Dermatology is a separate branch in medicine that studies the work and structure of the skin, hair, mucous membranes, nail plates, sweat and sebaceous glands, and the treatment of their diseases. Lesions may also appear on the legs. Skin diseases of the legs are accompanied by discomfort that can disrupt the usual way of life and cause malaise.
Causes and mechanisms
The skin on the legs is exposed to external and internal factors that contribute to the development of pathological processes in it. The first include heterogeneous effects - mechanical, physical, chemical or biological:
- Traumatic injury (abrasions, cuts, bruises).
- High and low temperature.
- Excessive sun exposure.
- High humidity.
- Microbes (bacteria, viruses, fungi).
- Neglect of personal hygiene.
- Occupational hazards, etc.
The epithelium has barrier properties, preventing the negative influence of external conditions. However, with severe damage, compensatory processes become insufficient to eliminate the violations. The skin's protective mechanisms are also weakened as a result of internal reasons:
- Poor nutrition and vitamin deficiencies.
- Allergic predisposition.
- Immunodeficiencies.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Endocrinopathies (diabetes mellitus).
- Circulatory disorders (atherosclerosis, endarteritis, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis).
- Hepatic and renal dysfunction.
- Psycho-emotional stress.
- Genetic conditioning.
Against the background of systemic disorders, the activity of general and local immunity decreases: the number of lymphocytes decreases, the synthesis of antibodies and nonspecific resistance factors is inhibited. Under such conditions, any external irritant, especially of infectious origin, will fully demonstrate its pathogenic properties.
The list of causes and factors predisposing to skin diseases of the legs is quite diverse. And to establish the source of the violations, you need to contact a specialist.
Possible complications
The sole of the feet is a place that, if not treated systematically and regularly, if trophic ulcers appear on the feet, then the penetration of microorganisms into the skin will quickly spread throughout the body through the bloodstream. This will cause serious complications:
An ulcer exposed to toxic damage will begin to rot. Decay tissues, releasing toxic products, will quickly disperse through the blood with the lymph flow and further throughout the body.
Against the background of infection, the disease will begin to progress, and as a result, oncology and tumor development can occur.
The risk group includes not only patients with diabetes, but also those with weak immune systems and those infected with HIV, for whom even a minor ulcer on the leg becomes deadly.
Prevention is paramount. Important:
- follow a diet;
- avoid injuring the skin on the legs;
- wear comfortable shoes;
- Keep your blood glucose levels under control to avoid developing diabetic foot ulcers.
Trophic ulcers have long been known to people, although treatment and prevention remain relevant to this day.
Types of pathology
Various diseases occur in the lower extremity area. They can be infectious-inflammatory, allergic, toxic, neurotrophic or other in nature. The most common pathology on the legs is:
- Dermatitis and dermatoses (eczema, neurodermatitis).
- Mycoses (athlete's foot, onychomycosis).
- Plantar warts.
- Trophic ulcers.
- Psoriasis.
- Erysipelas.
Of course, the skin of the lower extremities can be affected by other diseases, for example, pyoderma, scabies, secondary syphilis, and tumors. The range of possible disorders seems to be very wide, but a pathology that has become widespread requires careful consideration.
Symptoms
Skin diseases of the legs are of a different nature, therefore the signs of pathology will be varied. To find out the cause of what is happening, you need to analyze the clinical picture, which is what the doctor will do. After the interview, he will conduct an examination, confirming it with palpation, and, if necessary, refer the patient for additional studies. All this is necessary for one single purpose - to make an accurate diagnosis.
Eczema
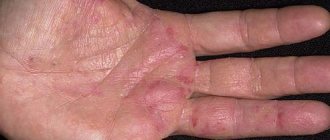
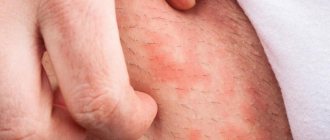
The disease, known as eczema, occurs in several stages. First, a swollen area of redness appears on the skin - erythema. Then, against this background, multiple small vesicular eruptions (vesicles or seropapules) appear, which very quickly burst with the formation of erosions. From the depths of the latter, a transparent liquid constantly oozes, which creates a continuous wet surface. The serous exudate gradually dries out, transforming into yellowish crusts, under which epithelization occurs.
Different elements can be present simultaneously, creating a polymorphic picture. The acute process gradually turns into a chronic form, manifested by increased infiltration and lichenification (emphasis of the skin pattern). The color of the affected areas becomes more stagnant (bluish), and peeling appears. The lesions do not have clear outlines, and the inflammatory process is accompanied by intense itching. Eczema is also characterized by symmetry of the lesion and a tendency to spread peripherally.
There are several types of eczema: true, microbial, seborrheic, occupational, etc. But all forms of the disease have a number of common symptoms.
Neurodermatitis
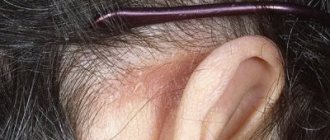
The development of neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis is caused by an allergization of the body to a certain substance. Signs of the disease on the lower extremities are usually localized in the area of the popliteal folds. At first, limited neurodermatitis does not manifest itself in any way; patients are only bothered by intense itching, which causes them to scratch their skin.
Over time, dense papules covered with small scales appear at the site of the lesion. Individual nodules merge into larger flat plaques - they have an oval or round shape, and are colored pale pink or brownish-red. The skin pattern becomes more pronounced, lichenification forms, and the period of exacerbation intensifies redness and peeling.
The course of atopic dermatitis is long. Due to intense itching, patients develop neurotic disorders:
- Emotional lability.
- Irritability.
- Insomnia.
- Exhaustion, etc.
This is accompanied by functional disorders of the autonomic nervous system in the form of white dermographism, impaired sweating, enhanced pilomotor reflex, etc. These disorders, in turn, support the course of the disease, forming a vicious circle.
Athlete's foot
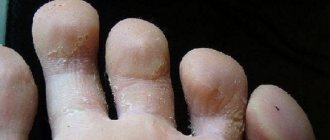
Athlete's foot is a skin disease of the legs that is of fungal origin. First, red scaly spots with a diameter of up to 10 mm are formed on the skin, which increase in size. As a result, the lesions become quite large, with a hyperemic and flaky surface, on which blisters and crusts can be seen.
Further development of the disease leads to the formation of large areas with polycyclic outlines. Their center gradually turns pale and sinks, and along the periphery, on the contrary, a more raised edge is noticeable, covered with macerated and flaky epithelium. Patients report mild itching as a subjective sensation. The onset of epidermophytosis is acute, but it quickly becomes chronic with a long, undulating course.
Onychomycosis
When the skin of the feet is affected, the fungus can spread to the nail plates, which leads to the development of onychomycosis. The disease is accompanied by a change in the appearance and normal structure of the nails:
- White or yellow spots.
- Loss of transparency.
- Thickening.
- Fragility.
Damage to the skin of the fingers is accompanied by peeling, cracks and itching. Redness and secondary infection may appear around the nail.
Onychomycosis is a common fungal disease that primarily affects the toenails.
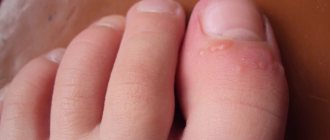
Plantar warts
Plantar warts are localized on the skin of the feet. A deep process is accompanied by the appearance of a rounded compaction, which is a focus of hyperkeratosis. When pressing on it, pain is felt. After removing the central part, the papillary surface becomes visible, surrounded by a ridge of keratinized skin.
Superficial warts do not cause physical discomfort. They disguise themselves as calluses and corns because they are very similar to them. Diffuse foci of hyperkeratosis can exist for years. Both types of plantar warts are caused by the human papillomavirus.
Trophic ulcers
Trophic ulcers can form on the legs and feet, the development of which is associated with microcirculatory, neuropathic and metabolic disorders. In diabetes mellitus, ulcers are usually localized on the sole in areas of greatest pressure and over bony protrusions. Against the background of a decrease or loss of sensitivity, pain is practically not felt, so the wound can be quite deep. If the process progresses, gangrene may form, requiring amputation.
With venous insufficiency or pathology of the arteries, trophic ulcers are localized mainly on the legs. First, a small whitish spot forms, in the center of which an epithelial defect appears, and the latter gradually increases in size and deepens. The bottom of the ulcer is covered with fibrin clots, exudate with an unpleasant odor oozes from it, and when the wound becomes bacterially infected, pus is formed. Along the periphery, the ulcer is surrounded by a rim of hyperemia and infiltration; with deep defects, pain occurs.
Interdigital (intertriginous) form
The most common and unpleasant type of pathology is the intertriginous form of fungal infection. It appears quite often in the summer and begins to develop between the third and fourth fingers. Over time, the lesion spreads to areas between other fingers.
At the very beginning, a small crack, funnel or sore appears in the fold that is located between the fingers. It is surrounded by diaper rash or flaky skin that is slightly greenish in color. Most often, the injury becomes wet, and sometimes pus oozes from it. The erased type of fungus is characterized by pronounced or mealy peeling, as if there is flour on the surface of the finger.
In advanced forms of the disease, nail separation, severe coarsening, multiple cracks, callus-like horny seals, and pronounced yellowing are observed.
In very rare cases, a weeping type disease develops - exudative fungus. Its main difference is that vesicles appear on the affected areas - bubbles filled with liquid inside. Therapy should be carried out comprehensively. Mycozoral, Lamisil, and Clotrimazole are used as topical agents.
Nail fungus (mycosis)
Fungal diseases are very common. The chance of becoming infected with a fungus awaits us in the pool, sauna, bathhouse and even, unfortunately, at a party if you wear the slippers of an infected person. The human body is an ideal environment for the development of fungus, especially if a person suffers from excessive sweating, as well as if he has a weakened immune system and a low level of personal hygiene. The fungus affects the nail tissue and adjacent skin. Its symptoms include a change in the color of the nail plates to a sickly yellow, their thickening or, conversely, fragility, a feeling of itching around the nails, an unpleasant odor, small cracks in the folds between the fingers. Also, nails may begin to peel and crumble, making them simply impossible to grow back. If you notice the above symptoms, you should immediately consult a specialist. Treatment of fungus is very long and painstaking, and the more advanced the disease, the more difficult it is to treat. For treatment to be most effective, the type of fungus must be correctly identified.
Skin diseases on the legs with diabetes
With diabetes mellitus, the following changes occur in the skin of the legs:
- It becomes rough and dry.
- The nail plates begin to grow.
- More calluses appear.
- The skin becomes bright yellow.
Let's celebrate! All skin diseases of the legs that can occur with diabetes are pathological. Most often, diseases are associated not only with changes in the skin, but also with a deterioration in metabolic metabolism, problems in blood vessels and the enrichment of the skin with nutrients.
Photo and treatment
With diabetes, the skin first becomes covered with spots that become inflamed. Diabetics must adhere to a special diet, which is important for improving the condition of the skin of a sick person.
