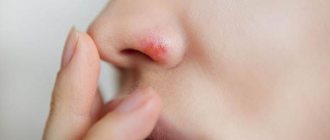
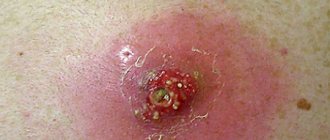
Any mechanical damage to the skin and underlying soft tissue, which is accompanied by pain and bleeding, is defined in medical practice as a wound. In situations where, during the process of regeneration a constant release of fluid , which significantly slows down healing, the wound is considered weeping .
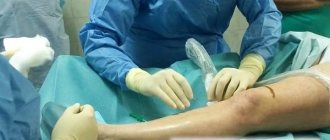
Photo 1. First aid for wounds - treatment with an antiseptic and application of a sterile bandage. Source: Flickr (Rawa Law Group Workers Compensation Attorney Long Beach)
How it manifests itself
With such an injury, soft tissues (skin, muscles) are damaged. A wound differs from an ulcer in that it is located externally, whereas an ulcer begins from the inside. If the wound does not dry out and ichor is constantly released from it, then we are talking about a weeping wound. Most often, a weeping wound occurs if it is associated with a secondary, often bacterial, infection. In this case, the immune system tries to remove the bacteria from the wound on its own by releasing excess blood plasma. There are three degrees of wound healing:
- The wound begins to cleanse itself;
- Inflammation develops around it;
- Granulation occurs and the injury site begins to dry out.
But it happens that the wounded surface is not able to dry out on its own, this can lead to the development of sepsis.
Symptoms and diagnosis
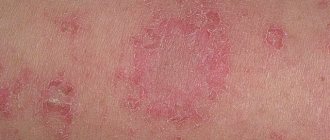
Symptomatic manifestations of dermatitis are determined by the age of the patient and the timeliness of treatment. Dermatologists distinguish several phases in the development of the disease:
- In children under 3 years of age. Cracks and pinpoint erosions appear on the skin, from which a light yellow liquid is released. Later, weeping ulcerations become covered with dense crusts of light or dark brown color. In young children, the rash is localized on the cheeks, as well as on the knees and elbows. In isolated cases, grouped weeping vesicles appear on the trunk.
- For children 3-12 years old. Rashes appear on the back of the palms, in the bends of the legs and on the neck. The affected areas of the skin acquire a reddish tint, swell, after which oozing blisters and cracks form on them. For a long time, the weeping rash cannot be treated, and after the tissues heal, it leaves pigmented spots.
- For children 12-16 years old. The clinical manifestations of dermatitis in this category of patients are not much different from the symptoms for the early age group. They manifest themselves as severe redness in the affected areas, a blistering rash, and the formation of crusts. Light brown compactions appear after spontaneous opening of the vesicles. Clinical manifestations of dermatitis may suddenly disappear or worsen with decreased immunity or disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- In adults. At the age of 16-20 years, weeping vesicles are localized on the ankles, hands, folds of skin, and neck. When the blisters open, areas of weeping ulceration appear. If you do not treat the skin with disinfectant ointments/solutions, secondary infections penetrate into the lesions. This often causes purulent inflammation of the soft tissues.
Dermatitis is determined by characteristic clinical manifestations:
- the formation of small bubbles and nodular seals on the body;
- microcracks, ulcerations, from which serous or purulent exudate is released;
- redness, swelling in areas affected by dermatitis.
To confirm the diagnosis, microscopic and laboratory examination is performed. Using a skin test, irritating substances that cause an allergic reaction and rash on the body are determined. After clarifying the cause of weeping dermatitis, the most appropriate medications are selected.
Reasons for appearance
A weeping wound on the leg most often occurs in cyclists, skateboarders, and rollerbladers. These are the people who are at high risk of falling on asphalt. At the same time, weeping wounds can be on any part of the body and appear for many reasons:
- from various burns (thermal, laser, chemical, electrical);
- when there is a disruption in the blood supply to the tissue;
- for inflammatory diseases of the skin, for example, eczema, dermatitis;
- from damage to the skin by bacteria and fungi;
- due to irritation from synthetic underwear;
- after rubbing and calluses on the skin;
- due to diaper rash in the armpits, in the groin folds or under the female breast;
- from bedsores, which almost always occur in bedridden patients;
- with torn skin or cuts.
Sometimes an infection leads to the appearance of such a wound in a newborn baby at the site of the umbilical cord. Treatment of weeping wounds in such small patients must be careful and often medications cannot be used for healing; only safe drying agents are acceptable.
