.
- Fresh or dried blueberries. Consume at least 10 grams per day after meals. There is no course of treatment with this method, since the berries are harmless and help strengthen the immune system.
- Cottage cheese. Wrap the freshest cottage cheese in a sterile cloth and apply eye lotions at any convenient time.
- Garlic vapors. Grind a couple of cloves of garlic in a blender and deeply inhale the evaporation of the mass. Exhalation must be done through the oral cavity.
- Dill. Pour 10 grams of dry dill into one glass of boiling water and leave for one hour. Then strain thoroughly through gauze and apply a compress to your eyes at any time convenient for you, but you should not repeat the procedure more than five times a day.
- Clover inflorescence. Grind the clover and squeeze the juice out of it using gauze. This remedy is applied three drops to the mucous membrane of the eye once a day.
- Tea and wine. Take black and green tea in a 1 to 1 ratio and add a teaspoon of dry grape wine. Mix all the ingredients and rinse your eyes until they are completely healed.
- Aloe juice. Place squeezed juice from aloe leaves into the eyes three times a day.
Traditional medicine recipes
Folk remedies with effective recipes:
- Warming up. This method is effective only for the initial manifestations of the disease. Boil potatoes or chicken eggs. Wrap in a scarf to avoid burning your eyes. Keep the bag on your eyelid until the potato or egg has cooled completely. Remember that heating is strictly contraindicated when a purulent core has formed, since the wound may burst and pus will flow out under the eyelid.
- Flax seed compress. Warm up the flax seeds and put them in a bag. Apply to the sore eyelid 2 times a day.
- Aloe therapy. Grind one medium-sized aloe leaf, fill it with boiling water for about 2/3, leave to brew for 10 hours. The resulting mixture should be applied to the affected area of the eye 3 times a day. The paste should be washed off 10 minutes after application.
- Plantain compress. Wash several leaves of young plantain and grind them to a liquid mass. Pour the resulting mixture with one glass of boiling water and leave to steep for 1 hour. Moisten a piece of bandage or a cotton pad and apply to the inflamed area for 10-15 minutes. Repeat the procedure at least 5 times a day.
- Washing with decoctions of medicinal plants. Take birch buds, bird cherry flowers, chamomile, and marsh rosemary. Mix the plants and pour boiling water over them. After 30 minutes, express the liquid and rinse your eyelid with it every 2-3 hours. After the abscess begins to disappear, reduce the number of washes to 5 times a day.
- Compress of calendula flowers. This plant is famous for its anti-inflammatory effect. Pour boiling water over one tablespoon of calendula inflorescences. Leave the infusion for 1 hour to infuse. After this, moisten a cotton pad and apply it to the wound for 10 minutes. This compress should be done 5 times a day. This remedy for treating an abscess does not damage the mucous membrane of the eyelid.
Remember that self-medication can lead to unpredictable consequences. If you notice strange symptoms, be sure to consult an ophthalmologist.
An acute abscess on the eyelid provokes the appearance of a host of unpleasant symptoms.
It is often difficult to determine the cause of the formation of an abscess on the eyelids in the first two days, since most diseases begin the same way.
You can find out what disease the resulting papule with purulent contents means from your doctor. The ophthalmologist will not only determine the cause, but also prescribe the most effective treatment.
How to remove a pimple under the eye
How to treat a pimple in the eye area depends on the reason for which it formed, what size it is and what symptoms it causes. In any case, there is no need to self-medicate. This will not give the desired result and may provoke negative consequences.
Skin care around the eyelids
In order for acne on the upper and lower eyelids to disappear faster, you need to properly care for the area around the eyes.
Care should begin with thorough cleansing of the skin. To do this, you need to choose soft hypoallergenic products that are specifically designed for this area. You need to apply a nourishing cream to your eyelids at night, and a moisturizer in the morning. It should also be designed specifically for this area and be age appropriate. 5 minutes after applying the cream, blot your eyelids with a cotton pad.
Scrubs should not be used in the eyelid area, as this can injure the skin and cause new rashes to appear.
