There are a huge number of types of moles. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification there are several hundred of them. How can an ordinary person who has nothing to do with medicine figure out how dangerous his mole is? At least roughly? There are several signs that we will talk about today.
I would like to point out right away that this article is not intended to help you diagnose yourself. Its main purpose is to reduce any tension you may have that has arisen after independently studying information about melanoma on the Internet.
What is a mole
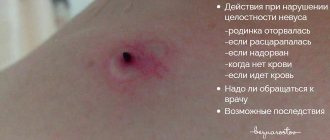
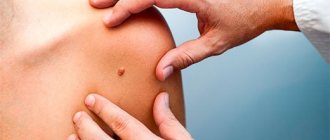
If a mole has changed color, is inflamed or hurts, you should immediately consult a doctor
In medical terminology, moles are called nevi. They may appear as small specks, small formations slightly raised above the surface of the skin, or large pigmented areas. It doesn't hurt when pressed.
Moles on the back of men and women can grow in large numbers. They consist of special melanocyte cells. These cells in the body are responsible for producing the pigment melanin, which turns the skin different shades of brown. Under the influence of external factors or internal causes, excess pigment is formed in certain places. This is how moles appear.
Nevi are rare in newborns. They are formed gradually throughout life. About 90% of them occur before the age of 30. Then moles appear less and less often. Some remain unchanged throughout their lives, others can change shape and color. In a child, they can grow as he grows up. In some situations, they become a threat not only to human health, but also to human life.
Cause for concern
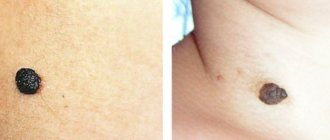
Harmless moles photo
It is necessary to pay attention to the manifestations of moles.
You should worry when the following changes appear:
- the color changes - dangerous moles become light, matching the skin tone or turn black, and coal-colored nodules may form along the edges;
- smooth moles change their texture due to the appearance of a pattern or its complete disappearance, if it was there initially. In this case, peeling of the tumor body occurs;
- the edges blur and nodules or crusts appear on the surface of the moles;
- dimensions change towards increasing diameter;
- the body of the tumor thickens;
- burning, itching, tingling occurs in the area of formation, hair falls out if there was any there.
Types of moles
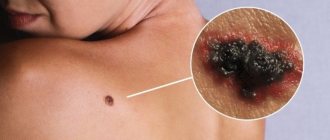
Moles that pose a threat have uneven, blurry edges and uneven coloring
Nevi differ in size and color, shape and structure, as well as the nature of formation. There are very small ones, no larger than the head of a pin, or very large ones, occupying a large area of the skin.
Vascular moles, or angiomatous, are overgrown cells on the inner surface of the vessel wall. Most often appear in infancy. They resemble a spilled red wine stain and do not grow as the child grows older.
Pigment spots form in children after 5 years of age. These are somewhat compacted spots of different colors and shapes, the structure of normal skin.
Moles differ in the following characteristics:
- place of formation - on the surface of the skin, in the boundary layer or in depth;
- may be flat or convex, have a stalk, be located under the skin or protrude above the surface;
- there may be round, hemispherical or shapeless spots of large size;
- by origin - congenital and acquired;
- Depending on the mechanism of development, there are safe ones and those with a potential threat to degeneration.
Another type of formation on the body is warts. Sometimes they are very similar to moles, but are viral in nature. More often they protrude high above the skin, have a rough surface, and can spread throughout the body. They cannot be torn off. Warts tend to become inflamed and have a negative effect on internal processes in the body.
Briefly about the main thing:
You should not try to make a diagnosis yourself; this should still be done by an oncologist. On the other hand, it’s also not worth making a mountain out of nothing out of the blue.
If your mole does not have a single “bad” sign, but has several good ones, you should still see the oncologist. Calmly, without haste and fuss, as time permits.
The main point of this article is not for you to be able to understand for yourself whether a mole is malignant or not. My goal is to help you not go crazy because of the horror stories you have previously read on the Internet.
If doubts still overcome you, you can ask me any question in the format of an online consultation.
Other articles:
- Find out your chance of getting melanoma!
- Can melanoma appear after mole removal?
- Laser removal of moles: is histology possible?
