The body of a small child is not able to resist allergens, infections, viruses and bacteria to the same extent as the body of an adult. Children's skin is like an open book, it is the first to respond to any irritant coming from the outside, and it is by looking at the skin that parents can often assess the general condition of the baby and take therapeutic measures at the first rash on the skin.
One of the most serious panaceas of the last decade has been pyoderma in children - round pustular rashes with white or black contents inside. The disease is rapidly getting younger. And if previously it mainly affected young people during adolescence or the older generation due to hormonal imbalances and chronic diseases, now pyoderma is not uncommon even in newborns.
There is scant information from official sources and pediatricians about this disease, and parents’ anxiety is quite understandable: they want to not only understand how to treat the disease, what to do, how to help the baby, but also to know what caused the appearance of adult “acne” on the skin of a little person "
Concept and characteristics
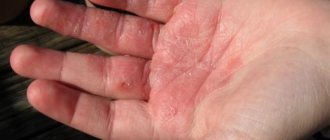
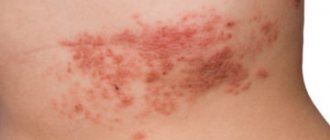
Pyoderma in children - photo:
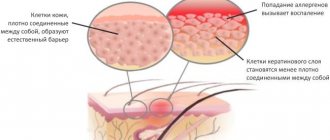
Pyoderma in a child is an inflammatory-purulent disease caused by a bacterial infection. The most common causative agents of the disease are staphylococci and streptococci.
As a result of the negative impact of pathogenic microflora, small areas of inflammation appear on the child’s skin, which over time take the form of pustules.
With a mild course of the disease, these pustules practically do not cause any discomfort to the baby, however, the disease tends to progress and, therefore, needs timely treatment.
Dr. Komarovsky about pyoderma
Dr. Komarovsky recommends placing 1% hydrocortisone ointment in your home medicine cabinet. This is a safe drug for home use that helps get rid of pyoderma in the initial stages. The active substance of such a medicine is not absorbed from the surface of the skin.
The doctor recommends contacting a specialist at the first signs of a pathological process. He will conduct an examination and prescribe effective treatment.
Causes
The most common cause of the occurrence and development of pyoderma in a child is considered to be improper hygienic care . However, there are other unfavorable factors that can trigger the onset of the disease.
| External factors | Internal factors |
|
|
Recommendations for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in infants can be found on our website.
Prevention
Compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene is the main preventive measure. In addition, it is recommended:
- Healthy food;
- sunbathing;
- avoid stress and overwork;
- regularly carry out vitamin therapy;
- maintain a daily routine;
- provide the child with adequate sleep;
- cut your nails regularly;
- strengthen immunity;
- promptly treat any damage to children's skin;
- fight excessive sweating.
All preventive measures that help avoid infection of children with pyoderma are familiar to parents. These are their direct parental responsibilities. If a child is instilled with a healthy lifestyle from childhood, he will not be afraid of any cocci. The only exceptions are unforeseen external circumstances that cannot be predicted (accidental microtrauma of the skin, contact with a pathogen carrier, etc.).
At-risk groups
The most susceptible to developing the disease are newborn children, whose skin is very thin, sensitive, and the functions of the sebaceous glands are not yet sufficiently formed.
However, manifestations of pyoderma can often be observed in older children.
This is especially true for children living in dusty or damp rooms , children from disadvantaged families in which the child is not provided with adequate nutrition and proper hygienic care.
Classification of pathology
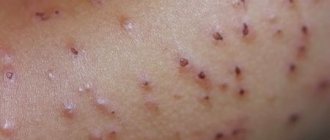
Depending on the nature and type of skin manifestations, various types of pyoderma are distinguished. So, a child exhibits such forms of pyoderma as:
- Follicles are nodular formations of red-blue color. When exposed to the affected area of skin, the child experiences unpleasant, painful sensations. Over time, purulent heads appear on the nodules, filled with light, opaque contents.
- Ostiofolliculitis is a rash that affects areas of the body where there is hair.
