- 1. Treatment process for sebaceous cysts 1.1. How to treat a sebaceous cyst - step-by-step description
A sebaceous cyst is a bubble filled with keratin, secreted by the sebaceous gland and emitting a rather unpleasant intense odor when the cyst fills. A sebaceous cyst is formed as a result of injury or simply an unpleasant set of circumstances when a follicle of the skin or the hair itself becomes inflamed. Therefore, such a cyst most often forms on the scalp and pubic area, in the armpits. But they can also form on other parts of the body where little hair grows. How to remove a sebaceous cyst in 2021? Let's walk through this process with removal photos.
Classification and characteristics
Despite the fact that these neoplasms can increase in size and have a membrane, they are not classified as tumors, therefore, by definition, they will never be malignant and will not degenerate into cancer, even if they reach a large size. The mechanisms of formation of a malignant tumor and atheroma are different.
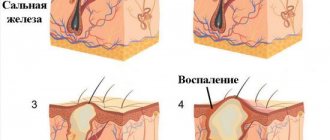
Any cyst, including atheroma, is a kind of cavity, which is formed by a capsule, which is both the shell of the neoplasm and the producer of the contents of the cyst. Inside, on the surface of the tumor shell, cells constantly produce certain substances that gradually accumulate inside the formation. Due to the fact that the secretion of these membrane cells is not able to be removed from the closed capsule, over time it stretches it, which is why the neoplasm increases in size.
The progression and formation of the cyst occurs in accordance with the mechanism described above. The main distinguishing feature of atheroma is that it is formed from the cells of the sebaceous gland of the skin, which constantly produces sebum. And this suggests that a cyst is formed when, for some reason, the excretory duct of the glands of the skin is clogged, which is why the formed sebum is not able to be removed to the surface of the skin.
But the gland cells do not stop producing fat, which after some time accumulates in large quantities. The resulting fat begins to stretch the excretory duct of the gland, which is why the cyst gradually begins to increase in size.
In addition, cysts can form by another mechanism, for example, due to some kind of mechanical injury:
- Scratches.
- Cut.
- Abrasions, etc.
At the same time, cells of the surface layer of the skin penetrate into the excretory duct of the sebaceous glands. In such a situation, these cells, right inside the ducts of the sebaceous glands, begin to actively produce keratin, which begins to mix with sebum and turns it into a very dense mass. The resulting mass cannot be removed from the ducts of the sebaceous glands to the surface of the skin, since the consistency is very viscous and thick.
As a result, the mixture begins to clog the lumen of the sebaceous glands, after which atheroma forms. At the same time, keratin and sebum continue to be actively produced inside the flow of glands, which accumulate in large quantities over time, while the atheroma slowly but steadily continues to grow.
Danger level
Regardless of how exactly the cysts were formed, they have the same clinical course and appearance. As a rule, epidermal cysts are not dangerous, since even if they are large, they are not able to compress any vital organs and cannot grow deep into underlying tissues.
The only factor that makes atheroma a potentially dangerous formation is the possibility of its inflammation. This manifests itself in the development of edema, redness, soreness and suppuration. In such cases, an abscess often forms.
If the inflammatory contents are removed, this is considered a favorable outcome, since the surrounding tissues will not melt, and toxic substances will not penetrate the bloodstream. If the contents of the atheroma are released into the surrounding tissues, then this will be an unfavorable outcome, since toxic substances and pathogenic microbes enter the bloodstream and can also cause infectious and inflammatory diseases of the subcutaneous fatty tissue, muscles, and bones.
How are cysts treated?
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
What a thyroid cyst is in the photo can only be understood after undergoing a full examination and surgery of the tumor. In general, a cyst of this type is a small or medium-sized fatty growth that can press on neighboring organs and provoke infections and accompanying diseases.
Appearance
Externally, this neoplasm has a round or oval shape, clear contours that protrude above the level of the epidermis, and at the site of the cyst, the skin most often changes or becomes reddish. The cyst is elastic and dense to the touch and can move to the side.
An epidermal cyst mainly forms on the face under the skin, on the chest, scrotum, neck and scalp. Atheromas can be either malignant or benign. Any cyst looks like a lipoma, but these neoplasms are completely different in structure. Lipoma is a benign tumor of adipose tissue; atheroma is a neoplasm from the excretory duct of the sebaceous glands of the skin.
Cysts can appear on any part of the skin, but most often they are localized in areas with a large number of sebaceous glands, for example:
- Face, including the area around the eyes.
- The scalp.
- Armpits.
- Neck.
- Torso.
- Crotch.
- Genital organs.
Sometimes atheromas can appear in areas of the skin that do not have many sebaceous glands, for example:
- Legs.
- Hands.
- Fingers.
- Ears.
- Mammary glands in women.
People suffering from acne are at greatest risk of developing atheromas, since the gland ducts are often clogged, which is considered the main factor in the formation of atheromas. In such cases, neoplasms are localized on the skin of the cheeks, neck, behind the ears, as well as on the back and chest.
