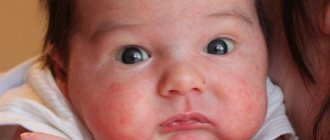
The organs of vision are often subject to the development of pathologies. Quite often, especially in older people, there is a growth on the eyeball. It may be colorless or have a yellow tint. In medicine, this pathology is understood as a disease such as pinguecula. It does not pose a threat to life and health, and vision is also not impaired in the presence of a neoplasm. But it is not recommended to ignore this phenomenon. The appearance of such a pathology may indicate a malfunction in the body; it can be assumed that there are certain disturbances in it, the amount of fats and proteins in this case is several times higher than normal, which affects metabolism.
Causes of growths on the eye
The theory of the occurrence of pinguecula due to wearing contact lenses has not been confirmed by modern medicine.
An excess of fats and proteins in the human body is the impetus for hyaline degeneration of the tissue of the organs of vision. Changes in the conjunctiva contribute to the formation of a pinguecula - a tumor-like thickening on the inner side of the eye mucosa. The disease occurs not only in older people. Multiple external and internal environmental factors that daily influence human eyes lead to the appearance of growths on the eyes among different age groups of the population. Medical practice encounters cases where such a growth appears on the eyeball of a child. The exact cause of the disease has not been found. Factors contributing to the development of pinguecula:
- elderly age;
- climatic conditions (dry, hot air);
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- infrared radiation;
- poor ecology (dust, smog);
- weather factors (wind).
Various growths on the eye can cause swelling, itching, dryness, and redness.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
Pinguecula develops slowly, without pronounced symptoms, and does not degenerate into a malignant form. In the corner of the eye near the nose, a transparent yellow nodule is clearly visible, which over time can grow to the pupil. The patient feels the presence of a foreign body while blinking, as if hit by a speck. 90% of people do not go to the doctor after noticing similar symptoms. A health concern is pingueculitis, an inflammation of the growth. It is accompanied by unpleasant painful symptoms:
- swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye;
- redness of the eyeball, eyelid;
- pain and burning when blinking;
- feeling of dryness.
The disease is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist during a routine examination. Using a special device - a slit lamp - the ophthalmologist assesses the condition of the conjunctiva of the eyelid, the body and vaults of the eye, blood vessels, the nature of the discharge, the presence/absence of inflammatory and degenerative processes. Examination of the organs of vision under a microscope is painless. Additional laboratory tests are not performed to diagnose eye growths.
Treatment of a growth on the eye must be carried out with an ophthalmologist.
Treatment of the disease
In the absence of discomfort and pain from the pinguecula, the doctor does not prescribe treatment. The patient is recommended to visit an ophthalmologist once every six months to monitor the disease. In case of inflammation, significant growth or for aesthetic purposes, modern clinics and traditional medicine offer to eliminate the problem in various ways: medication, hardware, non-traditional. Removal of the pinguecula and pterygium can provoke the appearance of conjunctivitis and astigmatism.
Conservative method
With the help of medications in the form of eye drops, they overcome the feeling of dryness, irritation and redness of the eye membrane. Based on their effects, they include moisturizing, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, vitamin, and analgesic drops. The pharmaceutical industry provides a wide selection of drugs in the field of ophthalmology. To relieve symptoms caused by pinguecula, the following eye drops are prescribed:
- moisturizing (“Vidisik”, “Oftagel”, “Natural Tear”, “Quainax)”;
- antibacterial (“Vitabakt”, “Albucid”, “Garazon”);
- anti-inflammatory (“Garazon”, “Hydrocortisone”).
Most uncomplicated growths on the eye can be treated with eye drops.
Drops with a moisturizing effect can be purchased independently at a pharmacy without a doctor's prescription. Transparent, like a tear, the medicine contains boric acid. The moisturizing effect is achieved due to the lubricating and softening effect of the drug. Red eyes can indicate not only inflammation, but also irritation. Therefore, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drops should be selected only by the attending physician. Antibiotics for the eyes have a different spectrum of action and chemical composition, some can cause allergic reactions. Antimicrobial drops will prevent the entry and subsequent spread of infection on the mucous membrane.
Removing growths
Most cases of pinguecula removal are initiated by patients themselves for cosmetic purposes. The doctor prescribes surgical treatment if the disease causes physiological discomfort to the patient or there is a threat of visual impairment when a lump appears on the pupil. Surgical intervention is carried out using laser or classical surgery.
