Author of the article
Dmitry Savelyev
Practicing dermatovenerologist, graduated from the Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov.
Articles written
60
According to the World Health Organization, there are currently more than half a million cases of cervical cancer reported annually. About 250 thousand women die from this disease due to too late diagnosis and ineffective treatment. The human papillomavirus is one of the most dangerous oncogenic viruses that provokes the development of malignant tumors.
What it is?
HPV is the name for a unified family of viruses that includes more than 100 different species. All these strains are divided according to the degree of oncogenic risk. About 13 strains lead to various types of cancer. After recovering from the virus, a person can become infected again.
Types of virus
According to statistics, more than half of the Russian population are carriers of different types of the virus, which shows the enormous prevalence of the virus. But this does not mean that HPV becomes a fatal diagnosis for everyone. Many types of papillomavirus do not affect human health in any way and only cause aesthetic defects in the form of papillomas and warts.
There are strains of the virus in which the development of cancer is almost impossible, the so-called low-oncogenic risk HPV. Types of the intermediate oncogenic type are also widespread, and these two categories include most varieties of papillomavirus.
There are significantly fewer types of viruses that provoke the occurrence of malignant tumors. This includes types 31, 33, 6, 11, 16 and 18. The last two pose a greater threat to women. Today, with the help of numerous studies, a connection has been reliably established between the development of cervical cancer and infection with types 16 and 18 of HPV. In 70% of cases, the appearance of malignant neoplasms is associated with the destructive effects of infection. Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer among women.
Already in the first two years after the virus enters the body, 15-30% of women experience changes in the cervical area, and a precancerous condition occurs. During the same time, such changes occur in only 2% of women not infected with HPV.
Types 16 and 18 are dangerous due to the complete absence of external manifestations. Only appropriate tests can indicate the presence of papillomavirus, while the infection itself is asymptomatic.
Even with a routine examination by a gynecologist, it is impossible to detect infection with these types of viruses. This manifestation of the virus is called the latent form and without treatment can lead to the development of cancer.
How dangerous it is and its prevalence
The majority of people who are sexually active have several types of papilloma viruses in their bodies. Its prevalence among people 20-25 years old is very high. The most dangerous types of viruses are those called oncogenic. Every year in Russia, about 4 thousand female representatives die from cancer caused by this disease. It is especially dangerous for women, since the virus cells have the ability to parasitize on the surface of the cervix. This is the danger, since men do not have this zone, they rarely get sick.
In almost 90% of cases of infection, recovery occurs on its own, without the use of therapy, without causing oncological processes in the body or any symptoms. The human immune system is able to independently overcome the papilloma virus as soon as it enters the body. This way you can get rid of papillomas forever.
In some cases, the ability of pathogenic agents to persist in the body for a long time remains, becoming more active in the presence of favorable conditions, causing a precancerous condition and cancer. Such “positive” factors include: a weakened immune system, smoking, sexually transmitted diseases, various forms of autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiencies.
Once introduced into the body, HPV can cause the following complications: the development of neoplasms, cervicitis, vaginitis, cervical dysplasia, and oncological processes.
Transfer methods
The most common route of transmission is unprotected sex with HPV carriers . The risk of contracting the virus in the first three years after first sexual intercourse is 46%. That is why those women and girls who can only have one sexual partner are added to groups traditionally at risk, for example, prostitutes. In particular, a high percentage of infections occurs among adolescents. Infection can occur through any type of sexual contact, including anal and oral.
Another method of infection is infection of newborns passing through the birth canal. If the expectant mother is a carrier of HPV, the child has a high chance of catching the virus during natural childbirth.
Subsequently, such children may develop laryngeal papillomatosis, a viral disease characterized by the appearance of papillomas in the larynx. Therefore, before planning a pregnancy, a woman needs to treat the infection, if present.
Forecast
It is almost impossible to completely eliminate HPV from the body. After eliminating formations from the skin (medication or hardware), the probability of relapse is more than 50%. To prevent the occurrence of malignant tumors due to the degeneration of HPV of high oncogenic risk, timely relief of pathology is recommended.
HPV is a viral pathology that manifests itself as formations on the skin. Papillomas (with medium and high risk of oncogenicity) can have different structures and can degenerate into malignant cells. Therefore, it is necessary to promptly examine formations and undergo tests to reduce the likelihood of developing cancer.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
How does infection occur?
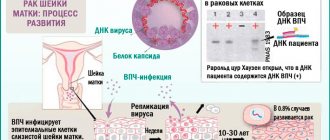
HPV infects stratified epithelium, which determines the affected area - the skin and mucous membranes. The DNA of the virus seeks to penetrate the nucleus of a human cell. Its goal is the reproduction of oncogenic proteins there. After this happens, they begin to rapidly replicate. If this is a benign growth, then the cells do not extend beyond the epithelium. If malignant, the spread of the pathological process triggers the occurrence of metastases. The incubation period lasts about three months.
