Last update: 01/14/2020
Burns resulting from exposure to high temperatures are called thermal. They are among the most common household injuries. Unfortunately, this kind of damage can be caused not only by touching a hot iron or knocking over a cup of hot tea, but, so to speak, by simply being in the wrong place at the wrong time.
Imagine that you are bending over a saucepan to see if the water has boiled, you are cooking dinner in a double boiler, or you have decided to fix a small breakdown of the radiator pipes yourself. Unfortunately, the consequences can be very unpleasant: the most likely outcome is a steam burn. Less common, but no less dangerous, are oil burns.
Classification
As the water heats up, steam appears. Its temperature, especially if it is formed under pressure, is above 100 ℃. Once on the skin, the steam transfers its heat to it and causes serious damage .
There is a special classification of steam burns according to severity:
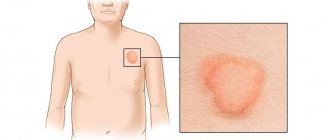
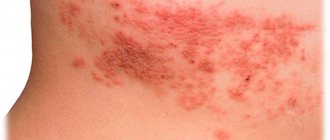
- The first degree is diagnosed when redness and slight swelling of the surface layer of the epidermis are detected. The affected area hurts and looks inflamed.
- The second degree is characterized by the appearance of blisters filled with yellowish liquid. The surrounding skin turns bright pink and swells.
- The third degree is necrosis of the upper layers of the epidermis. Long-healing wounds and blisters with blood form on the body.
- The fourth - causes necrosis of the middle layer and can affect the fat layer, muscles and bones.
The severity of the condition depends on the area of the lesion. 1st and 2nd degree burns, if less than 5% of the skin is injured, do not require hospitalization. Grade 3 and 4 hot steam wounds require professional therapy in a medical facility.
Possible affected areas
Steam can easily damage any part of the human body. In addition to the skin, the eyes and larynx can be injured.
The strong influence of steam provokes a painful shock, leads to an infectious process and intoxication of the body.
Skin
At risk are:
- arms and legs;
- back;
- breast;
- face and neck;
- groin area.
After receiving an injury, it is important to determine its area. To do this, you can apply the palm rule. According to it, an open human palm is equivalent to 1% of the human body. If the affected area is more than 5 palms, the genitals, face are burned, or necrosis is observed, you should urgently call an ambulance. Self-treatment is not allowed.
Eyes
If you handle boiling water carelessly, steam particles can damage your eyes. Long-term exposure destroys the cornea, conjunctiva and can lead to blindness. Such burns are rarely diagnosed. In times of danger, a person reflexively closes his eyes, so the hot stream burns the eyelids and skin around the eyes.
The severity of a thermal burn of the visual organ is difficult to diagnose in the first hours. The victim may not experience severe pain due to the destruction of nerve endings.
To prevent pathological changes in the structure of the eye, you need to contact an ophthalmologist, even if the injury seems minor. This will help preserve your vision.
Airways
Respiratory tract burns occur when vapor is swallowed or inhaled. In most cases, the face and neck are simultaneously injured.
Hot air can damage:
- language;
- trachea;
- larynx;
- mucous membrane of the mouth and nose;
- lungs;
- esophagus.
Symptoms include swelling, hoarseness, pain when swallowing, difficulty breathing, and cough. A person may experience painful shock and lose consciousness.
A medical examination is required to determine the extent of the damage. It is urgent to provide primary aid and send the victim to the hospital.
Symptoms
Internal injuries may be suspected if the victim's upper torso, head, or face are burned.
The main symptoms are:
- painful sensations behind the sternum;
- burning in the mouth and throat;
- labored breathing;
- temperature increase;
- hacking cough;
- dry wheezing;
- coughing up blood particles;
- hoarseness of voice.
Taking a closer look at the person, you can notice swelling of the tongue and lips. In some cases, suffocation and heart failure develop.
Thermal burn
Signs depend on the type of burn injury. Thermal burn provokes:
- severe pain;
- blueness and swelling of the lips;
- shortness of breath;
- dizziness.
Burns of the trachea and lungs caused by exposure to smoke lead to bronchospasm. During the examination, particles of soot are observed in the oral cavity, and the surface of the face is often burned.
Chemical burn
Burns to the mucous membrane are caused by various chemicals.
The victim has an inflamed throat, vomiting, bloody sputum, and a painful cough.
The clinical picture is complemented by:
- pale skin;
- redness of the eyes;
- swelling of the nose and throat;
- burning in the chest.
In the first day after injury, bronchial burns cause swelling of the mucous membrane and difficulty breathing. An inflammatory process gradually develops, threatening the patient’s life.
First aid
- If the skin is burned, human contact with the steam should be interrupted. Carefully remove clothing without touching the wounds with your hands.
- To prevent the affected area from deepening, you need to cool the sore spot by placing it under a weak stream of cool water for 20 minutes.
- If there is no access to water, you can take ice from the refrigerator, wrap it in a towel and apply it to the burn.
- Ice should not be placed directly on burned skin. A sharp change in temperature provokes cell death and aggravates the problem.
The wound needs to be treated with an antiseptic. Chlorhexidine, Furacilin solution or potassium permanganate diluted with water are suitable. If you have a healing ointment in your medicine cabinet, you should carefully apply it to the affected area with a swab.
To provide first aid, you can use Panthenol, Levomekol, and Rescue balm. After applying the ointment, a sterile gauze bandage is required.
For eye burns
If your eyes are damaged, they must be immediately cooled in clean water. The procedure should last at least 20 minutes. You can lower your face into a container of liquid and periodically open and close your eyelids, or wipe your eyes from the inner corner to the outer corner with a wet gauze cloth.
Then you should drop 2-3 drops of an antiseptic, for example, Albucid, into your eyes, apply a bandage, take a painkiller tablet and go to the doctor.
For burns of the larynx
Ingestion of steam is fraught with dangerous consequences. The patient needs to provide an influx of fresh air, lay him on his side, making sure that his head rises above the body, rinse his face and mouth with cool water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate and urgently call an ambulance.
What not to do?
When providing assistance to a victim, it is important to adhere to established recommendations and know what not to do. The main task is not to worsen the patient’s condition. You should not try to rip clothing from a wound on your own. It is enough just to cut it around the lesion. Under no circumstances should the wound be cleaned with non-sterile means. Such manipulation is carried out only after preliminary anesthesia.
Do not puncture blisters.
You should not apply the first product you come across if you are not sure of its need. It's better to consult a specialist. Also, you should not apply a bandage if you do not know how to do it correctly. An incorrectly applied bandage can cause swelling.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures depend on the severity of the injury. First and second degree burns can be treated at home using anti-burn medications . The dressing should be changed every 4 hours and ensure that there is sufficient air flow to the skin.
Grade 3 and 4 injuries require professional intervention, so treatment occurs in an inpatient setting. Wounds are regularly washed with antiseptic preparations and treated with antimicrobial ointments. For pain relief, injections of Lidocaine or Novocaine are used.
To restore the mucous membrane of the eyes, the doctor prescribes Levomycetin or Albucid drops. The affected eyelids are washed with Furacilin, then a bandage is applied with Syntomycin ointment. Treatment should be carried out in the ophthalmology department.
Drug therapy
To treat thermal burns from steam, doctors recommend:
- Panthenol, available in spray form. The drug contains panthenolic acid, which stimulates cell regeneration and normalizes metabolic processes. Treatment should be carried out by evenly distributing the foam over the wound.
- Cream Bepanten based on dexpanthenol. Using the product reduces inflammation, relieves swelling and accelerates tissue healing. The cream is good for superficial burns.
- Aerosol Olazol. The composition contains chloramphenicol, sea buckthorn oil and painkillers. Application soothes burning sensation, prevents infection, promotes tissue restoration.