Additionally, the attending physician may prescribe the use of medicinal ointments that have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. It is recommended to regularly anoint your hands and feet with vegetable oils; such a massage will not only improve blood circulation, but also soften dead skin.
Stages
The incubation period after infection with the fungus is 3–14 days. Its duration depends on the state of the immune system.
The following stages of disease development are distinguished.
- Initial. Dry skin and small cracks appear. The foot area becomes swollen and red. The patient complains of constant itching in the feet.
- Average. Peeling spreads to the entire foot, dark spots appear.
- Launched. Characterized by damage to the nail plates. They begin to exfoliate, the skin of the feet becomes covered with cracks and separates in large layers.
- Chronic. Occurs in the absence of adequate treatment. In this case, periods of temporary extinction of symptoms alternate with exacerbations.
Main causes
Not only the symptoms, but also the causes of the pathology differ significantly from each other. Dermatologists divide provoking factors into external and internal.
External reasons include:
- Negative environmental impact.
- Excessive tanning.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
- Problems with the activity of the central nervous system.
- Infectious diseases.
- Constant stress.
- Visiting beaches, swimming pools and bathhouses without slates.
Among the internal reasons are:
- Diseases of the kidneys, liver or intestines.
- Weakening of the immune defenses.
- Cardiovascular pathologies.
- Disturbance of the internal intestinal microflora.
- Avitaminosis.
Proper nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of skin diseases. Natural and healthy food will help fill the body with vitamins and minerals, which will activate the immune system and speed up the fight against pathology.
Mycosis of the foot in humans - diet and treatment
Mycosis of the feet is infection of the nails and skin of the foot by a parasitic fungus of various nature. Among all fungal diseases, this is the most common.
Below we will talk not only about the causes of the disease, but also about its treatment. Traditional methods of treatment are also used very widely.
Main causes of infection
The cause is mainly a simple failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene. You can acquire this disease:
- when walking barefoot in public places (baths, saunas, swimming pools);
- when using the same towel and other personal items;
- when wearing wet shoes and dirty socks.
If a person has once suffered from mycosis of the feet, then next time it will be much easier to develop fungus. The disease most often manifests itself in the folds between the toes (interdigital mycosis of the feet) of the feet and the base of the foot (mycosis of the nails and feet). It is very rare, but fungus on the hands occurs. This occurs when scratching mycosis #8212; the infection remains under the nails and spreads to various parts of the body.
When nails become infected with fungus, they change color: they become gray or acquire a green tint (the fungus settles between the nail and the skin). The structure of the nail is destroyed. Its treatment is more difficult, since the fungus lingers in some areas of the nail plate and is easily transferred to other parts of the skin. You can see the manifestation of mycosis of the legs, namely the feet, in the photographs below.
Onychomycosis
This disease is a type of foot fungus characterized by fungal infection of the nail. You can become infected in public showers, saunas, baths, and swimming pools. Scales containing a pathogenic microorganism are quite easily separated from the nail plate and can remain on floors, carpets, bedding, and unpainted benches. High humidity allows them not only to survive, but also promotes active reproduction, and therefore the risk of infection increases significantly.
At the initial stage, the infection reaches the epidermis of the feet, causing severe itching. In order to ease the discomfort, a person begins to comb the infected area, but this only worsens the situation. Areas of skin affected by the fungus become covered with small scratches and cracks, microorganisms begin to spread, penetrate under the nail plate, and then begin to multiply uncontrollably.
Severe illnesses such as diabetes or HIV, poor circulation, or injury to the nail greatly increase the risk of infection.
Onychomychosis is divided into 3 types.
- Normotrophic. With this type of onychomycosis, a change in the color of the nail from normal to yellow-brown is observed. The natural shine, shape of the nail and its thickness remain unchanged.
- Hypertrophic. A final change in the color of the nail occurs, its shine disappears, its shape changes, thickening develops and partial destruction begins.
- Onycholytic. The color of the affected nail changes to brown, it becomes thinner and begins to break. Its gradual separation from the bed begins. Uneven layers may appear on the exposed part of the nail bed.
Treatment of this type of fungus on the palms and soles with topical medications is ineffective due to the fact that the fungal spores are located under the nail. Before starting treatment, the nail should be removed. This is done with the help of keratolytic drugs, and patches are also used. In some cases, it is possible to remove the nail mechanically: parts of the nail that have died are cut off with a nail file or nippers. It is important to remember that all instruments used must be sterile.
The combined use of mechanical removal and keratolytic patches is the most effective way to remove diseased nails. For keratolytic agents, you can use the ready-made Mycospor kit. It contains a special ointment, files for scraping the nail, and a patch.
It is quite difficult to determine the type of foot fungus from a photo.
Calluses
Every person has encountered calluses. The main reasons for their appearance are considered to be inappropriate shoes, excessive stress on the feet, and excessive sweating. They are very painful and often make walking difficult or even impossible. The callus can be dry or wet. A wet callus develops very quickly, within one day, while a dry callus can take a long time to form. Typically, dry calluses are less painful.
To prevent calluses, you need to take good care of your foot skin and regularly use emollients. But if a callus does form, you need to cover it with a band-aid and provide your feet with complete rest. To remove dry calluses and calluses, you need to contact a specialist, since doing this at home is quite difficult. You can get rid of core calluses using laser, cryotherapy or hardware procedures.
Advice
Under no circumstances should you try to pierce a wet callus. The liquid contained in it protects tissues from infection. Over time, it will resolve on its own.
Erased form
Mycosis of the erased form is almost invisible, its symptoms are minimal. These include: mild itching, burning, flour-like peeling, microcracks located in the interdigital areas. If you do not contact a specialist when the first signs of the disease appear, the pathology can develop into the form of onychomycosis, which is much more difficult to treat. In this case, the peeled nail will grow back from one month to six.
Mycosis of the erased form is treated with local preparations: ointments, creams, foams. They allow you to create a layer on the foot that will protect against infection by other infections. It is not recommended to wash your feet for 24 hours after applying this drug.
Only in extreme cases can systemic therapy be prescribed. The problem is that such drugs are toxic and negatively affect some internal organs, such as the liver. Accordingly, if there is an effect from the use of local remedies, then it is better not to take pills.
Causes of skin diseases of the legs
Basically, there are several reasons that can cause problems with the skin of the legs. Let's look at them in more detail:
- First of all, it is worth highlighting that not all people are accustomed to following the rules of foot hygiene, so skin diseases arise, as crazy as it may sound, precisely because of dirt and germs that get on the skin.
- Prolonged exposure to water can also cause skin diseases.
- Prolonged exposure to high temperatures does not have a beneficial effect on the epidermis of the lower extremities; ulcers may open on the legs, which take a long time and are difficult to treat.
- Problems with the skin on the feet can occur in a person who has to wear tight or poor-quality shoes.
Let's celebrate! Naturally, these are not all the reasons that can cause skin problems on the legs, but they are considered the most common today.
External reasons
External factors in human health also play an important role, so leg health can deteriorate for the following reasons:
- Detrimental effects of the environment.
- Strong temperature changes and ultraviolet radiation.
- Varying degrees of injury and cuts that are complicated by infections and bacteria.
- Constant stress and depression.
- Being in a risk area, for example, in a pool, beach or bathhouse.
- A trip to a pedicure salon, where insufficient attention is paid to the treatment of tools, can have a detrimental effect on the health of your feet.
Let's celebrate! There are more external causes than internal ones, but there is no difference in their danger; whatever the influencing factors, they all pose threats to human life and health.
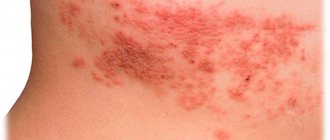
Eczema
Eczema on the legs can develop in anyone, regardless of their age and lifestyle. The patient notes a burning sensation, severe itching, watery pimples, and erosive formations. After the blisters burst, the skin becomes covered with a dry crust. Subsequently, it cracks and causes a lot of unpleasant sensations. Its occurrence is facilitated by high environmental humidity, since pathogenic bacteria develop most quickly in it. Sometimes eczema is a consequence of an advanced allergic reaction, but among the causes of its development are also hormonal imbalances in the body, weakened immunity, frequent and severe stress, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and metabolic disorders. It is very difficult to cure eczema on your own; you need to consult a dermatologist.
Advice
Proper nutrition plays an important role in treating eczema, so try to reduce your intake of fatty and fried foods.
Manifestations of psoriasis on the skin
Squamous-hyperkeratotic form
This type of foot fungus (pictured below) is not very common.
Squamosis is the process of penetration of pathogenic fungi into the outer skin cells. Hyperkeratosis is the formation of the stratum corneum, resulting in thickening of the dermis. In this regard, the squamous-hyperkeratotic form of mycosis has several other names, for example, “moccasin fungus” and “athlete's foot.”
The squamous-hyperkeratotic type of mycosis is characterized by the following symptoms.
- The sole of the foot is covered with a compacted keratinized layer of dermis, resulting in the impression that the foot is wearing moccasins.
- The coarsening of the sole occurs so strongly that it begins to become covered with wide and rather thick calluses.
- Painful cracks appear on the calluses.
- Peeling takes on a flour-like type, and a pattern on the skin can be seen with the naked eye.
- Unbearable itching appears.
- Over time, nails begin to thin, break and crumble.
When treating moccasin fungus, it is first of all very important to eliminate the stratum corneum of the skin. This is done using soap and soda foot baths, wraps, salicylic compresses, and ichthyol ointment. Salicylic ointment is used in dosages up to 10%. Vaseline-based creams and ointments containing lactic acid are effective.
Subsequent treatment for the type of foot fungus will depend on the type of pathogen. It should be started only after an accurate diagnosis has been made. It is not recommended to treat moccasin mycosis without first removing the stratum corneum of the skin - the active components in the medicine will not be able to penetrate through it and reach the source of infection. As a result, all efforts will be nullified.
Photos of types of foot fungus cannot fully reflect all the unpleasant symptoms that a person experiences.
Psoriasis
With psoriasis, plaques called psoriatic plaques form on the legs. Another name for them is papules. The acute period of the disease is replaced by remission. At first, the papules are single, they look like peculiar compactions that protrude slightly above the skin and have a reddish color. On top of them you can see whitish-gray scales that can be scraped off with a fingernail. Over time, the papules enlarge and merge with each other. This is how psoriatic plaques form. During the period of remission, a Voronov's rim appears around the plaques, which is a kind of whitish border.
Psoriasis, like other skin diseases of the legs, gives the patient a lot of unpleasant painful sensations, in addition, patients may experience psychological discomfort, since psoriatic plaques look very unattractive. The exact reasons for the development of psoriasis have not been identified, but among the provoking factors are a stressful environment, genetic predisposition, mechanical injuries, hormonal imbalances and disturbances in the functioning of the body’s immune system.
Nails affected by fungus
Athlete's foot
Athlete's foot occurs if the feet are constantly in a damp environment, for example, people who work in baths, gyms or saunas most often suffer.
This disease is contagious and can be transmitted to another person. Athlete's foot may not be noticed immediately, so the first symptoms appear a long time after the infection itself.
Photo and treatment
The main treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause. As a rule, doctors prescribe almost the same ointments as for mycosis.
If ulcers and cracks appear, they should be constantly treated with special medications. Today, there are a sufficient number of ointments and creams.
Dyhydratic form
Vesicular fungus, or, as it is also called, dyshydratic mycosis, is the rarest type of disease. Its main manifestation is numerous vesicles united in conglomerates. Vesicles are bubbles filled with pus or nutrient fluid from the inside. When the fluid begins to become cloudy, the vesicles burst, leaving ulcers in their place. They begin to merge into one line, forming pronounced scars on the skin. This occurs due to drying and peeling of the skin layers.
About 70% of infections with vesicular fungus are accompanied by allergic rashes. A variety of bacteria and viruses begin to penetrate the ulcers. As a result, the disease becomes mixed, and identifying the original pathogen becomes more difficult. Therefore, you should consult a doctor as soon as the primary symptoms appear (pictured): he can quickly identify the type of foot fungus and begin therapy.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TidPKxmyLIM
Moreover, this should be done immediately. First of all, before using antimycotic drugs, the acute process should be eliminated. It is better to entrust this task to a specialist: he can carefully puncture the vesicles, treat the remaining ulcers with two percent boric acid and apply a brilliant green solution or methylene blue.
Treatment of advanced disease involves the use of corticosteroid ointments. After eliminating the inflammatory process, it is recommended to use topical antimycotic agents. This will suppress the pathogen.
We continue to consider the names and types of foot fungi.
Malignant melanoma
Melanoma on the leg may appear as a dark brown growth. It is considered dangerous as it can cause metastases. Malignant melanoma progresses very quickly and is classified as an oncological disease, so at the first detection it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Photo and treatment
There is only one way to cure malignant melanoma - removal. In the first and second stages, it is removed with small areas of skin around it, but if lymph nodes were involved in the process, then they are also removed surgically.
Self-medication is dangerous because the bones may be affected in the future and then radiation therapy cannot be avoided. In the third and fourth stages, the patient is given a course of chemotherapy.
How is the treatment carried out?
The therapy is long-term and complex. Self-medication is excluded, since often with a trophic ulcer there is only one solution - surgery. If the case is simple and not advanced, then the doctor will probably decide to conduct a course of medication.
If an operation is to be performed, the preparation consists of:
- cleansing the wound with antiseptics from dead particles that slow down healing;
- prescribing medications to improve trophism and blood microcirculation;
- infrared radiation to detect pathogenic microflora at the site of the lesion;
- carrying out ozone therapy, laser irradiation, vacuum therapy to accelerate healing, stimulate growth and granulation, improve trophism at an early stage of the ulcerative process.
Patients are advised to go to bed and elevate the affected leg to an elevated position so that the blood does not stagnate.
Medications
Therapy is aimed at eliminating the root cause that led to the disease. Appointed:
- non-steroidal drugs (Diclofenac);
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Diazolin);
- antiseptics (Furacilin, Chlorhexidine) for local use;
- antiplatelet agents (Pentoxifylline, Clopidogrel, Curantil, Cardiomagnyl, Aspirin);
- regenerating ointments and gels (Levomekol, Solcoseryl, Dimexide);
- anesthetics (Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, chamomile decoction);
- ointments to improve blood circulation (Venolife, Rutozid);
- sensitizing agents (Tavegil);
- phlebotonics (Antistax, Detralex);
- NSAIDs to relieve painful symptoms and enhance tissue regeneration (Curiosin, Actovegin).
The patient must reconsider their lifestyle and diet.
Even in the case of surgery, there is no way to do without preparatory procedures: daily treatment of a weeping wound with special gels, antiseptics, compounds to accelerate tissue regeneration (Triderm, Solcoseryl, Levomekol, Dioxide).
UHF irradiation, magnetic therapy, and treatment of affected areas with oxygen and nitrogen are indicated.
Surgical intervention
If a trophic ulcer on the leg has grown to a large size, then drug treatment is ineffective.
Surgical intervention is carried out by excision of dead epithelial tissue and removal of inflamed necrotizing tissue.
Today, doctors practice curettage, vacuuming an ulcerative defect on the skin caused by hypertonic or venous stagnation of blood, also with a neurotic form of ulcer.
Skin transplantation from part of the thigh or buttock is possible. It is necessary to return the patient to a normal level of life.
Attention! A trophic ulcer has an unclear etiology, and even with a minor non-healing wound on the leg, treatment cannot be carried out at home. Folk remedies are not able to eliminate impaired blood circulation in the joints.
If trophic ulcers on the legs are small, then with the permission of a doctor you can use at home:
- soap solution to cleanse the wound from necrosis and pustular lesions;
- treating the wound with antiseptics (Heparin, Levomekol), but under the supervision of a doctor. Antiseptic dressings must be changed daily (2-3 times a day) to avoid wound infection. In addition, ointments (Solcoseryl, Argosulfan) will help for regeneration, stimulation of cell division and activation of metabolic processes.
The work should not be in vain. Gradually, the ulcerative defect will begin to dry out and heal. The main thing is to treat it with ointments every day until the ulcer is completely healed.
Prevention of skin diseases of the feet
Often we encounter skin diseases because we are not armed with the knowledge of how to prevent their development. The second reason is laziness to carefully care for your feet. But preventing a disease is always easier than treating it, so it’s worth remembering a number of simple rules.
- Selection of quality shoes. Shoes are not something you should skimp on. Synthetic materials that make your feet sweat a lot, a bad last, and an uncomfortable heel cause significant harm. Therefore, shoes should be as comfortable and convenient as possible, and the foot should “breathe” in them. Good ventilation is very important in preventing the proliferation of pathogenic microbes.
- It is important not only to choose good shoes, but also to carefully care for them. Dry it in time, wash it, get rid of sand and small particles that get inside.
- Do not walk barefoot in places such as a swimming pool, sauna, or bathhouse. This will reduce the risk of contracting a fungus. It is also best not to go barefoot on the beach, but this carries the risk of mechanical injury due to broken glass or other debris.
- After water procedures, it is necessary to thoroughly wipe the feet, and especially the space between the toes.
- If your feet sweat too much, you need to take action. Special baths, deodorants, creams - all this will help cope with the problem.
Diagnostics
An examination for suspected foot fungus begins with a consultation with a dermatologist, which includes taking an anamnesis and examining the patient. After this, additional diagnostics are prescribed.
- Microscopy of clinical material - the epidermis is scraped from the affected area, which is subjected to microscopic examination. This allows you to distinguish fungal infections from other skin diseases.
- Sowing scrapings on special nutrient media is necessary to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antifungal drugs.
These include examining the skin under a Wood's lamp with an ultraviolet light source. The affected areas and the type of foot fungus are determined by a specific glow.
After diagnosis, a second consultation with a doctor is held, where, based on the data received, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Types of skin diseases on the legs, feet and toes
Taking into account the international classification of diseases, skin lesions of the legs can be divided into the following types:
- Infectious, which often manifest themselves through various rashes and neoplasms and are of infectious origin. We are talking about boils and abscesses.
- There are diseases that are transmitted at the genetic level, the most common of which is psoriasis.
- There is a separate classification of autoimmune diseases.
- Neurotic types of diseases are caused by stress and constant emotional swings.
- The parasitic species is most often caused by various parasites.
- A separate category includes various types of tumors, for example, melanomas and moles.
Each type of disease requires special attention and treatment. It should be remembered that there are diseases that can be temporary, and there are those that poison a person’s life all the time.
Note! With proper treatment in the early stages, you can get rid of many ailments within two weeks, but if you ignore all the symptoms, you can get a chronic disease.
Features of the disease
Mycosis of the feet is included in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). In describing this disease, synonyms are used such as: dermatophytosis, dermatomycosis. Such definitions are used for mycosis of the skin. If the disease has spread to the nails, then we are talking about onychomycosis (mycosis of the nails).
According to ICD, mycosis of the feet has the following types:
- interdigital fungus (the most common disease caused by mycosis);
- hyperkeratosis is a pathology in which excessive peeling and peeling of the upper layer of the skin of the feet affected by the fungus occurs;
- dermatophides - an allergic rash due to fungal diseases (allergic contact dermatitis).
This is what the interdigital form of toe fungus looks like
What these diseases look like can be seen in the photo.
Sometimes mycosis of the skin is confused with candidiasis. The diseases are similar in initial symptoms - the appearance of peeling and watery blisters on the epidermis between the fingers. In such cases, you need to pay attention to other symptoms (itching, burning, cracked heels).
Mycosis of the foot in late stages
Important!
Candidiasis does not affect the feet. It develops on soft skin and mucous membranes.
The infection can occur for a long time with almost no symptoms. Minor peeling between the toes and on the sides of the foot does not cause much inconvenience, so the infected person does not immediately pay attention to it.
Depending on the duration of development, there are several forms of foot fungus, each of which has its own specific symptoms.
- Intertriginous (interdigital) form. The skin between the toes and soles are affected. The epidermis turns red and peels, itching and sometimes burning appear. The back of the foot remains unharmed and there is no inflammation.
- Squamous form. The disease is accompanied by peeling of the epidermis and redness in the areas of greatest damage. At this stage, the skin may itch periodically.
- Hyperkeratotic stage of mycosis. The appearance of watery blisters (papules), rough bluish or red plaques, which eventually merge into one whole. The fungus affects the foot and its lateral parts, the heel (cracks appear).
- Dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the feet (wet fungus). The skin is covered with a large number of bubbles with liquid, which, when bursting, leave deep ulcers. An advanced stage of fungal infection is similar to eczema or psoriasis and is difficult to diagnose.
The change in the condition of the skin of the feet during each stage is clearly visible in the photo.
Apart from obvious signs of infection, foot skin fungus may not show itself for a long time. Minor signs are smoothed out (slight peeling, dry skin) - this is an erased form of mycosis of the feet. At this time, the infected person writes off such symptoms as a normal phenomenon or diaper rash, and does not suspect that the fungus is developing and getting worse.
Complications with mycosis may require hospitalization
Venous
Experts distinguish several main types of mycosis of the feet, depending on the causative agent of the disease. Each variety has its own characteristics and occurs with a number of unpleasant symptoms.
Rubrophytia
The causative agent is the fungus Trichophyton rubrum. The clinical picture of the pathology begins with the fact that the disease covers the feet and folds between the toes, but in the process the infection spreads throughout the body through the lymphohematogenous spread of foreign protein structures.
Candidiasis of the feet
It develops as a result of the penetration of a fungus of the genus Candida into the human body. Candidiasis of the feet begins with damage to the interdigital spaces and nails. In this case, the area of the nail fold becomes hyperemic and swollen, and the patient may be bothered by throbbing pain in the affected area and severe itching.
Onychomycosis
Damage to the nail plates caused by dermatophytes, fungi of the genus Candida or mold forms. Fungi are unpretentious to living conditions and are highly resilient, so in advanced forms the disease is difficult to treat.
The most typical form of mycosis, which is determined by damage to the interdigital folds without the appearance of signs of a pathological process on the foot. As it develops, cracks, peeling, erythema and maceration appear on the patient's skin. In the future, any bacterial infection can develop against the background of the disease.
Characterized by simultaneous damage to both feet. The disease occurs with severe peeling and keratinization of infected areas of the skin, as well as with the appearance of deep cracks in the affected areas. There is little or no itching.
After the infection enters the body, many blisters with a rough surface appear on the patient’s skin, hyperemia and swelling increase, which makes the dyshidrotic form of the disease similar to eczema. Once the blisters rupture, they form areas of erosion on the heel or instep of the foot.
Erased form
A type of mycosis has minimal clinical manifestations in the form of invisible microcracks in the interdigital folds of the skin and mealy peeling. The patient does not experience any discomfort, which is why treatment of the pathology is delayed for a long time.
Madura foot
A long-lasting deep mycosis that primarily affects the feet. The disease begins with focal inflammation in the subcutaneous tissue and gradually spreads to soft tissues, internal organs and bones.
At the initial stage, the pathology does not manifest itself, but then a compaction with purulent contents and a specific odor forms on the infected person’s foot. The surface of the skin becomes disfigured and resembles a turtle shell.
Statistics say that about a third of the world's population suffers from foot fungus. Among all mycoses of the skin, this form of the disease is the most common. You can become infected with fungus at any age. About 20% of patients are children and adolescents, about 40% are elderly people and patients with diabetes.
A fungal infection provokes the development of erysipelas on the feet. This reduces local cellular immunity and complicates treatment. A fungal disease detected in a timely manner is quite treatable, but therapy for an advanced form of the fungus can take many months.
Mycosis of the skin of the feet (dermatophytosis) is highly contagious. In this disorder, the surface layer of the skin, which is constantly separated by scales, contains many fungi and their spores. The infection is transmitted from person to person through household items: shoes, socks, rugs (in showers, locker rooms, swimming pools), sun loungers on the beach, footstools, flooring and basins in baths and saunas. It is rare, but possible to become infected in a pedicure salon when using poorly disinfected instruments.
At the first stage of the disease, the interdigital folds are affected, itching of the skin appears, and then the infection covers the entire foot and nails.
Dermatophytes penetrate the skin through wounds, microcracks, diaper rash, cause itching and flaking of the skin, and the feet acquire an extremely unpleasant odor that is difficult to hide even while wearing shoes. Sometimes the itching is so unbearable that it prevents a person from sleeping.
Age can also influence the course of mycosis: in older people the dry form is more often diagnosed, in young people and in adulthood - acute, with the release of exudate.
The fungus is rarely localized to just one area. If treatment is not started at an early stage, the disease will spread throughout the body. In severe advanced cases, the person has to be hospitalized.
Mycosis of the foot can be asymptomatic, but the person remains a source of infection. This condition can last for months and years, with periods of unsuccessful self-treatment.
Treatment of foot fungus
Mycosis of the foot (foot fungus) is an infectious disease caused by parasitic fungi and transmitted from person to person.
It should be noted that in the past, fungal skin infections were so common that only a small number of people managed to avoid infection. The situation changed dramatically in the 60-70s of the last century, when many effective medications became available, which not only brought relief to the patient, but also allowed recovery. Today, the disease remains the most common skin disease, followed by ringworm.
With mycosis of the feet, the surface of the foot and the skin between the toes are often affected; in rare cases, the hands are involved in the pathological process. The latter is caused not so much by the spread of the fungus itself, but by the circulation of fungal toxins in the bloodstream. In addition, additional infection of the hands is caused by scratching the skin of the legs, after which the parasitic agent can be transferred from the hands even to the scalp. This route of spread should be taken into account by patients with mycosis of the foot in order to protect not only themselves, but also those around them.
This is what skin affected by a fungus looks like
Causes of fungus
Mycosis of the foot is caused by opportunistic and pathogenic fungi.
- Pathogenic varieties of fungi always cause a pathological process and lead to the development of disease.
- Opportunistic fungi colonize the human skin from birth, but cause disease only in the presence of predisposing factors.
Infection occurs when visiting the pool, trying on shoes and not maintaining personal hygiene.
The fungus often affects the skin of people over 40 years of age with a history of diabetes.
Skin trauma is a predisposing factor that contributes to the development of the disease: reduced immunity, chronic diseases, and circulatory disorders.
The ideal environment for the growth of fungi is humid and warm, so athletes, military personnel, miners, and those people who, due to their duty and due to the specifics of their work, are required to wear tight and closed shoes for a long time, are at risk.
It should be noted that in children such a pathology is extremely rare, which is due to the acidic reaction of sweat and the rapid replacement of the epidermis.
Symptoms of foot fungus
The following forms of foot fungus are distinguished:
- Squamous . the skin peels between the toes and at the base, on the arch of the heels and feet. As a rule, there are no subjective symptoms.