Cosmetology procedures
If there is a regular pimple above or below the eye, a cosmetologist may recommend classic cleansing.
Mechanical facial cleansing in the salon is performed in the following order:
- the skin is washed and disinfected;
- the Uno spoon is applied so that its hole is in the center of the pimple;
- the instrument is pressed against the skin (at this time its contents come out of the pimple);
- manipulations are repeated until the skin becomes clean;
- the skin is disinfected and a soothing, anti-inflammatory mask is applied to it.
It is not recommended to try to squeeze out a pimple on the eye at home.
Minor surgery
Pimples in the eye area can be removed using electrocoagulation. The essence of the procedure is that a specialist cauterizes the formation using high-frequency current. Finally, the wound is treated with an antiseptic. A crust subsequently forms in its place. If there is a pimple in the eye on the lower eyelid, increased tearing may occur during the procedure. This is fine.
Another way to get rid of acne is curettage. The doctor scrapes off the formation with a special instrument. The disadvantages of curettage include prolonged wound healing and a high likelihood of scar formation.
Medical cosmetics and medicines
Before starting to use medicinal cosmetics and medications, the patient should consult a doctor. Self-medication can lead to corneal leaks and even blindness.
Typically, the following medications are used to treat acne:
- Benzoyl peroxide. It is especially effective for styes and acne, which are located near the mucous membranes. The product perfectly relieves inflammation. It should be used morning and evening.
- Creams with salicylic acid. If the pimple does not go away for a long time, such a cream will dry out the pathological areas and disinfect them. This will speed up your recovery.
- Acyclovir. This ointment is used if a pimple near the eye is caused by a herpes infection. The medicine is used three times a day until complete recovery.
Traditional methods
Home remedies can also help if you have a pimple on your eye.
The most effective are:
- Bodyaga. Helps to draw out and dissolve millet grains. To do this, you need to dilute the bodyaga with hydrogen peroxide to a pasty consistency. Apply the resulting mixture pointwise to the formations. After 15 minutes, wash off the medicine.
- Cucumber mask. You need to mix cucumber juice with cottage cheese in equal proportions. The resulting mask is applied to the eyelids, left for 30 minutes and washed off.
- Aloe juice. You need to cut the aloe leaf into pieces. Apply them to the rash and secure with a band-aid. It's better to do this at night. The product will help draw out pus and reduce inflammation.
Before using folk remedies, experts advise conducting an allergy test. Apply a few drops of the selected drug on the inner bend of the elbow. If there is no redness or swelling, then you can begin treatment with this recipe.
Localization and code according to ICD 10
Eyelid abscess (ICD 10 code H 00.0) is what ophthalmologists call a limited inflammatory process located near the organ of vision. Inflammation leads to the formation of a cavity through purulent melting of tissue.
Based on location, abscesses of the upper and lower eyelids are distinguished. More common is the formation of a cavity with purulent contents on the upper mobile fold of skin covering the eye. The pathology can be localized at the eyelash growth line.
An abscess can be:
- External. A common type of pathology in the form of an abscess formed on the edge of the orbit. Ripening is observed from the outside. Infection of nearby tissue leads to development.
- Internal. Formation of an abscess on the side facing the eyeball. The cause is an infection of the meibomian glands located near the base of the eyelashes.
An abscess on the inside of the lower eyelid is more often diagnosed than an abscess hidden on the upper skin fold.
Effective treatments
A disease of a bacterial nature is treated with antibacterial drugs. In this regard, ointments such as tetracycline and hydrocortisone have proven themselves well. The ophthalmologist will prescribe antibiotic drops, which are usually used for 5-7 days.
Therapeutic drops help with inflammatory processes on the eyelid, regardless of the location of the stye. Among bactericidal solutions, Albucid, Floxal and Tobramycin are popular. These drugs block the spread of bacterial infection, promote rapid healing of opened ulcers and prevent the development of complications.
For treatment to be successful, general recommendations should be followed:
- avoid heating – when heated, suppuration occurs faster, increasing the likelihood of neighboring tissues being involved in the inflammatory process;
- refrain from using cosmetics - do not mask boils on the eyelid with foundations and shadows. Women often try to hide an external defect with the help of decorative cosmetics, especially when stye appears on the upper eyelid. This complicates treatment and increases the likelihood of contamination of the lesion;
- choose alternative methods of vision correction - you will have to forget about contact lenses for a while. They not only complicate treatment measures, but also react poorly to medications.
If the lower eyelid is affected, recovery occurs faster, although the treatment regimen will be the same, regardless of the location of the stye. It’s good when the source of inflammation is outside, then you can achieve a therapeutic result quickly. The upper eyelid is treated with an ointment with antibactericidal properties twice a day. After a few days the formation will disappear.
It’s worse when multiple boils appear on the lower or both eyelids at once. The specialist injects novocaine, which relieves pain and alleviates the patient’s condition. Eye lotions will help speed up the healing process. The doctor often prescribes a 1% solution of silver nitrate, which is applied to a napkin and applied to the lesion.
If the boils do not want to open, then surgical removal of the contents - infiltrates - is necessary. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and does not pose any danger to the patient. In the future, antibacterial therapy and physiotherapy are required as prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment with drops
Treating stye on the eyelid with drops is an effective way, since this disease is caused by infection . This is a conservative method of treatment, which may not be as fast as using ointments, but it gives one hundred percent results.
Important! All ointments used in this case are antibiotic drugs , before using which you should consult your doctor.
Among the drugs used to treat this ophthalmological disease, the following are popular:
- Albucid . Despite the fact that this medicine is eventually being forced out of the pharmacological market by more effective modern analogues , these drops still remain one of the most inexpensive and safe means for treating a number of infectious ophthalmic diseases. However, albucid has a number of side effects , and when used, it can cause itching, burning and discomfort.
- Torbex . A modern alternative to albucid. Such drops have a targeted effect on the source of inflammation, striking the infection and accelerating the process of resorption of the abscess. The only disadvantage of such a drug is that it may be ineffective in treating a group of ulcers .
- Gentamicin . Gentle antibiotic drops that can be prescribed in severe cases or for styes that have not been eliminated with Tobrex.
After removal of the chalazion, the same swelling remained
| Search the forum |
| Advanced Search |
| Find all thank you messages |
| Search by diaries |
| Advanced Search |
| To the page. |
| Page 1 of 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | > |
Good time. I am 27 years old. In June 2012, she began treatment for demodex (confirmed by analysis). Course: Tobradex 4r. two drops per day. At night, wipe with calendula tincture, massage, Floxal ointment. There are only three courses lasting 10 days, with a break after each of also 10 days. In September, the upper eyelid of the left eye swollen a little, forming a swelling of about 1 cm by 1 cm on the moving part. When pressed, the swelling went away, only near the ciliary edge a ball could be seen like two match heads. I thought it would be barley. At the end of October, a formation appeared on the lower eyelid of the left eye on the inside; it grew by 4 mm in about two days. Upon examination, the ophthalmologist said that it was a chalazion, and that the swelling on the upper eyelid was also a chalazion, but internal. Tobradex and Floxal ointment were dripped in courses again, on the hydrocartisone there were unpleasant sensations in the form of swelling, warming up with a warm egg. There were no changes. After 4 months, another one, about 1 mm, appeared on the lower eyelid. I stopped the treatment because on the 7th day of using the drop, my vision began to defocus, it seemed to me that everything was becoming blurry. Around February 2013, they went away on their own in the lower eyelid. The upper eyelid was unchanged. I wanted to remove the chalazion, but I had a broken arm and the doctor told me to wait for the body to fully recover. At the beginning of May of this year, I had this chalazion removed through an incision from the side of the conjunctiva. During the operation, the doctor was surprised that he found very little of the chalazion itself, as they expected more. During the operation, I started bleeding, the doctor said that apparently there were problems with clotting (the general analysis was good, but poor clotting was later confirmed). In the evening I took off the bandage. The eyelids were very swollen, below, everything below the eyelash edge 1 cm was burgundy. I took Maxitrol drops 4 times a day for 9 days. Then a 2-day break and another 3 days of maxitrol. 