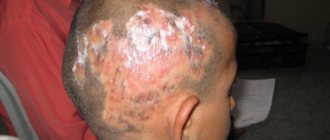
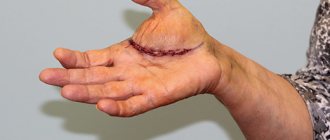
A common problem is itching and redness on the hands, which causes particular discomfort and physical inconvenience. The mechanism of its appearance is not fully understood; the reasons may be varied.
Most often - exposure to allergens, penetration of bacteria (germs) through small cuts, abrasions, injuries. In older people, dry, swollen skin is observed due to decreased function of the sebaceous glands.
Before selecting ointments or creams for treatment, it is important to establish the true causes leading to discomfort on the skin of the hands.
Why do itching and redness occur on the hands?
Many factors can cause itching and redness on the skin of the hands:
- Exposure to household chemicals , cosmetics;
- Dry indoor air with humidity less than 30%;
- Dehydration;
- Wearing tight, synthetic clothing in hot weather;
- Constant contact of hands with hot water , leading to vasodilation and increased itching;
- Abuse of strong tea , coffee, drugs, alcohol, and some medications;
- Food intoxication in case of taking products containing additives (dyes, vitamin A, E);
- Diseases of the liver , gall bladder due to the accumulation of bilirubin and bile (strong irritants of nerve endings) under the skin;
- Skin diseases - atopic dermatitis, eczema, urticaria, neurodermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, scabies;
- Hereditary factor and diabetes mellitus;
- Nervous overexcitation , frequent stress, leading to irreversible changes in the structure of the skin;
- Insect bites;
- Fungal skin infections - lichen ruber, candidiasis.
Folk remedies
If the cause of redness is cold, then you can rub them with cream, adding fir or any pine essential oil, which promotes gentle gentle heating. Don't put your hands in hot water! Otherwise, if you overheat, you should never put your hands in ice water, because in both cases this can lead to damage to blood vessels. To cool, you should use a cool bath with sea salt or mint infusion dissolved in water, and after the procedure, gently rub a soothing cream into your palms. Sometimes a bath of cooled green tea can save you from skin irritation. After drinking it, you need to wipe your hands with a dry cloth, but do not rinse the tea itself with water. A mask made from starch (preferably rice, but potato starch will do) and chamomile infusion, which you need to mix until the consistency of sour cream, and add a few drops of lavender essential oil to the resulting mass, helps well against redness, peeling and itching on the hands. This mask should be applied to your hands and left for 20 minutes.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis if you have persistent itching, flaking, or redness on the skin of your hands, you should consult a dermatologist or therapist.
Steps to carry out diagnostics are step-by-step:
- Examination of the skin;
- Taking anamnesis;
- Redirection for testing - blood, urine, feces.
- Skin scraping for subsequent histological examination;
- Colonoscopy;
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound, ECG for suspected diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine, nervous, cardiovascular systems.
Itching and redness on the hands due to an allergic reaction
Hand allergy is a process of sensitization when the human body comes into contact with allergens, which begin to produce antibodies.
Allergic reactions on the hands can be caused by:
- Consumption of allergenic foods - citrus fruits, honey, nuts, chocolate, milk;
- Use of medications leading to side effects;
- Overheating or hypothermia of the body , as well as exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- Contacts with chemicals and cosmetics;
- Excessive excitability of the nervous system and the development of a viral or infectious process in the body;
- Prolonged stay in environmentally unfavorable areas.
Local signs of allergy:
- Peeling, burning, dryness and blanching of the upper layer of the dermis;
- Non-healing wounds , cracks and bursting blisters, accompanied by itching;
- Urticaria-type burns , swelling and redness;
- Pustular rashes , itching, burning, swelling from contact with water;
- Dry cough , redness of the conjunctiva of the eyes and tearing;
- Digestive disorders in the form of vomiting and nausea;
- Sore throat , sneezing, runny nose and nasal congestion.
During the acute course of an allergy, angioedema, laryngeal stenosis and anaphylactic shock can occur.
Possible causes of allergies
When a skin rash occurs, it is important to understand whether it is due to an allergic reaction or another medical condition.
The following signs will help determine the nature of the rash:
- short time for the rash to appear after contact with the allergen. For example, an allergy to the fingers that occurs after contact with an acidic detergent.
- an increase in the size of the spots and the appearance of blisters, accompanied by severe itching.
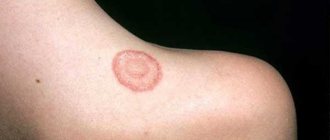
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergies on the hands in the form of red spots in adults and children can be caused by contact dermatitis - inflammation resulting from direct contact of the skin with irritants or allergens. In this disease, exposure to a certain substance causes adverse reactions in the body, resulting in the formation of a rash on the surface of the skin.
