Any neoplasms, especially in the genital area, cause certain concerns, and not without reason. The appearance of a lump on the scrotum is a serious reason to contact a specialist, since such a sign may indicate the development of a cancerous tumor. But there are also less serious reasons for the appearance of lumps on the skin of the genitals.
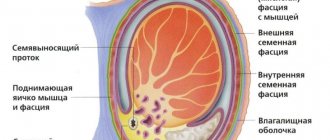
Size and localization area
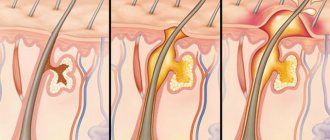
A man who is attentive to his health can detect a suspicious neoplasm already in the first stages of development. Initially, the size of the lump on the scrotum does not exceed 0.3 cm in diameter, and such a lump can be located near the anus, in the center of the testes, or at the base of the genital organ. In some cases, the location of the lump can determine the nature of the neoplasm.
A lump located on the left or right side of the penis may represent an inflamed lymph node. A round lump in the hairy part of the genitals is a wen or atheroma. The depth of location may also vary:
- between the testicles or inside them;
- in the cavity of the scrotal sac;
- subcutaneously
Self-diagnosis will help a man detect subcutaneous tumors that are not very deep. Such bumps can be insensitive or painful, static or mobile, bluish, white or red.
Inguinal hernia
Testicular enlargement can be caused by an inguinal hernia, which is caused by:
- lifting weights;
- severe, prolonged cough;
- tendency to constant constipation;
- heredity.
Under the influence of traumatic factors, pathological pressure on the abdominal cavity increases, pushing the hernial lump into the inguinal canal. At risk are obese men with intestinal and stomach pathologies.
The patient complains of swelling of the groin area, pain, and the skin of the scrotum becomes bluish.
Causes
White balls on the eggs in men appear for many reasons - from blockage of the sebaceous ducts to the development of oncology. The most common reasons are:
- dropsy;
- spermatocele;
- inguinal hernia;
- phlebeurysm;
- benign/malignant tumor;
- lymphadenitis.
Cyst and hydrocele of the testicle
A spermatocele (cyst) is a blockage of the vas deferens or epididymis. The disease is characterized by a violation of the outflow of seminal fluid and its accumulation in the testicular cavity. The stagnation phenomenon can manifest itself in one or several channels at once. As a rule, blockage occurs due to irregular sex life, the presence of inflammatory processes or trauma to the genitals. Cysts can be either acquired or congenital. The latter is diagnosed immediately after birth.
The following symptoms are characteristic of spermatocele:
- erectile dysfunction;
- lump on the testicle;
- pain of the neoplasm.
Diagnosis consists of palpation of the diseased organ and ultrasound examination. If such a lump is detected, you should contact a surgeon or urologist. Among the complications are the following:
- development of inflammation outside the seminal canal;
- the addition of a bacterial infection with subsequent rupture of the vas deferens and penetration of the contents into the testicular cavity.
Hydrocele (dropsy) appears as a large growth on one side of the testicle; in rare cases, both organs are affected. The pathology is characterized by the accumulation of fluid between the leaves of the testes. Hydrocele can be congenital or appear in younger boys, as well as in men after 45 years of age. In the latter case, the cause of the lump is inflammatory processes, age-related changes in the structure of the scrotum, a sedentary lifestyle or trauma to the genital organs.
The compaction can reach significant sizes, and the skin of the scrotum is greatly stretched, but does not change color.
To differentiate dropsy from a tumor-like neoplasm, a specialist performs diaphanoscopy. The watery contents do not interfere with the transillumination of the testicles, since they completely transmit the light of the medical device. If this is not the case, we can assume the presence of pus or blood (pyocele, hematocele) or the presence of oncology.
In order to determine the treatment regimen, the volume of accumulated fluid and the size of the tumor are calculated. Research is carried out using ultrasound.