Fat cyst treatment
A breast fatty cyst is a direct consequence of fat necrosis, a condition in which the fatty tissue in the breast dies. Such cysts most often occur in women aged 35–50 years. They are benign in nature and do not transform into malignant tumors.
How do fatty cysts occur in the mammary gland?
The mammary gland consists of glandular tissue, which produces milk during breastfeeding, connective tissue, which acts as a kind of frame, and fat, which gives the breast volume and shape. In some women - most often after injury and surgery - a patch of fatty tissue in the breast dies. This condition is called fat necrosis.
Gradually, the area of necrosis, consisting of dead cells and fats, softens and turns into an oily liquid. It is fenced off from neighboring tissues by a capsule of connective tissue. The resulting formation is called a fatty cyst.
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations depend on the size of the cyst. If it is very small, the woman will not feel it on her own. The fluid cavity will only be detected during the examination. A large cyst feels like a lump in the breast and is usually painless.
Even when they are not bothered by pain and other symptoms, many women experience severe psychological discomfort. Many are afraid that the formation may turn out to be a malignant tumor, despite the fact that the doctor conducted an examination and ruled out cancer.
Leave your phone number
Does a fatty cyst increase the risk of breast cancer?
A fatty cyst is an absolutely benign formation. It does not leave its original place, does not grow into the surrounding breast tissue, and cells cannot break away from it and metastasize. However, some malignant tumors also appear as a cavity filled with fluid. In order to establish the correct diagnosis, it is important to conduct an examination.
How is diagnosis carried out?
The examination is carried out in order to confirm the benign nature of the formation, exclude breast cancer, distinguish a fatty breast cyst from a seroma (fluid accumulation that occurs after injury, surgery), lipoma (a benign tumor from adipose tissue).
Ultrasound is the best way to detect cavity formations in the mammary gland. Mammography, an X-ray examination, is less advanced in this regard, but can also be prescribed. If necessary, resort to biopsy.
Modern methods of treatment
Fatty breast cysts do not always require treatment. Many of them decrease on their own over time. The doctor may recommend dynamic monitoring and periodic visits for examination.
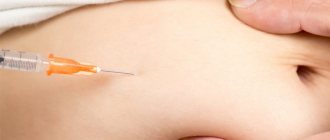
If the cyst is large, causes pain, or the woman herself insists on treatment, a puncture can be performed. A needle is inserted into the cyst and its contents are removed. After such treatment, relapses often occur, and repeated punctures may be required.
Surgical removal of a fatty cyst is rarely resorted to, usually when it is very large and has dense, calcified walls.
A fatty breast cyst is not a dangerous condition. But it is important to correctly and timely diagnose and exclude a malignant tumor. Make an appointment with a mammologist and get examined at the Medicine 24/7 clinic. Call: +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Lipomas or lipomas are benign tumors that develop in the subcutaneous loose connective tissue. Sometimes they can penetrate deeper and form vascular bundles.
The tumor is painless and has a soft consistency. Most often, the neoplasm can be found in those areas of the skin where there is almost no adipose tissue. Wen is absolutely safe for human health and does not cause cancer.
Where can a lipoma appear?
Unfortunately, most often the cyst appears in the subcutaneous tissue or between the muscles. Lipoma can occur on absolutely any part of the body. Very often a person simply does not attach importance to the new formation , because the defect does not cause any discomfort.
A fatty deposit that forms on the face is not a very pleasant phenomenon, but it can be overcome. The most dangerous development of the disease is when the wen affects the internal organs, but this happens extremely rarely.
How to recognize a fatty cyst?
Many people are interested in what a wen looks like and is it possible to accurately recognize it? If you feel a new formation or swelling of a round or oval shape , you can assume that this is a lipoma.
Even a small lipoma can hurt, especially when pressed. In turn, a large wen not only spoils a person’s appearance, but can also disrupt the functioning of neighboring organs. In this case, a person may experience the following unpleasant symptoms:
- lipoma on the bronchi - severe dry cough;
- wen on the esophagus - nausea and cough;
- tumor in the mammary gland - chest pain;
- fatty formation on the tendons – joint pain.
It is worth saying that independently determining the presence of a lipoma is not enough; and conducting research is mandatory
Varieties of atheroma
Atheromas are usually divided into four main types, depending on the histological structure, as well as the nature of the contents. These varieties include the following:
- Sebaceous gland cyst.
- Steacytoma.
- Dermoid.
- Atheromatosis.
All of the above varieties have the same clinical course and similar symptoms, so experts do not use this classification. They cannot be distinguished from each other externally. The type of atheroma is important only for scientific research. There is also another type of cyst called a mucocele. As a rule, it forms in the paranasal sinuses.
In clinical practice, a completely different classification is used, which is based on the location, characteristics of the formation and course of atheromas. Based on this classification, all cysts are divided into acquired and congenital.