- Epidemic pemphigus is a serious disease that affects the feet and palms of a child. The pathology occurs in newborns. Over time, these areas become covered with a rash in the form of blisters. If their integrity is violated, painful wounds appear on the affected area of the skin.
- Boils are large pus-filled formations that initially form in the inner layer of the skin. Over time, the purulent head appears on the surface of the skin and opens, which is accompanied by the release of a significant amount of purulent contents. After this, the wound gradually heals and a scar forms on the skin.
- A carbuncle is several boils combined into one large formation. When the purulent head is opened, a large amount of pus is released, a deep and painful wound is formed, and over time a deep scar is formed.
- Hidradenitis is a purulent inflammation of the sweat glands. It appears in the form of small pink bubbles, which are localized in the folds of the skin and the armpit area. The bubbles are filled with a translucent liquid.
- Streptococcal impetigo. The rashes are localized, most often, in the facial area. Initially, the rash appears in the form of blisters of various sizes; over time, erosions and crusts appear on the affected area. The child feels severe itching, discomfort and pain.
- Periporitis develops against the background of increased sweating. The rash affects the area of skin folds and manifests itself in the form of weeping small rashes. Over time, the affected areas of the skin grow, merging with each other. The rash becomes covered with a yellow crust.
- Diaper dermatitis appears as a small papular rash in the form of blisters. When their integrity is violated, small pustules and wounds appear on the skin.
Depending on other classification criteria, pyoderma in children can be acute or chronic, deep or superficial, limited or widespread.
How does an allergy to formula manifest in infants? Find out about this from our article.
Staphyloderma
Who successfully cured demodicosis Staphyloderma (staphylococcal pyoderma) is a set of purulent-inflammatory skin lesions caused by staphylococci. It is a very widespread dermatological condition - almost every person experiences purulent inflammation of the skin of varying severity caused by these bacteria during their lifetime. Such a frequent occurrence is due to the fact that staphylococci are quite widely represented in the environment - they can remain in the air and on household objects for a long time, and be part of the microflora of the skin and mucous membranes of humans. In addition, staphyloderma is sometimes provoked by the introduction of pathogenic bacteria from other purulent foci in the body. The lesion can occur at any age, but in children staphyloderma occurs differently than in adults (epidemic pemphigus of newborns) due to certain anatomical features of the skin structure. Due to the bacterial nature of the disease and the persistence of staphylococci in the external environment, such conditions are highly contagious and can be transmitted by touch or through shared objects (towels, bed linen, washcloths), which must be taken into account when treating the pathology.
Symptoms and signs
How does the disease begin? Depending on the location of the rash , the initial manifestations of the pathology may be different.
| Damage to the scalp | Skin lesions on the face and body |
|
|
There are also a number of common signs characteristic of all forms of the disease:
- pain, itching, burning in the affected areas of the skin;
- changes in the relief and structure of the skin;
- redness;
- swelling;
- in severe cases of the disease, the child experiences a significant deterioration in well-being and hyperthermia.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic criteria are the clinical manifestations of pyoderma: the nature of the lesion, location, shape of pustules or conflicts. Additionally, anamnesis is taken to determine the time of appearance of the primary lesion, the presence of patients with pyoderma among close relatives and chronic pathologies in the child.
Laboratory methods:
- exudate studies;
- histological examination of the skin (determination of dystrophic changes);
- blood tests (anemia);
- microscopy of ulcers and exudate;
- PRC (pathogen detection).
To identify underlying diseases, additional examinations are carried out:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- coprogram;
- immunogram;
- dysbacteriological studies;
- general blood analysis.
For certain indications, a consultation with an immunologist and gastroenterologist is carried out. Differential diagnosis is carried out with drug toxicoderma, lichen planus, rosacea, and fungal skin lesions.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely treatment, pyoderma threatens to develop serious complications .
In particular, severe itching and pain cause significant discomfort to the baby, disrupt sleep patterns, and lead to loss of appetite.
All this negatively affects the physical and mental development of the baby.