There are two types of contact dermatitis.
The first and most common is irritant contact dermatitis. This type of dermatitis develops when the skin comes into contact with acids, solvents, soaps, or other chemicals. For example, repeated immersion of hands in any of these substances may result in allergies on the hands and rashes between the fingers.
Allergic contact dermatitis (photo)
The second type is allergic contact dermatitis. In this case, the skin has increased sensitivity to certain substances, such as plants, metals, drugs or other substances. Skin contact with these allergic substances causes an immune response from the body, in which antibodies are produced and histamine is released into the blood, damaging epidermal cells. As a result, allergies may appear on the hands in the form of blisters.
Irritant contact dermatitis (photo)
Contact dermatitis can be caused by substances such as laundry detergent, detergents, latex, soap, antibiotics, nickel and other metals, poison ivy, preservatives, sunscreens, tattoo ink and black henna, etc.
Symptoms may begin 12 to 48 hours later and last two to four weeks after onset.
Dermatitis can be recognized by the following signs:
- red spots on the skin and between the fingers;
- blisters and wounds accompanied by severe itching;
- dry, flaky areas of skin;
- “burning” painful skin.
Allergic urticaria
The occurrence of urticaria can be triggered by food, plant pollen, medications, animal epidermis, insect bites, etc. It is worth noting that an allergy to cold on the hands also manifests itself in the form of urticaria.
The main symptom is itchy pinkish-red rashes on the hands, which can be distributed either singly or multiplely, merging into large spots.
Allergic urticaria (photo)
As a rule, urticaria spreads simultaneously to different parts of the body. For example, with a drug allergy, allergies may occur in the arms and legs.
Allergies in a child’s hands in the form of urticaria are a common occurrence that most often occurs as a result of a food or insect allergy (to poison and insect bites).
The inability of the digestive system of infants to digest certain foods, such as citrus fruits, sweets, nuts, etc., can provoke allergic rashes that are localized, including on the child’s cheeks, knees, elbows, feet, etc.
Allergy in the hands of a child (photo)
The second common cause is insect bites.
In some cases, the allergic reaction is local in nature: urticaria appears, accompanied by severe itching. Children often scratch the bite sites, thereby causing even more harm: the skin rash begins to ooze and becomes susceptible to infection. Therefore, parents should ensure that this does not happen and use medications to eliminate itching.
As a rule, an allergic reaction in the hands in the form of hives goes away within 24 hours.
Itching and redness on the hands due to urticaria
A dermatological disease of allergic origin is caused by the release of histamine under the skin.
Provoking reasons:
- Wearing synthetic clothing;
- High air temperature;
- Exposure to sunlight;
- Food;
- Cold;
- Diabetes;
- Immune system disorders;
- Hormonal imbalance.
Chronic urticaria on the hands can be caused by dermatitis, hepatitis B, gastritis, herpes and infectious diseases with an inflammatory course, for example, cholecystitis, tonsillitis, adnexitis.
Symptoms of urticaria on the hands:
- Red, flat, irregular rash;
- Severe itching;
- Blisters like bite marks.
Itching and redness on the hands due to contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a general concept for a group of diseases with an acute or chronic course that can occur on the skin upon contact with irritating substances that cause inflammation.
Causes of contact dermatitis:
- Irritants (chemical, medicinal);
- Burns or frostbite;
- Exposure to sunlight;
- Household chemicals (washing powders, paints, emulsions);
- Decorative cosmetics (creams, ointments).
Symptoms of acute contact dermatitis:
- Redness and swelling;
- The appearance of small nodules and bubbles with the formation of crusts;
- Necrosis of areas;
- Severe burning and itching;
- Feeling hot and sore.
Symptoms of chronic contact dermatitis:
- Compaction and thickening of the epidermis;
- Hyperkeratosis with the development of infiltration;
- Erythema in the form of violet-bluish papules;
- A kind of scab followed by the appearance of erosive ulcers.
With contact dermatitis caused by an allergic reaction, symptoms usually develop more slowly.
Diseases manifested by itching and redness of the hands
Often itching and redness on the hands are caused by dermatological diseases, which cause patients a lot of anxiety.
Eczema
Eczema is a recurrent disease of allergic origin with a course in acute, subacute, chronic stages and the development of inflammation in the upper layers of the dermis.
Causes:
- Imbalance of metabolic processes , as well as hormonal imbalance;
- Impaired function of the kidneys , thyroid gland, digestive tract;
- Frequent contacts with chemical components (dyes, varnishes, solvents);
- Fungal infection (streptococci, staphylococci).
Symptoms:
- Thickening, redness and hyperemia of certain areas of the skin;
- The appearance of inflamed lesions , small red nodules;
- Severe itching leading to sleep disturbance.
