Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
8 years of experience
Make an appointment
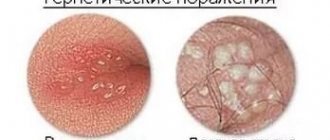
Hyperkeratosis is a general name for a group of pathologies, the main symptom of which is excessive keratinization of the skin. Cells of the outer, stratum corneum, under the influence of a certain factor, activate the process of division, while the desquamation of dead cells slows down. As a result, the skin is covered with a stratum corneum, the thickness of which varies from fractions of a millimeter to several centimeters. Any part of the body can undergo keratinization, depending on the causes of the pathology.
Varieties of the keratinization process
There are hereditary and acquired hyperkeratosis of the skin. Depending on the clinical manifestations, pathology can take various forms:
- follicular - flakes of exfoliating skin clog the ducts of the follicles, which is why numerous small tubercles appear on the skin, similar to pimples;
- lenticular - horny papules appear on the hair follicles of the lower extremities; when they are removed, small depressions remain on the skin;
- disseminated - formations resembling short and thickened hairs appear on the skin;
- seborrheic - on the scalp, sometimes on the facial skin areas of peeling form in the form of a greasy, easily removable crust, under which reddish skin spots are found;
- diffuse – large areas of skin on any part of the body are affected, sometimes even the entire skin, the sebaceous glands stop working, the skin dries out and peels;
- warty - formations appear on the skin that resemble warts, but without the participation of papillomavirus, and sometimes they degenerate into tumors;
- senile – dark, keratinized spots appear on the skin of older people.
Disseminated and lenticular forms tend to develop in older men. They rarely affect women and young people.
Symptoms of the disease by type
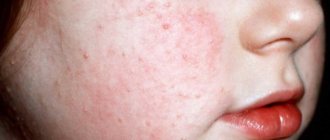
Chicken skin is a harmless condition. Keratosis pilaris got its name because the rashes look like chicken pimples - small, light-colored pimples. They usually form on the shoulders and forearms, thighs or buttocks. In very rare cases they may appear on the face. The structure of the rashes is harsh. Occasionally accompanied by redness.
Formations often appear during the cold season, but by summer they may disappear. At the same time, traces of keratomas remain on the body. If the spots become larger than 3 mm, they can cause pain.
The main cause of “chicken skin” is excess keratin. It accumulates in the body, thereby blocking the development of the hair follicle. But experts still don’t know why this happens.
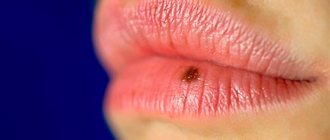
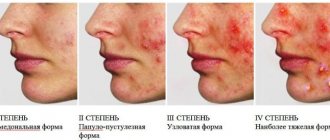
Solar keratosis (actinic) is characterized by reddish spots on the skin. Their size varies from 1 to 3 mm, and can occasionally exceed these values. The spots feel rough to the touch, but over time they develop into compacted, flaky growths. A distinctive feature is irritated, reddish skin around the rash. The rash may appear on the neck, chest, face, head, and arms.
Actinic keratoses should be taken seriously as this type can develop into skin cancer. Regular monitoring by a dermatologist is recommended.
The causes of seborrheic keratosis are unknown. The pathology is manifested by formations on the skin, which are covered with a black keratinized substance. The disease is often called actinic keratosis because it develops in older people. The main places of appearance are arms, chest, neck, face. The size of the keratoma can range from a few millimeters to 2.5 cm.
This type of disease develops quite slowly and does not develop into a malignant tumor. If the affected area begins to grow rapidly, bleed and at the same time cause pain, you should urgently consult a specialist. It is possible that cancer is disguised as actinic keratosis.
Symptoms
The main symptom of hyperkeratosis is the appearance on any part of the body of thickened skin with reduced sensitivity, often with a changed color that differs from the main shade. In the initial stage, the skin gives the impression of being rough, then the thickness of the stratum corneum increases, sometimes to such an extent that it begins to cause discomfort. In particular, advanced hyperkeratosis of the feet can lead to changes in gait. The keratinized skin flakes off or partially peels off; painful cracks may appear in the thickest and driest areas, which take a long time to heal and become sites of infection. Often the pathology is accompanied by dry skin and decreased function of the sebaceous glands.