Causes and conditions of occurrence
The main mechanism for the appearance of a weeping wound is excessive release of plasma through injured areas of the skin. This can happen under the influence of various factors:
- Pathogenic bacteria, fungus.
- Some skin diseases (dermatitis, eczema, etc.).
- Scuffs, diaper rash, bedsores on the skin.
- Allergies to metals or synthetics.
- Insufficient nutrition of the skin due to weakened blood supply.
Any of these factors can trigger a sequence of certain reactions in the body, the result of which will be high permeability of blood vessels passing through the tissues under the wound.
Plasma from the blood begins to abundantly leak through the walls of blood vessels into the wound, preventing it from drying out. In essence, this is a protective mechanism of the body, which thus tries to flush out toxic decay products of dead cells from the wound.
Unfortunately, plasma can become an ideal breeding ground for dangerous microbes . That is why it is necessary to eliminate such a problem at the earliest stages, before a dangerous infectious process begins in the wound.
Initial processing
In order to reduce the risk of complications, the wound should be thoroughly washed to remove purulent masses and external irritants (dust, dirt, etc.). Antiseptics are used for this, most often hydrogen peroxide, but if this is not at hand, then ordinary soap and water will do. The skin that surrounds the wound should be treated with brilliant green or a thin layer of iodine, this will prevent bacteria from entering it and will help dry the edges of the wound a little. Next, a bandage is applied to the wound to protect it from harmful microbes. If the damage is deep, then further treatment cannot be avoided; in some cases, it may even be necessary to perform an operation to clean the wound and stitch it together.
Prevention
To avoid the development of weeping dermatitis or to prevent its recurrence, it is necessary to fulfill several simple conditions:
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- Eliminate nervous disorders, depression and stress, avoid situations associated with such conditions;
- Eat rationally;
- Allergen-dependent people need to exclude all possible contacts with allergic factors;
- Treat pathologies of internal organs in a timely manner; when the first symptoms of dermatitis appear, you must immediately consult a specialist.
In acute forms, strict adherence to all medical recommendations ensures rapid elimination of symptomatic manifestations and complete cure of the disease. If weeping dermatitis has become chronic, then during its remission it is extremely important to carry out immune-strengthening therapy.
Drying
For shallow but slowly healing wounds, an alcohol solution of iodine, brilliant green solution, and fucorcin are used. It is worth saying that iodine cannot be smeared in a continuous layer, as this can lead to a chemical burn from iodine. An iodine network is enough for the drug to have its effect. The skin from which exudate oozes can be wiped with an alcohol-based tincture of calendula or birch buds.
If a crust forms on the skin very quickly, and due to suppuration the ichor cannot come out, then you need to make the wound soft, but not allow it to become weeping. To do this, the crust is softened with water and salt in the proportions of 1 part salt to 10 parts water. In addition to the drying effect, this product also has a healing effect, since it fights bacteria that cause suppuration and draws pus to the surface. To do this you need to make a wet compress:
- Take one liter of saline solution;
- One minute pour it directly onto the bandaged wound;
- Carry out this action once every four hours.
Thanks to this procedure, you can bandage the damaged area and put medicines on it once every two days.
Treatment
The main therapeutic principle for dermatitis is the elimination of the irritating factor in order to stop the further spread of the lesions.
In general, the treatment of weeping dermatitis is complex and combines:
- hygiene of affected areas;
- anti-inflammatory treatment;
- antiallergic treatment.
To relieve allergic symptoms, antihistamines such as Telfast, Claritin or Tavegil are prescribed. It is noteworthy that the newest drugs in this group do not cause attention disorders or drowsiness at all, so during treatment the patient can safely lead a normal and familiar lifestyle.
Often therapy also involves the use of local drugs such as hormonal ointments (Akriderm, Diprosalik, Sinaflan, Advantan, Elokom, etc.). It is better not to use such products in children, but to give preference to zinc-based ointments - they have effective antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory effects.
It is also recommended to treat areas affected by weeping dermatitis with infusions of oak bark or chamomile. Such procedures contribute to drying of the skin. Furacilin lotions also give a similar effect.
Iodine solution should not be used to treat affected areas; it is only suitable for lubricating the edges of wounds in order to prevent further spread of the infectious process.
