The appearance of lichen on the skin is very often accompanied by a large number of unpleasant symptoms that interfere with a person’s normal life. Many people are interested in the question of how lichen is transmitted from person to person and methods of preventing infection with this type of disease.
It is also very common to become infected with lichen, possibly through contact with animals that are carriers of certain types of skin disease. It is almost impossible to determine the type of viral infection at an early stage and it is necessary to undergo appropriate diagnostics.
The disease manifests itself in a person with a large number of unpleasant sensations and has an external unaesthetic appearance that repels others. Very often, lichen appears in childhood, since the child’s immunity is most severely affected by viruses.
A person can become infected with such a skin disease anywhere, so many are interested in the question of how to reduce the likelihood of this type of disease and how to properly treat skin lesions.
What kind of disease is lichen?
Ringworm is a skin type of disease that is viral in nature and affects epidermal cells. With this type of skin disease, a person experiences inflammatory processes on the skin, resulting in swelling and flaking of the skin.
Lesions can appear as single or multiple lesions, affecting the entire area of the body; the degree of spread of lichen is most often associated with its type.
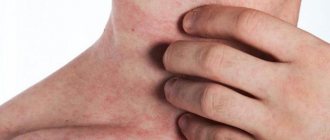
A person who has become infected with such a viral infection may experience a large number of unpleasant sensations, aggravated by contact with water, so experts recommend not delaying treatment and seeking medical help when the first symptoms appear.
Otherwise, a person may experience an increase in formations, which will complicate treatment and take a long time.
Traditional treatment
Most often, the disease lasts a very long time, so a person’s lichen is treated at home. In most cases, patients use pharmaceutical drugs; they are prescribed by a dermatologist after examination. There are also folk remedies for lichen, which have a number of advantages. Firstly, they are more accessible, and secondly, such drugs are considered universal and are used for different types of diseases.
The most popular are the following:
- homemade mash, it contains tar, ethyl alcohol, glycerin;
- celandine juice, it has a bright yellow color, you need to smear it locally, on each affected area;
- birch tar in its pure form, used only for topical use;
- baking soda, used as an antiseptic.
You can also use tar soap or tar shampoo for prevention. Experts strongly recommend using only those products of which they are confident. And do not forget about the key rule of treatment - constant care and hygiene of the body.
Causes
A person may develop lichen for the following reasons:
- Weak immunity, unable to cope with viral infection;
- Heredity;
- Transference of acute respiratory diseases, which, if complicated, can cause certain types of lichen;
- Contact with animals that are carriers of infection;
- A side effect of taking certain medications that cause disease, most often these include products for external use;
- Exacerbation of an allergic reaction;
- Frequent stressful situations;
- Damage to the skin that was not promptly treated with an antiseptic drug.
There are a large number of causes of the disease, most often depending on the type of lichen.
Microsporia
This type of lichen is transmitted from animals; its causative agent is a fungus of the Canis class. Mostly children under 12 years of age are affected. The danger of this disease is that the spots are widely localized and can appear anywhere: on the face, arms, torso, head.
Ringworm has a round shape, up to 8 cm in diameter, and is light pink in color. The treatment has a fairly positive prognosis. Using antifungal ointments for 10-15 days allows you to completely get rid of the manifestations of microsporia.
How is lichen transmitted from person to person?
Many types of lichen are contagious and can be transmitted through contact with an infected person.
Infection most often occurs when particles of damaged skin enter healthy areas, due to which the virus begins to gradually progress and infect the epidermis.
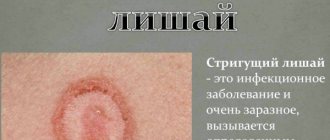
Ringworm
Ringworm is caused by trichophytosis infection and tends to quickly spread to healthy areas of the skin. Most often it is transmitted through contact with animals, but as a result of human infection, transmission of the infection through contact is possible.