Classification
In order to somehow understand the many forms and manifestations of dermatological diseases, they were divided into 2 large groups:
- hereditary keratosis;
- acquired keratosis.
Some experts isolate actinic keratosis, considering it a separate pathological condition with its own causes and symptoms.
Hereditary forms
This is the largest and most diverse group. Hereditary keratoses develop with equal frequency among men and women, affecting both very young people and the elderly.
Common genetic forms:
- Ichthyosis . Distributed throughout the body, keratinization of the epithelium resembles fish scales;
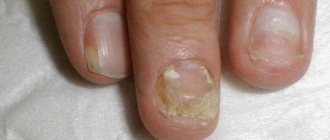
- Palmoplantar keratosis (hereditary keratoderma). The disease usually begins in childhood and only progresses with age. It affects the palms, soles, fingers and toes. In its advanced form, it spreads to the elbows and knees;
- Follicular keratosis simplex. It occurs against the background of blockage of hair follicles by overgrown scales. Appears at an early age and reaches its peak during puberty. Localized in the area of the shoulders and elbows, on the hips, less often on the stomach and back;
- Hereditary polykeratosis. The disease includes signs of other forms of keratosis and proceeds in waves, with periodic exacerbation of one or other manifestations.
Each of these forms is combined with numerous lesions and disorders of body systems and has many subtypes with varied symptoms.
Acquired forms
This group includes keratoses formed against the background of adverse external influences or as a result of chronic pathologies, hormonal imbalances and disorders of nervous trophism.
Among the acquired forms the most interesting are:
- Menopausal keratosis. It is observed in women during menopause. Accompanied by obesity, hypertension and thyroid dysfunction;
- Professional keratosis. Caused by constant exposure to traumatic factors. Manifested by callus on the hands;
- Infectious keratosis. Develops against the background of sexually transmitted diseases, tuberculosis.
Horny epidermis can also appear from a lack of vitamins A, E and C, a one-sided diet or constant adherence to strict diets. In some cases, keratosis develops as a symptom of metabolic disorders in the body.
Senile
It occurs due to degenerative changes in the tissues of the epidermis and dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. It can be senile and seborrheic. In the first case, the provoking factor is excess ultraviolet radiation. Actinic keratosis occurs on exposed areas of the skin.
The seborrheic form resembles flat, loose, dark-colored warts. Such growths can be located throughout the body.
Reasons for the development of pathology
All causes of keratosis development can be divided into two groups. The first includes external influences - tight shoes or clothing that rubs certain areas of the skin, intense physical labor, constant contact with chemicals or other substances that negatively affect the skin, failure to comply with hygiene rules, etc.
The second group includes diseases and pathological conditions that lead to excessive formation of the stratum corneum:
- systemic disorders, congenital or acquired - ichthyosis, diabetes mellitus, psoriasis, keratoderma, etc.;
- circulatory disorders, most often occurring in the lower extremities - varicose veins, obliterating atherosclerosis;
- lack of vitamins;
- fungal diseases of the skin (lichen) and feet;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- stress;
- excess weight, foot pathologies, lameness.
Under the influence of certain factors in the upper layer of the skin, capillary blood supply is disrupted and innervation worsens. Because of this, the process of cell division in the stratum corneum is activated, with a simultaneous slowdown in their desquamation and the formation of thickened keratinized areas.
Forecast
It should be noted that this disease is well treated, especially if therapy is started early in the development of the pathology. The prognosis is very good. Naturally, if you do not adhere to certain preventive measures, relapses of the disease may occur.
If the patient has too frequent occurrence of keratomas, and their treatment requires a long time, then you should definitely contact an oncologist. The fact is that during the diagnosis of the disease, the dermatologist must take part of the tissue for a biopsy to make sure that the neoplasm is not malignant.
Diagnostic methods
As a rule, with hyperkeratosis, diagnosis consists of identifying the disease that led to the formation of keratinized areas. The dermatologist conducts an external examination and interviews the patient, checking for signs of skin diseases. As a rule, a qualified specialist can recognize the disease by external signs. For clarification, differential diagnosis may be necessary, which is necessary if the manifestations of the pathology are similar to other skin diseases, which are also characterized by peeling and dry skin. If there are difficulties in determining the diagnosis, a biopsy of the affected area of skin is performed with histological examination of the tissue.
Diet for illness
To improve the condition of the skin with keratosis, you need to follow a diet. The foods consumed must contain vitamins A, E, B, ascorbic acid: herbs, vegetables, cereals, fatty fish.
