There are always a number of moles on the human body, regardless of genetic predisposition. And patients who have become infected with a skin virus may also develop warts that look like large moles. The difference between a wart and a mole is significant, since they have completely different natures. How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma? The formation can be classified visually or using skin analysis.
Types of skin neoplasms
Today, specialists know several types of neoplasms that can appear in different areas of the skin. However, the most commonly diagnosed are papillomas, moles, and warts.
What is papilloma
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm of various shapes and sizes that appears on the skin as a result of activation of the human papilloma virus in the body.
It is worth noting that more than 70% of the world's population is infected with this virus. In some patients it is in a latent form and does not lead to the appearance of growths, but in many it manifests itself in the form of multiple papillomas.
The growths are localized in different parts of the body; quite often they are diagnosed in internal organs, for example, the gallbladder or mammary ducts in women.
It is important to remember that many people are unaware of the presence of the virus in the body, which leads to its spread and infecting others.
Papillomas can have a round or pointed shape, a wide base or a thin stalk. In addition, the growths do not cause pain unless they are injured.
Features of moles
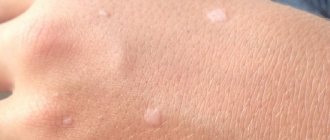
Distinguishing a mole from a papilloma is not so difficult. A mole, or nevus, is a benign neoplasm that occurs as a result of improper distribution of the melanin pigment in the upper layers of the skin. Typically, such growths appear in a person in early childhood and can increase in size.
Moles are not dangerous as long as they are not damaged. In addition, intensive growth of tumors can be provoked by exposure to sunlight. It is also worth remembering that a nevus has clear edges and a regular shape.
The localization of moles is different; they, like papillomas, can appear on different parts of the skin, scalp and even the genital area.
However, internal moles in people are not diagnosed. Nevi can be large or small in size, and can also protrude above the surface of the skin. The latter are often confused with warts, especially when they are not dark in color.
It is important to know that at the base of each mole there is a vascular bundle that supplies it with nutrients and blood. If this part of the tumor is damaged, severe complications may develop, and bleeding can be quite difficult to stop.
Signs of warts
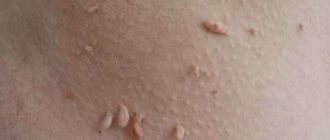
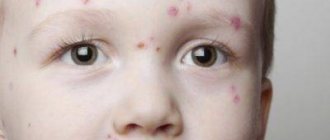
Warts are also benign skin growths, the cause of which is believed to be the activation of the human papillomavirus in the body. The growths come in different sizes and shapes and appear mainly on the face, legs or arms, especially in the area of the hands.
For several centuries, it has been a common belief among people that the cause of warts is skin contact with toads or frogs.
However, experts have refuted this theory. Despite this, even today many are so confident in its accuracy that after contact with animals a person actually develops a wart. This is self-hypnosis and has no scientific confirmation.
There are several common types of growths:
| View | Peculiarities |
| Common or vulgar warts | The most common type of neoplasm, especially among adolescents. Appear as a result of weakened immunity and infection with the human papillomavirus. They have different sizes and appearances, in most cases they are localized on the hands, between the fingers, and sometimes in the area of the nose and mouth. Such growths are quite easy to remove at home, since today you can buy special quick-acting products at the pharmacy without a prescription. Typically, such warts do not pose a danger to humans and almost never degenerate into a malignant neoplasm. |
| Flat neoplasms | Flat warts appear on the legs and arms, less often on the face. They are almost no different in appearance from vulgar ones, but can affect adults, children and the elderly. The neoplasms are flesh-colored or slightly pink, usually have a small or medium size, but in patients over 60 years of age they grow quickly. In most cases, such warts do not pose a threat to the life and health of the patient, but if they are located in a place where they are constantly damaged, they can provoke complications. |
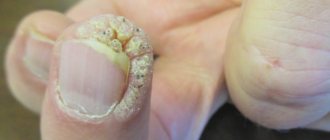
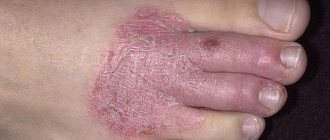
| Plantar growths | Warts on the feet are most often localized between the toes or on the soles of the feet. The latter are one of the few types that actually cause discomfort to the patient as a result of permanent damage. Friction, shoe pressure, and increased work of the sweat glands in the summer lead to the growth of the wart, the appearance of pain and other symptoms. Most often, patients visit a doctor to remove a plantar wart. |
Regardless of the type of wart, it rarely causes serious complications. If the tumor causes significant discomfort to the patient, he should immediately visit a doctor and undergo an removal procedure, which will solve the problem and prevent consequences.