Most often, this type of disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- The appearance of plaques with the presence of bubbles, with unclear edges;
- When the hair part is damaged, the hair becomes damaged, which leads to bald patches;
- When scratching the formations, the disease moves to healthy areas of the skin;
Has the ability to be transmitted to other people using the following methods:
- During physical contact with a person, such as shaking hands;
- When using personal care items such as towels and combs;
- When using things of an infected person, such as hats;
- Upon contact with an animal with the presence of the lichen virus;
- During contact with pieces of furniture with which the animal was in contact;
- In public places, if there is damage to the skin.
Ringworm can also be contracted in baths and saunas, so after visiting such places it is necessary to treat the skin with an antibacterial agent. During the presence of skin lesions, it is necessary to avoid visiting public places with high humidity.
Pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea or Zhibert's pityriasis is a disease that very often appears without any symptoms. Medical specialists cannot say with certainty the causes of the disease.
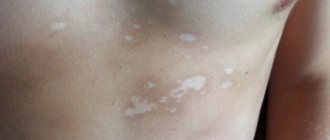
Most often, ringworm appears as pink and brown patches that first appear in places such as the inner thighs and chest. Most often, the disease does not cause unpleasant symptoms and tends to disappear on its own.
This type of skin disease does not require special external treatment and is not contagious to another person.
Most often, the following reasons contribute to the appearance of lichen:
- Reduced immunity;
- Failure to maintain the required level of hand hygiene;
- Untimely treatment of internal organs;
- Heredity.
Many people who have a high level of excitability and experience frequent stressful situations are most likely to develop this type of disease.
How not to get infected
It is possible to avoid infection with lichen if you follow a number of important rules. The main task facing a person is to limit contact with carriers of the infection during the active period.
On this topic
- Lichen
Everything you need to know about lichen planus
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 25, 2021
The presence of the disease in other people or animals can be determined by the characteristic signs of lichen:
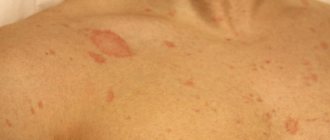
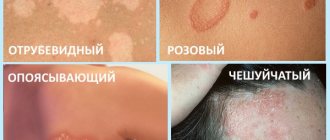
- Shearer . Spots of various sizes appear on the body, around which small bubbles are located. The central part of the tumors peels off. Hair falls out at the site of the lesion.
- Shingles . It appears in the form of small bubbles, running mainly along the body. During the period of relapse, the patient experiences intense pain and itching in the affected area.
- Pityriasis . Externally, it is distinguished by the presence of gray spots on the body, which lighten under the influence of water or ultraviolet radiation.
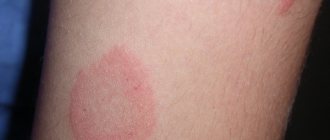
- Pink . During the period of disease activity, small (up to 5 cm in diameter) spots appear on the patient’s body.
Due to the fact that the causative agents of lichen remain viable outside the human body, in order to avoid infection it is also recommended:
- do not wear clothes ;
- avoid bodily contact with carriers of infection (including animals);
- use your own household items (dishes, combs, towels, etc.);
- wash regularly ;
- use slippers when visiting bathhouses, swimming pools and other public institutions.
Incubation period of lichen in humans
| Type of lichen | Incubation period |
| Ringworm | The incubation period ranges from 4-5 days when infected from an animal. When infected from humans, the period is up to 2 weeks. |
| Shingles | The incubation period in humans ranges from 3 days to one month. |
| Pityriasis rosea | The incubation period lasts for several months, depending on the degree of immunity reduction |
| Lichen planus | The incubation period is from 7 to 10 days. |
| Pityriasis versicolor | The incubation period is from one to three months, depending on the degree of infection of the skin. |
| Ringworm | The incubation period is from 3 to 7 days. |
| Pityriasis alba | It can manifest itself within several weeks and last up to several months, depending on the individual characteristics of the human body. |
| Squamosal lichen | The incubation period can last for 1 week and up to several months. |
| Tubular lichen | The incubation period is from 7 days to 1 month. |
| Asbestos lichen | This type of disease may appear within several weeks. |
Regardless of the length of the incubation period, when the first signs of the disease appear, you must consult a doctor.
