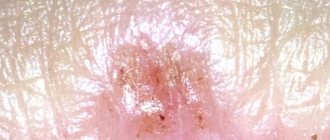
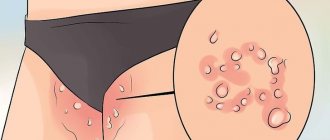
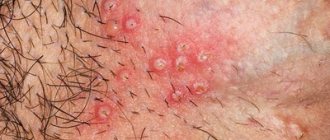
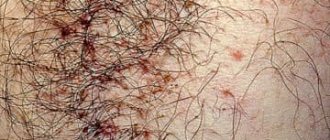
Not only women, but also many representatives of the stronger sex prefer to remove excess vegetation in the intimate area. But since depilation often causes itching and irritation, many men are afraid to carry out such a procedure in order to avoid further discomfort.
Experts assure that irritation on the pubic area appears only when shaving technique is violated or there is a lack of subsequent care. How to prevent such an undesirable effect from occurring, and what to do if your groin itches after shaving?
The main causes of pubic irritation after shaving
When shaving, the skin on the pubic area can be injured by razor blades. However, in order for irritation to occur, the presence of other provoking factors is necessary: penetration of bacteria through microtraumas of the skin;
- wearing synthetic or too thick underwear;
- wearing too tight clothes in hot weather;
- using detergents or cosmetics that could cause an allergic reaction;
- the use of allergenic washing powders for washing underwear;
- shaving across the hairs; shaving too often; dry shaving;
- neglect of skin care products after shaving; using a dull razor;
- using someone else's shaving machine;
- using a low-quality shaving machine.
A blade intended for shaving not only cuts hair, but also damages the surface of the skin. If the skin is sensitive and thin (and on the pubic area it is most often like this), then irritation is inevitable. Microdamages on the skin soon turn red, and when an infection occurs, pustules and pimples can form.
Forms
A healthy person has a uniform skin color, without inflammatory processes or neoplasms. Melanin is responsible for coloring the epidermis brown, that is, pigmentation. If the amount of melanin increases under the influence of certain reasons, then the skin changes its color. First of all, this pathological process begins in areas of inflammation and infection of the epidermis.
Hyperpigmentation in the intimate area can be expressed in several forms:
- Birthmarks;
- Chloasma;
- Erythrasma;
- Athlete's foot;
- Tinea versicolor.
Methods for treating pubic irritation after shaving
What to do if signs of irritation appear on your pubic area after shaving? To reduce discomfort, you can use both modern cosmetic products and folk remedies. Antibacterial creams and ointments can be purchased at almost any pharmacy. The active components of such products are substances that promote rapid healing of microdamages and prevent bacteria from entering the wounds.
To prevent germs from getting into microcuts, the pubis should be treated with alcohol lotion or a solution of hydrogen peroxide. There is no need to apply alcohol products often and in large quantities, otherwise you can dry out the skin and aggravate the painful condition.
To soothe irritated pubic skin after shaving, you can apply lotions with infusions of medicinal herbs: celandine, chamomile, string, sage. Immediately after the depilation procedure, it is recommended to use special products - aftershave lotions or gels.
Prickly heat
The problem is for people who suffer from excessive sweating and prefer synthetic underwear. A lot of moisture accumulates under the panties because it does not have time to evaporate. The problem is aggravated by friction, especially if there is a lot of coarse hair in the groin. The result is flaking on the pubic area, redness and swelling, and a weeping rash. To get rid of symptoms, do not apply ointments to the inflammation. They will only make the problem worse. Wash the inflamed areas with soap and water and dry them naturally. Then you can use talcum powder or baby powder. If necessary, hyperhidrosis should be treated. It also doesn’t hurt to change your tight swimming trunks to loose briefs made of natural fabric.
The best folk remedies for treating pubic irritation
Take two tablets of acetylsalicylic acid, some warm water and a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide; mix the tablets with water until a thick paste forms; Apply to the pubic skin with massaging movements, then rinse off; wipe the pubic area with a cotton pad previously soaked in a peroxide solution. Instead of peroxide, fresh lemon juice can be used. There is another remedy: take a small amount of zinc ointment; crush the chloramphenicol tablet; mix both ingredients; Apply to the pubic skin when irritation occurs, for 3-4 hours, then wash off. The essence of this recipe is that zinc ointment has a healing and drying effect, and chloramphenicol prevents the penetration of microbes into wounds.
Comments
Good afternoon, girl, 27 years old, office work, sedentary. Today I noticed that 3 small dark spots appeared in my groin. There is no itching or pain, there have been no sexual contacts in the last month. There are problems with excess weight. Could this be related? Thank you.
Good afternoon, problems with excess weight almost always provoke the appearance of spots in the groin area and increased sweating. I recommend getting tested by a dermatologist to determine the fungal culture. There is a possibility of developing candidiasis of large folds - a common disease in overweight people. Get well!
Medicines for pubic irritation after shaving
Malavtilin is a cream based on herbal ingredients that quickly heals all kinds of cracks and areas of irritation. Malavtilin is applied to the pubic area 1-2 times a day, in a thin layer. Sometimes it can cause an allergic reaction.
Panthenol spray is a healing preparation with dexpanthenol – provitamin B5. The drug is evenly applied to the pubic area damaged by shaving, after shaking the can. The product can be used as needed, since no cases of spray overdose have been observed.
Zinc ointment or paste is a pharmaceutical product based on zinc oxide, which is used to treat many dermatological and cosmetic problems. To eliminate irritation on the pubic area after shaving, apply the ointment 3 times a day until the problem is completely resolved.
Boro Plus is a well-known antiseptic ointment that can be used even for allergic irritations on the pubic area. The drug has virtually no contraindications or side effects, since it contains only natural ingredients. The ointment is used up to 3 times a day.
Chlorhexidine is an aqueous solution with a pronounced bactericidal effect, which is used 2-3 times a day. Frequent use of the product is not recommended, as increased dryness of the pubic skin may occur.
Miramistin is an antibacterial ointment that is widely used in medicine, including dermatology. For irritation on the pubic area, the ointment can be thinly applied to the skin twice a day. There is rarely a burning sensation when using the product. It is undesirable to use hormonal ointments - for example, hydrocortisone or prednisolone. Such drugs cannot be used without a doctor’s prescription, as they have a large number of contraindications and side effects, and with prolonged use they can cause an addictive effect.
Possible pathologies
Viruses, fungi, bacteria and parasites leave rashes on the skin. Unusual pigmentation in the groin, caused by pathogens, requires qualified medical care.
Pediculosis
Dark spots in the groin in women can be caused by pubic lice. Parasites are most often transmitted from person to person through close physical contact. The disease affects people with hair in the groin area. Insects do not live on smooth skin. Their bites leave burgundy, blue or purple bruises on the body. The saliva and excrement of lice cause severe itching and irritation. Discomfort increases after water procedures. Parasites can often be seen with the naked eye. They get rid of them using special insecticides. But it is best to completely remove vegetation in the intimate area.
Athlete's foot
Inguinal fungus, affecting large skin folds. With excessive sweating, excess weight and weakened immunity, the risk of getting sick increases significantly. Pathologically, the process begins with the appearance of itchy round spots. They gradually increase in size and merge with each other. The lesions are rings with clear skin in the center and a hyperemic edge covered with blisters and crusts. Physical discomfort increases when walking. The affected areas are treated with antiseptic solutions and antifungal ointments. Antimycotics are also taken in tablet form.
Erythrasma
A pseudofungal disease that affects large folds of the body. The causative agent is Corynebacterium. With this pathology, yellowish, red and brown spots appear in the groin of women. The surface of the foci of inflammation peels off, and a brown pigment appears in their center. In rare cases, itching occurs, and a rash in the groin area appears only from scratching. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory ointments are used for treatment. Ultraviolet radiation has a beneficial effect. For extensive damage, systemic antibiotics are used.
Rubromycosis
Pathology caused by pathogenic fungi. Mainly affects the skin of the feet and large folds. Sometimes vellus and long hair are involved in the process. The affected areas dry out and turn red. Skin grooves clearly appear on them. Severe peeling is noted. The spots have uneven edges and are framed along the contour by an intermittent ridge. Growing lesions form semi-arcs, arcs, rings and garlands. The treatment is long-term. Includes the use of topical soothing agents, keratolytics for exfoliation, antifungal ointments and tablets.
Genital herpes
A viral disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes around the external genitalia. The pathology is characterized by severe itching and the formation of watery blisters. When scratched, the pimples easily burst, leaving ulcers in their place. After the erosions heal, pink spots form. At the same time, the temperature rises, general weakness occurs, and the inguinal lymph nodes may become enlarged. Therapy consists of the use of local and systemic antiviral drugs and external antiseptic treatment.
Spots in the groin in women can be caused by various reasons. It is not always possible to independently understand what causes the appearance of unusual pigmentation. It is better not to self-medicate, but to consult a dermatologist. He will prescribe adequate therapy, which will help avoid complications and other unpleasant consequences.
Ways to prevent pubic irritation
In order to reduce the risk of developing a rash in the pubic area, you just need to follow a few simple shaving rules: Use only new razors for each shave. Before the procedure, make a warm steaming compress (apply a washcloth moistened with warm water for 5-10 minutes). Shave only in the direction of hair growth. Use shaving gel. Be sure to lubricate the resulting wounds with antiseptic preparations. Use an intimate scrub once or twice a week to remove dead skin flakes. Wear cotton underwear. Use antibacterial intimate soap.
Contact dermatitis
Appears when there is intolerance to certain components of hygiene products. The fabric of underwear can also serve as a source of allergens. Contact dermatitis is characterized by redness and peeling, severe itching. Pimples and weeping areas may form. Antihistamines help prevent allergies. You should also eliminate the product that caused the problem from use. People prone to skin reactions should wear underwear made from natural fabrics and wash with products without dyes or fragrances. It is also recommended to use powder intended for washing children's clothes.
Preventing pubic irritation
To avoid irritation on the pubic area after shaving, during the procedure you need to follow simple rules:
- You should not dry shave your pubic area. You should first steam your skin in the shower or in the bath. You can also massage damp skin before applying shaving cream, gel or foam.
- Before shaving, the razor must be moistened with warm water and rinsed as often as possible during the procedure.
- Shaving should not be done against the hair growth, but along the way.
- Do not allow skin folds to appear in the direction of the razor: to do this, use the fingers of your other hand to slightly stretch the skin to ensure easier sliding of the blade.
- You should not press too hard and move the machine over the same place.
- If the blade becomes dull, it needs to be replaced.
- At the end of the procedure, the pubis should be thoroughly rinsed from the detergent, then gently dried and applied with any aftershave preparation of your choice.
In addition, to avoid skin irritation in the future, use the following recommendations:
- Do not rub the skin in the shaving area, and do not use a hard towel; Simply blot the shaved area with a soft cloth;
- When washing off shaving foam or gel, it is advisable to carry out the last rinse with cool water;
- you can use special antibacterial soap; the use of talc after depilation is undesirable, since its microparticles “clog” pores and aggravate inflammation;
- pay attention to the release date and shelf life of detergents, as spoiled soap or shower gel can also cause irritation of the pubic skin;
- After the procedure, you should wear clean, non-synthetic underwear.
If you listen to all the suggested recommendations, then irritation on the pubic area after shaving will cease to be a problem. However, if the symptoms of irritation still do not go away, despite all the measures taken, then you must definitely visit an experienced dermatologist: perhaps the cause of the discomfort is associated with some disease or allergic condition.
Inguinal fungus (athlete's foot) in men and women: causes, signs, diagnosis, how to treat
Athlete's groin is a chronic disease caused by a fungus that affects the epidermal layer of skin mainly in the groin area.
The main morphological element of the pathology is a scaly pink spot with pustular rashes located along the periphery. The lesions itch and cause discomfort to patients.
Athlete's groin is a delicate disease that leads to sexual dysfunction, decreased libido and sexual arousal.
The disease affects men more often than women. In children and adolescents, the pathology develops extremely rarely. The spread of fungal infection occurs through household contact through direct contact, through household items, personal hygiene products, and cosmetics.
With a decrease in the general resistance of the body, a primary focus is formed at the site of entry of the pathogen, which gradually grows along the periphery and spreads to healthy skin. The main location of the fungus is the inguinal folds.
In more rare cases, the disease can affect the skin of the buttocks, scrotum, perineum, penis, inner thigh, and pubic area. In women, the skin under the mammary glands, in the armpit and popliteal fossa often becomes inflamed.
Fungi of the genus Epidermophyton floccosum settle in the epidermis of the skin, destroy and utilize collagen, which leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the skin. Microorganisms have a low degree of pathogenicity, so the disease rarely develops in healthy people with full immune protection.
The diagnosis of pathology is made after microscopic detection of fungal mycelium in scrapings from the surface of spots and obtaining the results of bacteriological examination of biomaterial from patients.
Groin fungus requires a patient and careful approach. Causal treatment involves the use of antimycotic drugs that can completely cure the disease.
Etiology
Athlete's foot is a dermatomycosis caused by the fungus Epidermophyton floccosum. This is an anthropophile that grows and develops only on the human body.
It is located in the scales of the epidermis and nail plates. Under a microscope, fungal spores and well-branched mycelium are determined in skin scrapings.
After isolating a pure culture, the mycelium becomes yellow and the spores look larger.
Fungi are resistant to environmental factors. They grow and develop quickly at high humidity and temperature.
The infection spreads through contact and household contact through contaminated household items, as well as through touching and shaking hands. For rapid growth and development of fungi, moisture is necessary. Excessive sweating in a patient significantly increases the risk of infection.
In medical, preventive and public institutions, neglect of sanitary norms and rules can provoke an entire epidemic of mycosis.
Factors contributing to infection:
- Hyperhidrosis,
- Stress,
- Skin microtraumas
- Tight clothes,
- Obesity,
- Failure to comply with sanitary rules and regulations,
- Decreased immunity
- Hormonal disbalance,
- Metabolic disorders.
Symptoms
single spot of athlete's foot
With inguinal athlete's foot, pink or red-brown spots appear on the skin, having a round shape and a diameter of no more than one centimeter. The spots are located symmetrically, itch, peel and gradually grow.
Along the periphery of the spot on hyperemic and edematous skin, multiple blisters, pustules, suppurations, crusts and small flaky inclusions appear. Foci of inflammation are limited to an edematous ridge.
Plaques can merge with each other, forming a single erythematous area that spreads to surrounding tissues. Itching and burning are especially felt when walking, squatting and while bathing.
Fungus in the groin in men itches and burns, and severe discomfort occurs when walking. The areas are painful to the touch. Vesicles and pustules can burst, forming erosions and ulcers.
When a secondary bacterial infection occurs, severe complications develop.
athlete's foot inguinal in men and women
Additional symptoms of athlete's foot include swelling of the groin area, hyperemia of nearby skin, and the appearance of specific blisters with turbid serous fluid.
With epidermophytosis, not inflammatory, but allergic rashes - epidermophytide - may appear on the skin.
They are located symmetrically, do not contain fungi and disappear on their own after undergoing antimycotic treatment.
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, the disease can last for years. Athlete's disease is characterized by an acute or subacute course with pronounced signs of inflammation.
The disease quickly becomes chronic and takes on a wave-like course, during which periods of remission are replaced by exacerbations, forming from time to time new foci of skin lesions.
Even after complete recovery, the disease can recur.
Constant stress, friction in the affected area and hyperhidrosis complicate the course of the pathology.
Stages of the disease
- The initial stage is characterized by increased proliferation of the fungus in the epidermis and the appearance of pink spots with papules and vesicles on the skin.
- Clinical signs of the acute stage are weeping spots that grow, itch and are replaced by rings with scalloped edges.
- Chronic stage - lesions on the skin periodically lighten, and then become inflamed again under the influence of unfavorable factors.
- The advanced stage develops with a complicated course of the pathology.
If left untreated, large blisters appear on the skin, which become infected when damaged. The blisters are opened, necrotic tissue is removed and the wound is treated.
ethnoscience
Currently, there are a large number of traditional medicine recipes intended for the treatment of inguinal epidermophytosis at home.
- Infusion of St. John's wort, chamomile and lingonberry leaves is taken 100 ml daily for a month.
- Lotions made from a decoction of string, yarrow, and oak bark give good results. After the procedure, zinc ointment is applied to the skin.
- Radish seed pulp is applied to the affected areas of the skin.
- An alcohol tincture of poplar and birch buds is used to treat inflamed areas.
- Crushed celandine is applied to the lesions of inguinal athlete's foot for half an hour.
- Onion gruel helps get rid of pathology.
- A thick paste is prepared from soda, which is rubbed onto the affected skin.
- Ointment with essential oils is rubbed into the affected areas daily.
- Almond essence will help cure athlete's foot in the groin.
Prevention
Preventive measures to avoid the appearance of fungus in the groin:
- Disinfection of patient care items and common areas,
- Boiling and ironing linen, socks, shoe treatment,
- Use of removable shoes in baths and saunas - slates or rubber slippers,
- Fighting sweating
- Regular hygiene procedures,
- Wearing underwear made from natural fabrics in hot weather,
- Daily treatment of skin folds with cologne, salicylic alcohol, resorcinol and powdering them,
- Examination of contact persons,
- Prevention of stress,
- Strengthening the immune system.
Without adequate treatment, the spots will not disappear, and the disease will only progress. At the first symptoms of inguinal athlete's foot, you should consult a specialist. Pathogenic fungi and foci of epidermophytosis on the skin grow rapidly.
The prognosis of the disease is favorable. Acute and chronic stages of inguinal athlete's foot respond well to therapy. Modern antimycotic drugs can prevent relapse and re-infection.
Molluscum contagiosum
This term refers to a pathological condition of a viral nature. Both men, women and children are susceptible to the disease. The pathogen is transmitted not only during intimate intimacy, but also through contact and household contact.
The main sign of the disease is red spots on the pubis, scrotum, labia or penis. The rashes have the shape of a hemisphere. Often, nodules then form, and when pressed, a plug of curdled consistency emerges.
The red spots do not itch or flake, and they are also not painful. The genital form of the disease does not require treatment. In most cases, the rash disappears on its own within 2-3 months after its appearance.
If the spots are located in such a way that they are often injured, your doctor may recommend removing them in one of the following ways:
- curettage;
- cryodestruction;
- husking;
- laser excision;
- electrocoagulation.
Herpes
A viral infection that causes the formation of watery pimples on the pubic area. The causative agent is the herpes simplex and genital virus. Therefore, infection is possible not only through sexual contact. The disease is recurrent and it is impossible to get rid of it forever. During an exacerbation, itching and tingling occurs in the skin.
The most common infection that is sexually transmitted. It passes, accordingly, from an infected partner to a healthy one. First of all, herpes manifests itself in small blisters localized both on the pubis and on the genitals themselves. The incubation period of the pathology does not exceed 10 days, so the first symptoms appear fairly quickly.
Among the unpleasant factors, it is worth highlighting that if you have been infected with genital herpes at least once, most likely, relapses will occur after treatment. In this case, itching on the pubis is possible, since the formations appear very quickly.
They are small bubbles with a clear liquid inside, which eventually burst on their own. For some time, an inconspicuous wound remains in this place, healing absolutely without traces. There is a very small chance of post-acne formation after genital herpes. Especially in the pubic area, where the skin is quite dense.
Symptoms
single spot of athlete's foot
With inguinal athlete's foot, pink or red-brown spots appear on the skin, having a round shape and a diameter of no more than one centimeter. The spots are located symmetrically, itch, peel and gradually grow. Along the periphery of the spot on hyperemic and edematous skin, multiple blisters, pustules, suppurations, crusts and small flaky inclusions appear. Foci of inflammation are limited to an edematous ridge. Plaques can merge with each other, forming a single erythematous area that spreads to surrounding tissues. Itching and burning are especially felt when walking, squatting and while bathing.
Diagnostics
The answer to the question of how to treat peeling and with what depends on the reasons that led to the appearance of unpleasant sensations. To clarify them, the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- you will have to donate blood and urine for general and biochemical analysis to the laboratory;
- the doctor will take a smear of flora from the urethra or vagina;
- They practice collecting scrapings from the affected area for further diagnostic procedures.
The doctor may recommend taking blood tests for HIV, syphilis, and other serious and dangerous sexually transmitted diseases, even if there are no other accompanying symptoms.
If such a problem occurs, you should contact the following specialists:
- A dermatologist will help in the diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases; he will rule out fungal infections, bacterial damage to the epidermis, and select appropriate medications.
- If there are signs of a hypersensitivity reaction, an allergist will help. The doctor will take samples, identify the allergen and prescribe medications to relieve itching, burning and swelling of the skin.
- A gynecologist, urologist or venereologist - one of these doctors will have to be visited. This will help rule out the presence of genital diseases.
Doctors may recommend that the patient undergo other examinations to clarify the diagnosis if certain problems arise with this. More often they are sent for an ultrasound of internal organs, and secretions or skin flakes are collected for further examination in a laboratory.