Eczema can cause severe itching for patients, especially if they start scratching the affected areas. This can lead to a secondary infection and long and painful treatment.
Scabies
A disease of the superficial parts of the skin caused by scabies mites, namely parasitizing females, which begin to move into the layers of the dermis, make passages, leaving waste products.
Provoking factors are direct contact with an infected person and his household items.
Signs of scabies:
- Severe itching , as a reaction of the body to irritants - waste products of the tick, with intensification in the evening or night hours;
- The appearance of a whitish line in the form of scratches during the daily movement of ticks;
- Peeling and thickening of the epithelium in places of scabies and larvae hatching from eggs;
- Small rash in the form of red bumps or papules with an elevation above the skin up to 2 mm in diameter;
- Pustules filled with liquid with an amount depending on the presence of embedded mites.
The peculiarity of scabies is the appearance of a rash between the fingers of the hands, on the flexor areas of the wrist joint, on the lateral areas of the fingers, and enlargement of the regional lymph nodes.
Lichen planus
Lichen planus is a chronic dermatological disease.
Causes:
- Disruption of metabolic and immune processes of the endocrine system;
- Exposure to internal and external aggressive factors leading to an inadequate reaction of tissues in the hand area;
- Exposure to medications such as tetracycline or bismuth, as well as chemical irritants;
- Frequent stress and diabetes.
Symptoms of lichen planus:
- A multimorphic crimson-red rash consisting of flat nodular papules up to 5 mm in diameter, accompanied by itching, leading to sleep disturbances and neurotic disorders;
- Dryness and tightness of the dermis with the acquisition of a waxy surface;
- Formation of plaques in the case of a group arrangement of papules merging with each other;
- Clouding of the nail plates.
Lichen planus has many forms of formation, most often appearing on the back of the hands.
Candidiasis
Infectious fungal skin lesion. The fungus is a parasite that destroys the upper layers of the dermis with its appendages.
Causes:
- Low immune status;
- Antibiotic abuse;
- Contacts with an infected person;
- Visiting public places.
Symptoms:
- Severe itching and burning;
- Pinpoint rash between fingers;
- Peeling and redness of areas of the dermis;
- Thickening of the nail plates with a yellow tint.
Skin fungus most often affects the skin folds on the hands.
The danger of pathology is an increased risk of secondary infection. The areas begin to fester, causing physical discomfort to the infected person.
Other diseases
Causes of itching and redness on the hands:
- Neurodermatitis - provoking factors are stress, pathology of the nervous system, aggressive effects of detergents, sunlight, cold and skin aging;
- Diabetes mellitus against the background of high blood sugar levels causes scratching, itching and weeping, poorly healing vesicles to appear on the skin;
- Streptococcal folliculitis , caused by staphylococci with the formation of plaques, scales, papules and rashes on the skin.
Redness between fingers
This type of skin irritation is considered separately from redness of the skin of the hands, as such, because it is caused by other reasons, mainly fungus, and has a different nature of manifestations. Redness of the skin between the fingers is accompanied by the formation of blisters, which burst and cause bleeding, after which inflammation occurs and the skin begins to peel off severely. Only a doctor can prescribe treatment for this fungal disease. The second most common cause of severe itching and redness of the skin of the hands between the fingers is dry eczema, during which peeling is observed, turning into cracks and changes in skin pigmentation. And the third reason is scabies mites, but in this case not only the skin between the fingers turns red, but also the sides of the palms and wrists. Scabies is accompanied by severe itching, leading to scratching. In any case, redness between the fingers should always be examined by a doctor.
Itching and redness on the hands of children
Reasons that cause unpleasant reactions on the skin of the hands in children:
- Hives;
- Neurodermatitis;
- Chapping of the skin;
- Lack of personal hygiene;
- Atopic dermatitis;
- Measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever and rubella;
- Allergies to food and household chemicals;
- Miliaria, leading to severe itching and scratching of the skin until it bleeds;
- Vitamin deficiency, especially lack of vitamin B in the child’s body;
- Endocrine and nervous system disorders;
- Long contacts of the child with the ground.
In addition to severe itching, the following symptoms may occur in childhood:
- Lethargy and apathy;
- Temperature increase;
- Decreased appetite;
- Skin cracking;
- Swelling of the fingers;
- Swelling of the upper lymph nodes.
Signs of itching and redness on the hands of children are specific and depend on the irritant. Children usually immediately begin to scratch the rashes, thereby provoking an increase in unpleasant symptoms.
Itching and redness on the hands of pregnant women
During pregnancy, the female body experiences great changes. Redness and itching on the hands are provoked by hormones, namely high levels of estrogen, leading to the development of telangiectasia.