18 days after the operation: the general swelling has passed, but the place where the chalazion was remained the same size, denser to the touch, more swollen at the ciliary edge. Sometimes I feel a tingling sensation. There is an unpleasant sensation when pressed. When stretching, I see either a red vein in this place or this place is still inflamed from the incision. The outline of the hematoma does not go away, the hematoma itself has passed and the outline is still burgundy. Upon examination, I discovered two very small new chalazions on the upper eyelid of the same eye. They appeared quite recently. After 2 weeks, I made an appointment with a doctor, but in the meantime, over the phone, he prescribed Maxitrol without a break and warming up with an egg. My questions: 1. Could chalazions initially appear due to drops that I used like Tobradex? (maybe this is paranoia, but they appeared precisely after the drop courses, and now new ones again after Maxitrol, although I understand that this could be a relapse). 2. Why does the place where the chalazion was remain swollen? Maybe not enough time has passed yet? Either the capsule was not completely removed, or it was not completely removed, but the place was even slightly smaller than before the operation. 3. Is it possible to massage the area that was operated on? 4. Does it make sense to add floxal ointment? Or something else?
5. Is it possible to lubricate the hematoma contour with Badyaga gel? Or tell me what to do with it...
6. Is it possible to take some kind of picture or CT scan to see their number and location? Tell me what to do next? Cut again? Thanks for your time and answers.
Surgeon's report [ Links are available to registered users only
]
Treatment of recurring styes
It happens that a child or an adult develops abscesses one after another, which can be very disturbing and interfere with their normal lifestyle. This problem is most often associated with decreased immunity. An organism weakened by a severe illness or lacking beneficial microelements cannot fully resist infectious agents in the environment. Therefore, the first thing to take care of is not only eliminating symptoms, but also restoring immunity.
In addition to medications, there are more accessible folk remedies.
- Tansy - a plant with flowers in the form of yellow flat circles, is famous for its effectiveness in treating inflammation. The easiest way to take it is to eat one flower every two hours with water. It is especially useful to do this in parallel with treating barley with other methods. After the abscess goes away, there is no need to stop drinking tansy. The full course of treatment is a month, but you can take it not in such quantities, but 3-4 times a day. Tansy will protect against repeated styes and remove harmful substances from the body.
- When chronic barley appears, brewer's yeast can help. It is enough to choose a vitamin complex containing this substance and take it regularly.
- Sulfur powder is a popular remedy for chronic boils. It is enough to drink a quarter teaspoon of sulfur with a glass of milk for a week. Children can sprinkle the powder on a piece of bread so that it is not so unpleasant to take the medicine.
The most correct decision in case of constantly recurring relapses would be to contact a medical specialist. He will not only advise the most effective method of struggle, but will also give advice on whether it is worth using folk remedies. The famous pediatrician Komarovsky also believes that it is best to strengthen a child’s weakened immunity immediately, without waiting for serious illnesses.
To prevent inflammation, it is recommended to follow simple rules of personal hygiene: use only individual face towels, do not touch your eyes with dirty hands, and for women, be sure to wash off your makeup every day and carefully monitor the expiration dates of the products in your cosmetic bag. It is also important to protect your eyes from dust particles and dirt, and if this has already happened, immediately rinse your eyes with clean water.
With the right treatment tactics, the disease goes away quickly and does not reappear for a long time. You need to carefully monitor your well-being so as not to miss alarming symptoms that indicate complications or concomitant diseases. If you have any concerns or doubts, it is better to consult a doctor and take a course of prescribed medications. Folk remedies can also help in the fight against barley, but they need to be selected based on the individual characteristics of the body.
Pimples on the eyelid
- What is barley?
- Milium
- Other inflammatory diseases of the eyelids
The person is most exposed to negative environmental factors. Sun, dust, cold air - all this leads to a decrease in the protective functions of the skin. One of the manifestations of decreased immunity is a pimple on the eyelid. The problem cannot be ignored. Without timely treatment, the inflammatory process can spread. As a result, vision will suffer.
