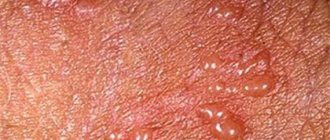
A rash on the labia is a fairly common occurrence that occurs in women of all ages. In addition to affecting the labia minora and majora, rashes can be localized in the pubic area, as well as the vestibule of the vagina. The appearance of small pimples, blisters and pustules is often accompanied by itching, burning, pain of varying intensity or, on the contrary, does not cause any inconvenience.
There are many reasons that provoke such a pathology, but they do not always indicate the presence of some serious deviations in health. In some cases, a rash may occur as a result of individual physiological factors and may not require treatment. Conventionally, all genital rashes are usually divided into external and internal.
External causes of rashes
The reasons for this include the following:
Genital allergy
In normal condition, the skin of the female labia has a smooth, even structure without visible lumpiness or roughness. The color of the genitals varies from flesh-colored to brownish, and slight pigmentation is allowed in the folds of tissue.
When interacting with an allergen, the skin may become covered with spots of different diameters, accompanied by redness, burning, swelling, and in exceptional situations, such a reaction is even complicated by anaphylactic shock. The following may act as irritants:
- hygienic cosmetics for body care;
- gels, liquid and solid soaps for intimate care;
- mechanical contraception (latex condoms);
- preparations for lubricating the vagina during sex (ointments, lubricants);
- topical medications (suppositories, sprays, antiseptics);
- sanitary pads for daily use, tampons;
- synthetic underwear, as well as underwear that is uncomfortable to wear or is the wrong size;
- unsuccessful epilation of the pubis, the scalp of the labia majora and the perineum.
Scabies
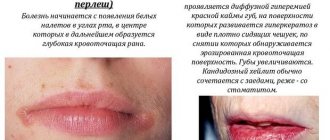
Scabies belongs to the category of parasitic infectious diseases caused by a microscopic scabies mite. The highest concentration of groin mites in women is most often observed on the labia majora. Characteristic signs: a scattering of follicular pimples arranged in pairs, which, after opening, turn into blood crusts. The places where eggs are laid and larvae reproduce have the appearance of longitudinal scratches on the skin. The infection is accompanied by constant and unbearable itching.
Treatment: use of anti-scabies (Spregal, Medifox), anti-inflammatory drugs (Indomethacin, Presocil), steroid ointments, as well as physiotherapy.
Pediculosis pubis
A parasitic disease caused by pubic lice. Parasites prefer to “settle” on the scalp of the labia, pubis, and the area around the anus. Against the background of incessant itching and constant scratching, the skin turns red, small ulcers and eczema, and an allergic rash appear on it. The inflamed surface becomes vulnerable to the penetration of secondary infections. In places where lice absorb blood, you can notice bluish spots from hemorrhages, which go away on their own over time.
Treatment: to get rid of pubic lice, use specialized sprays (Pax, Medifox), ointments (sulfur, mercury), soap and other hygienic detergents.
Reaction to partner's sperm
The so-called burning semen syndrome can trigger the development of postcoital allergies, which looks like a small rash visually reminiscent of hives. About 30% of women who are sexually active experience similar discomfort after sexual intercourse to one degree or another. The presence of such hypersensitivity is due to various reasons, for example:
- hereditary predisposition;
- pregnancy;
- while taking contraceptives (pills, suppositories);
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- after surgery to remove the uterus and tubal ligation.
Physiological features
In approximately 2-6% of the female population, multiple rashes are observed on the surface of the genitals, which are not classified as pathologies and do not indicate any disease, but are an individual physiological feature. This type of “healthy” rash is usually interpreted as a natural cosmetic defect. For example:
- Fordyce granules . They are small whitish cysts that appear at the base of the sebaceous glands. They do not pose any threat to health and are considered normal. A scattering of pimples can be localized on all parts of the genitals, from the pubis to the labia minora and the entrance to the vagina.
- Epidermal cysts . Usually combined with acne (on the face, neck, head) and oily seborrhea. Inside the cystic formations there is sebum or hardened particles of the epidermis. Overactivity of the sebaceous glands can lead not only to the quantitative growth of such cysts, but also to an increase in their size. In such cases, they resort to their removal.