Reasons for appearance
Moles (nevi) and warts (papillomas) have different causes. Nevi are formed as a result of genetic predisposition. Most neoplasms appear before the age of 10. But new moles can occur even in adulthood. The reasons for their appearance are:
- excessive doses of sunlight or ultraviolet radiation in a solarium;
- sunburn;
- hormonal imbalances or surges.
Often nevi form during pregnancy, menopause or puberty. All these conditions are characterized by a sharp increase or decrease in a number of hormones. Moles appear during hormonal therapy, as a result of disruption of the endocrine system. Warts arise exclusively as a result of a skin virus - papillomavirus.
This disease is mainly characteristic of southern countries, common in Mexico and Cuba. Papilloma is transmitted from person to person through sexual contact or kissing. It can affect the body in the following ways:
- through blood transfusion;
- through uncleaned instruments;
- upon contact of the mucous membrane with infected objects (this could be infected cutlery, dishes, personal hygiene products);
- in rare cases - when visiting the pool, if there are bleeding wounds on the skin.
The spread of the virus in the modern world is significant: according to various sources, every 4 or even 3 people on Earth are infected. However, papillomavirus is not dangerous to the body in the early stages of development. If the patient has good immunity, then the pathogen will simply remain in the blood without developing. The incubation period can last decades.
The disease will manifest itself as soon as the immune system weakens as a result of one of the following problems:
- blood loss;
- hormonal changes;
- surgical intervention;
- immunodeficiency disease;
- acute respiratory illness;
- vitamin deficiency;
- stress.
With a strong decrease in immunity, the pathogen penetrates the upper layers of the skin and changes the structure of some cells. These cells stop dying properly and begin to grow. As a result, papules appear - growths of various types. They can be flesh-colored, or they can take on a dark shade. Warts are dark-colored papules that communicate with the circulatory system. That is, warts are of viral origin, while nevi are of genetic or systemic origin.
Similarity of formations
It is not so easy to distinguish a mole from a papilloma or wart if the neoplasm is colored in a neutral flesh-colored or pinkish color, and also has other similar features.
The main ones include the following:
- Small size. In more than 70% of cases when a wart, papilloma or mole is detected, the growth is small in size.
- Form. All types of skin formations can have clear, smooth edges, a round or slightly elongated shape. That is why specialists cannot determine the type of growth without a special device.
- They do not cause discomfort. If a mole, papilloma or wart is located on the body, is not damaged, it does not provoke pain or other manifestations.
- May protrude above the surface of the skin. All new growths are distinguished by this feature, and in combination with a neutral color, an inexperienced person will not be able to determine the type of growth.
- Affects the top layer of the skin. This general feature can only be attributed to papillomas and warts, since moles can be deep. However, in many cases, growths affect only the epidermis, which also complicates diagnosis.
Despite some similar features, there are many differences that will help differentiate the growths and accurately determine the cause of their origin.
How is diagnostics carried out in the clinic?
The difference between a nevus, papilloma, condyloma, a wart of another group, or a manifestation of a skin disease is not always obvious. For this reason, it is possible to find out whether a growth that has popped up on the skin is a wart or a sign of other diseases only after undergoing tests. During the initial examination, a dermatologist can only suspect a manifestation of papillomavirus. But since warts in the genital area may have a nodular shape similar to genital herpes, and a growth on the skin of the arm may turn out to be dermatofibroma, any doctor will first send the patient for testing. As a rule, papillomavirus is found in the blood of seven out of ten people.
If you suspect sexually transmitted infection, your doctor will advise you to get tested for HIV, syphilis and other diseases transmitted during unprotected sex.
How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma and a wart
There are several criteria that allow one to distinguish one or another type of neoplasm on a person’s skin.
Main Difference
The most important and basic difference between moles and papillomas and warts is the origin of the neoplasm. The former are congenital abnormalities of melanin distribution and are usually inherited from parents.
How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma
Warts and papillomas always arise as a result of penetration of the human papillomavirus into the body. It does not matter whether it was transmitted sexually or during childbirth from mother to child.
Appearance
It is not so easy to distinguish growths by appearance, but it is possible if you take into account all the features that separate a mole from a wart or papilloma.
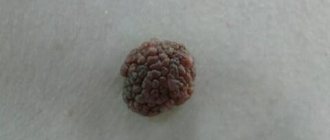
The mole is usually brown in color, the shade may be darker or lighter depending on the concentration of melanin. New growths can be quite large, up to 6-10 mm in diameter. They always have clear edges, uniform color and almost regular shape.
There are no irregularities or depressions on the mole. Its structure is in most cases homogeneous and dense. When touched, the patient may feel a density, but it is moderate. Only in some cases, moles are light in color. However, clarity of outline and shape is the most important external feature.
Papillomas can be soft to the touch, have a wide base or are attached to a thin stalk, are located in several pieces at once and are colored slightly pink or flesh-colored.
They are mobile, in most cases they are small in size, slightly or strongly raised above the surface of the skin. Additionally, the formations have a uniform color, there are no depressions on their surface.
Warts are also pink, flesh-colored, or light brown in color. They have a uniform structure and are very dense to the touch. The edges of such growths are clear, the shape is in most cases round, and the base is wide and is well attached to healthy skin.
It is worth noting that warts on the hands and face are always convex, but on the soles internal growths may appear that do not protrude above the surface of the skin.
Locations
Depending on the location of the growths, their type can be determined.
It is worth noting that any type can appear on different parts of the body, but experts have identified some patterns:
- Nevi appear on the body, face and scalp. Less commonly, they can be seen on the feet, hands and genital area.
- Papillomas are localized in the axillary area, in the genital area, on the neck, and back. Less commonly, they can be found on the body, face, and scalp. The main difference between these growths is that they can even affect internal organs.
- Warts most often affect the hands, feet and face.
Each patient is individual, so neoplasms can be localized in atypical places.
Causes and time of appearance
Most patients know that nevi are the result of improper distribution of melanin in the upper layers of the skin. They are hereditary neoplasms that appear in the first years of a child’s life and do not disappear throughout life. The exception will be forced deletion.
The main reason for the formation of warts and papillomas is considered to be the penetration and activation of the human papillomavirus in the body.
The following are considered predisposing factors:
- Poor nutrition with insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals.
- Chronic vitamin deficiency.
- Violation of the work and rest regime.
- Regular contact with toxins and harmful substances.
- Weakening of the patient's immunity as a result of frequent colds.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, ignoring barrier contraception.
Unlike moles, warts and papillomas can appear at any age, and their growth depends on the immune system of the individual patient.
Need for removal
Papillomas and warts always require removal. This is due to their fragile attachment to the skin, high risk of damage and unaesthetic appearance. Many patients do this on their own, which is quite acceptable in the case of warts. However, it is strongly not recommended to remove papillomas at home.
Nevi are also allowed to be removed if they are located in a place where they are constantly damaged and also spoil the appearance. However, not every mole can be removed. In addition, such a procedure is fraught with risk, so the decision should only be made by a doctor after examination.
Degree of cancer risk
You can also distinguish a mole from a papilloma and a wart by the degree of cancer risk. Nevi constantly receive nutrition from blood vessels, and can also penetrate deeply into the skin. They more often degenerate into a malignant tumor, and also react very negatively to exposure to sunlight.
Warts almost never provoke the development of a malignant neoplasm, since they are not only easily removed at home, but can fall off on their own.
Papillomas are more susceptible to degeneration because they are localized in places where they are constantly damaged. Despite this, nevi pose the greatest cancer risk.
Is the appearance of moles a sign of HPV?
HPV has nothing to do with moles.
Nevi are congenital formations and are inherited. HPV is an infection. Does not apply to heredity. Nevi are not a disease or its symptoms. Such benign growths are not dangerous in themselves, regardless of the size of the spot.
HPV is a pathology. Present in the bodies of approximately 80% of the population, they often do not manifest themselves in any way.
There is no need to treat moles, remove them, or worry. The appearance of other formations should be cause for concern.
Diagnostics
Several modern methods are used to diagnose education. The first step is to examine and interview the patient. Doctors clarify the time of appearance of the growth, the conditions, as well as the symptoms that could accompany the process.
After this, an additional examination is prescribed, including several methods:
- Clinical and biochemical blood test is a standard method in which venous blood is examined and the general condition of the patient is assessed.
- A blood test to detect the human papillomavirus is a specific type of study, which is always carried out to clarify the presence of the virus in the body, as well as to identify a specific strain. This examination is necessary when warts and papillomas appear; it allows one to detect strains with a high degree of cancer risk.
- Dermatoscopy - a type of study in which a tumor is examined using a dermatoscope. The dermatoscope directs special rays at the growth, which help to see deviations in the development of the tumor, as well as signs of degeneration.
- A histological examination of a sample of a neoplasm is carried out when signs of cell degeneration into malignant ones are detected during dermatoscopy. The specialist takes a sample of the growth, using a microscope and soaking it in a special solution, examines the cells.
A comprehensive examination allows you to determine the type of neoplasm.
Methods of treatment and removal
Most methods for removing both moles and warts are similar. These include:
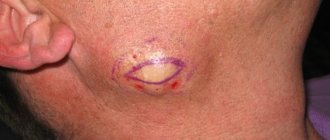
- Surgical removal . It is used in the case of large moles and papillomas or suspected malignant nevus. The method allows you to completely get rid of the tumor and conduct a histological examination of it, but leaves behind a scar.
- Cryodestruction . The most common way to remove warts. Its use in relation to moles is questionable due to the risk of their incomplete removal with the further launch of a malignant process. However, removing small (up to 3 - 4 mm) nevi using liquid nitrogen has a fairly positive effect, not accompanied by complications.
- Electrocoagulation . It is relatively widely used in the elimination of uncomplicated moles and papillomas without signs of malignancy.
- Laser removal . A highly accurate and high-quality method of getting rid of benign skin tumors, especially those located on the face, neck, arms and other open areas of the body. It leaves no traces behind, but is contraindicated for large nevi or suspected malignancy.
- Use of keratolytics . Used only for removing warts. The use of keratolytic agents on a mole can lead to its degeneration into skin cancer.
Controversial cases
There are controversial cases in which even a specialist finds it difficult to establish an accurate diagnosis. Usually in this case, additional examination is carried out.
Papilloma with black dot
When burgundy or black dots appear on a papilloma or wart, patients begin to worry. However, doctors say that if there are no other manifestations such as bleeding, severe pain, or changes in the structure of the growth, there is no need to worry.
Most likely, the vessel inside the formation was damaged. If the dots cover the entire growth and additional signs appear, you should consult a doctor.
Papilloma grows from a mole
If a patient discovers a sprouted papilloma on his mole, he should immediately consult a doctor. This deviation is due to the fact that the human papillomavirus can even infect areas of melanin accumulation.
Such a growth requires immediate removal with subsequent observation by a doctor.
Papilloma or melanoma
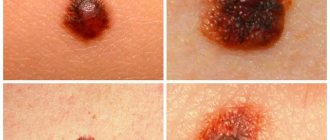
You can distinguish a mole from a papilloma after becoming familiar with the features of these neoplasms. However, patients should also know when to see a doctor, because the growth can develop into melanoma.
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm of the skin, which most often occurs as a result of the degeneration of cells of a common nevus. Papillomas extremely rarely degenerate into melanomas.
The main signs of malignancy:
- Pain and burning in the area of the tumor.
- Change in color, rapid increase in the size of the mole.
- Change in the outlines of the nevus to indistinct, blurred.
- Bleeding from a neoplasm.
If such signs appear, you should immediately visit a doctor.
What is a mole
Moles are distinctive features of our appearance
Moles are distinctive features of our appearance, therefore, when a person disappears, it becomes easier to find someone with a birthmark or a feature such as a small black mole on the face or arm. But what is each mole on our body? This is a benign tumor, it can also be malignant, but in rare cases, which, nevertheless, should not be written off. But in essence, moles are our skin cells that have accumulated pigment and become darker due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. The color of a mole can be light or flesh-colored, pink or red, or brownish and even black.
Pink and red nevi should be approached a little differently, because... These are vascular moles that are formed not by melanin, but by small blood vessels. Hence the color of such moles, varying from light pink to dark scarlet.
Not every mole becomes malignant, so don't assume that all moles on the body are dangerous. In order not to worry about the health of moles, you should regularly visit a dermatologist or oncologist, who can carefully and competently identify any changes that have begun. Moles appear for several reasons:
- An unexpected sharp surge or decline in hormones, especially in women and adolescents;
- Ultraviolet radiation, which can come from both the sun and solarium;
- Hereditary factor. Genetics can explain a lot, including the appearance of many moles on the body.
But what could be a sign of a nevus changing in a negative direction, its degeneration into melanoma?
- Pain, itching and burning in and around the mole,
- The appearance of a light or dark halo around the nevus,
- Bleeding and redness of the mole,
- Discharge of fluid from the birthmark,
- Injury to a mole, both partial and complete.
When does a formation need to be removed?
It is recommended to remove all raised papillomas and warts to reduce the risk of malignancy. Moles are removed quickly if
growth, bleeding or pain in the area where they are located. An additional indication for nevus removal is an unaesthetic appearance and permanent damage. In each case, the decision is made by the doctor after examination.
Only an experienced doctor can distinguish between various neoplasms on the skin. However, the patient is able to detect a mole at home and note features that help separate it from a papilloma or wart. Additionally, the person is recommended to study the symptoms indicating that the growth has degenerated into a malignant tumor. This will reduce the risk of developing severe complications.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Nevi
Synonyms for the name are mole, birthmark. In essence, all these neoplasms are pigmented nevi (naevus). These are accumulations of nevocytes - skin cells containing a lot of melanin (the pigment responsible for the color of the integument, hair and iris of the eyes).
It is believed that such elements are formed in the fetus in the womb. Some of them appear immediately after birth (4–10%), others during puberty (up to 90%), and others throughout life under the influence of environmental factors. 75% of Caucasians have moles.
Among the causes of malformations of the skin of the unborn baby, there are unfavorable factors to which the woman’s body was exposed during pregnancy:
- hormonal changes - sharp jumps in estrogen and progesterone;
- genitourinary system infections, sexually transmitted diseases;
- intoxication with poisons, alcohol;
- genetic disorders.
Attention! The main enemy of moles and spots is ultraviolet radiation. Under the influence of rays, neoplasms can transform into melanoma, a malignant tumor.
There are about a hundred varieties of pigmented nevi. They are located in the superficial epithelium, at the border of the epidermis and dermis or directly in the dermis.
Moles can be flat or raised above the integument, ranging in size from 1 mm to several tens of centimeters. If the spot occupies most of the skin, then it is called giant. Hairs may grow on the surface. Other neoplasms are also classified as nevi:
- hemangiomas - red vascular tumors;
- nevi of the sebaceous glands - do not contain melanin and are localized mainly on the head;
- anemic spots - light areas with a cluster of underdeveloped blood vessels.
The most dangerous type is dysplastic (atypical) nevi, found in 5% of people on the planet. They are initially prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor, and therefore require constant monitoring. This is a transitional form between a regular mole and melanoma or a precancerous condition.
The following symptoms of malignancy of any nevus should alert you:
- change in size, shade;
- bleeding;
- itching, pain, feeling of tension, tingling;
- transformation of a smooth surface into a rough one, the appearance of tubercles, cracks and foreign inclusions;
- changing the shape and smoothing the contours of the spot;
- peeling of the skin.
Diagnosis is carried out through visual examination, a magnifying glass or fluorescent microscope, laboratory tests, and a computer. In case of danger, the nevus is surgically removed along with part of the healthy integument and fatty tissue.