Phlebeurysm
Varicocele is another cause of lumps in the genital area. Most often, varicose veins develop in the left testicle. This is explained by the specific structure of the male genital organs. In this case, the cone is elastic and soft to the touch, slightly mobile. An increase in the size of the growth causes difficulties with ejaculation, problems with erectile function, difficulty urinating and pain.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes
With lymphadenitis, the growth is usually located on the testicles themselves or in the side of the groin above the scrotum. This is a large (up to 5 cm in diameter) and hard lump, which upon palpation, loading and walking responds with sharp pain. Characterized by an increase in temperature in the affected area. In this case, the lump is nothing more than an inflamed lymph node. The pathology is caused by a viral or bacterial infection entering the lymphatic system.
Inflammation of several lymph nodes may indicate the development of certain sexually transmitted diseases (hepatitis, AIDS, syphilis, etc.). When such a disease is detected, a thorough diagnosis is carried out to determine the source of infection.
Inguinal hernia
The muscle fibers located between the tissues of the abdominal cavity and the scrotum are leaky. Excessive physical activity causes spasms, which causes gaps to appear into which a loop of the small intestine penetrates. The hernia can be easily palpated and does not interfere with intestinal patency when slightly compressed by muscle tissue. In this case, compaction (in a calm state) does not cause any particular problems. But when pressure on the affected area increases (during sexual intercourse, playing sports, etc.), the patient may feel some discomfort.
In some cases, the intestinal loop returns to its original location on its own. If this does not happen, emergency surgery is performed. This can happen when the process of tissue necrosis or intestinal obstruction begins.
Benign neoplasms
A growth on the egg in men may be a formation of lymphatic, adipose or epithelial tissue. The following types of seals occur on the male genital organs:
- basal cell carcinoma;
- epidermal cyst;
- lipoma;
- papilloma;
- leiomyoma;
- epithelioma;
- fibroma.
In rare cases, teratomas and hemangiomas occur on the testicles. The dimensions of such compactions do not exceed 5 mm in diameter; in appearance, they resemble movable or partially movable papules with clear boundaries. Their color can vary from yellowish-white to black, depending on the etiology. As a rule, these bumps do not bother a man at all, unless they touch the nerve endings.
In some cases, slight pain is felt upon palpation, and itching may be present. A complication of the pathology can be calcification of the growth, as well as inflammation and growth of the tumor. If there is a risk of malignancy of the tumor or the lump bothers the patient in some way, it is removed surgically. The operation does not require hospitalization of the patient.
Malignant formation
Among oncological pathologies, cancer of the scrotum or testicle is far from the first place and is quite rare. Oncology develops under the influence of the following factors:
- inflammation of the groin area;
- genetic predisposition;
- the presence of a benign seal;
- groin injury;
- prolonged contact with combustion products, radioactive substances and heavy metals.
The danger of the disease lies in the rapid metastasis of tissues and the absence of pronounced signs.
Cancer of the scrotum (soot wart) was a common occurrence in the 17th-18th centuries. , when chimneys were cleaned by hand and young men of 15-25 years old did this. And even now this pathology occurs mainly in young men. In older men (over 40 years of age), the scrotal tumor is part of prostate cancer.
The appearance of a malignant neoplasm is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swollen lymph nodes;
- painful sensations;
- heat;
- difficulties with ejaculation and urination;
- erectile dysfunction;
- enlargement of the mammary glands;
- swelling.
However, the absence of these symptoms does not mean that there is no cancer, so any lump in the scrotum area should be a reason to visit a doctor. Cancer detected at the initial stages of development has a favorable prognosis.
Hydrocele or hydrocele
An increase in testicular size is possible due to dropsy. The cause of the disease is the accumulation of fluid around the testicle due to disruption of blood circulation and lymph outflow, which contributes to the appearance of serous fluid between the membranes of the testicle. Usually the accumulation is characteristic of one side of the scrotum, but bilateral hydrops are possible.
The disease can develop in both adolescents and older men, asymptomatically; the first manifestations will be swelling of the testis, which appears in the evening and disappears in the morning.
With severe dropsy, the testicle greatly increases in size, high temperature, pain, and inflammation begin.
Dropsy is caused by a number of diseases. These include:
- scrotal injuries;
- inflammation of the epididymis;
- organ infection;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Possible causes of hydrocele can be congenital pathologies.
To diagnose the disease, the doctor performs palpation of the scrotum, external examination, and ultrasound.
If, as a result of prescribed conservative treatment with antibiotics, the swelling does not begin to decrease, surgical intervention is performed.
Elimination of pathology is carried out using several methods.
If the operation is performed according to the Bergman method, then the surgical manipulation involves a combination of methods - partial excision of the membrane, partial stitching of it. The scrotal tissue is sutured, and absorbable material is used for the suture.
Operation using the Bergmann method
It is possible to perform the operation using the Lord's method, according to which the testicular membrane is specially processed, the trauma to the testis is minimal.
Another possible method of treating dropsy is a puncture, during which excess fluid is removed from the scrotum, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are administered to relieve pain.
If the disease is not treated, the testicle can grow to a very large size (more than 10 cm), causing pain during movement, any physical activity, or urination. The main group of men who need surgery are those of childbearing age from 30 to 45 years. Hydrocele of the testicle, which is not addressed to a doctor, disrupts blood circulation in the scrotum, normal production and separation of sperm, which leads to infertility.
After surgery for dropsy, the following complications are possible, related to the characteristics of the man’s anatomy and the technique of the operation:
- after surgery for dropsy using any of the methods, the testicle became hard, which confirms infection;
- suture dehiscence or infection as a result of the patient’s violation of the postoperative regimen;
- the formation of edema, the cause of which is a violation of the outflow of lymph;
- allergic reaction to the suture material;
- development of a painful keloid scar.
The most long-term consequences of dropsy include the repeated accumulation of fluid in the membranes of the testis and scrotum.
Diagnostic measures
An accurate diagnosis is made by a specialist based on the results of a visual examination, palpation, laboratory and hardware tests. Initially, the doctor sends the patient for an ultrasound examination, which confirms the presence of a compaction and establishes its structure.
After this, the following diagnostic measures may be prescribed:
- scrotal biopsy;
- MRI;
- urine and blood tests;
- diaphanoscopy;
- spermogram and others.
All studies are prescribed on an individual basis, and their type is determined by the preliminary diagnosis. For example, with the help of diaphanoscopy, hydrocele (dropsy) is diagnosed, Dopplerography, which determines the condition of the blood vessels, makes it possible to determine the presence of varicose veins, and if testicular cancer is suspected, MRI and biopsy are prescribed.
Testicular torsion
Swelling and abduction of the testis can be caused by twisting of the organ. The exact cause that causes this pathology is unknown, but it is observed in men of all ages. The most likely cause is excessive physical activity, which causes tension in the muscles responsible for raising the testicles and provokes torsion.
The lesion changes the blood supply to the organ due to the blocking of the feeding vessels, multiple hemorrhages are provoked, the veins of the spermatic cord are clogged with clots.
The pathology leads to severe pain, the testicles increase in size and harden.
Additional symptoms will be:
- discoloration and enlargement of one half of the scrotum;
- the injured testicle has become painful, hard and raised upward;
- increase in body temperature.
The pathology of testicular torsion is a very serious condition that threatens the patient’s life. If he is not provided with timely assistance, then within a day the testicle will die and will need to be removed. A possible complication is sepsis, which can be fatal.
For diagnosis, the doctor uses ultrasound and blood tests, confirming symptoms are:
- heat;
- increased level of leukocytes in the blood according to the results of laboratory analysis.
To eliminate the pathology in mild cases of twisting of the testis around the pedicle, the surgeon performs a reduction of the organ. If the pathology is serious, then the patient is prepared for surgery immediately after diagnosis.
One of the long-term complications of torsion of the testicular pedicle is testicular cancer, which is observed in every second person who has had the disease.
Self-identification
Every male, both young and old, should independently conduct regular examinations of his genitals. This will allow the compaction to be detected in the early stages of its development, and timely diagnosis and treatment to be carried out. When independently examining the genital organs, the sequence of actions should be as follows:
- It is recommended to warm up in the bathroom first - this will help relax the testicular tissue, which will facilitate self-examination.