- Levomekol. The ointment contains chloramphenicol and methyluracil, which cope with pathogenic microflora and saturate with oxygen. The drug can be used to treat burns with blisters.
Ointments based on silver ions help heal wounds well. They eliminate germs and restore the integrity of the epidermis. Damage from water vapor should be treated with Argosulfan and Dermazin, which include silver sulfathiazole.
Medications should be applied to the affected areas 3-4 times a day. Apply a bandage if necessary.
Folk remedies
In addition to traditional therapy, the use of traditional methods is allowed. Ointments made from natural ingredients are useful.
- Melt 100g unsalted butter. Pour in 40 g of linseed oil and add the same amount of beeswax. Stir, cool and smear the sore areas 3 times a day until complete healing.
- Combine three large spoons of crushed calendula flowers with 100 g of pork fat. Heat in a water bath for one and a half hours. Cool slightly and strain. Add the contents of the vitamin E ampoule to the cool mixture. Apply the ointment in a thick layer 3-4 times a day.
- Boil a large onion without peeling and mash with a fork. Mix with a spoon of olive oil. Apply to the wound and cover with gauze. Change the bandage twice a day.
- You can make a compress from raw potatoes. Grate the washed vegetable. Wrap in gauze and place on the injury site. Apply a new compress every 2 hours.
- Aloe or Kalanchoe juice quickly soothes the pain from a steam burn. You need to squeeze the juice out of the plants, moisten a sterile bandage and place it on the inflamed skin. After an hour, remove. Repeat the procedure 3-4 times a day.
Lotions made from medicinal herbs have worked well. Suitable for therapy:
- oak bark;
- series;
- chamomile;
- calendula.
Steam two spoons of any of the herbs in 0.5 liters of boiling water. After half an hour, pass through the filter. Soak the bandage in the cooled liquid and apply it to the sore spot several times a day.
What not to do
When providing emergency care, you must adhere to strict hygiene rules to avoid infection.
- Do not apply vegetable oil or fat to fresh burns . They create a transparent film that disrupts heat transfer. As a result, the burn deepens into the skin.
- During treatment, disinfection with alcohol-containing solutions is prohibited. Aggressive substances dry out the epidermis, irritate it and delay recovery.
- It is important that the affected area has access to oxygen. To do this, you need to leave the wound without a bandage for several hours a day.
Actions are strictly prohibited in case of thermal burns
It is forbidden:
- Lubricate burns with any oil: vegetable, cosmetic, and the very common sea buckthorn;
- If blisters appear, you should not try to open them yourself, as this may lead to infection of the wound. Opening of formations can only be performed by a surgeon in a hospital or treatment room, using sterile instruments;
- Use alcohol or alcohol-containing solutions for processing;
- Bandage burns tightly.
These are the most common mistakes that people make because they do not know the rules of first aid.
When to see a doctor
Any burn of the mucous membrane of the eyes, respiratory tract and epidermis needs to be examined by a specialist. Superficial injuries not exceeding 5% of the skin do not require hospitalization. The doctor prescribes treatment, which the patient carries out at home.
You should seek medical help in the following cases:
- the bubble burst and the wound became infected;
- an accumulation of pus appeared at the burn site;
- I am worried about severe swelling and pain for several days;
- The temperature rose to 38 degrees.
Even minor injuries caused by steam should not be underestimated. Without proper treatment, they take a long time to heal and can cause serious complications.
Why is a steam burn more dangerous than a boiling water burn?
- Water and the steam formed when it boils differ in temperature. The temperature of steam is much higher than water. This is the reason for the increased danger when exposed to steam; the burn from it is much stronger and more severe.
- When hot water hits the human body, the liquid quickly cools to a normal temperature of 36.6ºC. The transition of steam from a gaseous substance to a liquid creates condensation and releases much more heat. This is another danger of steam burns.
- Treatment of burns with boiling water