In addition, the child often scratches the inflamed areas of the skin, which leads to further spread of the infection, and this, in turn, threatens with complications such as extensive intoxication and blood poisoning .
Treatment
How to treat pyoderma in a child? Treatment of the disease is complex. The choice of one or another treatment method (or a combination of them) is made by the doctor, depending on the severity of the lesion.
Drugs
Oral medications are prescribed for severe cases of the disease, when there is a risk of extensive infection of the body.
The child needs to take the following medications :
- antimicrobials (Ampicillin, Lincomycin);
- sulfonamide drugs (prescribed for intolerance to antibiotics);
- antihistamines (Zyrtec, Zodak);
- immunomodulators (Immunal, Amiksin).
How to cure diathesis on the cheeks of an infant? Find out the answer right now.
External products
- The affected areas of the skin are treated with iodine .
- To prevent the spread of infection, it is necessary to use antiseptics ( Chlorhexidine ).
- To dry a weeping rash, apply compresses with a solution of potassium permanganate .
- It is necessary to use antibacterial ointments ( Lincomycin ).
- For deep skin lesions, for example, with the formation of boils or carbuncles, Vishnevsky ointment .
- sulfur- based ointments .
- In severe cases of the disease, it is necessary to use hormonal ointments ( Lorinden ).
ethnoscience
Time-tested folk recipes help eliminate the symptoms of the disease:
- Aloe juice has a pronounced antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, healing effect. You need to take a fresh leaf of the plant, chop it, add a small amount of water. Moisten a clean cloth with the resulting solution and apply it to the affected skin as a compress.
- Ginger root . A small root is grated on a fine grater, poured with a glass of boiling water, and infused. After this, the product must be filtered, moistened with a soft cloth, and applied to the child’s skin.
Physiotherapy
To eliminate skin manifestations of pathology and regenerate a child’s skin , today the following physiotherapeutic treatment methods are successfully used:
- UV therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- oxygen baths;
- UHF and microwave therapy;
- treatment with infrared radiation;
- therapeutic baths (based on hydrogen sulfide, mineral waters).
Surgical intervention
Surgery is necessary if multiple boils or carbuncles .
The operation is performed under local (in some cases, general) anesthesia.
First, it is necessary to thoroughly disinfect the affected area of skin, after which, using surgical instruments, the body of the formation is opened and the pus is removed .
Specific scars , to remove which special ointments are used.
If the scar is large or located on an open area of the body, such as the face, plastic correction may be required.
Application of diet
Be sure to prescribe a balanced diet containing useful substances. The body must receive vitamins, trace elements, and minerals to speed up metabolism and regeneration of damaged cells and tissues. Adhere to the following rules:
- balanced nutrition, content of proteins, carbohydrates, fats in the right quantities;
- prohibition of drinking alcohol in any quantity;
- exclusion of fatty, fried, spicy, smoked, excessively salty foods;
- limiting simple carbohydrates contained in baked goods, sweets, and other sweet foods;
- drinking plenty of water to maintain water-salt and mineral balance, and to prevent dehydration in case of increased body temperature.
In order for tissues to heal faster and metabolism to normalize, it is better to switch to a dairy-vegetable diet. If the patient has a primary disease that has led to a breakdown of the immune system with the formation of pyoderma, follow the nutritional rules according to the recommendations of the attending physician. For example, in case of diabetes mellitus, the consumption of carbohydrates in any form is excluded.
A strict diet is followed only during the period of formation of pyoderma, with the exception of severe metabolic pathologies.
Be sure to eat vegetables, fruits, and lean meats. For example, turkey, beef. When dieting, it is important to receive all the necessary substances so that additional hypovitaminosis does not occur.
Features of care
A child suffering from pyoderma needs special care. In particular, it is necessary:
- Regularly observe hygiene rules, carry out hygiene procedures 2 times a day.
- Treat affected skin areas with antiseptic agents.
- If the disease affects the scalp area, the child needs to have his hair cut.
- It is important to explain to the baby that you cannot scratch the rash (for newborns it is recommended to use special gloves and trim your nails as often as possible).