However, there are other reasons:
- Excessive sweating of hands;
- Stress, anxiety and anxiety;
- Allergenic foods;
- Constant contact with household chemicals and water;
- Skin dermatitis, fungal infection;
- Increased bilirubin in the blood.
Women can get an allergic reaction to external irritants if their skin is excessively dry.
It is important to identify and eliminate true triggers or allergens at an early stage. Otherwise, the constant nervousness and irritation of the expectant mother can negatively affect the health of the newborn.
How to get rid of redness and itching on the skin of your hands?
Once the reason why your hands itch has been established, you need to move directly to methods of combating it. For therapy to be effective and give the expected results, follow these recommendations.
- Regularly see an allergist, dermatologist and endocrinologist, especially if you have unfavorable heredity.
- Take good care of your hand hygiene.
- Choose hand care creams and soaps that contain a minimum of dyes and scent enhancers and a maximum of natural ingredients.
- If the skin on your hands itches and cracks due to allergies, take antihistamines: Eden, Loratadine, Citrine, Tavegil (a potent drug, so consult your doctor first), Catotifen, Diazolin, Fenkarol, L-cet and others. However, be extremely careful and careful: many of the above tablets can cause drowsiness and loss of coordination. To prevent this from happening, you should take medications only in the evening, before going to bed. Only a doctor can prescribe daily antihistamine medications.
- Itchy hands can be relieved with menthol or peppermint based creams.
- To relieve irritation, which causes the skin on your hands to itch and cracks to appear, you can prepare a decoction of chamomile or chamomile. These medicinal plants have an anti-inflammatory and soothing effect, due to which redness and itching quickly disappear. However, you should not expect a long-term effect from this procedure - after about 1-2 hours, the unpleasant sensations will appear again.
If itchy hands were caused by scabies or any other dermatological disease, you should consult a doctor. Treatment is often carried out using sulfur ointments, antihistamines, and antifungal creams. The main thing in this situation is making the correct diagnosis. Only on its basis will a dermatologist or allergist be able to select treatment methods that will not only help get rid of the disease, but also carry out its effective prevention.
Drug treatment for itching and redness on the hands
Let's consider what drugs can be used to treat itching and redness on the hands due to a particular disease.
Itching and redness due to temperature changes
The basis for the treatment of cold or sun allergies is antihistamines with antifungal properties.
Most popular:
- Sinaflan is a glucocorticosteroid to relieve itching, allergies, and inflammatory reactions. Contraindications: precancerous conditions, psoriasis, acne. Use for children from 2 years of age, not for long. Average cost 90 rubles ;
- Advantan is a non-halogenated corticosteroid medication. Indicated for atopic dermatitis and eczema. Rub into skin 2-3 times a day. Can be used by infants from 1 month. The course of treatment is no more than 4 weeks. Average cost 350 rubles ;
- Hyoxysone - to provide an anti-inflammatory effect. Prescribed for carbuncles, furunculosis, frostbite. Apply by applying a thin layer to the affected areas 1-3 times a day, applying sterile gauze on top, securing with a bandage. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. If the lesions are extensive, it is not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age. The average cost is 50 rubles .
Sinaflan Advantan Hyoxysone
Itching and redness from insect bites
Most prescribed drugs:
- Dimexide is an analgesic anti-inflammatory medication. Apply applications to the affected areas, moistening a napkin with the solution and applying for 30 minutes. The course of treatment is 10-15 days. Apply ointment 1-3 times. Use for children from 12 years of age. Average cost 60 rubles ;.
- Tavegil is an antiallergic, antipruritic drug, a histamine receptor blocker. Release form: tablets. Do not use during pregnancy, lactation and bronchial asthma. For children under 1 year of age, the acceptable form of use is syrup, solution. Tablets only from 6 years of age. The average cost is 180 rubles .
Dimexide Tavegil
Itching and redness during an allergic reaction
The basis of treatment is antihistamines with antipruritic, antifungal, antibacterial effects, to relieve hyperemia, itching, burning and redness.
The most effective drugs:
- Psilo-balm is a local anesthetic with a cooling effect. Use in a dose of 2-3 g up to 3 times a day. Children - from 2 years old, pregnant women - with the permission of a specialist. Average cost 300 rubles ;
- Levomekol - with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effects. Can be used during pregnancy and for children over 2 years old. Apply in a thin layer. Average cost 110 rubles ;
- Skin cap - with antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects. Process up to 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks. Can be used by children from 1 year of age. Average cost 780 rubles ;
- Elidel - with anti-inflammatory effect. Treat skin areas up to 2 times a day until symptoms are completely eliminated. Can be used from 3 months. The average cost is 960 rubles .
Psilo-balm Levomekol Skin-cap Elidel
Itching and redness with eczema
When treating eczema on the hands, antihistamines with antipruritic and sensitizing effects are used:
- Hydrocortisone ointment - apply twice a day for 14-20 days. Apply dressings for hypertrophic ulcers every 24-48 hours. Can be used in children from 1 year of age, but without using occlusive dressings. The duration of treatment is no more than 2 weeks. Average cost 130 rubles ;
- Elokom - with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory effect. Treat the affected areas once a day, for children only from 1 year. In severe cases of the disease - from 6 months under the guidance of the attending physician. Average cost 160 rubles ;
- Beloderm - with antiproliferative and vasoconstrictive effects. Treat twice a day, for children from 6 months. The course of treatment is 4 weeks. Average cost 130 rubles ;
- Flucinar is an anti-exudative drug with treatment of skin areas twice a day, applying no more than 2 g. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. Contraindications: pregnancy up to 12 weeks and children under 1 year of age. Average cost 260 rubles ;
- Triderm - with antifungal and vasoconstrictor effect. Treat skin areas twice a day (morning, evening). During pregnancy, use with the permission of a doctor, for children from 2 years of age. The average cost is 450 rubles .
Itching and redness with scabies
When your hands are affected by scabies mites, the following medications help:
- Sulfur ointment - before use, wash and dry the affected areas. Apply in the evening before bed. The course of treatment is 5 days. Use for children over 3 years old. Average cost 30 rubles ;
- Benzyl benzoate - apply in the evening during the period of mite activation on dry skin of the hands, evenly distributing the composition and rubbing into the affected areas. The course of treatment is 3 days. Use for children from 1 year of age. Average cost 230 rubles ;
- Spregal is an aerosol for suppressing subcutaneous parasites. Spray onto the affected dermis every 12 hours, keeping the can at a distance of 30 cm from the body. Use for children from 6 years of age. The average cost is 940 rubles .
Sulfur ointment Benzyl benzoate Spregal
Itching and redness with lichen ruber
Effective ointments for treating rashes:
- Fenistil - with an antiserotonin effect. Apply the composition 3 times a day. Use for children from 1 month. Average cost 400 rubles ;
- Salicylic ointment - with an antiseptic, keratolytic effect. Apply a thin layer and place a sterile bandage on top. Dose 4-5 ml per day. Suitable for children from 2 years old. Average cost 30 rubles ;
- Zinc ointment - with a drying, astringent effect. Apply a thin layer to previously cleansed skin areas up to 3 times a day. Can be used for infants from 1 month. The average cost is 40 rubles .
Fenistil Salicylic ointment Zinc ointment
Itching and redness due to skin fungus and candidiasis
To eliminate fungal infections on the hands, systemic remedies are prescribed:
- Fluconazole - to suppress microbial stearin synthesis. Children use from 1 month. Apply once a day. The course of treatment is from 2 weeks to 0.6 months. Average cost 60 rubles ;
- Terbinafine is an antifungal drug in tablets to suppress infections on the skin and nail beds. Use for children over 3 years of age and weighing at least 20 kg. Average cost 140 rubles ;
- Ketoconazole - take 1 tablet for up to 7 days. The drug is contraindicated for children under 18 years of age. It is acceptable to take it with the permission of a specialist if you weigh over 30 kg. Average cost 130 rubles ;
- Nystatin - apply to fungal-infected skin areas, rubbing up to 3 times a day. Single dosage – a strip of ointment up to 0.5 cm in length. Duration of use is 3 weeks, including 10 days of treatment after the symptoms subside. Use for children from 2 years of age. The average cost is 130 rubles .
Fluconazole Terbinafine Ketoconazole Nystatin The following
are used to treat candidiasis:
- Lotrimin - perfectly destroys all types of fungal infections and some forms of bacteria. Treat the skin of the hands together with the nail plates up to 3 times a day, rubbing in with massaging movements. The duration of therapy is 2-3 weeks, depending on the severity of candidiasis. After symptoms pass, continue therapy for up to 2 weeks. Before handling, wash your hands with soap and warm water. Use for children from 1 year of age. Average cost 170 rubles ;
- Canesten - apply and rub a thin layer into the affected areas of the dermis, especially between the fingers. A single dose of 4-5 mm of ointment column in length. Duration of treatment is 4 weeks. Use for another 14 weeks for preventive purposes. For children only in consultation with the pediatrician. Average cost 320 rubles ;.
- Clotrimazole - Wash hands with soap and dry before use. Apply a thin layer, lightly rubbing 2-3 times a day, covering nearby healthy areas of skin. A single dose for treating the palm is 5 mm strips of ointment. Pregnant women can use the drug only from the 2nd trimester, children - from 6 months. The average cost is 70 rubles .
Lotrimin Canesten Clotrimazole
During treatment it is important:
- Maintain personal hygiene;
- Do not use rough pumice stones or washcloths;
- Gently wash the folds with liquid baby soap to relieve itching;
- Do not wet your hands during treatment;
- For dry skin, use natural formulations with propolis, calendula and chamomile.
Treatment of itching and redness on the hands during pregnancy
For pregnant women, many drugs are prohibited. The main goal of treatment is not to harm the baby’s health and not lead to negative reactions within the body.
Drugs approved for use during pregnancy:
- Fenistil - average cost 400 rubles ;
- Radevit - average cost 420 rubles ;
- La-kri - average cost 360 rubles ;
- Uniderm - average cost 250 rubles ;
- Bepanten - average cost 500 rubles ;
- Pantestin Darnitsa - average cost 260 rubles .
Treatment of itching and redness on the hands of children
For excessive skin sensitivity, the following will help:
- Special emollient creams with a softening, moisturizing effect, for example, Mustela cream, the average cost of which is 600 rubles ;
- Non-hormonal ointment Gistan - average cost 170 rubles .
Mustela Gistan
You should only consult a doctor to select medications for the treatment of unpleasant symptoms in children.
The best baby creams containing panthenol, herbal extracts and vegetable oils.
The safest ointments and creams:
- Panthenol can be used for children with various dermatitis and diaper rash from birth. Average cost 40 rubles ;
- Skin-cap - use for children from 1 year of age with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis and weeping eczema. Average cost 780 rubles ;
- Protopic - can be used by children from 2 years old. It is not advisable to use 0.1% cream before the age of 16. Average cost 900 rubles ;
- Fenistil gel - to relieve itching and irritation on the hands. Use for infants from 1 month. The average cost is 400 rubles .
Panthenol Skin-cap Protopic Fenistil
If the disease is severe, children are prescribed hormonal compounds:
- Advantan - for treating skin with atopic or allergic dermatitis, true and microbial eczema on the hands of children from 4 months. Average cost 680 rubles ;
- Elokom - for use in children from 2 years of age. The average cost is 430 rubles .
Advantan Elokom
Hormonal formulations based on hydrocortisone are prohibited for children under 18 years of age - Loracort, Diprospan, Celestoderm Triderm, Sinalar, Diprosalik.
Treatment of redness of the skin of the hands
You can eliminate redness of the skin of the hands and feet with the help of special medicinal ointments and creams containing vitamins, especially C and group B. These products relieve inflammation and peeling and make the skin more resistant to internal and external adverse effects, while simultaneously softening and nourishing it. In some cases, medications with antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed. Of particular benefit are medicinal cosmetics with extracts from medicinal herbs and cereals, which, in particular, SpaBelle uses in its compositions, because they effectively fight inflammatory processes and increase local skin immunity. Products with plant extracts can disinfect and soothe the skin, which is often enough to relieve redness. In addition to creams, you can use moisturizing gel socks and gloves, which are equipped with a unique impregnation and, due to natural heating from movement, have a healing effect on the skin; moreover, they can be used as a preventive measure and for basic hand care. You should start treating redness with medicinal herbal cosmetics, which is often sufficient, and move on to hormonal ointments only if there are no positive results.
Folk ways to get rid of itching and redness on the hands
If you are concerned about itching and redness on your hands, then it is useful to use traditional methods of treatment.
Effective recipes:
- For itching caused by stress, lemon balm tea helps - to prepare the tea, you will need to take a tablespoon of the herb and brew it in one glass of boiling water. The duration of treatment is one month;
- Homemade ointment with medicinal herbs will help against allergies on your hands - to prepare the herbal remedy, take 15 g of burdock root, celandine leaves, mint, marigold flowers, mix the ingredients, and combine the herbal raw materials with sunflower oil in a bowl. The liquid should cover the herbs by 1 cm. Simmer the homemade ointment in a water bath for forty minutes, cool and filter the product, pour into a glass container, and store at room temperature. Apply daily to areas with severe itching and flaking of the skin;
- Apple cider vinegar helps well against lichen planus - it is recommended to apply undiluted apple cider vinegar to the area affected by lichen planus for 10 minutes 4-6 times a day. Instead of vinegar, you can use viburnum or cranberry juice;
- For psoriasis, a herbal, antiseptic collection in the form of a bath helps - combine chamomile, string, lavender, St. John's wort, celandine, nettle and yarrow in equal quantities. Dilute with a small amount of water and heat in a water bath. Keep your hands in the composition for 20-30 minutes 2 times a day;
- Ointments based on celandine help against scabies - for the first recipe, mix celandine juice (1 tbsp) and plain petroleum jelly (4 tbsp). Apply the resulting product to damaged areas of the skin daily. For the second recipe, celandine is also used in dry form. 1 tbsp. l. of this powder is combined with 2-3 tbsp. l. pure cream. The mixture should be tightly closed and left overnight in the refrigerator to infuse. The next morning the ointment is ready for use;
- A herbal mixture helps against insect bites - peppermint + St. John's wort + oak bark. 2 tbsp. Pour boiling water (1 cup) over the herbs and leave for 2 hours. Apply gauze pieces soaked in infusion to the bites daily until the unpleasant symptoms are completely eliminated;
- Baths with the addition of sea salt or a decoction of pine needles will help against itching due to injury and mechanical damage to the skin of the hands
- A recipe with cabbage helps against eczema - boil 2-3 cabbage leaves in milk for up to 45 minutes, apply as a lotion to the affected areas;
- Soda and salt help against fungus - 2 tbsp each. dilute in water (2 l), treat the skin of the hands;
- For itching and redness from cold and temperature changes, a recipe with oils helps - cocoa butter (1 tsp), peach seed oil (0.5 tsp), add water, heat in a water bath to 40 degrees, cool. Wrap your hands by cutting out a piece of fabric from gauze, soaking it in an oil solution;
- Honey compresses will help against chapped hands - mix honey (100 g) + almond seed oil (100 g), heat in a water bath until a homogeneous paste forms. Add salicylic acid (1 g). Wipe areas of the dermis with a cotton pad, then wrap with polyethylene or a terry towel. Leave for up to 20 minutes, then rinse and wipe with lemon juice.
How to quickly get rid of redness and itching of hands?
Redness of the hands is a problem that modern people are increasingly faced with recently. Itching and redness of the hands can be caused by a number of different reasons.
Folk skin care products will help relieve redness of the skin of the hands, the causes of which can be different. In some cases, proper treatment can eliminate redness permanently.
Often people have to deal with such an unpleasant condition as redness of their hands. The causes of redness and dryness can be very different. Dermatologists often associate sudden redness of the hand and itching with allergic reactions.
Allergies can manifest themselves to certain chemicals, chlorinated water, and cold. In addition, itching and redness of the hands can be associated with overheating in the sun and the occurrence of thermal burns.
If a person has certain suspicions that the skin of the hands is reacting to some environmental factor, it is necessary to immediately exclude contact with the irritant. For example, if you have a cold allergy, you should go outside in the winter only wearing gloves. If the redness of your hands is associated with eating certain foods, you need to give up such foods and switch to a healthier and more balanced diet. In any case, it would not be a bad idea to contact a specialist for help. The doctor will definitely determine the exact cause of redness and irritation on the skin of the hands and prescribe treatment. As a rule, specialists prescribe special ointments for allergies and skin redness. In particularly severe cases, the doctor prescribes hormonal medicinal ointments for allergies and itching to the patient. If the situation is not so serious, you can cope with the redness of your hands with the help of traditional medicine and proper skin care. If you perform all the procedures regularly, you can cure the redness of your hands almost completely.
It happens that after complex treatment, the patient forever forgets what excessive sensitivity of the skin of the hands is. First you need to decide on basic care. As a rule, hands turn red from excessive dry skin. If you do not care for it correctly, it will experience some discomfort, which can also manifest itself in the form of redness. Not all creams are suitable for sensitive hand skin. Many women make a big mistake when they do not take care of their hands for a long time because after using the cream, severe itching begins on their hands. In this case, you just need to choose a hypoallergenic fatty cream without artificial flavors and dyes. You can use creams and ointments for atopic dermatitis or use products that contain D-panthenol. Bepanten ointment and cream are extremely popular. These products are not capable of irritating even very sensitive skin.
In addition to lubricating your hands several times a day with a suitable type of cream, you should periodically apply masks to the skin to help fight redness. There can be a lot of options for nutritional compositions. One way to soften the skin of your hands and eliminate redness is a raw potato mask. To prepare it, you need to peel the potatoes, grate them on a coarse grater, add a little olive oil to it and apply on your hands for 15-20 minutes. In this case, it is better to use someone’s help, since applying the nutritional composition yourself is very inconvenient. To prevent the mask from dripping from your hands, you can add a little flour to the mixture of potatoes and butter. The mask will work much faster if you wrap your hands with a towel or some warm thing during the procedure. Olive oil in this case plays the role of an intense nutrient. It helps saturate the skin with vitamins, antioxidants and essential fatty acids. In addition, it does not cause allergies and is very useful for those who have certain problems with dry hands.
An excellent remedy for redness is a mask made from boiled potatoes. To prepare it, you need to boil the potatoes directly in their skins, peel them, and then mash them with a fork, after adding a little milk and vegetable oil to the container. The resulting mixture should be applied to your hands for 15-20 minutes, then washed with boiled water and lubricated with cream. When redness occurs on the skin, it is very important not only to lubricate it with cream and apply masks, but also to wash your hands properly. You should be very careful with the soap you use. It should not cause allergies or contain harmful components. If there is redness, it is better to avoid aggressive detergents altogether. Dermatologists recommend filtering water to remove chlorine impurities using modern filters, and then boiling it. You can wash your hands with boiled and cooled water.
If your skin is very irritated, you can try wiping it with an infusion of parsley leaves. To prepare it, you need to grind the plant material, pour it with hot water, and then leave it for several hours. The resulting infusion should be strained and washed with it, or simply wiped over reddened skin. A mask with cottage cheese helps a lot against itching and peeling. To prepare it, you need to take cottage cheese, place it in some container, add olive oil, mix and apply to reddened hands for 20 minutes. This procedure is suitable for owners of all skin types.
If your hands are very dry and peeling and cracking often appear on them, you can try bathing with heated olive oil 1-2 times a week. This procedure is quite simple. You need to heat the olive oil a little in a water bath, and then immerse your hands in it for 15 minutes. There is no need to wash your hands at the end of the procedure. It is enough to simply remove any remaining oil from their surface. As a last resort, you can simply wipe the skin with a piece of cloth. To increase the effectiveness of the mask, you can add additional components to olive oil. These could be essential oils or vitamins. Redness and dryness of the skin are often associated with a lack of vitamins A and E. You can purchase these vitamins separately at the pharmacy, or you can buy the very effective drug “Aevit”. This product can not only be added to the cream, but also taken capsules daily, while observing the restrictions associated with the duration of the course. When taking vitamins, it is important not to overdo it, since their excess is just as harmful to the skin as a deficiency. If there is an excess intake of vitamins into the body, the skin of the hands may begin to redden and peel even more.
If the skin on your hands is not dry, you can try to get rid of redness with a clay mask. White and pink clay are perfect for these purposes. The powder should be diluted with warm boiled water, then apply the composition to your hands. Attention should be paid to those areas where redness is most noticeable. In some cases, it is allowed to add a small amount of olive, peach, lavender oil or vitamins to the nutritional composition. The consistency of the clay mask should be such that it is convenient to apply to the skin.
Some dermatologists advise getting rid of redness on your hands with carrot juice, honey and various masks. Honey itself is a strong allergen, so it cannot be used in all cases. When dealing with redness and flaking, it is very important to take care of your skin regularly and comprehensively. If you apply masks to your hands from time to time, this will not lead to the desired result, but will only cause temporary relief. The skin of your hands should be lubricated every time after contact with water. It is important to exclude its contact with aggressive detergents. All housework should be done with gloves. In this case, it is better to use higher quality models, the inside of which consists of materials of natural origin. In the absence of such skin protection means, you can use thin rag gloves and put medical gloves on top of them. It may be slightly uncomfortable, but your hands will not be irritated from contact with latex.
Currently, many people have to deal with such an unpleasant condition as redness of the hands. The causes of this condition may vary. You can relieve redness using folk recipes.
Preventing itching and redness on the hands
To prevent itching and redness on your hands, you should follow these tips:
- Wear rubber gloves when in contact with water , soap, powders, detergents and disinfectants;
- patients are prone to food allergies,
- When going out into the cold, wear gloves and treat the skin of your hands with a rich cream;
- Carry out wet cleaning in the room more often , ventilate, wipe off dust.
Causes of redness of the skin of the hands
Many factors can cause redness or red spots on the skin of the hands. They are not always harmless, so it is better to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis, especially if the change in skin color is accompanied by itching and swelling. And if it is definitely established that this is not an infectious disease or allergy, then the causes of irritation of the epidermis may be as follows:
- exposure to cold temperatures is the most common cause. This happens, for example, when going outside in the cold without gloves, or prolonged contact with cold water. In this case, the smallest vessels are damaged and the skin turns red.
- high temperature or, in other words, overheating. Here the vessels, on the contrary, expand, blood rushes to the surface of the skin and, accordingly, it turns red. Overheating can occur during prolonged exposure to the sun, wearing rubber gloves for a long time (which do not allow not only moisture, but also air to reach the skin of the hands), prolonged work in hot water during housework, etc.
- poor diet - surprisingly, red skin on the hands can occur as a result of an excess of flour, fatty, sweet, smoked and fried foods, as well as coffee and tea in the diet. Since the skin is the largest excretory organ, it reflects the general condition of the body and slagging can appear in this form.
- nervous excitability - in this case, stress, depression, excessive emotionality can cause the appearance of so-called “nervous” spots on the hands, which are quite difficult to get rid of. Although in some cases, to get rid of such redness, it is enough to take a few drops of valerian or desert.
- heredity - if thin vessels are present in the family, then this will ultimately cause redness of the skin.
It may happen that the cause of redness on the hands is not a specific factor, but a complex of factors, so you need to treat the problem extremely carefully and try to exclude any possible causes one by one in order to determine the “root of evil.” In some cases, redness of the skin on the hands may even indicate diseases of the internal organs.