- Congenital cysts are multiple cysts that are located in different areas of the skin and are small in size. Their size does not exceed 0.5 cm in diameter. Most often, such cysts appear on the skin of the pubis, scrotum and scalp. They are formed on the basis of genetically determined defects in the structure of the glands, as well as a violation of the outflow of sebum produced by the sebaceous glands.
- Acquired cysts are often called secondary or retention; they are dilated gland ducts that are formed due to blockage of their lumen. As a rule, secondary atheromas include dermoids, sebaceous cysts and steacytomas. The main causes of acquired atheromas can be any physical factors that contribute to blockage of the lumen of the glands, for example, injuries, inflammatory skin diseases, acne, excessive sweating and much more. Such atheromas can grow up to 10 cm in diameter.
A cyst in newborns will be no different from neoplasms in adults, since it has exactly the same clinical course, causes of formation, symptoms and treatment methods. Most often, congenital atheromas are observed in children, since they do not have other factors that will contribute to the formation of acquired epidermal cysts.
Treatment methods
Not wanting to go to the doctor, many people wonder how to cure a wen at home. This is not recommended. The only radical and complete treatment for these tumors is to remove them using various methods. Atheroma will never go away on its own; sooner or later it must be removed in one of the following ways: laser, surgical, radio wave.
In addition, the atheroma cannot be squeezed out, even if it is first pierced with a needle and a hole is formed through which the contents can escape. In this case, the contents will come out, but the capsule with the cells that produce the secretion will be in the gland duct, so after some time the free cavity will again be filled with sebum.
To get rid of this pathology forever, it is necessary to completely remove its capsule, which clogs the lumen of the gland duct. It is recommended to remove the cyst before it reaches a large size, since in this case there will be no scar or scar left at the location. If for some reason the tumor could not be removed, but it has grown to a large size, then you will have to resort to local surgery to remove the tumor with a skin suture.
Against the background of inflammation, it is not recommended to remove the atheroma, since in such cases there is a high risk of relapse due to incomplete removal of the capsule. In such situations, it is necessary to carry out anti-inflammatory therapy and wait until the inflammation completely subsides.
If the atheroma is inflamed by suppuration, then it must be opened, all the pus released, leaving a small hole for the outflow of newly formed inflammatory contents. When the inflammatory process subsides, it is necessary to peel off the walls of the formation.
As a rule, the cyst is removed under local anesthesia. The patient can return home within a few hours after the operation. Hospitalization will be required only in cases where large inflamed purulent atheroma will be removed. When opening the capsule, its contents are squeezed out or removed with a special spoon. The remaining shell is removed using tongs. If the incision is larger than 2.5 cm, then stitches will be necessary.
This treatment method is very effective. In this case, the cyst is removed using the following methods:
- Photocoagulation is the removal of subcutaneous tumors, the size of which does not exceed 0.5 cm. Removal is carried out using a laser beam through evaporation. In this case, no stitches are applied.
- Laser excision is performed for tumors up to 2 cm in diameter. An incision is made from above with a scalpel, the skin is moved apart so that the line of contact of the atheroma with the tissue can be clearly seen. They are evaporated with the help of a laser, releasing the atheroma. After this, it is removed with forceps, drainage is inserted and sutures are applied.
- Laser evaporation of the capsule is carried out when the size of the atheroma exceeds 2 cm in diameter. The capsule is cut and its contents are removed. Using surgical hooks, the wound is expanded, and a laser is used to evaporate the capsule shell. Next, drainage is inserted and sutures are applied.
This method of therapy is used only in cases where the cyst is small and does not have purulent contents. For this, a special device is used, in which the atheroma is exposed to radio waves that promote cell death. After the procedure, a crust appears at the site of the tumor, under which the regeneration process begins.
Originally posted 2018-01-31 08:03:42.
Tumor-like formations, in particular cysts on the face, cause considerable aesthetic discomfort. Even if they are small in size, they are noticeable and spoil the appearance. Such conditions cannot be ignored, requiring timely and high-quality correction.
How to cure lipoma at home?
You can get rid of a wen at home, but this is only possible if the formation is not very large in size. Also, using some methods, you can stop the development of a fatty cyst.
Vishnevsky ointment is popular, despite its not very pleasant smell. The ointment contains tar, castor oil and xeroform. The therapeutic effect of the drug is that it relieves pustular formations, ulcers and relieves inflammation on the skin.
To cure a lipoma, you need to apply a little ointment to a cotton pad and stick the compress with a band-aid to the affected area for 8-10 hours. After this time, the cotton pad is replaced with a new one. The procedure must be done over three days with a one-day break. The ointment relieves inflammation and draws out accumulations in the wen. With these simple steps, you can remove both newly formed and old lipomas.
You can also make lotions from aloe. For treatment, you only need a patch and a fresh aloe leaf, which needs to be cut lengthwise. The inner part of the plant must be applied to the wen and secured with a band-aid. It is better to do such procedures at night. When the wen shrinks, you can gently squeeze it out.
