Causes
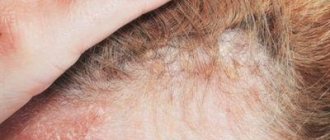
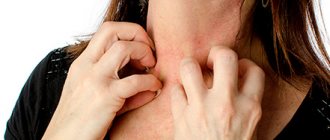
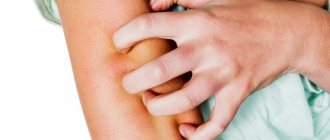
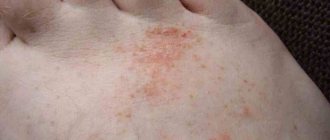
Eczema is one of the most common skin diseases of the hands and feet: according to dermatologists, this type of skin rash occurs in 20 percent of people inhabiting the globe. Symptoms of the disease are severe inflammation and redness of the top layer of skin, which is accompanied by dry scaly patches and blisters that visually resemble pimples.
Finding the exact trigger of inflammation is like looking for a needle in a haystack. Often the trigger for skin disease is psychological stress and allergies to chemicals contained in cosmetics or clothing.
Another 3 common causes of the disease:
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Excessive sebum production.
- Hereditary predisposition to disruption of the protective and barrier function of the skin.
Nutrition for adults with eczema on the legs and hands
There is no evidence of which foods cause eczema on the hands and feet or outbreaks of symptoms of this skin condition.
Despite this, people insist with a persistence worthy of better use that their skin condition worsens after they eat certain foods.
Believe me, it is not so easy to answer the question of what caused skin inflammation in a given situation. The connection between the food we eat and a skin rash seems obvious at first glance, but since we are faced with many possible triggers of the disease every day, it is difficult to say what the real cause was.
The same applies to foods that supposedly relieve symptoms. Most of the products and supplements studied by scientists did not show any clear improvement in skin condition.
What to do in this situation? We recommend choosing a balanced meal plan. Although there is no evidence of a link between food and eczema, there is no doubt that consistent consumption of fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products and whole grains is generally beneficial for maintaining healthy skin.
Interesting article: Hypoallergenic diet for atopic dermatitis
Diet for eczema in children
Some young children suffer from eczema due to allergic reactions to certain foods. Whereas in children over 3-4 years of age, eczema caused by allergic reactions to food is very rare. In these children, the food may cause rashes and other skin reactions, but not eczema.
If you suspect that your child's eczema is due to food allergies, be sure to consult with your doctor. Keep in mind that food allergy test results are not always reliable; it is best to double-check them. Test results for food allergies to certain foods are often positive, even if the child does not have any allergies at all. Therefore, these tests must be taken as prescribed by your doctor.
What can you eat?
Next, we'll look at possible ways to relieve symptoms through diet.
80% of patients suffering from eczema have high levels of antibodies that exceed the norm. Essentially, they have an allergy.
Common sources of allergic reactions:
- soy;
- eggs;
- milk;
- peanut;
- wheat;
- citrus;
- chocolate.
By using an elimination diet, you can find out which foods negatively affect the body. The point is to eliminate the above foods from your diet one by one, in order to determine which of them contribute to skin disease. This process is usually carried out under the guidance of the attending physician or nutritionist, who provides timely recommendations for food replacement and ensures that the patient is not missing out on important nutrients in the diet.
The second way is to follow an anti-inflammatory diet. Inflammation is a key component in the development of eczema, so eating foods with anti-inflammatory effects may be beneficial.
Foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates increase insulin levels, which promote inflammation, so try replacing them with whole grain carbohydrates, protein and vegetables.
The right balance of fats, especially foods high in omega-3s, also have an anti-inflammatory effect. In the absence of allergies, it is useful to eat fish and other seafood, as well as nuts, flax seeds and flaxseed oil.
Third way. If it's hard to find something to apply to sensitive skin, honey is a useful alternative. This product has antibacterial, antifungal and antiseptic properties that support the health of the immune system. We recommend eating a small amount of honey every day or applying it topically.
Fourth way. The balance of vitamins and minerals in the diet has a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin.
Useful vitamins and minerals:
- Zinc – Found in seafood, pumpkin seeds, dark chocolate and lean red meat.
- Vitamin C – found in brightly colored fruits, vegetables and rose hips.