Laser cauterization
The method is used to remove small tumors. Pre-anesthetize the eye with anesthetic drops. During the procedure, the surgeon uses a laser beam to cauterize the head of the growth, then uses surgical devices to remove the dried areas. The duration of the operation is 10−20 minutes. 2 hours after removal, the patient leaves the clinic.
Laser cauterization of a growth on the eye allows you to quickly and painlessly get rid of the problem.
Laser removal of conjunctival tumors is performed without sutures or additional plastic surgery in 92% of cases, but in 60% of cases a subsequent relapse occurs.
This method is safe, sterile, non-traumatic and bloodless. The patient must wear an eye patch until complete recovery, which takes up to 1 month. During this period, the eye may become red. Postoperative care includes wearing sunglasses with a high degree of UV protection, treating the mucous membrane with antibacterial and moisturizing drops.
A growth on the eyeball in humans is one of the most common benign neoplasms that develops on the mucous membrane of the organ of vision. Foreign formations have a completely transparent or yellowish tint. Growths form on the eyeball in the conjunctival area, and their appearance is associated with an excess of fats and proteins in the tissues of the body. In medicine, this pathology is called pinguecula. Its formation does not harm human health and does not impair the quality of vision. However, this does not mean that the tumor should be ignored. Superficial epithelial growths on the eye indicate that a person has serious metabolic problems, consisting of poor absorption of fatty and protein foods.
Factors in the formation of anomalies on the eyelid
Bubbles formed on the eyelids are not harmful to health, but at the same time they bring a lot of trouble. They provoke the development of itching and irritation. There remains a feeling of the presence of foreign objects in the organs of vision. What influences the formation of bubbles?
The main reason is disruption of the sweat gland of the eyelid. A cyst can be caused by:
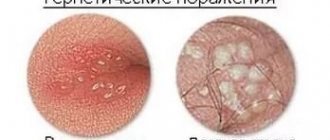
- herpes;
- allergic reactions;
- papilloma virus;
- unsuitable cosmetics.
The papilloma virus can cause blisters on the eyelids. It is a neoplasm that looks like small growths. They can appear not only on the eyelids, but also in the lips, armpits and groin.
It is extremely rare that bubbles appear due to the use of low-quality or unsuitable cosmetics. New growths are temporary and similar to an ordinary allergic reaction. Changing your usual cosmetic products should solve the problem.
To clarify, you need to seek help from an ophthalmologist. He will conduct an examination and prescribe appropriate therapy.
In this case, the viscosity of the secretory fluid plays an important role - it becomes so thick that it cannot leave the gland. The thick mass does not leave the gland in a timely manner, as a result of which exudate accumulates and a dense capsule is formed on the lower or upper eyelid.
Factors influencing the occurrence of the disease:
- herpes virus;
- allergic reactions - conjunctivitis, hay fever;
- human papillomavirus;
- use of cosmetics;
- constant friction caused by contact lenses, false eyelashes;
- inflammation of the eyelids - stye, demodicosis, blepharitis;
- hereditary factor, congenital anomalies of the iris;
- injury to the eyeball;
- long-term use of potent medications to treat eye diseases.
Causes of penguicula
photo of how a growth appeared on the eye
The main causative factor for the appearance of a penguicule is the degeneration of a certain area of the epithelial tissue of the eyeball and the formation of a compaction from cells that have changed their structure. The localization of a benign neoplasm is the cornea of the eye or its conjunctiva.
The following main reasons for the appearance of pinguecula can be distinguished according to its types.
Yellow growths on the eyes
Their formation is directly associated with an excess of animal fats in the human body, which are absorbed daily with food and the organs of the digestive tract are simply physically unable to absorb large amounts of fatty foods. As a result, a metabolic disorder develops, one of the manifestations of which is the formation of benign growths on the surface of the mucous membrane of the eyeball.
Transparent growth on the white of the eye
Completely transparent penguicles are associated with excessive consumption of protein foods. In 76% of cases, patients with a transparent growth on the white of the eye are simultaneously diagnosed with stones in the kidneys or bladder. These are all interrelated symptoms indicating an excess of proteins. The appearance of a transparent penguicule on the white of the eye is an irreversible process that will not resolve on its own, unlike the same. Nevertheless, restriction in products containing a large amount of proteins will help to avoid further deterioration of well-being.