There is another recipe based on black pepper. Sprinkle a little freshly ground pepper onto a piece of cloth and soak it in alcohol. Place the compress on the affected area and hold for 20-30 minutes. The procedure must be done twice a day for a month. This method is not suitable for dry and sensitive skin , as it can cause new problems.
Classification
A cyst is a benign cavity formation. It can occur on any part of the body, including the face. Based on morphological features, true and false cysts are distinguished. The former have their own capsule (inner shell), while the latter lack it. True cutaneous cysts are represented by the following:
- Epidermal (atheromas).
- Dermoid.
- Implantation.
- Retentional (milia).
False cystic formations (without internal epithelial lining) are synovial, have the appearance of calcification, or are represented by pseudomilium. Each of the presented forms has its own origin, morphological and clinical features.
Causes and mechanisms
The most common is an epidermal cyst or atheroma. It occurs as a result of blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland and the accumulation of secretions there. The mechanism for the formation of such a state has three components:
- Increased secretion.
- Hyperkeratosis of the excretory duct.
- Imbalance of neuroendocrine regulation.
Sebaceous cysts can occur in people with oily or combination skin types, but under certain conditions. It is known that the glands and epithelium are under the influence of sex hormones (primarily androgens). And if the balance with estrogen is disturbed (for example, during menopause or ovarian tumors), then the risk of developing atheroma increases. They usually occur in places where the glands are most dense: on the back, face, upper chest.
Compensatory hyperkeratosis of the excretory ducts accompanies not only sebaceous gland cysts on the face, but also occurs during trauma or inflammatory processes (acne, seborrhea). Mechanical damage can lead to the penetration of the epidermis into the skin, which will become the source of an implantation cyst. Calcinosis, like atheroma, is mediated by neuroendocrine changes, in particular disturbances in the functioning of the parathyroid glands or an imbalance of thyroid hormones.
Milia or retention cysts, unlike atheroma, are filled not with sebaceous secretions, but with horny masses. Therefore, their main development mechanism will be hyperkeratosis with increased division of epidermal cells. If we talk about dermoid cysts, they most often arise when embryogenesis processes are disrupted, i.e. they are congenital in nature.
A cyst on the face can have different origins, which the doctor will have to find out. Only after establishing the cause of the formation and its nature can we begin further correction.
Localization of pathology
Atheroma in the head area has an external resemblance to a bunch of grapes, since against the background of clogged pores, a whole group of neoplasms is formed. An increase in the diameter of the growths leads to a visible cosmetic defect. However, in most cases, this type of neoplasm appears singly and is almost invisible.
The growth can also be localized in the shoulder area. Such growths most often have a large diameter. Less commonly, cysts appear in the area of the hearing organs. These epidermal growths have a tendency to suppuration and inflammatory processes. Atheromas are located in the area of the earlobe or on areas of the skin surface located behind the auricle.
Atheromas in the eyelid area can be either single or form in small groups. The average diameter of the tumor is about fifty millimeters. The danger of this growth is that inflammation of the atheroma can cause disruption in the functioning of internal organs. That is why it is very important to remove such growth in a timely manner.
Atheroma is a tumor-like formation resulting from blockage of the sebaceous gland duct
Symptoms
A mass formation on the skin of the face (even a small one) is not a cyst on the leg, which no one will pay attention to. And when a similar problem arises in a child, it brings even more anxiety. But only a doctor can dispel all doubts regarding the benignity of the tumor and methods for its elimination. After conducting an examination, the specialist will give answers to all your questions.
An epidermal cyst of the facial skin is a closed formation containing horny masses mixed with sebum. The epithelium above it remains unchanged, probably only the expansion of the pores and the appearance of a vascular mesh. The size of the atheroma is usually in the range of 5–10 mm, but can also be significantly larger.
Atheroma develops gradually over quite a long time. Such a cyst is localized in various areas: on the head under the hair, on the forehead, cheeks, in the area of the lower or upper eyelid. The latter is also called atheroma of the eye, although the apple itself, of course, is not affected.
An epidermal cyst does not cause physical discomfort. But there are two situations when a tumor is cause for concern: when it becomes large and becomes inflamed. In the first case, there is likely to be pressure on neighboring structures, including vessels and nerves, and in the second, an abscess (microabscess) may form. Then other signs appear in the clinical picture:
- Redness of the skin.
- Swelling.
- Soreness.
An infected atheroma proceeds like a boil, only without a necrotic core. Despite this, pus accumulates in the center of the tumor, which can break out or, much worse, spread to neighboring tissues. Therefore, if you suspect an inflammatory process, you should not hesitate to consult a doctor.
Regardless of where the atheroma arose - on the back or on the cheek - its objective symptoms are the same. However, in the facial area, a complicated tumor has a much greater health risk.
Another subcutaneous cyst is a dermoid. It has an oval or spherical shape, has a dense capsule and can be multi-chambered. The contents of the cyst are various elements of the skin and its appendages:
- Epidermal cells.
- Sebum.
- Hair.
- Nails.