- Vitamin E – found in sunflower seeds, almonds, pine nuts, avocados and dried apricots.
Interesting article: Diet for psoriasis
Research into identifying foods that may help with eczema
Although many types of foods and dietary supplements have not been shown to be effective in combating eczema, research in this direction continues.
Separate studies have found that taking probiotics, beneficial live microorganisms found in foods such as yogurt and various supplements, may help relieve symptoms of eczema in children. Most of these studies have been conducted in different countries using different types of probiotics, so the question of which type of live microorganism is most beneficial remains an open question.
The next product that has been researched to help relieve the symptoms of eczema is tea. However, to date there is no reliable evidence that drinking black, green or oolong tea actually improves the symptoms of the disease.
In addition, research is being conducted on omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and fish oil and their possible beneficial effects on eczema flare-ups.
What can't you eat?
Experience shows that there are a number of foods that cause skin allergies more often than others. Products with a high allergenic potential include:
- sour varieties of apples;
- nectarine;
- peach and kiwi;
- papaya and mango;
- carrots and celery.
People with food intolerances are particularly sensitive to additives such as dyes, preservatives and biogenic amines. Biogenic amines are protein building blocks that are found in perishable foods such as meat, fish and sausage.
In addition, alcohol, coffee and black tea also stimulate allergies.
The products or food ingredients listed do not necessarily cause allergies and associated discomfort, but are often related to them, so consult your doctor before consuming them.
Interesting article: Nutrition and diet for dermatitis on the hands, face and body
When is a diet indicated?
A diet for eczema is necessarily prescribed in the acute stage of the disease. Typically it should be followed for 3 weeks.
During this period, it is recommended to eat only boiled or steamed food. Fruits, vegetables and red berries, meat broths are excluded, and a limit is placed on table salt. Nutrition for eczema should not put too much strain on the liver, kidneys and gastrointestinal tract.
During the remission stage, restrictions become less strict. But the fewer allergens in food, the lower the likelihood of a relapse.
Menu: food table
Below is a table with the recommended menu:
| Monday |
|
| Tuesday |
|
| Wednesday |
|
| Thursday |
|
| Friday |
|
| Saturday |
|
| Sunday |
|
Interesting article: Treatment and diet for acne: 6 rules for creating a menu!
Proper nutrition for different types of eczema
For eczema of any type, you can follow general recommendations, but each type has its own specific rules to avoid exacerbation.
For hand eczema
The diet should help relieve symptoms and put the disease into remission. Regular proper nutrition helps reduce the likelihood of relapse. With such eczema, you need to avoid sweet, spicy and fried foods. Semi-finished products, marinades, pickles and canned foods are also prohibited.
carriers of vitamins PP and B
Diet for eczema on the hands allows the consumption of lean meat (preferably turkey and rabbit) and fish. But during an exacerbation, it is advisable to adhere to a vegetarian diet. Vegetables will benefit the body, the amount of potatoes is reduced, and it is advisable to avoid pasta altogether.
To restore the deficiency of vitamins PP and B, you need to eat more lettuce, turnips, carrots, rutabaga and fresh cucumbers. Greens will also be useful: parsley and dill. There are usually no restrictions on the amount of liquid, but it is better to exclude coffee, store-bought juices, alcohol and carbonated drinks.
In some cases, eczema causes weepy patches on the hands. They occur when the water-salt balance and the inflammatory process are disturbed. With this pathology, the diet for eczema excludes foods rich in carbohydrates. You can include lean meat, dairy, and vegetables in your diet. You cannot eat cabbage and legumes, and salt is also not used when cooking.
For eczema on the legs
The diet for eczema on the legs excludes foods with difficult-to-digest fats. These include:
- fat;
- sweets;
- flour;
- pork;
- pates;
- lamb;
- meat dishes with butter.
During an exacerbation, you need to include fermented milk, porridge with water, and vegetable soups in your diet. In the first few days of illness, diluted vegetable and fruit juices are needed to cleanse the body.
For meat products, you should give preference to boiled or stewed turkey and rabbit, boiled fresh fish and lean beef. In this case, you need to steam, boil or bake.
Fermented milk products and plant foods should be present in the diet every day. Cabbage, peas, cucumbers, zucchini, carrots, beets and other vegetables have a beneficial effect on the body. Leaf and watercress contain vitamin C, iron, iodine and carotene, therefore they are useful for the patient.