Folk remedies
Folk formulations can be used only in the absence of contraindications; consultation with your doctor is necessary.
The most effective and popular recipes:
- dandelion. You can lubricate the growth 4 times a day with fresh dandelion juice. It disinfects and burns HPV cells. The juice should not get on healthy cells due to the likelihood of developing a burn;
- chamomile and St. John's wort . Steam 10 g of chamomile and St. John's wort in 1 liter of boiling water. Insist. Use for sitz baths (to get rid of HPV on the genitals and rectum) or for foot baths. Before use, you need to dilute the composition with 2 parts of water;
- aloe _ Squeeze fresh aloe juice and make lotions with it for 10-15 minutes 3-4 times a day.
The duration of treatment is determined individually based on the dynamics of therapy.
Manifestations of HPV
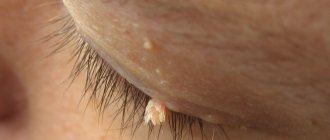
- Warts. Dense growths with an uneven surface and color from gray to black. Appear after infection with low-oncogenic types of the virus. They do not threaten human life and health, but cause cosmetic problems. They are most often localized in the area of the hands and feet, but can also appear on the surface of the entire skin. There are also plantar warts, which become thicker and rougher when walking. Their characteristic difference is the appearance of blood when the top is cut off.
- Genital warts. They are benign neoplasms located on the skin and genitals. There are growths that are flesh-colored, pink or brown. Their characteristic feature is rapid spread. They can occur in the cervix, but it is also possible that the urethra, rectum and anus are affected. Condylomas cause discomfort in the form of itching and burning. At an early stage, single growths most often appear. At later stages, condylomas show the ability to merge. They do not pose a risk of degeneration into malignant neoplasms.
- Flat condylomas. More dangerous in terms of the development of cancer. The likelihood of cancer increases as new growths appear. This type of condylomas is usually located on the vaginal mucosa.
- Bowenoid papulosis. A viral disease considered precancerous. A characteristic feature is a rash in the genital area. Pigmented papules also appear - smooth brown formations. Papules often appear together with condylomas and warts. The components of the rash can lead to various types of cancer that are dangerous for women.
- Cervical cancer. For every woman, there is a risk that the virus will degenerate into a chronic form, and the precancerous condition may ultimately develop into cancer. If you don't treat the virus, it will just be a matter of time. In women with good immunity, such processes occur within 15 years. For those whose bodies suffer from weakened immunity, for example, HIV-positive women, this will take only 5 years.
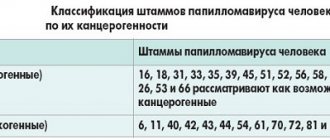
Papillomavirus classification table
The table shows the classification of papillomavirus
| Danger level | Strains | Pathogenesis |
| Non-oncogenic types of papillomavirus | 1-5 | Formations of this type are benign and do not degenerate into oncology. If they do not cause discomfort or cosmetic defects, they are not removed. In case of frequent injury, they are eliminated with liquid nitrogen, laser, radio wave therapy or diathermoelectrocoagulation. |
| Low oncogenicity | 6,11,42-44 | Vaccines have been developed against the first two strains. Such strains of human papillomavirus are dangerous types of infection for patients suffering from immunodeficiency. Most people infected with these types of infection remain relatively healthy and do not develop cancer. |
| Highly tumorigenic | 16,18, 31,33-35,45,51,52,56,68-70 | The activity of the strains accompanies the development of cancerous tumors, the localization of which is noted on the genital organs. |
The classification of virus types is based on the clinical picture of manifestation. Dermatologists and oncologists note that the same type of virus is capable of detecting its presence in a particular organism in different ways. Papillomatosis is not always a harmless, curable disease; sometimes it indicates the development of a serious pathology.
Diagnosis of the disease
It often happens that a woman can discover problems in the body after a routine visit to the gynecologist, where a smear is taken from her. To identify the causes of possible diseases, the doctor has to conduct a number of additional studies and tests.
So, the procedure for diagnosing the disease should be as follows:
- An initial external examination by a doctor, during which a smear is taken to determine the state of the vaginal microflora, the level of leukocytes and identify diseases.
- If the test results are unsatisfactory, as indicated by an increased level of leukocytes, the gynecologist prescribes additional tests for STDs, which necessarily include several strains of HPV. In particular, PCR analysis is used to help determine not only the presence of the virus in the body, but also its types. Together with the PRC, a quantitative test is performed to diagnose the level of virus concentration. This indicator, as well as the number of tumors, influence the possibility of oncology.
- When the result shows one or more types of HPV, the woman is scheduled for colposcopy. This is a procedure for examining the cervix using a colposcope, a device designed for multiple magnification. In this way, a detailed examination of the cervix, vagina and vulva is carried out. Using colposcopy, you can assess how much the virus has affected the condition of the cervix, identify lesions, and view the presence of precancerous changes and genital warts. Typically, the gynecologist performs an extended colposcopy using chemicals to identify atypical lesions.
- When HPV is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed according to the type of virus and its manifestations.
Treatment of papillomavirus
The human papillomavirus can be hidden in the host’s body for a long time and not manifest itself in any way. Its development is stopped by the immune system, which should inhibit the spread of foreign DNA. One of the areas of treatment is aimed at maintaining and activating the immune system. This method is called conservative and includes the prescription of immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs (Isoprinosine, Allokin-alpha and others).
Another direction is aimed at eliminating the consequences of infection: removing existing papillomas and condylomas. There are several ways to do this:
- Surgical intervention. It is an operation to cut off tumors. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The disadvantages of this method are not only possible consequences in the form of scars, but also the risk of blood loss. In addition, this method does not guarantee the removal of all papillomavirus cells.
- Electrocoagulation. The most common method of removing papillomas and warts due to its low cost and availability. It is carried out using high-frequency current, which acts specifically on the growths. Like the previous method, it leaves marks on the body from removed papillomas. It also does not guarantee the absence of relapses.
- Laser destruction. One of the most modern methods of removing papillomas. For this, a laser beam is used, which completely removes papilloma cells, affecting atypical tissues. This method is considered the most reliable and safe. It does not leave undesirable consequences in the form of scars and immediately seals the vessels to prevent bleeding.
- Cryodestruction. The procedure is carried out using liquid nitrogen, which is applied to a special applicator. Under the influence of liquid nitrogen, the growth gradually disappears. However, with this method it is possible to get burns, which will ultimately result in an unwanted scar. This is due to the deep effect of the substance on the skin.
Types of virus
So, human papillomavirus, what does this mean, what types are there, what danger does this type of infection pose, what are the characteristics of the invasion?
HPV is the largest group of diseases of viral etiology, uniting more than two hundred strains of pathogenic flora, and is the most common STI.
HPV types differ in their modes of transmission, as well as in their potential targets, that is, the skin, mucous membranes of the vagina, urethra, and oral cavity may be affected. Each type of HPV causes the formation of papillomas in a specific area of the body.
Also, HPV types are divided according to the degrees of oncogenic risks. Most viral strains belong to non-oncogenic groups, that is, infection with them provokes the appearance of exclusively dermatological problems. But there are also much more dangerous types of HPV, the pathological activity of which, against the backdrop of favorable conditions, can cause the development of malignant diseases.
HPV prevention
Prevention of this disease comes down to a few simple rules:
- Using condoms as a means of contraception during sexual intercourse. This point is especially important, since sexual transmission of infection is the most common.
- Examination by a gynecologist. Women need to be examined by a doctor and have a smear every six months to know about the condition of their body.
- Maintaining immunity. It is the immune system that gives the main resistance to papillomavirus, and good immunity can suppress its manifestations even before the infection develops.
Nonspecific methods of prevention include vaccinations against highly oncogenic HPV types. These vaccines protect against types 16 and 18 and may provide some protection against other types of the virus. Having successfully completed clinical trials, the vaccines are considered safe and effective. However, vaccination should be carried out before the first sexual contact, because it only prevents the virus from entering the body, but cannot cure an existing infection. They recommend vaccinating girls aged 10 to 13 years.
About what oncogenic HPV is in women and what it can lead to, watch our video:
Reasons for activation of papillomavirus
HPV of high oncogenic risk, after entering the body, can remain in it secretly, without showing symptoms (the period can take from 3 weeks to 10 years). At this time, the immune system fights the pathogen. A complete recovery is possible without taking medications (by the body’s own efforts).
If the immune system weakens, the pathogen becomes active and begins to multiply, which is expressed by the appearance of formations on the epidermis. With further development of the pathology, the affected cells can develop into malignant ones, that is, cancer begins to develop.
Probable reasons for HPV activation:
- frequent violation of the integrity of the skin. This not only increases the likelihood of HPV activation, but it is also dangerous for new types of viruses to enter the body through open wounds;
- the presence of chronic pathologies (or frequent infectious diseases), both dermatological and internal organs. With long-term illnesses, the immune system weakens;
- diseases of an endocrine and autoimmune nature;
- HIV and radiation therapy. Accompanied by virtually no immunity;
- the presence of hormonal imbalance (during adolescence, menopause or pregnancy);
- abuse of alcohol, nicotine or drug use. As a result, the likelihood of additional infection increases, and bad habits also contribute to a decrease in immunity;
High-oncogenic risk HPV can be activated by alcohol, tobacco or drug abuse. - living in an environmentally polluted area or working in a hazardous industry. Due to slagging in the body, the activity of the immune system decreases;
- frequent overheating or hypothermia;
- genetic predisposition to HPV and cancer;
- taking medications to reduce the functioning of the immune system.
Long-term depression, constant stress, irregular sex life (or frequent change of sexual partners) also contribute to the intensification of HPV reproduction.