- Micropapillomatosis . It is characterized by small papillomas spreading over the surface of the labia majora and partially minor (in the internal tissues). They are soft to the touch, slightly pinkish in color, almost merging with the overall color of the genitals. Indicate hormonal disorders in the body or the presence of papilloma virus in the body (in rare cases).
Lichen planus on the vagina
A disease of unknown etiology.
More often affects women.
Pimples may appear on the vagina.
They are red papules that slightly rise above the surface of the mucosa.
Occasionally, blisters form on the vagina.
The elements of the rash are located in groups.
They form lines.
Sometimes the location of the rashes is chaotic.
On the mucous membranes, a mesh form of lichen planus is most often observed.
Spots and areas of hyperkeratosis appear in the vagina.
They form a lace.
The most severe form is the bullous form.
Bubbles form.
They can be large - up to several centimeters.
After rupture, erosions form.
Internal causes of rashes
A rash on the labia can be one of the manifestations of sexually transmitted or infectious diseases. In this case, the clinical picture of the rash and the patient’s condition will be as follows:
Vulvovaginitis
It is a bacterial disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida. Usually occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance, accompanied by a disruption of the vaginal microflora. Main symptoms: white curdled discharge, itching, burning, vesicular rash spreading to the labia majora and minora, as well as the perineal area and anal area.
Treatment: based on taking antibacterial drugs (Amoxiclav, Cefazolin, Cefriaxon), vaginal suppositories (Iodoxide), antiseptic ointments (Betadine), as well as the use of douching, baths with solutions of soda, potassium permanganate, and medicinal herbs.
A gynecologist talks about the treatment of vulvovaginitis in this video.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease that, if not properly treated, leads to damage to the cardiovascular system, internal organs, destruction of bone tissue and, as a result, death. The primary signs of syphilis are the appearance of a small hard chancre in the genital area, which initially looks like a red spot and subsequently develops into a painless ulcer; secondary signs are a small pink rash that affects not only the genitals, but also other parts of the body.
Treatment: the main method of therapy is taking long-acting antibiotics (Erythromycin, Doxycycline, Penicillin, Tetracycline).
Important! It is necessary to involve all sexual partners who have had sexual contact with an infected person in the treatment of syphilis.
Genital herpes
A viral disease in which the labia majora and minora become covered with small pustules filled with a whitish liquid inside. After ulceration, a crust forms at the site of the rash, dries out and disappears within 7-8 days after the appearance of the rash. Blistering rashes are accompanied by burning, itching, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes, body aches and fever.
Treatment: consists of taking antiviral drugs (Zovirax, Gerpevir, Acyclovir, Valtrex), vitamin complexes (A, E, C), immunomodulators (from the interferon series).
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum. It belongs to a number of skin dermatoses and is of an infectious nature. External manifestations: small dome-shaped nodules covering the labia and pubic area with a small halo. The number of pimples usually varies between 10-20 units. The color is flesh-colored, almost identical to the shade of healthy skin. Inside, the nodules are filled with a dense, waxy substance. Minor itching may occur.
Treatment: as a rule, the rash goes away on its own, disappearing from the skin of the genitals within 2-3 months after its appearance.
Athlete's inguinal
Fungal infection (Hebra eczema), localized in the area of the labia, perineum, pubis and adjacent tissues. General symptoms: ring-shaped pink spots up to 1-1.5 cm in diameter, strewn with a vesicular rash along the perimeter of their borders. Over time, the blisters begin to dry out and the skin begins to peel. The process of mycosis is accompanied by an unpleasant itching and burning sensation.
Treatment: for a speedy recovery, complex therapy is used in the form of antifungal ointments (Mikoseptin, Lamizin), antihistamines (Suprastin, Zodak), lotions with a solution of silver (0.25%) and iodine (2%).
Psoriasis
Chronic skin disease of a non-infectious nature. Distinctive features: a pink rash, merging into characteristic plaques of various diameters and configurations. During exacerbations, a woman may feel itching, which causes a reflexive and persistent desire to scratch the genital area.