- Open access to the testicles: take off your panties and place your right/left leg on some elevation (chair).
- Then take a mirror and examine the genitals from all sides to look for rashes, bumps, growths or redness on the penis or scrotum.
- Now you should begin palpation: the man should hold the genital organ with one hand and at the same time palpate the testicle with the other hand. Palpation must be carried out very carefully so as not to miss even a centimeter. In its normal state, the testicle is uniform and smooth, in its upper part there is a soft formation - this is the appendage.
You should listen carefully to your sensations - there should be no pain during palpation, as well as during urination and sexual intercourse. Otherwise, we can talk about the development of some pathology.
Such self-examination should be carried out at least once a month. If you find extraneous tubercles, growths, etc., you should contact a specialist.
Treatment
As a rule, treatment is carried out taking into account absolutely all indicators of medical tests and the individual characteristics of the patient. The main treatment method is based on the use of antibiotics, which destroy the infection, which is often the main cause of the disease; for this, appropriate sensitivity tests and various microbiological studies of the microflora are first carried out.
Similar article - Compression socks for pregnant women
If the testicle has become hard and increased in size, only a doctor can determine the cause of the disease and prescribe treatment.
Monitoring the condition of the most vulnerable parts of a man’s body – the genitals – will help him maintain health and performance for a long time. To do this, a man needs to periodically conduct an examination on his own in order to notice alarming changes in the testicles in time and consult a doctor for help. During such an examination, you need to carefully and thoroughly palpate the scrotum.
If determined:
- formed enlargement of one testis;
- soreness;
- seals.
You should consult a doctor. Additionally, a man should be alerted to discomfort when walking or having sex.
The reasons for this phenomenon may be:
- addiction to steroids and long-term exposure to synthetic testosterone on the body;
- drug addiction;
- diseases that lead to a decrease or blockage of blood flow inside the testis, which leads to atrophy;
- dropsy of the testis.
Any discomfort in the area of the testicles and scrotum obliges a man to immediately see a doctor. This is necessary for the timely detection and treatment of diseases that can lead to infertility and loss of potency.
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader got rid of PROSTATITIS using an effective method. He tested it on himself - the result was 100% - complete relief from prostatitis. This is a natural remedy based on honey. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast. EFFECTIVE METHOD.
CPHealthGroup
Surely you have ever felt that one of your testicles has become hard. This sensation can be somewhat unpleasant, but you should know that it is most common among men and that there are several factors that can cause this condition. First of all, we must emphasize that it is not the same as it is difficult to feel the presence of a small lump in the scrotum, so we invite you to read this article where we will point out why the testicles become hard and the most common reasons why you may notice a lump in this area of your body.
You may also be interested in: How to protect your testicles
Traditional methods
In some cases, the formation of a wen is associated with the formation of atypical fat cells. In this case, treatment can be carried out using traditional methods, and surgical intervention is usually not required. Before starting treatment at home, consultation with a specialist is mandatory.
You can remove the wen using a fresh Kalanchoe leaf. You need to cut the plant and apply it to the damaged area, securing it with a bandage. The bandage needs to be changed approximately once a day. The course of treatment is usually not too long. It takes about one to two weeks for the fat to disappear on its own.
You can use coltsfoot dressings for ten days. The sheet should be applied to the sore spot and changed as needed. Lamb fat is quite effective. A tablespoon of the product is melted in a water bath and then cooled to room temperature. Then a small amount of fat is applied to the wen area and massaged a little. After just a couple of procedures, you can notice that the tumor becomes smaller.
Judging by the reviews, cosmetic red clay, which is mixed with sour milk and salt to enhance the effect, helps a lot. The mixture is applied to the wen, after which you need to protect the damaged area with a piece of polyethylene. The procedures must be repeated until the wen completely disappears.
You can take burdock root internally. First you need to pass the plant through a meat grinder (500 g is enough) to get a paste. Next, the slurry is poured with 700 ml of vodka, and then left to infuse for about a month. When the infusion is ready, you need to take one tablespoon twice a day.