Dermoid cysts are usually found in children or young adults. This is a painless and fairly dense tumor, not fused with surrounding tissues. It grows slowly, but under certain conditions (heredity, the influence of carcinogens) it can degenerate into malignant.
The forehead and bridge of the nose, behind the ear area, and neck are most susceptible to the formation of such cysts. But dermoid can also appear in other areas: on the back, abdomen, lower extremities, above the sacral spine, in internal organs (ovaries).
White spots on the face, especially common in adolescents and adults, but also common in the newborn period, are milia. These are intradermal cysts containing horny masses, not sebaceous secretions. They do not connect to the ducts of the glands, and therefore cannot empty themselves spontaneously.
Small nodules up to 3 mm in size are white or yellowish in color and rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Usually they are located in groups, but never merge with each other. Milia are prone to spontaneous disappearance, which is associated with the natural renewal of the skin.
Why does a wen appear on the body and why is it dangerous?
If a wen appears under the skin, you should consult a surgeon. In medicine, this disease is called lipoma, or lipoblastoma. This is a benign tumor of adipose tissue. Women get sick more often. This cosmetic defect can only be eliminated through surgery. Conservative methods of therapy are ineffective.
Lipoma formation on the body
Subcutaneous wen are small tumors that have a benign course. They do not cause physical discomfort and do not pose much danger. Most often, a fatty cyst forms under the skin. This localization is observed in 95% of cases. Less commonly, internal organs and bones are affected.
Some patients develop lipomatosis. With it, several tumors form at once. Women aged 30 to 50 years are most often affected. Often this pathology is detected in adolescents. The following types of lipomas on the body are known:
- fibroid;
- vascular;
- smooth muscle;
- myelolipomas.
A tumor can form in any part of the body. In some cases, the brain is involved in the process.
Main etiological factors
The exact cause of the development of this disease has not yet been established. The following predisposing factors are of greatest importance:
- genetic predisposition;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- poor nutrition;
- parasitic diseases (demodicosis);
- lack of personal hygiene;
- changes in natural hormonal levels;
- damage to the hypothalamus;
- liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis);
- pancreas pathology;
- alcoholism;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- malignant tumors.
This disease appears regardless of a person’s weight. Wen often forms in malnourished people. The most common genetic therapy for the origin of this disease. According to her, wen appears in people with impaired embryogenesis. This happens long before birth. The disease is inherited from parents.
What causes wen to appear is known to endocrinologists. This pathology is associated with impaired production of low-density lipoproteins. Against this background, there is an accumulation of fats in small vessels under the skin. Over time, a capsule forms and a lipoma appears. This pathology is often combined with atherosclerosis and fatty liver hepatosis.
There is another theory. According to it, lipomas throughout the body arise against the background of pustular diseases (boils). Acne can also be a cause. Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules contributes to this. The underlying cause is blockage of the sebaceous glands. The role of microscopic mites in the development of wen cannot be ruled out.
How does the disease progress?
Lipoma is fairly easy to detect. Most often, patients visit a doctor when the tumor reaches a large size. Subcutaneous wen is a cosmetic defect that can only be eliminated through surgery. This neoplasm has the following characteristics:
- movable;
- round shape;
- not welded to tissues;
- painless;
- dense to the touch.
Wen appear in a variety of areas. The back, chest, upper limbs, legs, face, and scalp are most often affected. Lipomas form where there is fatty tissue. Most often, these neoplasms do not exceed 5 cm in diameter. Their size is about the size of a pea. In rare cases, wens larger than 5 cm in size form on the shoulder or back.
A giant lipoma may appear. She's hanging down. There is a leg at the base. Such neoplasms are dangerous, as there is a risk of compression of blood vessels, the formation of ulcers and tissue necrosis. The wen that appears on the body grows slowly. Upon palpation, a lipoma can be easily distinguished from other neoplasms.
It has a soft elastic consistency. As connective tissue grows, the wen becomes denser. In most cases, there are no subjective signs such as pain or burning. The presence of multiple wen on the body is often observed. Their number sometimes reaches dozens. Often lipomas are located along the nerves.
Lipomas of various localizations
It is necessary to know not only the reasons for the appearance of wen on the body, but also how the disease progresses when a particular anatomical area is affected. In the vast majority of cases, benign tumors appear in the chest, abdomen and back. Every experienced attending physician knows what a wen looks like on the body.
In old age, multiple lipoblastomas are often detected on the anterior abdominal wall. Sometimes they reach gigantic sizes (up to 20 cm). In some cases, lipomas are found in the spinal column. Tumors can form in the thighs and forearms. Sometimes they are painful. This is possible when a nearby nerve is compressed.
Blood vessels are rarely affected. Their compression is possible during the formation of adhesions. Such people experience aching, dull, moderate-intensity pain that intensifies with physical activity. In case of germination of small vessels (venules, arterioles, capillaries), an angiolipoma is formed.
Not everyone knows why wen appear in parenchymal organs. This rarely happens. Most often the tumor is localized under the skin. Organs such as the liver, ovaries, spleen, and adrenal glands may be affected. Lipomas are often found in the scalp area. They look like simple cones. The skin in the area of the tumor is colder. Women often face this problem.