Pityriasis rosea
The disease is of an infectious-allergic nature; its formation can be triggered by mechanical damage to the skin, exacerbation of herpes, or previous colds. Zhiber's pityriasis rosea is diagnosed in people of any age; outbreaks of the disease are recorded in the autumn-spring period, which is associated with seasonal weakening of the immune system.
The pathology in the initial stages manifests itself with the formation of a small pink spot, its center gradually acquires a yellow color, becomes covered with flaky scales, the border remains free and has a red color (medallion). After 7–10 days, multiple rashes are formed on the body, smaller in diameter than the maternal plaque.
The primary lesion is most often localized on the chest, later spots form on the stomach, arms, legs, neck, and groin area. Some patients are bothered by severe itching of the skin, about ¼ of patients do not experience significant discomfort.
The incubation period for pityriasis rosea is 2–21 days. With a weakened immune system, the disease is difficult to treat and constantly recurs. In other cases, the pathology goes away on its own after 6–8 weeks; if a secondary infection occurs, the regeneration period is extended. Hyperpigmented areas remain in place of the spots.
Prevention of occurrence
In order to reduce the risk of contracting this type of skin disease such as lichen, you must first adhere to the following rules of prevention:
- Properly carry out all necessary hygiene measures;
- Use only personal hygiene items;
- After visiting public places, it is necessary to use antibacterial drugs;
- Avoid contact with people who are carriers of this type of skin disease;
- Avoid contact with stray animals;
- Keep your pet clean;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Avoid hypothermia.
A prerequisite for preventing the occurrence of lichen is the consumption of food to strengthen the immune system; if necessary, you can use special vitamin complexes.
How to treat in the early stages at home quickly
The pathology belongs to the category of infectious; fungal pathogens are easily transmitted from an infected person through contact and household contact (through touching, kissing, household objects, etc.).
Unlike other fungal infections, the patient is affected not only by the skin and nails, but also by hairy areas on the body. Most often, young children suffer from this disease. If treated inadequately or untimely, ringworm causes serious complications.
Precautions and infection prevention
There are 3 simple rules to minimize the risk of lichen:
- Live a healthy lifestyle to support your immune system's ability to fight disease without medication.
- Maintain good hygiene, especially after visiting public areas.
- Treat chronic pathologies in a timely manner so that they do not provoke hormonal changes and weakened immunity.
Also, do not neglect the help of doctors immediately after the end of the incubation period of the disease. This will help you avoid future recurrences of lichen.
Frequently asked questions about lichen
What does lichen look like in humans under ultraviolet light?
Ultraviolet light is used for diagnostic purposes. Ringworm is a colony of fungi. When exposed to UV light they exhibit a fluorescent effect. Lamps with a wavelength of 320-400 nanometers are used to examine patients. The color of the glow of fungal colonies of lichen on the head or body can be different: yellow and orange (pityriasis), blue-green (ringworm).
Is shingles transmitted?
Yes, it is transmitted through contact and household contact. For example, lichen from an animal often gets onto the hands of children when stroking it. Infection occurs. When immunity decreases, the disease develops. Ringworm on the skin of adults and children has scales or vesicles that facilitate the transmission of a fungal or viral infection.
Causes of disease development in animals
The main reason for the appearance of lichen in cats is contact with a sick animal. However, contact does not have to be direct. Fungal spores can live for a long time on a comb, bed, or toys of a sick cat. Therefore, there is also a risk of infection for a cat that does not walk or “communicate” with yard unvaccinated cats through any objects that were near a sick animal (this is why it is not recommended to pet yard cats, because spores can get not only on your hands, but also for clothes, and then for a domestic cat).
Animals most susceptible to developing the disease are:
- under the age of 1 year;
- with poor nutrition;
- with a weakened immune system due to a previous illness;
- infected with parasites.
If the cat is kept in good conditions, receives adequate nutrition and is vaccinated on time, then its immune system is able to cope with fungal spores and prevent infection.