A pimple on the eyelid can develop in various forms. The most common are barley and milia (millet).
What is barley?
The medical name of the pathological process is hordeolum. This is one of the most common inflammatory diseases in ophthalmology.
According to statistics, such acne sooner or later appears on the eyelids of 80% of the world's population. Barley develops due to the rapid proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the hair follicle of the eyelash.
Most often the disease is caused by a bacterial infection, so there may be pus under the eyelid.
A pimple on the inside of the eyelid may appear due to a decrease in general or local immunity. In 90% of cases, the disease is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Normally, pathogenic microflora is present on the skin of almost any person.
Bacteria begin to actively multiply when the body's defenses cannot resist them. Stye is often a complication of a cold. A person may encounter a problem after hypothermia. During the seasonal cold weather, your eyes water outside.
This can also lead to the development of the disease.
Rubbing your eyes with dirty hands can cause stye
The causes of stye may also be failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene: using a dirty towel, the habit of rubbing your eyes with your hands, refusing to remove decorative cosmetics before bed. An allergic reaction to mascara or eye shadow also often manifests itself in the form of a stye.
Chronic diseases such as diabetes, furunculosis, seborrhea, worms, and gastritis contribute to a decrease in local immunity of the eyelids. Poor nutrition, bad habits, frequent stress - all this negatively affects the protective functions of the skin and the body as a whole.
A purulent pimple on the upper eyelid should not be confused with cancer pathologies. Problems such as chalazion, tumors and cysts may initially look like styes. Therefore, you should not self-medicate. When the first symptoms of inflammation appear, it is recommended to make an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
Barley on the eye usually develops acutely. Initially, itching appears on the upper eyelid, and after a few hours the patient may notice redness. There is local hyperemia and swelling.
The risk of developing dangerous complications increases.
Already 2-3 days after the appearance of the first symptoms, the head of the rod (abscess) appears in the center of the inflammation. During this time, the patient's condition may worsen. Many people complain of headaches and general malaise. Body temperature often rises to subfebrile levels.
Other inflammatory diseases of the eyelids
A pimple on the lower eyelid may indicate the development of blepharitis. This is an inflammation of the ciliary margin, which can be either acute or chronic.
The disease can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection. In the first case, purulent rashes may appear on the eyelids. With viral blepharitis, water pimples often form.
The cause of the disease is often the herpes virus.
Blepharitis is a common eyelid disease.
Blepharitis can only be treated conservatively. Medicines are selected according to the sensitivity of the pathogenic microflora. The patient also has to adjust his diet. Sweets and overly spicy foods aggravate inflammation.
How to avoid abscess formation?
The best prevention is taking care of your health and following basic hygiene rules. It is enough to follow simple recommendations so as not to end up in a hospital for a long time and get rid of a number of unpleasant sensations that cause discomfort:
- Never squeeze pimples and blackheads on your face. To remove them, use cosmetic procedures or special ointments;
- Treat even minor wounds and cuts with an antiseptic;
- If you have an infectious disease, approach treatment carefully and carefully. Do not let the disease take its course, as it can “attract” additional “sores”.
Don't forget to strengthen your immune system, take vitamins, add more vegetables and fruits to your diet.
You will learn how to avoid eyelid abscess by watching the video.
Fungal diseases of the eyelids
Experts consider pathogenic fungi to be the causative agents of mycoses in the eyelid area. Primary skin lesions on the eyelids are a rare occurrence; the pathological process generally spreads from the skin to nearby areas (forehead, temples). The eyelids are affected by sporotrichosis, trichophytosis, scab, actinomycosis, blastomycosis and other fungal diseases.
During the treatment process, it is important to use fungistatic and fungicidal medications, the choice of which is made by a specialist based on the causative agent of the disease
Actinomycosis
The causative agent is a radiant fungus (actinomycete). In the outer or inner corners of the eyelids, a painless nodular compaction (nonspecific granuloma) appears, acquiring a soft consistency with the formation of an intradermal or subcutaneous infiltrate. After the formation breaks through, a slowly healing fistula appears, from which pus is separated (often mixed with yellow grains, in which there are plexuses of fungal threads).