Treatment: There is no clear “recipe” for how to get rid of psoriasis. Various hormonal ointments, drying preparations based on zinc and solid oil, tar soap, herbal oils and other traditional and folk medicine help reduce discomfort.
Features of the disease
The color of human skin and hair is determined genetically and depends on the ratio of red, blue, yellow and brown pigments. The lack of some natural dyes leads to dischromic spots.
Vitiligo (also called dog) is a disease characterized by the development of primary depigmented white spots without peeling or atrophy. The spots tend to cluster and grow slowly. White lesions on the periphery are surrounded by a weakly pigmented corolla.
This pathology occurs due to the loss or decrease in the functional activity of melanocytes (cells containing the substance melanin).
This is an exclusively acquired disease. It is characterized by clearly limited areas of depigmentation of various sizes and shapes. Occasionally, vitiligo also affects the hair follicles, in which the pigment disappears and the hair becomes discolored. The first foci of the disease appear at a young or very young age.
The etiology and pathogenesis of this disease is not fully understood. There are several theories that explain why this phenomenon occurs:
- The theory of melanocyte destruction. In theory, researchers are of the opinion that vitiligo occurs as an autoimmune disease or due to a violation of the redox status of melanin. Some scientists associate the disease with a neurogenic etiology.
- The second theory says that there is a violation of the inhibition of pigment cells or a violation of their adhesion.
Vitiligo is often considered a psychosomatic pathology.
Predisposing factors for the appearance:
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- constant stress;
- chronic inflammation of the urogenital area;
- diseases of internal organs;
- intoxication together with liver disease;
- destruction and physiological disorders of gland secretion;
- deficiency of copper, selenium and zinc ions;
- decline in the status of the immune system;
- occasionally – hereditary predisposition.
Groin rash in babies
The skin of infants is very delicate and sensitive, and therefore susceptible to various types of irritation and infections. Often a rash may appear on it, caused by a number of factors. The most common causes of rashes are:
- Heat rash . It is caused by an incompletely formed thermoregulation system, as a result of which the sweat glands cannot cope with the functions assigned to them, overheating of the body occurs, and, as a result, the appearance of a small red rash in the form of bubbles, dots, and nodules on the skin of the genitals. If proper hygiene is observed, as well as a number of preventive procedures (bathing in herbal mixtures, wiping the groin area with a solution of potassium permanganate), prickly heat quickly goes away.
- Diaper dermatitis . The main cause of occurrence is increased humidity inside the diaper, loose stools, and close, prolonged contact of the child’s skin with urine and feces. The rash looks like a scattering of small pimples against a background of general redness of the genital area. Diaper dermatitis is treated with ointments with an anti-inflammatory and drying effect: Destin, Zinc, Drapolen. An important condition is to keep the skin absolutely dry and clean, and change diapers regularly.
- Candidiasis . A fungal infection, most often activated after a course of antibiotics, as well as as a result of improper use of diapers. The disease manifests itself as a rash in the form of small red spots that appear first between the legs and then spread to the intergluteal region and the pubic area. In girls, the rash is accompanied by white discharge between the labia, severe itching, pain when urinating, and swelling of the genitals. To treat thrush, antifungal drugs are used, as well as local procedures: soda and manganese baths, compresses, lotions.
Condylomas in the vagina
Infection with papillomavirus leads to the appearance of condylomas in the vagina.
This type of rash is called vegetation.
It is a growth of the papillary layer of the dermis.
Small formations appear - papules with a thin stalk.
These condylomas have a good blood supply.
They are red or pink in color.
It interferes with the vagina because it causes pain during intercourse.
In addition, they can come off, resulting in bleeding.
An open wound can become infected.
The presence of condylomas is a sign that there is papillomavirus in the body.
And he can be quite dangerous.
In the presence of high oncogenic risk papillomavirus, the risk of cervical cancer increases.
Therefore, all women with condylomas should be seen by a doctor.
This will allow timely detection of precancerous processes and the necessary treatment.
Rash on the labia: when to see a doctor
Since the list of diseases that can cause a rash on the labia is quite extensive, it is not correct to make an independent diagnosis based only on the appearance of pimples, spots, plaques, pustules and other skin changes. Without knowing the cause of the rash, it is difficult to prescribe the correct treatment, so contacting a specialized specialist (dermatologist, venereologist, gynecologist) is a mandatory action if the following situations occur:
- the rash remains on the genitals without changes for 1-2 weeks or more;
- rashes are accompanied by itching and burning;
- there is severe swelling of the skin of the labia;
- the surface of the skin affected by the rash peels off, and the redness itself looks like spots with well-defined edges of a reddish or bright red color;
- the rash transforms into painful/painless ulcers or pustules filled inside with a cloudy liquid;
- the appearance of the rash was preceded by sexual intercourse not protected by a condom;
- body temperature rises, general malaise and loss of strength are felt;
- lymph nodes in the groin area become enlarged.
Care for intimate areas with vitiligo
Home care for intimate areas should not require any specific features. You can purchase the necessary products yourself or from a dermatologist.
Use creams, gels, capsules or body milk in individual care that can topically even out depigmented tone. In professional cosmetics there are a large number of similar lines of drugs and products. Sesderma is one of the most used companies to treat vitiligo and suppress its recurrences.
In a beauty salon, they can offer Elokvin whitening injections and laser therapy. It will also carry out extensive diagnostics, which cannot be obtained in a hospital setting.
General recommendations
To prevent illness and, if possible, minimize the likelihood of a sexually transmitted infection, it makes sense to take into account a number of simple rules regarding personal hygiene, as well as lifestyle in general:
- Lead an orderly sex life, and during casual sexual contacts, do not forget to use condoms.
- Keep your body and genitals clean, change your underwear daily, giving preference to things made from natural fabrics.
- Use common items (towels, bedding, dishes) in public places with caution.
- Eat right, take vitamins and medications that strengthen your immune system.
- Do not overcool the body, especially the genitourinary system.
- Avoid stressful situations, play sports.
It is important to remember that self-medication is obviously a false path, which can only worsen the situation and lead to various kinds of complications, especially when the appearance of a rash is associated with sexually transmitted or infectious diseases. The most correct way to respond to a problem is to contact a doctor of the appropriate specialization.
Molluscum contagiosum in the vagina
A rash of bumps on the vagina, nodules and papules may be associated with infection with molluscum contagiosum.
This is a viral disease with sexual transmission.
The infection affects the epidermis.
It goes away on its own, but after a very long time.
Inflammatory elements can persist for six months or longer.
They interfere with normal sex life.
Firstly, because they create an aesthetic defect.
Secondly, they can prevent the insertion of the penis into the vagina.
Molluscum contagiosum is especially difficult due to HIV.
The rash elements appear gigantic.
Their number is in the hundreds.
They do not go away without treatment.
Molluscum contagiosum rashes are characterized by the presence of an umbilical depression in the center of the papule.
They release a white mass when pressed.
Scabies in the vagina
The rash appears with scabies.
This is a parasitic disease.
It is caused by the scabies mite.
The elements of the rash may appear different.
They are due to:
- tick metabolic products;
- allergic reactions (there may be a rash all over the body);
- scratching as a result of severe itching;
- the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
Most often papules form.
Pustules appear, which can open to form ulcers.
When examined, crusts are often found - the result of damage to the skin due to scratching.
Some women who contract scabies do not develop a rash at all.
There is only itching.
Folliculitis in the vagina
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicles.
It is most often caused by staphylococcus.
Less commonly, the pathology is caused by gram-negative flora, fungi, demodex mites, and viruses.
Folliculitis can be superficial or deep.
Superficial ones occur more often.
The rashes look like pustules.
With timely treatment, the pathology goes away.
If there is no treatment, she may:
- spread deep into the skin with the formation of deep folliculitis;
- go into a chronic relapsing form.
Vaginitis
Or inflammation of the vagina , most often develops due to bacterial vaginosis. Often the inflammatory process also spreads to the external genitalia – the vulva; This condition is called vulvovaginitis. With this disease, a woman is bothered by pain, burning and itching in the vagina and vulva, aggravated after sexual intercourse, as well as yellowish, unpleasant-smelling vaginal discharge.
In addition to the pathological flora that multiplies in the vagina during bacterial vaginosis, vaginitis can be caused by candida fungus and the herpes simplex virus.