Wen appears on the body in the neck area. Large tumors can put pressure on the esophagus. This is manifested by difficulty swallowing. The voice of a sick person may change. The appearance of hiccups indicates compression of the phrenic nerve. When the wen is localized at the back of the neck, there are most often no symptoms. In women, a tumor may appear in the breast area.
Patient examination plan
Before getting rid of wen on the body, you should be thoroughly examined. Subcutaneous neoplasms are easily recognized by their appearance, soft consistency, painlessness and stretching of the skin in this area. Palpation is not always possible. In this case, the following studies are required:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- CT scan;
- puncture biopsy followed by cytological analysis.
Laboratory diagnostic methods are of little value. On an x-ray, lipomas are identified as a rounded clearing. Often tumors have a cellular structure. The enlightenment has clear contours. This is different from a malignant tumor. A wen formed on the body must be distinguished from atheroma and lymphoma.
This is important for subsequent treatment. The exact causes of wen, like atheroma, are unknown. In both cases there may be no complaints. Atheromas are most often localized in the head, armpits, neck and back. They are more dense.
Upon examination, excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands are often detected. Lymphoma is a malignant tumor. It causes itching, swollen lymph nodes and symptoms of intoxication.
To exclude malignant pathology, a biopsy is performed.
How to remove a tumor
You need to know not only why wen appears, but also what the treatment of patients should be. There are no drugs that can remove the tumor. The only way to get rid of the disease is to remove the tumor. Surgery is not always required. Indications for surgical treatment are:
- the presence of a large wen;
- active tumor growth;
- functional disorders;
- presence of pain syndrome.
Most often, removal is carried out due to a cosmetic defect. Not everyone knows how to treat this pathology. You can get rid of wen on an outpatient or inpatient basis. For multiple lipomas, several treatment courses may be required. The operation is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia.
For subcutaneous wen on the body, the following types of interventions are most often organized:
- excision together with the capsule;
- endoscopic removal;
- liposuction.
After surgery, an antibiotic is administered. This is necessary to prevent infectious complications. It is necessary to remove the entire wen along with the membrane. Endoscopic operations are less traumatic. Such treatment is being performed more and more often. The advantage of this method is the presence of a small incision.
Its size is about 1 cm. Despite this, such treatment has disadvantages. The main one is the possibility of relapse. This also applies to liposuction. It is inappropriate to call it a radical method of therapy.
If treatment is carried out in a timely manner, complications develop extremely rarely. The prognosis for this disease is favorable.
If the wen is localized in areas subject to mechanical stress (in the area of the butt, arms, back), then damage must be excluded.
Nonspecific preventive measures
It is necessary to know not only what a wen is and why it is dangerous, but also how to reduce the risk of developing a tumor. There is no specific prevention, as this is a non-infectious disease. If there is a wen on the body, the reasons for the appearance of lipoma are few. In order to minimize the risk of tumor formation, it is necessary:
- Wash your body regularly with hot water;
- change your underwear more often;
- Healthy food;
- treat endocrine diseases;
- normalize the daily routine;
- exercise;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- prevent diseases of the liver and pancreas.
You need to know not only the symptoms of a wen, what it is, but also how to prevent its occurrence. In case of lipid metabolism disorders and the presence of atherosclerosis, it is recommended to take statins. These medications reduce the level of low-density lipoproteins in the blood, thereby normalizing fat metabolism. Thus, small lipomas are not a threat to humans.
Source: //dermet.ru/onk_kg/opyh/zhirovik.html
Additional diagnostics
What caused the atheroma on the face or what the nature of the other cyst is - all this will become known based on the results of additional diagnostics. After a visual examination, the doctor must make sure that the formation is benign and make a final conclusion. They will help him with this:
- Complete blood count (leukocyte count, ESR).
- Blood biochemistry (hormonal spectrum, immunogram).
- Content analysis (microscopy, culture).
- Histological examination.
- Ultrasound of soft tissues.
When a cyst suppurates, it should be distinguished from acne or boils, and nodes under the skin require differential diagnosis with lipomas. But each case requires individual consideration.
The diagnostic program should confirm the doctor’s assumption and exclude the development of other conditions that occur with similar symptoms.
Treatment
If the cyst is small in size and does not cause physical or emotional discomfort, dynamic observation is indicated. In all other cases, it is necessary to fix the problem. There are several ways to remove atheroma on the face:
- Instrumental husking.
- Laser destruction.
- Electrocoagulation.
Similar techniques are shown for other formations discussed above. Large cysts require a full-fledged operation, but milia can be removed by mechanical curettage. If suppuration occurs, then conservative therapy (antibacterial, anti-inflammatory) is first carried out, and only then they begin to remove the pathological formation.
Skin cysts are a common problem that many people experience. They can be found both on the back (stomach, limbs) and on the face, which creates significant aesthetic discomfort. In such cases, the problem becomes not only medical, but also cosmetic, requiring appropriate correction.
A sebaceous gland cyst (atheroma) is a tumor-like neoplasm that appears when the sebaceous gland duct is blocked. Most people develop at least one atheroma during their lifetime.
Cystic formations of the sebaceous glands are divided into two groups:
- True (primary atheromas) are nevoid tumors that arise from the appendages of the epidermis.
- False cysts (retention or secondary atheromas) - appear due to thickening of sebum and/or blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland.
Characterized by slower growth, they can reach very large sizes. Such tumors are more often observed in females on the scalp.
Characterized by faster growth. They can be multiple and tend to merge to form lumpy conglomerates. They are usually painless, may have a cyanotic tint, and are localized mainly in the behind-the-ear fold, on the cheeks, neck, along the wings of the nose, on the chest, and back. On the surface of the retention cystic formation there may be a noticeably enlarged hole, from which the contents of the tumor may protrude from time to time (with pressure or spontaneously).
The difference between atheroma and lipoma
Wen and sebaceous cyst have great similarities, which can lead to confusion. Let's look at how atheroma differs from lipoma and how to distinguish these tumors. First of all, both growths have different natures of origin. Lipoma is a benign tumor, and atheroma is a cystic neoplasm.
There are a number of specific signs that help distinguish neoplasms from each other. First of all, the nature of the pathology can be determined due to the mobility of the neoplasm. Lipomas are almost immobile, and atheromas are much more difficult to press to a specific area of the body. Also, the structure of the lipoma is softer, and the neoplasm itself develops very slowly. Lipomas never become inflamed and can grow on the surface of internal organs.
However, all of the above signs can only be recognized by a specialist. That is why, when growths appear on the surface of the skin, it is very important to promptly seek medical help. This measure will avoid serious complications.
Atheroma is a “sac” that has a capsule and is filled with thick yellowish masses
Causes and risk factors for atheroma
Atheroma can occur on any part of the human body that has hair. However, most often this formation appears on the skin of the head, face (often localized below the mouth), neck, back, and genital area.
A frequent cause of the development of the pathological process is blockage of the sebaceous gland duct. Atheromas can also occur when the hair follicle swells (for example, when it is damaged), or when the sebaceous gland ruptures.
Secondary atheromas often occur when the outflow of gland secretions is disrupted in patients with phlegmonous acne, oily seborrhea, and hyperhidrosis.
Risk factors include:
- hormonal disorders (for example, increased testosterone concentrations);
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- frequent trauma to the skin (for example, when shaving);
- metabolic disease;
- improper use of cosmetics.
Symptoms
As can be seen in the photo, atheroma is a dense, elastic, mobile formation located superficially, which has clear contours. The skin over it is not changed.
With the development of an infectious-inflammatory process, the cystic cavity can be filled with purulent contents, sometimes mixed with blood. The skin over the cystic formation is covered with a network of dilated capillaries; dilated pores may be noticeable on the surface of the atheroma. Typically, the cystic formation is 0.5-5.0 cm in diameter, but with inflammation it can increase to large sizes.
When neoplasms become inflamed, the following may occur:
- redness and swelling of the skin over the atheroma;
- increase in size of formation;
- pain that increases when touching the affected area;
- release of a substance with an unpleasant odor, which may have a whitish-gray color;
- local temperature increase.
In case of inflammation and suppuration, atheroma can break out on its own. The breakthrough of an inflamed neoplasm into the subcutaneous tissue and its infection can lead to the development of an abscess and phlegmon.
Diagnostics
An examination by a dermatologist is usually sufficient to make a diagnosis. In doubtful cases, consultation with an oncologist may be required.
When collecting complaints and medical history, special attention is paid to the patient’s allergies, concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, etc.), and the use of medications that can affect the blood coagulation system.
For differential diagnosis purposes, you may need:
- Ultrasound - allows you to differentiate atheroma from fibroma (benign tumor of connective tissue), lipoma (neoplasm of adipose tissue), benign tumors of the sweat glands;
- histological laboratory examination – allows to exclude malignant neoplasm, epithelioma of Malherbe;
- X-ray examination of the skull bones - carried out in the presence of large cystic formations of the sebaceous glands on the head in order to exclude a cranial hernia.
Reasons for the appearance of wen
The answer to this question is given by endocrinologists. The reasons for the appearance of lipoblastomas are hormonal imbalance in the body and disruption of cellular metabolism. Diabetes mellitus, problems with metabolic processes, poor nutrition and thyroid pathology are factors in the onset of the disease. It is believed that this disease appears in people prone to obesity. But this is not true. Fatty cysts are inherited and appear in embryos during pregnancy. The causes of tumors are primarily hormonal imbalances: improper distribution of hormones.
Types of fatty tumors
- A diffuse lipoma does not have a membrane containing connective tissue.
- Capsulated wen forms on the surface of internal organs.
- Fibrous lipoblastoma is dense and composed of connective tissue.
- Petrified subcutaneous wen occurs due to salt deposition.