Treatment consists of the use of antibiotic drugs and Actinolysate, which must be administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously twice a week, 2-4 milliliters (start with 0.5 milliliters). The course of treatment is from 15 to 25 injections. It is necessary to carry out 3 to 5 courses of treatment with an interval of 1-2 months. Penicillin is prescribed intramuscularly and orally, as well as for injection into the inflammatory focus. In addition, tetracyclines and Phenoxymethylpenicillin (gram per day), Erythromycin 0.3 grams every 6 hours are prescribed.
Blastomycosis
The causative agent is a parasitic yeast fungus (blastomycetes). The disease is characterized by the appearance of ulcers and papules similar to malignant formations. The ulcerative process causes deformation of the eyelid area. With blastomycosis, there is an increase in regional lymph nodes. Possible damage to the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and central nervous system.
As a local treatment, a 1-2% alcoholic or aqueous solution of blue or brilliant green (methylene blue or brilliant green), 0.5% amphotericin, 5% nystatin, 3% octathione ointment is used. Nystatin is prescribed orally (500,000 units three times a day), Sulfanilamide (one gram 4 times a day). A 10% solution of potassium iodide (10 milliliters) is used intravenously.
Candidiasis (candidiasis)
Experts call candidiasis a disease provoked by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (often Candida albicans). Patients with candidiasis experience swelling of the skin on the eyelids and its hyperemia; it is strewn with small pustules.
Local treatment involves treating inflammatory lesions with 1% alcohol or aqueous solution of blue or brilliant green, 0.5% amphotericin, 5% nystatin, 0.5-1% decalin, 2.5% levorin, 3% octathione ointment. Nystatin (500,000 units 3-4 times a day), Levorin (500,000 units three times a day), 3% potassium iodide solution (a tablespoon three times a day), vitamin C and group B are prescribed orally.
Sporotrichosis
Experts believe the causative agent is a parasitic fungus of the genus Sporotrichum. Slowly growing purple nodules appear on the skin in the eyelid area, similar to a chalazion (a proliferative inflammatory process on the eyelid carb). After some time, the nodes disintegrate with the formation of fistulas and the separation of grayish-yellow pus. There is an enlargement of the lymph nodes, the process can spread to the conjunctiva of the eye and the orbit.
Sporotrichosis
Local treatment consists of using sulfonamide drugs (10% sulfapyridazine and 30% sulfacyl ointment). Nystatin (2,000,000 - 3,000,000 units), Sulfadimezin (4 grams per day for 7-14 days), 3% potassium iodide solution (a tablespoon 3-4 times a day) is prescribed orally.
Trichophytosis (ringworm)
The causative agent is a parasitic fungus of the genus Trichophyton. Experts distinguish between deep and superficial trichophytosis. Isolated lesions in the eyelid area are a rare occurrence. According to the morphological characteristics, the pathological process is similar to folliculitis (damage to the hair follicle). There is hyperemia of the edges of the eyelids, their swelling, and the presence of pustules with yellowish crusts. It is possible to detect areas of the eyelids where eyelashes are missing, or where they are broken off with traces in the form of black dots along the edge of the eyelid. A spore coating is found on the eyelashes. The pathological process on the eyelids is often supplemented by conjunctivitis and keratoconjunctivitis. After healing, scars remain and eyelash loss is noted.
Local treatment involves treating the affected areas with a 1% solution of blue or brilliant green, 5% iodine solution. Griseofulvin is prescribed orally.
Abscess on the lower eyelid: causes of appearance, removal
Every person can experience eye diseases. Inflammation of the eyelid can occur either independently or together with another infection. Pain, compaction, and swelling often provoke dysfunction of the organ of vision. To avoid this, it is necessary to identify the causes of the disease and begin treatment.