During the period of remission, it is useful to add berries (raspberries, blueberries, rowan, gooseberries, currants), nuts, and melons to the diet. But during an exacerbation, these products are contraindicated. The diet must include porridge, especially oatmeal, buckwheat and wheat. It is strictly forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, coffee and strong tea.
Diet for dyshidrotic eczema
diet for dyshidrotic eczema Diet for dyshidrotic eczema is an important component of treatment. Dyshidrotic skin lesions are a chronic disorder. Patients suffer from periodic rashes in the form of serous blisters on the skin of the soles and palms. A properly formulated diet prevents allergic reactions, and therefore the manifestations of the disease.
First of all, it is necessary to exclude red vegetables and fruits, as well as citrus fruits, from the diet. Any sweets and flour products are prohibited; sugar can be replaced with fructose. For meat products, low-fat dietary varieties of meat and fish are suitable. At the same time, many allergens are contained in smoked meats, pork and duck meat.
Spicy, fried, peppered and salty foods should also be removed from the diet, since such foods not only cause worsening of rashes and itching, but also negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The basis of the diet is fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and dairy products. Cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir and cheese contain lactobacilli, which are essential for the intestines and local immunity. Their regular use prevents relapses of dyshidrotic skin lesions.
So, therapy is based on following a strict diet. It is necessary to adhere to such a diet for 1-2 months, and to achieve lasting results - throughout life.
Diet for microbial eczema
The microbial diet is a vegetable-dairy diet. With this disease, the skin is covered with flat crusts, when removed, weeping areas appear. Most often, rashes appear on the legs, the back of the hands, and sometimes on the head. As a rule, a doctor compiles a list of permitted and prohibited foods. Coffee, chocolate, spices, pickles, soda, cheese, and alcohol are prohibited. The exception is plant allergens; the patient is allowed to eat nuts, corn, red vegetables, peas, and garlic. But if the disease worsens, these products are also prohibited.
The main diet consists of vegetable soups, unleavened porridges in water, river fish, steamed cutlets and meatballs, and dairy products. Restrictions also apply to the amount of spices in food. It is recommended to reduce or completely eliminate the use of salt and pepper. Don’t forget about maintaining water balance; you need to drink up to two liters of still mineral water every day.
Diet for allergic eczema
The diet for allergic eczema is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. Not only food products, but also dust, animal hair, pollen, cosmetics and much more can stimulate the appearance of skin rashes. Regardless of the pathogen, therapeutic nutrition can minimize the manifestations of the disease. It is necessary to adhere to a healthy regimen not only during the period of exacerbation to unload the body, but also during the period of remission.
Smoked meats, sausages, fried, fatty foods, and foods with spices are prohibited. As well as seafood, canned food, eggs, nuts, citrus fruits, mushrooms, grapes, carbonated drinks, confectionery.
It is necessary to limit the consumption of pasta, semolina, butter, full-fat sour cream and whole milk.
The diet should be based on fermented milk products, lean meat, light fruits (plums, currants, pears, apples), vegetables and herbs. You can eat grain breads and products made from second-grade flour, ghee and refined butter.
Diet for dry eczema
dietary rabbit meat The diet for dry eczema involves a vegetarian diet. The menu is based on protein and plant foods. During the period of remission, you can add weak meat broths, lean meats and steamed meat dishes to your diet. You should definitely eat porridge, but without oil and salt, vegetable casseroles and stews with a minimum content of potatoes. As for fish, it is best to eat river fish, baked or boiled.
Dairy products such as cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk, yogurt and kefir help the body recover faster and accelerate skin regeneration processes. Plant foods are very useful, for example, peas and cabbage. Peas contain a lot of protein, so it is better to eat them during the summer period of exacerbation of the disease. Your daily diet should include carrots or carrot juice, as they contain a lot of B vitamins and carotene. The content of precisely these beneficial substances in patients with eczema is significantly underestimated.
If hypertension appears along with skin rashes and itching, then you should eat beans and beets, watercress and lettuce, as they are rich in vitamin C, iron, iodine and carotene. Dill helps with gastrointestinal disorders. Greens can be added to salads or made into smoothies based on kefir and dill.