- Ossified lipoma is a growth of bone tissue.
- Tree-shaped fatty cyst penetrates into the joints.
We should also pay attention to fatty cysts in intimate places: on the labia in women and the scrotum in men. Wen has the appearance of a soft and sometimes hard nodule that rises above the skin. This is a yellow ball that consists of sebum. Such tumors are noticed when hygiene procedures are performed.
Fatty cysts on the body of an infant are not uncommon. If the baby is under 3 months old, there is no reason to worry. milia on the face disappear as the newborn ages. The persistence of wen is a genetic predisposition and a cause for concern.
A fatty cyst found in women is a galactocele or breast lipoma. Breastfeeding women suffer from the disease. The accumulation of milk occurs in the cyst, the nipple nearby. The disease is fraught with mastitis and abscesses, and it is in the woman’s interests to go to the doctor in time, who will give instructions and help avoid serious consequences of the disease.
Factors in the development of breast cysts
- narrow, uneven milk ducts;
- bruises or breast injuries received long before feeding;
- inflammatory process or bacterial infection;
- lactostasis or mastitis due to improper application;
- abnormal behavior of hormones
Recognition, formation and treatment of galactoceles (lipomas)
If a woman consults a doctor and complains of pain and discomfort, it is important to carry out a number of medical procedures:
- examination of the mammary glands;
- mammography;
- Ultrasound;
- puncture and cytology of fluid samples;
- additional blood test.
A female representative carefully takes care of her health when breastfeeding. If symptoms of galactocele appear, a visit to the surgeon should not be postponed. Based on the tests taken, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment and looks at the further results.
- It happens that a cyst in the breast resolves on its own.
- If the issue is a hormonal imbalance, then improvements are visible after therapy.
- Small cysts in the breast are monitored and not treated.
- Performing a puncture does not guarantee the avoidance of recurrent galactoceles.
- In other cases, a surgeon takes over the matter.
Sometimes breastfeeding is sacrificed for the sake of the mother's health. They prevent the disease so that malignant tumors do not develop: fibroadenoma and breast cancer.
Diagnosis of wen
In order to exclude a lipoma, a dermatologist or surgeon examines the patient. When identifying a fatty cyst in internal organs, muscles or bone tissue, ultrasound, CT or MRI diagnostics are prescribed. If the subcutaneous wen is more than 3 cm, a cytological examination of the cells is planned to identify malignancy. If there is more than one wen on the body, the doctor recommends taking blood tests for hormones, and also advises visiting an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist.
Treatment
If the atheroma is small in size and does not cause concern to the person, treatment may not be necessary. In such cases, a wait-and-see approach is usually chosen.
If there is an inflammatory process, the patient may be prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments and ultra-high-frequency therapy. After the inflammation disappears, the formation is removed. If there is an infectious process, the patient is advised to take antibacterial drugs.
Commonly used methods for treating atheromas in the early stages include:
- Laser removal of formation. It is performed under local anesthesia. When removing a tumor on the head, shaving the hair is usually not required.
- Electrocoagulation. Used in the absence of inflammation in relation to small atheromas.
- Cryodestruction. It is used in the presence of small inflamed cystic formations that are located close to the surface of the skin.
Surgery may be required to remove atheromas. The operation to remove a cystic formation of the sebaceous gland does not require hospitalization and is performed on an outpatient basis. In very rare cases, general anesthesia may be necessary (for example, in case of a giant cystic formation); generally, the intervention is performed under local anesthesia.
Before the operation you need:
- pass all necessary tests;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol one day before;
- do not eat 4 hours before surgery.
During surgery, according to one of the methods, the skin is cut with a scalpel (while avoiding damage to the tumor capsule), after which careful pressure is applied to the edges of the wound, removing the atheroma, then cosmetic sutures and a bandage are applied.
During surgical treatment of atheroma, special attention is paid to completely removing the capsule of the formation, since otherwise the remaining part of the capsule may cause a relapse.
On the first day after surgical removal of the tumor, the patient may experience an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels. If the level of this indicator increases significantly (more than 38 °C), swelling and pain develop at the operation site, you should seek medical help.
Complications
A sebaceous cyst is not a complex disease that has a negative impact on the functioning of the body. The growths do not spread deep under the skin, and also do not exert any pressure on nearby tissues. However, inflammatory processes in the area of the cyst are considered a rather dangerous complication. Suppuration can lead to the spread of pus into the deep layers of the skin, which is accompanied by an abscess . In this situation, you should immediately seek medical help.
Pus that spreads deep into the skin can cause blood poisoning, which can be fatal.
Prevention
To prevent the development of cystic formations in the presence of oily skin and/or acne, it is recommended:
- Conduct professional facial cleansing from a cosmetologist, as well as thoroughly cleanse the skin at home, following the recommendations of a specialist.
- Limit consumption of fatty foods and foods high in simple carbohydrates.
- Strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
- Limit the use of decorative cosmetics and use high-quality skin care products.