- Squamous-hyperkeratotic . the skin on the soles is infiltrated, thickened, the skin furrows and patterns are enhanced, and floury peeling is noted in the folds. The patient complains of itching, intertriginous . Skin folds are affected. On the skin between the fingers there is redness with cracks, detachment of the epidermis, peeling, the patient notes the presence of itching, burning sensation and discomfort.
- Dyshidrotic form . Against the background of erythema, bubbles with clear liquid appear. After themselves, the bubbles can leave erosions, areas of peeling or layers of skin detachment. Symptoms in this form are acute, with weeping, burning, increased body temperature in rare cases, constant itching and swelling.
to content #8593;
Treatment of foot fungus
Treatment of foot fungus requires a mandatory visit to a dermatologist, who, after tests and a thorough examination, prescribes appropriate treatment.
It should be noted that, even despite the effectiveness of modern antifungal drugs, it is not always possible to quickly cure a patient of foot fungus, which is explained by the patient’s late appearance to the doctor and the incompetence of the doctor himself.
At the preliminary stage, it is mandatory to disinfect shoes, linen, bathrooms and personal care items using a 25% formaldehyde solution. Feet require proper care, which means frequent baths, ironing socks, and changing them.
In the initial forms of the disease, the patient is prescribed:
Solutions of aniline dyes, silver nitrate, boric acid, resorcinol, etc. are used as local therapy.
In advanced cases, in addition to the main local treatment, oral medications are prescribed.
You should know that healing in the first stages of the disease occurs faster and more painlessly than in advanced cases. However, even with a low severity of the pathological process, treatment requires patience and scrupulousness.
Folk recipes
In the presence of erosions and scales, it is recommended to use baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. During the procedure, the maximum number of scales should be separated. If the skin is thick and there are a huge number of scales, you can use salicylic petroleum jelly, which is applied 2 times a day until all the scales are separated.
Only after removing the scales can you start using traditional recipes.
- Treatment with celandine . For the bath you will need 4 tablespoons of celandine, 1.5 liters of hot water. Soar your feet for 30 minutes. The course of treatment is 20 procedures. Sometimes celandine is replaced with wormwood.
- Treatment with burdock leaf . Use a hammer to remove the juice from the burdock leaf, then wrap the leg in burdock and secure with a bandage. The compress is changed 2 times a day. The course lasts 3 weeks.
- Treatment with rowan . To do this, you need to mash fresh rowan leaves, then apply them to the affected area of the skin and secure with a bandage. Keep the bandage on for 24 hours, change once a day. Before securing with a bandage, you can wrap the leaves with a burdock leaf.
- Treatment with sea salt . For the bath you will need 1 teaspoon of sea salt dissolved in 1 liter of water. Pour the prepared solution over your feet every evening for 2 weeks.
to content #8593;
Prevention
- do not wear someone else’s shoes, do not let others wear your shoes;
- a sick family member must have his own personal scissors, nail file and other personal hygiene items;
- disinfect the premises;
- do not use false nails for a long time;
- Dry your skin thoroughly after taking a shower;
- Change your socks daily.
Advice! Shoe treatment plays a very important role in prevention. Take acetic acid 40% or chlorhexidine 1%. Put on rubber gloves and use a cotton swab to clean the inside of the shoe and the insoles. Prepare a sealed plastic bag and place the treated shoes in it for 2-3 days.
Sources
- https://MoyaKoja.ru/bolezni-s-kozhnymi-proyavleniyami/kozhnye-zabolevaniya-na-nogax.html
- https://FeetInfo.ru/nedugi/dermatologiya/kozhnye-zabolevaniya-na-nogax.html
- https://skindiary.ru/zabolevaniya/kozhnye-bolezni-nog.html
- https://helplegs.ru/boli-v-nogah/bolezni-kozhi-na-nogah.html
- https://www.vzdorovomtele.ru/zabolevanija-kozhi/zabolevanija-kozhi-stopy-nog-foto-i-opisanie.html
Types of disease
To prevent infection with mycosis, it is not enough to exclude any contact with possible sources of fungal infection. In addition to minimizing communication with carriers of the disease and their personal belongings, preventive measures should also be aimed at:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- treatment of chronic diseases;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- strengthening the immune system.
Foot fungus creates a danger not only for the infected person, but also for his immediate environment, therefore, having discovered the first signs of mycosis, you need to take all possible measures to get rid of the disease.
To avoid complications, it is important to contact a dermatologist in a timely manner to carry out diagnostic measures and prescribe the correct treatment using medications.
Treatment of mycosis is carried out using effective medications, which can only be prescribed by the attending physician. Most often the patient is prescribed:
- antifungal agents for internal and external use;
- antimycotics;
- corticosteroids;
- antihistamines;
- multivitamin complexes.
Important!
At the initial stage of the disease, treatment can be carried out using alternative medicine recipes. Many of them help to quickly get rid of the problem, but in some cases they can cause an allergic reaction.
It is quite difficult to divide dermatitis into separate types. So far, there is no unambiguous classification of pathology. The disease is divided into types, taking into account the following characteristics:
- localization of lesions (face, limbs, folds);
- area of influence of negative factors (contact, atopic);
- the contact form of pathology is divided into simple and allergic;
- cause of the disease (allergic, toxic-allergic, inflammatory, infectious, fungal, stagnant);
- duration of course (chronic form and acute stage);
- type of rash (erythematous, vesicular, bullous, scaly);
- the nature of the symptoms (dry, weeping, itchy, purulent).
Venous
Next, we will discuss each type of disease separately in detail.