Also, the appearance of yellow and transparent growths on the eyeball is facilitated by the presence of secondary factors, which are as follows:
- Spending a long time on the street. There is a theory that penguicules are formed in people who are exposed to direct sunlight for a long time every day during the day. Ultraviolet contained in the rays of the sun, falling on the cornea of the eye, can provoke a change in the cellular structure of the epithelium with benign degeneration of its tissues.
- Senile age. As the body biologically ages, all life processes slow down. Metabolic rate also decreases. Proteins and fats are digested much less well, and if an elderly person has concomitant diseases of the digestive system, poor digestion of fatty and meat dishes is possible. As a result, yellow or transparent penguicles form on the surface of the eye.
- Professional activity. People whose work is associated with the constant negative impact of environmental factors on the mucous membrane of the eye are more susceptible than others to the appearance of foreign tumors of this type. At risk are men and women who work in workshops with toxic fumes of chemicals, with elevated air temperatures, and a high content of dust particles.
- Heredity. A predisposition to the appearance of benign neoplasms in the form of penguicula on the surface of the eyeball is transmitted along with genetic information to descendants from blood relatives. It does not matter in which generation the disease previously manifested itself. A gene with a mutation in the development of epithelial tissues of the organ of vision can manifest itself even after hundreds of years. Growths formed as a result of the presence of a hereditary factor do not respond well to traditional therapy, and after surgical removal they often form again.
- Climate specifics. Living in regions where arid climatic conditions prevail and dry and hot winds blow, carrying dust with them, contributes to the appearance of benign neoplasms on the surface of the eye in the form of pinguicula. Most often, patients with this pathology, caused by negative climatic conditions, are residents of the countries of the Middle East, where there is a desert landscape, high air temperatures throughout the calendar year, and there are also such phenomena as sandstorms.
It is extremely rare that an epithelial growth on the surface of the eyeball simultaneously affects two organs of vision. This is only possible if the pathogenic effect on the mucous membrane of the eye has reached a critical level and its tissues are under conditions of daily stress. It is also possible that visual acuity may decrease due to the presence of concomitant factors that not only act as a cause of degeneration of epithelial cells, but also destroy the iris of the eye, burn the retina and introduce other destructive elements into the process of the organ of vision.
Manifestations and signs
It is not difficult to recognize a cyst visually; it stands out on the white of the eye and is visible to the naked eye, without any ophthalmic instruments or devices. But there are also other symptoms that are common to all types of cysts.
Burning sensation, feeling of sand, a foreign body in the eye - signs that begin to bother you as the cyst grows
These include:
- lacrimation;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- itching, feeling of sand in the eye;
- pain when blinking.
Less commonly, the tumor causes pain and affects visual acuity. Such symptoms appear if the dermoid grows and increases in volume. When blinking, the cystic vesicle will be constantly injured by the edge of the eyelid and eyelashes, which can lead to infection and the development of secondary conjunctivitis. With this complication, the following symptoms are added to the listed symptoms:
- photophobia;
- swelling;
- copious discharge, clear or purulent.
In some cases, the cyst does not manifest itself in any way; it is simply noticeable visually as a yellowish or brownish spot on the sclera. There are cases when a bubble appears in the morning, resolves on its own in the evening, and appears again in the morning. The patient does not feel any discomfort.
Other symptoms depend on the form of the pathology. Congenital dermoid cysts are usually found in infants. At the initial stage, it can reach a diameter of 5 mm, has a regular round shape and a yellowish tint. If the formation is not treated, it will grow and can completely close the eyeball, right down to the ducts of the lacrimal glands. At the same time, the child’s vision drops sharply. In severe cases, the dermoid grows into the temporal lobes.
Important! If any formations are found in the eye, above or below the eye, under no circumstances should you touch them with your hands, rub them, or try to get rid of them yourself. The most reasonable thing in this case is to contact an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination
How and how to treat growths on the eyeball?
Modern medicine offers a wide variety of treatment methods for formed penguicules. The choice of treatment method is determined by the doctor on an individual basis. Much depends on the general clinical picture of the disease, the location of the benign tumor, the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant diseases of the organ of vision and the body as a whole. The following therapeutic manipulations can be applied to the patient.
Traditional treatment
Conservative therapy involves maintaining the health of the mucous membrane of the eyeball. First of all, the ophthalmologist eliminates dry eye syndrome (which also contributes to the development of dry eye), which is always present in people suffering from penguicula. To do this, use Oxycal or Artificial tear eye drops. They are dripped in the morning and evening. They soften the mucous membrane of the organ of vision, and also have a protective function against the effects of pathogenic environmental factors.
These medications contain boric acid, which acts as a gentle preservative. Therefore, the drops minimize the risk of irritation or an allergic reaction.
If the appearance of penguicula is accompanied by an inflammatory process and swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye, then it is advisable to take medications that eliminate pathological processes in the organ of vision and also have antiseptic properties. In this case, treatment of penguicula is indicated with medications such as:
- Maxitrol;
- Tobradex;
- Diclofenac.
The duration of treatment ranges from 10 days to 1 month. The dosage and timing of therapy are determined by the attending ophthalmologist or dermatologist. A patient taking these medications is regularly observed by a doctor to monitor the clinical picture of the disease.
Surgery
It involves removing a benign growth on the eyeball using a laser. Excision of the pinvicula with a laser beam is used only as a last resort if the neoplasm is large, interferes with the aesthetic appearance, or reduces the quality of vision. The laser pinguicula removal procedure itself lasts no more than 30 minutes. It is completely painless, but still carries certain risks. The danger lies in the possible infection or the occurrence of postoperative complications that can negatively affect visual acuity.
After laser excision of the growth, the mucous membrane of the eye is restored within 1 month. During this period, slight redness of the eye and profuse production of tears are possible. Patients are advised to wear sunglasses to prevent ultraviolet radiation from reaching the surface of the eyeball. If the main cause of pinguecula formation has not been eliminated, then in 85% of cases the benign growth appears again in the form of a relapse. Therefore, therapy for this disease must have an integrated approach with a complete diagnosis of the patient’s body.
Eye neoplasms – what are they?
The delicate and sensitive tissues of our eyes, unfortunately, are vulnerable to many carcinogenic factors: radiation, chemicals, some viruses, burns and injuries. There may also be hereditary reasons for their degeneration. Tumors of the organs of vision and surrounding tissues are so diverse that they are studied by a special branch of clinical medicine - ophthalmo-oncology. Due to the many variations of eye tumors, diagnosing the problem is not always easy; this requires a comprehensive examination by a highly qualified ophthalmologist. But, whatever the diagnosis, there is no need to be afraid - modern treatment methods have come so far that there is a suitable method for every case.
Classification of tumors of the eye and surrounding tissues
The same classification applies to tumors of the visual organs as to tumors in general. They are divided into:
- Benign - slowly growing, does not metastasize, and does not have a toxic effect. They can degenerate and become malignant. Among eye tumors, this type includes: papilloma, senile wart on the eyelid, benign nevus and a number of others
- With locally destructive growth - those that do not metastasize, but have invasive growth (intermediate category). Basal cell carcinoma and progressive nevus are characterized by such growth
- Malignant - fast-growing, destroying other tissues and releasing toxins. Their cells are transported with the blood to other parts of the body and can give rise to secondary lesions (metastases). Examples: cancer of the conjunctiva, meibomian glands, melanoma and sarcomas of the eyelids.
Eye tumors are also classified according to their location in the affected organ.
:
- Tumors of the orbit (eye socket)
- Tumors of the adnexal apparatus of the eye (eyelids, conjunctiva)
- Intraocular tumors (choroid and retina).
Is this dangerous for a person’s vision and which doctor should I contact?
Pinguecula extremely rarely changes the structure of its cells from a benign etiology to a malignant form of the neoplasm. Still, a certain amount of risk always exists. Based on this, patients who have a genetic predisposition to cancer in their family are recommended to undergo laser removal of the growth, as well as undergo diagnostics of the body to identify metabolic disorders. In general, the pinguecula does not affect the quality of vision, since in most cases it is located too far from the pupil and does not affect the visibility of the visual field.
If you find a foreign growth of yellow or transparent color on the surface of the white of your eyeball, it is recommended to visit an ophthalmologist for advice. The doctor will conduct a visual examination of the organ of vision and, if necessary, write a referral for tests and a comprehensive examination using special medical equipment. Only after this the patient receives a prescription to take conservative medicine medications or is offered to undergo laser removal of a benign tumor.
A white or yellow growth on the eye shell may look unsightly, but does not pose any health hazard. However, if the pinguecula begins to grow and/or bothers you with any unpleasant sensations, it is better to visit an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Pinguecula is increasingly appearing not only in older people, but also in children and young people. This is due to the deterioration of the general environment: when exposed to external factors, many particles of dust and other substances enter the eyes.
Prevention
For the purpose of prevention, doctors recommend protecting your eyes, preventing them from being injured or exposed to negative factors. In summer they are protected with glasses or wide-brimmed hats. If human activity is associated with unfavorable conditions, protective equipment must be used. When living in hot countries, it is recommended to periodically moisturize your eyes. You also need to eat right. Food must contain vitamins and minerals so that metabolism is not disturbed.
If there is a genetic predisposition, it is difficult to prevent the appearance of a growth, but it is important to prevent exposure to provoking factors. By following these simple rules and recommendations, you can reduce the risk of developing pinguecula and preserve your vision and health.
Pinguecula of the eye and the reasons for its appearance
A pinguecula is a benign formation in the form of a transparent, white or yellow growth on the mucous membrane of the eye. It occurs as a result of excessive fat and protein content in the body.
It most often forms on the inside of the eye closer to the nose, but can increase in size, reaching the space near the pupil. Such formation does not pose a health hazard and does not lead to loss of vision. It can occur in both children and older people. Most often it occurs in people who spend a long time outdoors: weather conditions such as wind create a favorable environment for the formation of growths.
Pinguecula is a very common disease that can appear on the membrane of both apples (both left and right eyes).
The main reasons for the appearance of a growth on the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva) are as follows:
- Elderly age. This is how the aging of the eye shell manifests itself. Growths occur not only in people over 50, but also in children.
- Exposure to sunlight, low humidity.
- Impact of external factors. Most often it occurs in people who spend a lot of time outdoors, as wind, dust and/or smoke create a favorable environment for the formation of growths.
How to recognize papilloma in the corner of the eye
The neoplasm may be similar to other skin growths in this area, however, there are a number of signs that will help distinguish the infectious nature of the formation from other pathologies.
The main signs of HPV appear as:
- Rough surface of the formation and loose connection with the skin (warts are often attached to the tissues with a kind of stalk).
- Single or multiple growths on the skin, which can be of different diameters. They are often located next to each other, sometimes they can merge.
- Difficult to diagnose formations that may not be visually noticeable upon initial appearance. A person may complain of discomfort and pain when closing the eyelid.
- If the wart grows rapidly, it can bother a person and impair his vision. In addition, a tumor in the inner corner of the eye can cause inflammation.
Benign growths that appear in the area of the visual organs require a special integrated approach to treatment. First of all, they need to be correctly diagnosed, removed using one of the proposed methods and undergo complex therapy to prevent formations in the future.
Symptoms of pinguecula
The formation of a growth is mostly asymptomatic, but the following symptoms may occur:
- redness in the area of the eye shell where the lump develops;
- increased dryness in the eyes;
- feeling of the presence of a foreign object;
- irritation that is strongly felt when blinking.
Diagnosis of the disease
In some cases, it will not be difficult for an ophthalmologist to diagnose a pinguecula. A routine eye examination and slit lamp examination are sufficient to make a correct diagnosis.
Treatment of growths
Since pinguecula is a benign formation, treatment is not necessary. But if symptoms appear or there is a need for treatment due to a cosmetic defect, you need to visit an ophthalmologist or try using folk remedies.
Treatment methods are chosen based on the individual characteristics of the patient:
- 1. Therapy aimed at moisturizing the eye membrane. It consists of the use of artificial tears (Oxial, Lacrisify), which have a softening effect and a lubricating effect. Most drugs contain boric acid, which itself is a mild preservative. This property of the component ensures that artificial tears do not cause allergic reactions and/or irritation.
- 2. Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drops. If the formation of a growth on the eyeball is accompanied by inflammation and/or swelling, drugs such as Tobradex, Diclofenac, Maxitrol, Cromohexal, Oftan are prescribed.
- 3. Laser removal. Surgery is necessary if the pinguecula increases in size and presents an unpleasant cosmetic defect. The most effective and safe method of removing growths is laser removal. The advantages of this method of operation over a scalpel are:
- quick surgery on the eyeball;
- absence or minimization of pain (anesthetic drugs are used - Innocain drops);
- safety;
- lack of blood during surgery;
- absence of subsequent scars.
You will need to wear a bandage for some time after surgery. This is done to prevent infections from entering the eye area.
Treatment with folk remedies
Along with classical therapy, traditional medicine is also widely used. Eating blueberries, possibly with sugar, has a very beneficial effect on vision. Blueberries stop its deterioration and partially restore visual functions. Here are the basic tips that have a beneficial effect on the structure of the retina:
- You can add more raw or boiled beets to your food, which has a beneficial effect on the eyes.
- Dry seaweed, poured with boiling water (three tablespoons per glass of boiling water), is infused until completely cooled, and then frozen. Ice cubes with seaweed are rubbed near the eye once a day to eliminate the pain that may accompany the development of pinguecula.
- The healing properties of clay have been known for a long time. A clay compress helps in treating growths on the eyes. Clay should not be allowed to penetrate into the eye. Clay compresses are made from powdered clay, which is sold in pharmacies. It is poured with warm water, bringing it to the state of soft plasticine. Place the required amount of clay on a clean, preferably linen, cloth so that the cake is about three centimeters thick, and place it on the eye. Keep this compress until the clay dries completely, after which you need to carefully rinse your eyes with warm water.
- Chamomile compresses can also be used to moisturize the eyes. They are prepared from a plant sold in the form of bags. One such package should be poured with boiling water and left for fifteen minutes, then lightly squeezed and make sure that there are no foreign particles on the surface of the compress that could get into the eye. Keep it on your eye until the bag has cooled.
- Regular tea is often used in the treatment of eye growths. Compresses made from strong tea help relieve pain in a short time.
All of the above compresses can be used an unlimited number of times until the unpleasant inflammation disappears.
Preventive measures for pinguecula include the mandatory wearing of sunglasses, which protect not only from ultraviolet rays, but also from dust and wind.
And a little about secrets...
Have you ever suffered from problems with your EYES? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, victory was not on your side. And of course you are still looking for a good way to improve your vision
back to normal.
Then read what Elena Malysheva says about this in her interview about effective ways to restore vision.
Benign tumors are the result of abnormal cell growth in a specific part of the body. The tissues of the eye are no exception in this regard; benign tumors are not uncommon in this part of the body. Benign neoplasms are not life-threatening and are not cancerous; in most cases, the prognosis is favorable. However, if blood vessels or nerve endings are pinched, the condition of a patient with a benign tumor may change: pain will appear. Therefore, these tumors require removal.
The growth of a benign tumor may be associated with:
- exposure to toxins;
- the influence of radiation, radiation (for example, due to the treatment of malignant tumors);
- hereditary factors;
- a strict diet poor in nutrients;
- exposure to severe stress;
- local trauma or contusion;
- inflammatory process;
- exposure to infection.
Benign neoplasms of the conjunctiva
Benign conjunctival tumors are tumors of the tissue that covers the white of the eye. They can be recognized by a slightly densified and raised area of tissue on the white. Diagnosed by examination using a slit lamp. Although benign growths in this area are rarely malignant, a biopsy is necessary to be completely sure that the tumor is not cancerous.
Types of benign neoplasms of the conjunctiva
Melanoma.
The most common malignant tumor of the conjunctiva. It manifests itself predominantly in middle and adulthood and has a 20% risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor. External signs: a pink or brown nodule on the white part of the eye. Treatment should begin when the tumor is small, because as it grows it can invade other areas of the eyeball and lead to the need for extensive surgery.
Nevus.
A small, flat area consisting of specific cells called melanocytes. In rare cases, it develops into malignant melanoma.
Lymphoma.
A salmon-colored tumor is often a sign of systemic lymphoma. To determine the malignant nature of the tumor, a biopsy is performed. Benign lymphomas also need to be removed.
Cyst.
Any type of thin-walled cavity filled with a liquid or semi-solid substance. Depending on the cause, it can be equally malignant or benign.
Inflammatory tumors.
They develop as a result of the body’s protective reaction to injury, infection or irritation. Removed surgically.
Treatment of conjunctival tumors
Conjunctival tumors are diagnosed during an examination using a slit lamp - biomicroscopy. Most treatment focuses on minimal surgery, since major operations often lead to removal of the eye or loss of vision. Sometimes, if the tumor is not growing, removal is not necessary. In such cases, only observation is carried out. If the tumor lifts or deforms the eyeball, cryotherapy and special eye drops are used.
How to remove an eyelid cyst
Often the neoplasm is benign.
Types of eye cysts
The disease is classified according to causes and clinical symptoms:
- Congenital cavity - occurs due to dissection of the iris. It can develop within several years after birth, but appears at a young age before 7 years.
- Spontaneous cyst on the eyelid - serous (in terms of fluid content) and pearly (resembles a white dense ball).
The causes are unknown, cavities appear at any age. It is known as a lower eyelid cyst because it most often appears on the lower eyelid. Serous tumor of the upper eyelid. - The traumatic type (or corneal cyst) is formed due to the impact of epithelial cells on the eye organ. For example, an eyelash can get into the mucous membrane of the eye and gradually grow.
- Exudative - develops due to eye diseases (for example, glaucoma).
- Cyst on the conjunctiva of the eye - there are two types: implantation (after surgical treatment) and retention (due to stagnation of lymph and purulent fluid).
Tumor on the conjunctiva of the eye organ. - Stromal - the cavity appears unexpectedly, can move throughout the eye, and then disappear. Causes significant discomfort.
- Dermoid cyst of the eye - is formed due to fragments of epithelial cells of the hair, skin and nail plates.
- A Moll cyst develops due to blockage of the sweat glands of the eye.
Symptoms
The neoplasm at the initial stage causes virtually no discomfort and grows asymptomatically. You can detect a cyst by external examination or palpation of the eyelids - the ball will be dense and painless, felt like a small nodule under the skin.
The tissues of the eyelid do not close tightly due to the tubercle that has arisen.
- narrowing of the field of vision - depending on the location of the eye, it ceases to cover most of the space. Most often it develops when the cyst is on the outside of the conjunctiva;
- clouding - vision becomes cloudy, the picture is not fully perceived, since the cyst actually blocks the view, being on the eyeball;
- flickering before the eyes;
- bright flashes on the back of the eyelids;
- dull pain that bursts the eye organ from the inside;
- the tissues of the eyelid do not close tightly due to the tubercle that has arisen, and deformation develops;
- redness of the eyeball;
- swelling of the eyelids (often affects the upper ones, less often the lower ones).
Externally, the cyst resembles a ball with yellow contents in the center. Many people mistake the tumor for a purulent pimple if it is located on the eyelids. The significant difference is that the cavity ball is dense and moves under pressure rather than being squeezed out like a pimple. Also, around the cyst on the eyelid there is no characteristic redness like inflammation.
A more radical method is to remove the cyst using traditional surgical techniques or laser enucleation. In addition to the cyst itself, the capsule is also removed, which significantly reduces the likelihood of chalazion recurrence.
A cyst on the eye tends to form in various parts of the eye. Cystic compaction can be external or internal.
Neoplasms of the cornea, lacrimal gland and duct
The most common types of benign tumors of the cornea, lacrimal gland and duct are:
- Cavernous hemangiomas.
- Pterygium.
- Pleomorphic adenomas.
- Histiomas.
- Hyperplasia of local tissues.
Cavernous hemangioma
A slow-growing tumor of the blood vessels of the eye. Most often it appears in adulthood, and only in one eye.
The main symptoms: a painful, wine-colored, red, or maroon-colored tumor that clearly protrudes beyond the eye, a feeling of eyelid distension, and deterioration in vision clarity.
Treatment: in the absence of growth - observation, with active growth - removal using PDT (photodynamic therapy), laser, cryodestruction and laser coagulation.
Pterygium
Pterygoid hymen on the side of the eyeball. Age of patients: from 20 to 50 years. Appears in the conjunctival area closer to the nose and can grow into the cornea. The incidence of pterygium is especially high in people living in dry, dusty, hot conditions. Symptoms: formation of a white film with sparse blood vessels, eye irritation, swelling and itching, decreased visual acuity.
Treatment: surgery, corneal and conjunctival transplantation.
Benign tumors of the lacrimal glands:
- pleomorphic adenoma;
- hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue;
- benign fibrous histioma.
These are slow-growing tumors, most often occurring at the age of 40-50 years.
Symptoms: painless displacement of the eyeballs, swelling of the upper part of the eyelid.
Treatment of benign tumors of the lacrimal gland is surgical; pleomorphic adenomas can recur.