Important! If the course of the pathology is accompanied by the formation of vesicles, then these blisters must be opened in accordance with antiseptic and aseptic requirements. These manipulations should only be carried out by a specialist in the sterile conditions of a treatment room. With the neurological nature of weeping dermatitis, the use of sedative herbal remedies such as Valerian, Motherwort, Glycine, Peony Tincture, Novo-Passit, Persen, etc. is indicated.
If the etiology of the disease is associated with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, then therapy is aimed at treating the underlying disease. Such treatment is often accompanied by adherence to a dietary regimen that involves the exclusion of allergenic foods (citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs, honey, etc.).
If the cause of the disease is dysbacteriosis, then it is recommended to take prebiotic drugs like Probifor or Linex, and you should also include fermented milk products in your daily menu.
After restoration of the intestinal microflora, all manifestations of weeping dermatitis gradually recede. Complex therapy, at the discretion of the doctor, can be supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures, water mud therapy, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser treatment, etc.
Treatment of weeping wounds with secondary infection
Not everyone knows how to treat a weeping wound if it has become infected, so if it is very festering, then you need to see a doctor. Wounds on the feet are often infectious because shoes contain a huge amount of bacteria. To speed up skin regeneration, an antibacterial powder is applied to it, thanks to which tissue restoration occurs. It could be:
- sulfonamide;
- penicillin;
- streptocide;
- chloramphenicol;
- xeroform.
In addition to these agents, baneocin can be used, which fights not only bacteria, but also fungi. The powder is added as follows:
- the damaged surface is cleaned, the powder is collected on a brush and a thin layer is applied to the wound like powder;
- a dry sterile gauze pad is applied on top and secured with a good layer of bandage;
- after 5 hours it is treated with a salt solution, as described above, but if there is no or little pus, then you don’t have to rinse it, but simply powder the damage; it will gradually dry out.
What to do if the wound gets wet?
The condition of a weeping wound is often caused by an increase in existing inflammation, as well as the addition of some kind of infection.
First (pre-medical) aid must necessarily include thorough washing of the weeping wound from various contaminants, exudate and pus that forms.
It is best to use special antiseptic solutions for this purpose, for example, Chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide, as well as other compounds. If you don’t have ready-made pharmaceutical preparations on hand, you can prepare a solution of furatsilin or potassium permanganate, and also use ordinary laundry soap.
After washing, the skin surrounding the wound should be treated using brilliant green or iodine solution.
Treatment products should not be poured into an open wound; they can only be used to treat the skin around it. After such treatment, it is necessary to apply a sterile bandage to the site of injury, the purpose of which is to prevent air, harmful microorganisms and possible contamination from entering the wound.
It is important to remember that the success of its treatment in the future will depend on the cleanliness of the wound.
Therefore, any dirt, discharge, or necrotic particles should be removed in a timely manner, while relieving tissue swelling and inflammation. Only with proper and timely care will treatment of injury be effective and faster.
After carrying out first aid procedures, it is very important to transport the victim to the nearest clinic as quickly as possible and place him in the hands of qualified doctors.
You should not delay going to the hospital, as this is fraught with serious complications and consequences.
Folk recipes
If there is no significant threat to the body, then weeping wounds can be treated at home. Olive oil, potatoes, beeswax, St. John's wort, spruce resin, honey and onions are used for this. Since ancient times, the following traditional medicine recipes have been used for treatment:
- Potato. Its juice perfectly draws fluid from the wound. The potatoes should be grated, squeezed out the juice, soaked in a bandage, applied to the damage and bandaged. This dressing is changed every 4 hours and left overnight.
- Onion relieves swelling and clears pus. Grated onion gruel should be applied to the wound. Despite the burning sensation that the patient experiences at first, the onion heals well.
- You can disinfect an injury with a product made from pine, spruce resin, honey, wax and vodka. All components must be heated by steam to obtain a homogeneous liquid mass. Next, strain it, pour it into a dark glass bottle and put it in the refrigerator. Twice a day you need to lubricate the damaged surface, even when healing.
- Aloe extracts pus perfectly. The juice should not be squeezed out from a young plant. Gauze soaked in this juice is placed on the wound.
- Calamus fights germs and heals. To prepare the infusion, pour a spoonful of dry root into a glass of boiled water, then steam it. After the product has cooled, it must be strained and the wound should be washed with it.
Shallow damage will heal in a week with proper therapy. If healing does not occur within two weeks, then you should not look for information on how to treat it, but you need to go to a doctor and take more serious measures, for example, undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures.