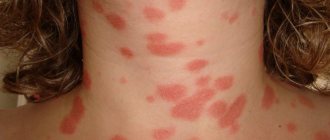
The appearance of watery blisters has always caused controversy. Some argue that this is an inexplicable process that means nothing to the body, others - that their appearance signals the presence of some kind of disease. Let's put aside the careless self-confidence of the first and listen, but without fanaticism, to the second. In any case, watery blisters on the skin do not appear by chance.
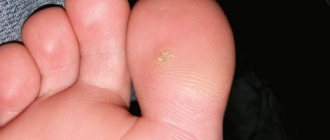
Watery formations can be the size of a match head, or can reach 5 cm in diameter, forming cavities on the surface filled with a clear, yellowish liquid formed from blood.
Bubbles can be a disease in themselves, or serve as symptoms of some pathology. In any case, they are a warning that inflammatory or infectious processes are occurring outside or inside the body. They can be just an ordinary sunburn or a fairly serious disease of the epidermis or even internal organs.
In order not to tempt fate and not self-medicate for unknown reasons, it is enough to visit a dermatologist. He will tell you exactly the nature of your rash, the reasons for its appearance and ways to combat it.
Causes and conditions of skin diseases
Pustular skin diseases are caused by streptococci and staphylococci
Among the causative agents of pyoderma, staphylococci and streptococci are in first place. Staphylococci often colonize the upper layers of the skin: the mouth of the follicle, sweat and sebaceous glands.
Streptococci colonize the epidermis: the face, areas of natural folds.
With normal homeostasis and moderate sweat production, microorganisms living on the skin serve as a kind of “brake” that displaces pathogenic microflora. Endocrine and immune disorders change the chemical composition of sweat and sebum, provoking the activity of foreign microflora.
Types of rashes
Two variants of the disease are serious: when the disease affects the eyes and ears.
- Herpes zoster ophthalmic: affects the trigeminal nerve, causing eye and surrounding pain, typical skin rashes and corneal ulcers, which in extreme cases can lead to blindness.
- Tinea ear: Rash appears on the skin of the ear, external ear canal, and eardrum, accompanied by severe ear pain, tinnitus, and hearing loss due to involvement of the auditory nerve. The virus can also attack the nearby facial nerve, disrupting both its sensory functions of taste and movement, causing paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles.
Mechanism of development of skin diseases
There are external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous) causes that influence the activity of pyococci and the occurrence of pyodermatitis. The first group includes:
- Skin injuries of various types (cuts, irritations, mosquito bites, scratching).
- Maceration (overmoistening) of the skin due to increased sweating or the constant presence of moisture on the stratum corneum.
- Skin contamination: at the domestic level (ignoring hygiene standards) or professional (constant irritation of the skin with fuels and lubricants, coal dust particles, etc.).
- General or local overheating or cooling.
Internal factors:
- Chronic infections (pathologies of the genitourinary system, consequences of untreated caries, ENT diseases).
- Endocrine problems associated with diabetes mellitus, hyperandrogenism, hypercortisolism.
- Chronic alcohol or drug poisoning.
- Unbalanced diet (protein deficiency, vitamin deficiency).
- Immune disorders provoked by the use of glucocorticoid drugs and immunosuppressants in HIV and after radiation.
Both of these reasons reduce all types of immunity and skin capabilities. Gradually the composition of the microflora deteriorates.
Possible pathologies
Blisters are a signal that a person may have one of the following problems:
- Mycosis is a disease associated with a fungal infection; pink blisters are accompanied by itching and begin to peel off over time.
- Insect bites - substances that get under the skin during a bite very quickly provoke swelling in the form of a blister and redness. A bite may carry the potential for side problems from insects:
- hornets,
- mosquitoes,
- ticks,
- flies,
- bumblebees,
- gadflies,
- ticks,
- bedbugs,
- bees,
- midges
We will tell you below what to do if your skin itches and blisters, allergies, itching, redness, rashes and other associated symptoms appear.
Classification of pyoderma
The types of diseases depend on the cause that causes them, therefore they are divided into staphylococcal, streptococcal and mixed pathologies. Each type of disease can be superficial and deep, acute and chronic. In the superficial form, the infection affects the epidermis and dermis, in the deep form – the dermis and hypodermis.
Staphylococcal species
Among pyoderma with an acute course of the disease there are:
- Superficial form: ostiofolliculitis, folliculitis, bullous impetigo (in children), pemphigoid in infants.
- A deep variety, found with boils, folliculitis, carbuncles, hidradenitis.
The chronic stage of staphylococcal skin diseases is:
- Superficial, as in vulgar sycosis.
- Deep – with furunculosis, folliculitis decalvans.
Pyoderma is a fairly common disease.
Streptococcal infections
The acute form is characteristic:
- For superficial types of impetigo and diaper rash.
- For deep erysipelas and ecthyma.
The chronic stage occurs with diffuse streptoderma.
Mixed type
Streptostaphylococcal pyoderma in acute form is:
- Superficial, like impetigo vulgaris.
- Deep – vulgar ecthyma.
Chronic forms of mixed pyoderma are distinguished:
- Ulcerative pustular disease.
- Ulcerative-vegetative pyoderma.
- Abscessing pyoderma.
Pustular skin diseases occur on completely clean skin or on the basis of previous skin problems - scabies, eczema, lice, dermatitis.
Self-diagnosis
Blisters are easily identified when they appear, because their presence is usually accompanied by the following sensations:
Visually, the presence of blisters can be detected on the skin if the formations that appear correspond to the description given above:
Read below about the reasons for the appearance of large and small watery blisters on the skin.
Clinical features
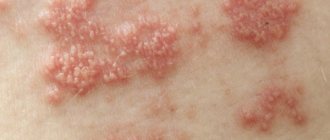
The rash with pustular infections is polymorphic. The type of primary rash will depend on the degree of tissue damage.
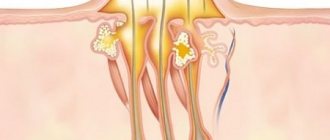
Staphylococcal pathogens multiply on hair follicles and sweat glands and provoke inflammation.
Rashes with pyoderma polyphora
Different types of skin lesions can look the same, for example, follicular pustules occur with ostiofolliculitis, folliculitis and sycosis, and an inflammatory nodule can be a sign of folliculitis or just a boil. Streptococcal infections prefer smooth skin.
The main external symptom of superficial streptoderma is a bubble. With a thin stratum corneum, it has a flabby appearance (phlytena); with hyperkeratosis (on the palms, soles), the surface blisters are harder, filled with serous fluid.
If the infection is deep, the rash will be in the form of ecthyma - an epidermal pustule with local necrosis, edematous erythema with a growing focus of inflammation (for example, erysipelas).
Staphylococcal skin infections
- Ostiofolliculitis is inflammation of the follicle. It looks like a small (2-3 cm) abscess in the shape of a hemisphere or cone with cream-colored pus, surrounded by a halo of hyperemia. An infection develops on an open part of the body (on the face, neck, head, bends of the arms and legs). These areas are often exposed to mechanical and chemical irritants (friction, shaving, household and industrial chemicals). After 2-3 days, the redness disappears, the brown crust dries out. After its rejection, the skin color changes slightly. With friction or maceration, the disease can progress and become more severe.
- Folliculitis is a purulent inflammation that affects the hair follicle. The superficial process begins, like the previous pyoderma, with a small abscess deepening into the mouth. The surrounding skin turns red and thickens, the abscess increases to 5-7 mm in diameter. If the infection is primary, the papule is in the shape of a cone or hemisphere up to 5 mm in diameter. After 2-3 days, a dense pustule appears, disappearing after a week. After peeling off the dried crust, stagnant redness is observed. In the deep form, the entire hair follicle is affected. The painful process is accompanied by redness, swelling, infiltration
- Impetigo develops in a child already in the maternity hospital (if hygienic standards of care are violated). Staphylococci that have penetrated into the dermis produce exfoliatin, which destroys the epidermis. Yellow purulent blisters form. The pathology is called infantile pemphigus. In children, the disease develops in the first week or month of life. Upon examination, you can see blisters the size of a hazelnut with a purulent filler. They appear on clean skin surrounded by an inflamed halo. When the bubble opens, wet erosion remains with the remains of the top layer without a crust. The rash can be seen on the chest, back, and in the folds of the limbs. The malignant form affects the entire body of the child. The illness begins with fever, increased erythema on the navel, around the mouth, in the folds. The skin peels off and hangs like petals on the damaged areas. Without timely treatment, impetigo in children can be fatal.
- Vulgar sycosis is a chronic form of the disease. The main signs: periodically manifested ostiofolliculitis and superficial folliculitis with infiltration of the problem area. Adult men are more often affected; rashes can be observed near the mustache and beard, on the pubic area, under the arms, eyebrows, eyelids and head. Prerequisites for pustular diseases of the scalp can be frequent shaving and chronic infections of the scalp. Inflammation begins with individual pustules that constantly recur in one area. Gradually, new follicles are involved, and the lesion grows. The skin in the problem area turns blue and infiltrates. When pustules are opened, accumulations of crusts are observed; after their peeling, a wet spot remains. The hair is removed painlessly, and in its place you can see a glassy muff. The disease lasts a long time, with periodic relapses. The discomfort is minor: itching and burning. If left untreated, the condition will normalize spontaneously after 2-3 months.
- Lupoid sycosis is a rare type of pathology when the skin atrophies, baldness is observed even without ulcers. The causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus, and other microflora are likely to be present. The prerequisites are a decrease in immunity in diabetics and chronic infections. Affects men over 40 years of age. Colonies populate around the mustache and beard, on the temples and crown of the head. With erythema with easily detachable crusts and gray scales, nodes and pustules develop in groups, forming a dark red plaque Ǿ 2-3 cm. Over time, it turns pale in the center, becomes thin and smooth and seems to be drawn inward. All signs of its atrophy are observed, new follicles no longer appear, individual hairs remain. The radius of the inflammation (up to 1 cm) is filled with follicular papules, its size gradually increases, the spot takes on an asymmetrical shape, apple jelly syndrome is not observed during diascopy. The process takes several years. Discomfort occurs only on the head due to the proximity of the aponeurosis.
- A furuncle is a deep inflammation of the follicle and tissues. The node develops around the affected follicle, where pus accumulates. Gradually, the disease covers the tissues and sebaceous gland, turning into a painful node. Swelling is noticeable on the face. After 3-4 days, a fistula is formed; after its opening, an ulcer with a green necrotic core at the base is obtained. After 2-3 days it is rejected with bloody discharge. Pulsation and pain decrease. At the site of the ulcer there will be a retracted scar. The furuncle settles anywhere with hair follicles. On the face they are most traumatic and, if irritated, can provoke thrombophlebitis of the face with swelling, high fever, and confusion. Injured boils of the extremities are dangerous due to complications in the form of acute glomerulonephritis.
- Furunculosis is boils with periodic repetitions in the acute form and isolated manifestations in the chronic form. It can be local or widespread. The acute form is provoked by exogenous factors, the chronic stage is caused by diabetes mellitus, infections, vitamin deficiency, dietary errors, poisoning, and decreased immunity.
- Carbuncle is a severe pyoderma that involves deep layers of skin and many follicles. Diabetes mellitus and immunosuppressive state are of particular importance in the pathogenesis. Localized on the lower back, neck, arms and legs. The formation of a node is accompanied by headache, fever, and blackening of the inflammatory zone. The carbuncle opens after 5-7 days. The ulcer gradually heals and the condition returns to normal. Without medical assistance, the process drags on for 2-3 weeks. A carbuncle on the face can cause complications in the form of venous thrombophlebitis, embolism, sepsis, and brain thrombosis.
- Hidradenitis is an inflammation of the apocrine glands in adulthood as a result of skin trauma or improper use of deodorants. It is localized under the armpits, but it may affect the area of the nipples, genitals, and navel. At first, the node under the skin can only be determined by touch. Gradually the area turns red and blue, and pain appears. The fistulas are opened and a yellow-green exudate is released. The scar at the site of the fistula is retracted. If treatment is prompt, an abscess can be avoided.
Streptococcal and mixed pyoderma
- Streptococcal impetigo most often affects children and women, especially in the summer. The rashes are localized near the ears, nose, mouth, arms and legs. The infection is transmitted through contact, injury, and maceration. Surrounded by a red border, the yellow-green crusts gradually grow. After opening the phlyctene, the infection progresses quickly. With a positive course, erosion epithelializes without lasting traces. Complications are possible in the form of lymphangitis and imphadenitis, eczematization, and in children – glomerulonephritis. Vulgar impetigo is provoked by pathogenic streptococci, staphylococci gradually join, causing suppuration and drying yellow-green crusts. Most often it affects children, and outbreaks of the epidemic are possible.
- Streptococcal diaper rash is a long-term, often recurring inflammation of contact tissues. With poor hygiene, the contact surface in the folds becomes irritated and sweat secretions decompose. Inflammation is often accompanied by yeast. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, gout, and seborrheic dermatitis contribute to diaper rash. In the edematous folds the skin becomes wet, erosions and cracks appear. Complaints of pain and itching. With regression, pigmentation remains.
- Streptoderma diffuse is a chronic skin disease of the skin of the legs after hypothermia, maceration, and problems with blood vessels. The lower legs are most often affected, especially in the presence of wounds and fistulas. The ulcers dry out, leaving erosions with serous pus under the crusts. When the lesion grows, complications are possible: lymphagitis and lymphadenitis. Without timely treatment, the disease becomes chronic.
- Ecthyma vulgaris is a deep type of streptoderma that develops against the background of trauma, pollution, impaired blood flow in the legs, and intoxication. In addition to the legs, damage to the thighs, buttocks, and lumbar region is possible. It starts with a large bubble with a cloudy filling and a red border. After necrosis, an ulcer with a brown crust forms. It heals on its own within a month, leaving a hyperpigmented scar. Possible complications in the form of phlebitis, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis.
- Erysipelas is a deep skin lesion, with symptoms of intoxication and fever. Sources of infection are any patients with streptococci (tonsillitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis, streptoderma). Frequent injuries, cracks, and scratching provoke relapses, leading to scarring and the formation of elephantiasis of the legs. The onset of inflammation is acute: swelling occurs with hot skin. Complaints of pain, burning, bloating, fever. There are the usual form (with erythema and edema), bullous-hemorrhagic, phlegmous (with suppuration) and gangrenous (with gangrene). Complications are severe: elephantiasis, phlegmon, abscesses, gangrene. On the face, sepsis and thrombosis of the sinuses of the brain are possible. It is advisable to hospitalize patients with erysipelas.
Symptoms, rashes
At the first stage of the development of infection, dermatitis of a varied nature occurs in the area of the body innervated by one sensory nerve, which may be accompanied by itching of the skin, tingling, numbness, etc. The patient also complains of a bad mood, headache, and body temperature may rise.
After a few days, an itchy rash identical to smallpox appears in the dermatome, with the morphology of spots, papules, follicles filled with serous contents and pustules. Rashes on the side leave behind painful erosions and ulcers that are covered with scabs, and those that subside reveal small scars and skin discoloration. The rash is still accompanied by general symptoms such as low-grade fever, distress and weakness.
The most common sites for herpes zoster are the torso, with the virus affecting the nerves coming from the thoracic spine and the head and face. Rarely, however, a rash occurs on the extremities.
Editorial advice
For the treatment and prevention of complications of pustular skin diseases, Elon K, produced by the famous German pharmaceutical company, has proven itself well.
Ilon is produced in the form of an ointment, the basis of which is turpentine substances - oil and larch extract, which have a healing, antibacterial and tonic effect. As an adjuvant, Ilon K is widely used for the treatment of mild, localized pustular skin lesions of various etiologies, such as folliculitis, boils, abscesses, felons and inflammation of the sweat glands. Depending on the degree of suppuration, the ointment should be applied to the affected area of the skin once or twice a day, and a sterile bandage or plaster should be applied on top.
Elon K ointment is not an antibiotic, and therefore has virtually no contraindications. The natural composition of the ointment allows it to be used not only for treatment, but also to prevent the appearance of purulent inflammation on the skin.
Now, widely known in many European, CIS and Baltic countries, Elon K ointment can also be bought in Russian pharmacies. Be sure to purchase it, and it will become a permanent “resident” of your home medicine cabinet.
Pyoderma is treated by a dermatologist, mycologist, and surgeon. In addition to symptomatic treatment, a thorough examination is required. A blood glucose test is required. Particular attention should be paid to acne after puberty. A fluorogram of the lungs will help exclude skin tuberculosis. A stool test will reveal intestinal dysbiosis. Women undergo an ultrasound to examine the uterus and appendages, since inflammation of the ovaries and changes in hormonal levels are accompanied by rashes (especially on the chin).
Pustular skin diseases are treated by a dermatologist, mycologist, and surgeon
To influence the cause of the disease, it is necessary to carry out antimicrobial therapy, block provoking factors, adjust carbohydrate metabolism, prescribe a vitamin complex, and eliminate chronic infectious pathologies.
Etiotropic treatment should suppress the pyococcal flora. They practice both local and general treatment. Systemic therapy is carried out for:
- Multiple pyoderma and rapid spread of infection.
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes.
- Fever, chills, malaise and other body reactions.
- Complicated and deep facial pyoderma with the threat of complications.
In weakened patients (after irradiation, with HIV syndrome, hematological pathologies), treatment should take into account all clinical data. General therapy involves the prescription of antibiotics and sulfonamides. The choice of drugs is based on the analysis of purulent exudate (culture, isolation of the pathogen, testing its sensitivity to drugs).
Medicines of the penicillin group can cause toxicoderma, so they are not prescribed to patients with purulent eczema. Exacerbations are also possible with psoriasis.
External treatment depends on the degree of damage and the form of the disease. In acute cases, the pustules are opened by treating the wounds with an antiseptic. For deep wounds, resolving therapy is indicated to accelerate the self-resolution of the infiltrate: dressings with ichthyol ointment, UHF, dry heat. Compresses, ozokerite, paraffin baths are contraindicated.
Treatment is selected based on analysis of purulent exudate
In case of deep abscesses, they are opened surgically, organizing drainage with turundas soaked in an antiseptic solution.
At the granulation stage, dressings with ointments based on biostimulants and antiseptics are recommended.
In the chronic stage, purulent crusts from the surface must be removed mechanically using tampons soaked in hydrogen peroxide. They are first softened with antiseptic ointment. After removing the crust, the wound is washed with an antiseptic.
Nonspecific methods include autohemotherapy, the introduction of protein blood substitutes, pyrogenal, prodigiosan, methyluracil and splenin. To strengthen the immune system in children and adults, herbalists recommend echinacea, ginseng, and Chinese lemongrass.
Treatment of the rash
A rash of blisters on your hands and face should prompt you to first stop contacting substances containing allergens: laundry detergents, detergents, creams, deodorants, and decorative cosmetics. As a warning, you should take antihistamines Diazolin, Loratadir. They slow down allergic reactions and reduce the threshold of sensitivity to allergens.
Warm baths with infusions of string, chamomile, St. John's wort, and oregano help soften the skin and reduce dryness.
Good liniments are hormonal creams Atoderm and Pimafucort. When using them, it is necessary to gradually reduce the dose.
The child has
Finding out the cause and treating the child is aggravated by the fact that he scratches the itchy area, spreading a possible infection throughout the body.
The appearance of pimples and blisters varies from the symptoms of diseases in adults, such as:
- allergy;
- herpes;
- sunburn;
- diaper dermatitis, which occurs from contact with urine-soaked diapers;
- chicken pox;
- diaper rash;
- streptococci;
- pustular infectious pathologies;
- molluscum contagiosum.
The latter has nothing in common with a marine animal; with electronic magnification, the dermatitis scales look like shells.
A child’s education should attract the attention of parents. Carbonated drinks, high-calorie foods, sweets, brightly colored vegetables and fruits that contain lycopene and carotene, which cause allergic reactions, should be excluded from his diet. In this case, it is recommended to eat green and yellow fruits. Underwear made from synthetic fiber should be replaced with cotton ones.
For treatment, the so-called mash based on chloramphenicol, sea buckthorn, castor oil, liniments from natural animal fat, and decoctions from string are used.