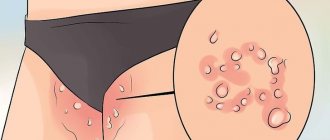
Itching and flaking in the groin occurs in both men and women. Such symptoms can be observed due to irritation of the delicate tissues, but can also be signs of dermatological or fungal diseases, which also provoke the appearance of spots in the groin area, various kinds of rashes and weeping. A delicate problem should not be ignored, much less self-medicate. You definitely need to see a doctor who will determine the exact cause of the discomfort and prescribe adequate therapy.
Why does itching occur?
Currently, there are different theories among specialists that explain the origin of itching. Of these, the most popular are the following:
- 1This is a type of pain. It is believed that it appears as a result of mild irritation of normal pain receptors.
- 2This is an independent sensation. Some experts believe that there are specific receptors in the body, the irritation of which prompts a person to itch. Receptors can be irritated by chemicals and nerve impulses.
As observations have shown, there are a number of substances, with an increase in the concentration of which, itching may appear or intensify - histamine, serotonin, adrenaline, kallikrein, substance P, opioids, cytokines, growth factors, eicosanoids and others. Heredity is also believed to play a role.
Sometimes itching is one of the symptoms of diseases of the internal organs or stress. He can be:
- 1Acute/chronic.
- 2Limited (local)/generalized (affects different parts of the body).
- 3Continuous/periodic.
- 4Weak/moderate/strong.
- 5With a known cause/idiopathic (the cause of which has not been established).
- 6Occurs in isolation/together with other symptoms: discharge, pain and cutting, rash, and so on.
Itching in the intimate area
The intimate zone is a fairly broad concept, including the area of the vulva, perineum and vagina of a woman. Unpleasant sensations can be concentrated in only one of these zones or affect them all. Their localization is one of the main points in gynecology, allowing the doctor to establish the correct diagnosis.
2.1. Vagina
The intensity of vaginal itching depends on the cause that caused it. It can be quite weak, moderate with cervical erosions, age-related changes, and vaginitis.
Itching of moderate intensity is observed with allergies to latex, spermicidal creams, vaginal tablets and suppositories, severe itching with infectious diseases (thrush, trichomoniasis and other STDs, bacterial vaginitis).
In combination with a feeling of burning, dryness and discomfort in the absence of heavy discharge, it is characteristic of menopausal changes in the vagina, atrophic vaginitis. Against the background of white cheesy discharge it occurs with candidiasis, and against the background of creamy, watery, white-gray, green or foamy discharge - with gynecological inflammatory diseases (vaginitis, bakvaginosis, cervicitis, etc.) and STIs.
2.2. Vulva
Vulva is a collective term that includes the external female genitalia. These include the vestibule of the vagina with the Bartholin glands, the clitoris, the labia majora and minora, and the pubis. The vulva area also contains the external opening of the urethra (urethra).
Itching can be limited only to the vestibule of the vagina, and also spread to the lips small and large. The mucous membranes of the vulva can be very itchy with genital herpes, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea and thrush, and psychosexual disorders.
Moderate itching is observed with inflammatory diseases of the vulva (vulvitis), allergic reactions to underwear and hygiene products, urethritis, as well as with enterobiasis (pinworms). A special category consists of benign and malignant tumors, kraurosis of the vulva.
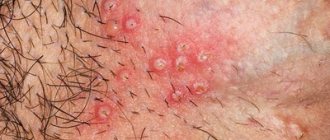
The skin of the pubis, inguinal folds and labia majora is very itchy due to the appearance of pubic lice and scabies, eczema, athlete's foot and other fungal infections (dermatomycosis). In this case, redness, weeping erosions and characteristic rashes are also observed.
Sometimes persistent, difficult-to-treat itching, extending far beyond the intimate area, is caused by the accumulation of metabolic products and bile acids in the body against the background of kidney or liver failure or oncology. This condition is painful for a woman.
2.3. Crotch
This is the area of the intimate zone located between the genitals and the anus. Itching in the perineum can be caused by fungal and allergic skin diseases, general somatic pathology (for example, diabetes mellitus, liver disease, kidney disease), benign and malignant tumors of the rectum and pelvic organs, helminths (pinworms), scabies mites.
“Bumps” due to hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and healing wounds can itch in the anus area.
Combined itching, covering the entire intimate area, is characteristic of helminthic infestations, herpetic and fungal infections, skin diseases and advanced forms of STIs.
Limited neurodermatitis
This pathology is localized in the femoral-inguinal folds, on the inner side of the thighs, in close proximity to the external genitalia. The main symptom is itching. Lichenification, peeling, and papular elements appear in the lesions. This disease develops against the background of neuroendocrine disorders, hereditary predisposition, dysfunction of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and functional disorders of the central nervous system.
Main reasons
The appearance of itching in women and men indicates some kind of malfunction in the body. There are more than a hundred reasons responsible for its occurrence: for example, it could be a reaction to washing powder or new underwear, as well as an undiagnosed infection or diabetes.
In addition, itching in intimate places can occur due to insect bites, natural changes during pregnancy, the menstrual cycle or climate change.
However, usually itching still indicates the presence of some kind of disease, problems with hygiene, or a change in usual lifestyle. Therefore, it is important to promptly consult a gynecologist for medical help.
Pediculosis pubis
Red spots in the groin in women may indicate lice pubis. This disease develops as a result of the parasitic activity of pubic lice. The leading symptom of infection is excessive itching, which intensifies at night. The skin in the groin with lice pubis turns red as a result of constant scratching. In addition to the groin area, pubic lice can spread to the armpits and perianal area. The disease has another characteristic sign - a spotted rash appears, which tends to disappear quickly. Quite often, women independently discover parasites and their eggs on their pubic hair. In some women, the symptoms of lice pubis are accompanied by an allergy to parasitic waste products. The danger is represented by the consequences that can develop when an infection enters the body through scratched skin.
Changes
4.1. Contact allergy
Quite often there is an allergic reaction from the genital organs to intimate hygiene products or the material from which underwear is made. In this case, the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina is itchy and itchy, there may be redness and slight swelling.
Another case is intolerance to the powder used in washing. Sometimes women notice the appearance of symptoms when using scented sanitary pads and tampons.
4.2. Irritation after shaving
The main source of itching in this case is growing hard hairs that resemble stubble. As a rule, itching occurs mainly in the pubis, the skin of the labia majora and the inguinal folds in contact with them.
The sensation intensifies when wearing tight, waterproof underwear, increased humidity and infection. A careful examination may reveal irritation, moderate redness of the skin, and ingrown hairs.
4.3. Low level of hygiene
Even physiological secretions from the genital tract under the influence of the environment can become a good environment for the proliferation of microorganisms. The situation is aggravated by dirt or dust, as well as exfoliating epithelial cells.
As a result, inflammation develops, leading to tissue damage. It is accompanied by burning, pain and itching. In this case, the symptoms are localized in the area of the vaginal vestibule, labia minora, and clitoris. The discharge changes color and smell.
You can avoid such feelings by following these simple rules:
- 1Change underwear daily.
- 2Wash yourself at least once a day, using special hypoallergenic intimate hygiene products or running clean water.
- 3It is important not to scratch the skin and mucous membranes (it is better to simply wash with cool water and consult a doctor).
- 4During menstruation, pads should be changed as often as possible.
- 5Make sure that the fabrics from which the underwear is made absorb moisture well and allow the skin to “breathe”. It is optimal to use white, cotton panties.
Depilation
Many modern women prefer to remove hair in the groin using wax, cream, machine or other depilation methods. If you remove hair in a hurry or with mistakes, redness and irritation may appear in the groin. Such conditions are accompanied by burning and itching. As a result, ingrown hairs can occur. To avoid such a situation, it is recommended to use only high-quality products for depilation.
In addition, it is important to pay more attention to the skin before depilation: before hair removal, it is advisable to scrub, which will remove dead epithelial cells. In this case, sugaring or shaving will be of better quality. After the depilation procedure, you should not neglect the use of a special sedative.
Physiological conditions
5.1. Pregnancy
Slight itching during pregnancy may occur due to changes in hormonal levels, leading to a decrease in the sensitivity threshold. However, the most common causes of its occurrence are thrush (candidiasis) and bacterial vaginosis. It usually itches the vagina and vulva area.
5.2. During your period
Discharge during menstruation is sometimes accompanied by moderate itching in the vagina and its vestibule. This is due to their irritating effect, especially when sanitary pads and tampons are rarely changed.
In addition, during this period, existing gynecological and venereal diseases worsen, so the entire intimate area may “itch” (this depends on the nature of the lesion and the intensity of the symptoms of a particular disease). To understand the nature of the itching and rule out possible infections, consult a doctor.
5.3. Ovulation
During ovulation, the discharge becomes most abundant and watery. They increase moisture in the area of the groin folds and labia and can cause itching, and tight underwear and shaving further aggravate the situation. Normally, symptoms should be short-lived and disappear at the end of the cycle.
5.4. After intercourse
After unprotected sex, a common cause of discomfort in the vagina, vulva and inguinal folds are STIs, as well as the reaction of the mucous membranes and skin to the partner’s sperm and microtrauma (during anal sex, itching can be in the anus and perineum).
Less commonly, symptoms after intimacy occur due to allergies to sperm proteins, barrier contraceptives, including condom latex.
5.5. Climax
Vulvovaginal itching during menopause is caused by the extinction of ovarian activity and corresponding hormonal changes.
A woman develops dry mucous membranes, soreness and increased vulnerability of the mucous membranes of the genital tract.
Rubromycosis
A red itchy spot in the groin in women can cause rubromycosis. It is a fungal disease of infectious etymology, characterized by the appearance of large reddish spots in the groin area. It can affect not only the epidermis, but also vellus hair, the structure of which changes, it becomes weak and brittle.
When treating rubromycosis, it is customary to adhere to an integrated approach, which includes the use of antihistamines and antifungal medications with systemic and local effects. Therapy can take up to 3 weeks if the disease is in an advanced stage. If rubromycosis was diagnosed in the initial stages of development, then treatment will take no more than 10 days, and only the use of ointments will be required.
Diseases
6.1. Thrush (candidiasis)
The main symptoms of the disease are severe itching in the vagina, vulva area and white, crumbly, cheesy discharge with or without a slight sour odor.
Often occurs during pregnancy, decreased immunity, after antibiotics, or taking systemic glucocorticosteroids. Sometimes the process involves the inguinal folds, anus, and urethra, and additional symptoms include burning and pain.
6.2. Bacterial vulvovaginitis
Itching in the genital area, unpleasant odor and purulent, mucous discharge are characteristic signs of inflammation caused by cocci, gardnerella, E. coli and other enterobacteria. A woman may also experience a burning sensation, pain during sexual intercourse, and discomfort.
6.3. Urethritis
With urethritis, during urination, urine provokes irritation of the mucous membrane of the urethra, resulting in pain, burning or itching. A similar situation occurs when fistulas occur connecting the vagina to the bladder or ureter.
6.4. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
This is one of the most common causes of itching in the intimate area. The symptom is characteristic of gonorrhea, donovanosis, trichomoniasis, syphilis and other similar infections. As a rule, typical discharge and other signs are observed.
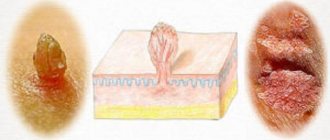
The classic symptoms of genital herpes are the formation of transparent blisters, which open after a few days, leaving weeping erosions in their place. All this is accompanied by a burning sensation and severe pain.
However, there is also an atypical “itchy” form of the disease, when, against the background of slight redness of the genital organs, severe local itching and burning occurs. As a rule, with a herpetic infection, the vagina, vulva area, and perineum may itch.
6.5. Parasitoses
The pubis and skin of the labia majora can be affected by pubic lice (phthiriasis) or scabies mites (scabies). Another common cause of itching in the genital area is helminthic infestations, in particular pinworms (enterobiasis).
6.6. Neuroses and psychogenic diseases
Sometimes unpleasant symptoms occur due to stress or nervous shock. As a rule, in this case, during a gynecological examination, no signs of any pathology are detected (itching without discharge, changes in their color and smell).
A special category is neurosexual disorders, in which case sensations occur in any area: in the vagina, perineum, and throughout the intimate area.
6.7. Endocrine disorders
Itching in the labia area, in the vagina and its vestibule occurs with diabetes mellitus, ovarian hypofunction, and thyroid diseases.
6.8. Eczema
Unpleasant sensations with eczema are very pronounced, localized in the area of the pubis, labia, inguinal folds, perineum and spread to other areas. You can also see redness, painful cracks, merging and weeping wounds on the skin.
6.9. Fungal skin infections
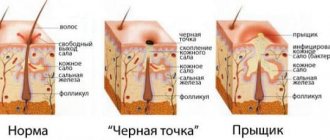
In the intimate area, dermatitis can be caused by fungi such as Candida, Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton floccosum. They are the cause of inguinal candidiasis, athlete's foot and ringworm. Their characteristic symptoms:
- 1Ringworm is an intensely itchy reddish-brown rash in the form of rings with scales and blisters that spreads to the buttocks and genital area.
- 2 Candidiasis - occurs in the area of the inguinal folds, where skin friction and damage occurs. It becomes covered with weeping cracks with a white coating and redness of the surrounding tissues. As the disease progresses, the itching becomes obsessive and unbearable.
- 3 Athlete's foot - pink spots and blisters with exudate form in the area of the perineum and inguinal folds. Severe itching and pain occurs.
Diagnostic methods
Due to the variety of causes of itching and gynecological diseases, a whole team of doctors is often involved in the examination:
- 1Gynecologist.
- 2Endocrinologist.
- 3Allergist.
- 4Dermatovenerologist.
- 5Neurologist.
- 6Therapist.
If necessary, consultations with an oncologist, hepatologist, nephrologist, hematologist, psychotherapist, infectious disease specialist and other highly specialized specialists are also scheduled. For in-depth laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, the following is prescribed:
- smear on flora and GN;
- STI tests using PCR;
- smear for oncocytology and colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood tests (general, biochemical), urine;
- stool examination for the presence of hidden blood, helminth eggs, coprogram, scraping for enterobiasis;
- study of hormonal profile and immunological status;
- allergy tests and other studies as indicated.
Drugs for treatment
First of all, it is important to eliminate any provocateurs of itching:
- Synthetic underwear, aggressive depilation.
- Scented sanitary pads.
- Replace washing powder, soap, and intimate hygiene products with hypoallergenic ones.
- Remove allergenic foods from your diet.
- Review medications taken based on possible adverse reactions.
- Change barrier contraception and so on.
Along with this, it is necessary to influence the very cause of unpleasant symptoms.
Depending on it, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- 1 Antihistamines: Desloratadine, Loratadine, Ketotifen, Fenkarol, Bikarven, Suprastin, etc.
- 2 Hormonal: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone, Advantan, Elokom, etc.
- 3 Sedatives: Phenobarbital, Amizil, Benzoclidine, Seduxen.
- 4Sorbents: activated carbon, Polysorb, Smectu.
- 5Antibiotics, antiparasitic and antifungal drugs for local use and orally (as indicated).
After making a diagnosis, the attending physician prescribes appropriate therapy.
Treatment of itching depending on the cause
| Disease | Drugs |
| Pubic lice | Paranit, Nittifor, Pedilin |
| Scabies | Benzyl benzoate, Spregal |
| Atrophic vaginitis | Ointments and suppositories with estrogen |
| STI | Antibiotics and antivirals depending on the type of infection. Both partners need to be treated. |
| Thrush | Locally - Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Butoconazole (Ginofort), Miconazole (Ginezol 7); orally - Fluconazole (Flucostat) |
| Fungal skin infection | Ointments with glucocorticoids and antifungals - Triderm, Lorinden S, Akriderm GK, Kanizon Plus, etc. Orally - suprastin, tavegil, fenistil. |
| Liver diseases with cholestasis | Cholestyramine, naltrexone. Sedatives - phenobarbital. |
| Eczema, allergic dermatitis | Locally - ointments with glucocorticosteroids - Elokom, Advantan, Akriderm, etc. Orally - desloratadine, loratadine, cetirizine, etc. |
| Neurosis | Psychotherapy and distraction medications can relieve discomfort |
| Vaginitis | Clindamycin, Terzhinan, Neo-penotran, Polygynax, etc. |
How can you treat yourself at home before consulting a doctor?
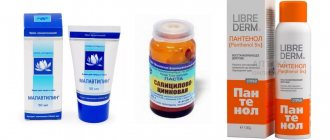
To get rid of itching while waiting for a doctor's appointment, you can use cold lotions and cool baths. Any creams and ointments that contain menthol, zinc, diphenhydramine can be applied to the skin (attention: not to the mucous membranes!!!). They have a distracting effect, somewhat improve well-being and do not interfere with the diagnosis:
- 1Tsindol, zinc ointment;
- 2Calamine, lotion;
- 3Menovazine, pharmaceutical menthol solution.
Ointments and gels with anesthesin and lidocaine can be used only in the absence of an allergic reaction to anesthetics. You should not use vaginal suppositories or douching before consulting a doctor; they make it difficult to make a diagnosis and identify an infection!
Folk remedies do not help cure the disease, so they cannot be used at home without examination by a gynecologist.
Erythrasma
It is a bacterial infection that belongs to the group of pseudomycosis. The period of relapse of erythrasma is characterized by the appearance of reddish, painless spots localized in the groin area. Quite often, the disease is accompanied by peeling of the skin on the pubis and the appearance of brown spots between the legs. The causative agent of erythrasma is present on the skin of any healthy person, and inflammation forms when the immune system is weakened. For the treatment of erythrasma, local antiseptics and exfoliants are used. If there is a large area of damage, the use of antibacterial agents is indicated.
Consequences
Itching, if left untreated or inadequately treated, can become a serious problem. It is capable of causing:
- insomnia;
- depression;
- depression;
- irritability;
- neurotic conditions;
- refusal to eat;
- decreased performance;
- social isolation.
When scratching, an infection gets into the wounds, inflammation develops, accompanied by pain, purulent discharge, the spread of rashes, and so on.
Some people with severe itching of the genitals try to fight it in a rather unique way: they use various objects that injure the skin and mucous membranes, which only aggravates the situation.