Include cold-pressed vegetable oils in your diet:
- sea buckthorn;
- pine nuts;
- walnut;
- amaranth.
By consuming oils daily, you can nourish the body with polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and minerals, which promote cell regeneration and are a good prevention of keratosis.
Exclude rich, flour products, fried and fatty (animal fat-based) dishes from your diet.
Treatment
The treatment method for hyperkeratosis depends on the form of the disease and the cause that caused it. As a rule, during periods of exacerbation, local use of corticosteroid ointments is indicated, which relieve inflammation and exfoliate dead skin. Mild acid peeling with the help of special creams helps to get rid of hardened layers of skin. Mechanical removal of hardened areas is not recommended, as this may increase the formation of the stratum corneum. Warm baths with the addition of salt, baking soda or starch, after which a moisturizer is applied to the skin, have a good effect.
Hyperkeratosis of the scalp is treated with softening compresses, for which castor oil, petroleum jelly or glycerin, fish oil, etc. are used. If necessary, ointments containing hormones can be prescribed. In the follicular form of the disease, external treatment of the stump is of great benefit, so therapy is aimed at eliminating disturbances in the functioning of the body.
In case of hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet, it is necessary to first eliminate the factor causing the pathology. Often the pathological factor is a skin fungus, which is treated with special antifungal ointments. A good effect is achieved by warm foot baths with table salt, after which the steamed stratum corneum is removed using pumice, and the skin is lubricated with a softening cream. It is necessary to choose comfortable shoes that do not squeeze or rub the foot. If the patient suffers from clubfoot or flat feet, care should be taken to choose special shoes.
Causes of neoplasms
To date, it is not known for certain why keratosis of the skin appears. Only one thing can be said for sure: this pathology is not caused by a virus, so it is not contagious. However, some internal and external factors can contribute to its development. For example:
1. Age (senile keratosis of the scalp). Most often, symptoms are observed in people over 40 years of age.
2. Genetic predisposition.
3. Poor diet with large amounts of animal fat.
4. Disturbance of metabolic processes in the human body.
5. Long-term hypovitaminosis.
6. Frequent exposure of the skin to direct sunlight.
Prevention
To prevent the re-development of hyperkeratosis, it is necessary to care for the skin, ensure its nutrition and hygiene. The following will help prevent relapses of the disease:
- normalization of nutrition, provision of a varied, balanced diet;
- avoidance of prolonged exposure to the sun or hypothermia of the skin;
- hygiene, skin care;
- use of protective equipment when working with chemical reagents.
Some forms of the disease are extremely difficult to treat and remain with a person throughout his life. In this case, it is especially important to pay attention to preventive measures that reduce the risk of relapse.
Folk remedies and recipes
To relieve the symptoms of the disease, you can use folk remedies.
- Freeze agave leaves for 3 days. Remove from the refrigerator and apply to the affected area overnight. After removing the compress, treat the keratoma with salicylic alcohol. The course of treatment is 3 weeks.
- Apply grated raw potatoes to the affected area. Cover the top with a clean cloth and polyethylene. After 40 minutes, remove the bandage and rinse off the remaining potatoes with water.
- Take 2 tablespoons of dried celandine leaves and pour 250 ml of boiling water. Leave for several hours. The product can be used to wipe the skin or make lotions.
- Pour 1 spoon of onion peel with a spoon of vinegar. Leave for 2 weeks in a dark place. Strain and make 30-minute lotions. It is important to avoid contact of acid with healthy areas of the skin to avoid causing a burn.
Attention! Before using folk remedies, consultation with a dermatologist is required.
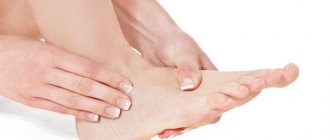
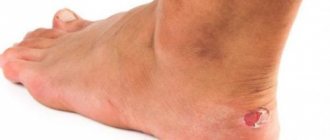
What is foot hyperkeratosis?
The skin of the feet has a unique structure when compared to the skin on other parts of the body. Its main task is to adapt to external stress during physical activity.
Content
- What is foot hyperkeratosis?
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
- Expert commentary
Hypertrophy of the stratum corneum, known as hyperkeratosis, is one of the main protective mechanisms and is caused by increased external mechanical stress.