Provoking factors
An abscess on the lower eyelid can be of either infectious or non-infectious origin. Most often, inflammation occurs under the influence of such factors:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules,
- using expired cosmetics,
- decreased immune defense,
- hypermetropia (farsightedness),
- hormonal changes
- chemical, mechanical damage to the eye,
- overwork, chronic stress,
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- metabolic problems
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation,
- diseases of teeth and gums,
- allergic reactions,
- sinusitis,
- infection by fungi, viruses, parasites.
Origin and symptoms of ulcers on the eyelid
Purulent formations can provoke the following diseases and conditions:
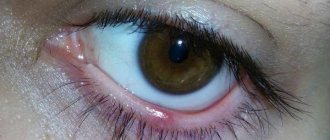
- An abscess is an acute inflammatory process in which an abscess with purulent contents forms on the mucous membrane of the eyelid. This process is a complication that provokes other eye diseases (hordeolum, blepharitis, meibomitis and others). The abscess has a yellowish, sometimes gray color, and it is very painful to touch. After the wound bursts, purulent fluid flows out of it, the pain immediately disappears. An abscess has the same symptoms as cellulitis.
- Molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease caused by poxvirus (smallpox virus). Previously, doctors associated the occurrence of pathology with the vital activity of the mollusk. You can become infected with the virus through contact with a carrier, using someone else's towel or other personal items. A feature of this infection is the formation of dense formations on the mucous membrane of the lower eyelid, which are painless when touched. The disease can lead to chronic keratitis, conjunctivitis, and blepharitis.
- Stye is an abscess on the edge of the lower eyelid. This disease is caused by staphylococcus of the sebaceous gland. The main sign of the disease is the appearance of a bulge on the mucous membrane of the eyelid, which causes pain. There is redness of the skin around the seal, and the conjunctiva also becomes inflamed. Usually the abscess breaks out in 2-4 days. Sometimes several seals form on the eyelid at once.
- Blepharitis is an inflammatory process in the area of the ciliary end of the lower eyelid. This disease is mainly chronic.
Types of blepharitis:
- angular,
- ulcerative,
- scaly,
- meibomian.
Symptoms common to all types of blepharitis are a feeling of eye fatigue, heaviness of the eyelids, and sensitivity to bright light. The eyelids become slightly swollen, dense, and reddened.
The patient feels itching and burning in the eye. In some cases, eyelashes begin to fall out.
Blepharitis is a complication of certain skin diseases, such as seborrheic or simple contact dermatitis, allergies, acne, lice.
- A furuncle or boil is a bulge in the eyelid area that has purulent contents and is accompanied by swelling. A black dot forms inside the boil, which is called a necrotic center. After the boil breaks out, the pus comes out along with the necrotic core. Almost always, after the wound heals, a scar remains on the affected area.
- Impetigo is a skin disease that spreads to the eyelid from other parts of the body. It is transmitted through contact and household contact. The abscesses are small in size and heal on their own within 2 weeks. This disease does not cause any complications. Its causative agents are streptococci and staphylococci. Children most often suffer from impetigo.
- Meibomitis is an inflammatory process in the meibomian glands (glands of the cartilage of the eyelid). This disease is caused by coccal forms of bacteria. The symptoms of meibomitis are similar to those of stye. They differ in that with barley, the abscess forms on the edge of the eyelid, and with meibomitis - in its depths. Sometimes the abscess needs to be opened surgically. Yellow or gray crusts form in the corners of the eyes. Discharges constantly come out of the glands, which can provoke the development of chronic conjunctivitis.
Treatment with ointments
One of the most effective means of treating ulcers on the eye are ointments. Most often, doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- Vishnevsky ointment - promotes rapid breakthrough of purulent formation, has a powerful disinfecting, anti-inflammatory effect on the source of inflammation, accelerates the restoration of the eyelid after opening of suppuration. Remember that the ointment should not be applied to the mucous membrane of the eyelid. The bandage with the medicine can only be applied over the eye. The only contraindication for use is individual intolerance to the ingredients of the ointment. No side effects were found
- tetracycline ointment - its use does not lead to burns on the mucous membrane and cornea. The use of the drug is recommended at the first manifestations of the inflammatory process. Apply the ointment to the inner area of the eyelid 3 times a day. The drug is contraindicated in case of fungal skin diseases, increased susceptibility to the active substance tetracycline, as well as in children under 11 years of age, pregnant and nursing mothers. Side effects include hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels of a certain organ), photosensitivity (increased sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet rays), itching, slight burning,
- hydrocortisone ointment - prescribed only for severe forms of the disease. The drug treats not the mucous membrane of the eyelid, but the eyeball itself. You need to use the ointment 3 times a day for one to three weeks. Contraindications for use are fungal, bacterial, viral skin diseases, ulcerative and wound lesions of the epidermis. Also, the medicine should not be used by pregnant women or patients with hypersensitivity to the components of the ointment. Undesirable effects may include hyperemia, itching, irritation, and swelling in the treatment area.
Drop therapy
The disadvantage of this treatment method is that the drops act more slowly than ointments. The most effective drugs are:
- "Albucid" - these drops have an antibacterial effect. In acute cases of the disease, drops should be used 6 times a day, at least 2 drops per eye. The drug is contraindicated in case of increased sensitivity to sulfonamides. Sometimes eye irritation occurs when using drops. In this case, you need to use a solution with a lower concentration,
- "Tobrex" - the drug is used as an alternative to Albucid drops. It is prescribed to both adults and children. Adults need to drip 5 drops every 4 hours for 10 days. Children should drip no more than one drop 5 times a day for 7 days. Tobrex is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to its components. Side effects may include swelling, redness of the mucous membrane of the eyelid, itching, burning in the eye,
- “Gentamicin” is a gentle antibacterial agent that is prescribed for advanced forms of the disease. No more than two drops should be instilled into the eye 3 times a day. The duration of therapy depends on the severity of the infection. The medication is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the active substance gentamicin, pregnant or lactating women. The medicine may cause tingling, itching, burning in the eyes, swelling, and redness of the conjunctiva.
Traditional medicine recipes
Folk remedies with effective recipes:
- Warming up. This method is effective only for the initial manifestations of the disease. Boil potatoes or chicken eggs. Wrap in a scarf to avoid burning your eyes. Keep the bag on your eyelid until the potato or egg has cooled completely. Remember that heating is strictly contraindicated when a purulent core has formed, since the wound may burst and pus will flow out under the eyelid.
- Flax seed compress. Warm up the flax seeds and put them in a bag. Apply to the sore eyelid 2 times a day.
- Aloe therapy. Grind one medium-sized aloe leaf, fill it with boiling water for about 2/3, leave to brew for 10 hours. The resulting mixture should be applied to the affected area of the eye 3 times a day. The paste should be washed off 10 minutes after application.
- Plantain compress. Wash several leaves of young plantain and grind them to a liquid mass. Pour the resulting mixture with one glass of boiling water and leave to steep for 1 hour. Moisten a piece of bandage or a cotton pad and apply to the inflamed area for 10-15 minutes. Repeat the procedure at least 5 times a day.
- Washing with decoctions of medicinal plants. Take birch buds, bird cherry flowers, chamomile, and marsh rosemary. Mix the plants and pour boiling water over them. After 30 minutes, express the liquid and rinse your eyelid with it every 2-3 hours. After the abscess begins to disappear, reduce the number of washes to 5 times a day.
- Compress of calendula flowers. This plant is famous for its anti-inflammatory effect. Pour boiling water over one tablespoon of calendula inflorescences. Leave the infusion for 1 hour to infuse. After this, moisten a cotton pad and apply it to the wound for 10 minutes. This compress should be done 5 times a day. This remedy for treating an abscess does not damage the mucous membrane of the eyelid.
Remember that self-medication can lead to unpredictable consequences. If you notice strange symptoms, be sure to consult an ophthalmologist.
Source: https://mfarma.ru/dermatologiya/simptomy-i-lechenie-gnojnika-na-veke