- The safest method for removing moles
Useful article? Repost on your social network!
Reasons for appearance
Sunburn can cause new moles or skin diseases to appear.
The appearance of moles in adults and children occurs spontaneously or is observed constantly in response to any irritant. Childhood is characterized by a wave-like growth of nevi in different periods. In girls and women, this is due to hormonal changes in the body - menopause, pregnancy, childbirth, menopause.
Predisposing factors to the appearance of new nevi:
- excessive amount of ultraviolet radiation;
- injuries, skin damage;
- influence of radiation;
- nutritional disorder – fast food, GMOs;
- bad habits;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- genetic predisposition.
Overgrowth can be triggered by frostbite or burns, as well as the effect of toxic substances and low-quality cosmetics on the skin.
The appearance of many red dots is associated with a pigmentation disorder. More often this is caused by pathology of the endocrine or hepatic system. When metabolic processes in the body are restored, the spots may disappear.
Removal
Getting rid of a mole on your own is very dangerous! The decision to remove it is made only by a specialist.
This is influenced by many factors:
- Formation in places of close contact with clothing.
- The mark can be easily damaged.
- The patient feels burning and itching.
- There is pain on palpation.
- Changes shape, size, contours, shade.
- The mole increases sharply.
- Bleeding and inflammation are diagnosed.
Now you know which skin formations should not cause concern. As well as alarming signs of incipient melanoma, if self-diagnosed, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. Do not forget to check the condition of moles on your body and on your child from time to time in order to avoid serious pathology.
Classification of nevi
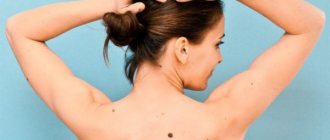
Safe moles are symmetrical, practically do not grow, have hairs
A birthmark or flat nevus is a pigmented area of skin that has borders. Its size is up to a centimeter, color from beige to almost black. It may consist of several brown formations that form in the upper layer of the epidermis.
A black mole on the back that protrudes above the skin can be smooth or bumpy. It can be damaged by clothing, swell, and swell. If you are careless, it can be torn off, causing bleeding. A raised mole on the back causes a lot of inconvenience.
A blue nevus rises above the skin. It looks like a smooth hemisphere, up to 2 cm in size. Shades vary from blue to dark blue.
A giant nevus may appear gray. But more often it is a brick, brown or black stain.
Hanging moles are small and flesh-colored. They can be located on any part of the body. Such a mole can be easily damaged, torn off by tight clothing, jewelry, during washing or massage. At the same time, they can bleed, and there is a risk of developing an inflammatory process.
Safe moles, which are least susceptible to degeneration, have the following signs:
- formations in the form of a speck;
- flesh color and soft consistency;
- the pattern of the nevus and adjacent tissues does not change;
- size no more than 5 mm;
- clear symmetry of the mole;
- hairs that grow on the surface of the nevus.
Hemangioma is a vascular tumor that many consider a mole
Melanocytic or flat moles are the safest and are the most common on the human body. They practically don't grow. Over the course of a lifetime, such a mole can increase by 1–2 mm.
Hemangioma is considered by many to be a mole. This benign tumor appears as a result of changes in blood vessels. It is formed in the fetus in the womb. They appear during the first week of life. By the age of two they change color, become faded, and eventually disappear completely.
Moles on a stalk are considered not dangerous and do not degenerate into cancer, since malignant cells grow randomly and cannot form a stalk.
The main differences between dangerous moles and safe ones
| Sign | Safe | Dangerous |
| Size | Small, up to 6 mm in diameter | More than 6 mm in diameter |
| Color | Uniform over the entire area | Uneven, with dark and light inclusions |
| Structure | Homogeneous, practically indistinguishable from skin | Heterogeneous, often dense |
| Symmetry | When dividing the formation into 4 parts, each of them repeats the other | Any imaginary halving results in asymmetrical parts |
| Surface | Matte | Glossy |
| Hair | Eat | No |
| Location on the body | Localization in the upper torso and head | Legs, areas of skin folds or close contact with clothing |
Note! The most dangerous moles are those that were suspicious and continue to change.
How to recognize dangerous nevi
Melanoma develops from a mole and gradually penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin.
The main cause of discomfort and pain in the area of the mole is its traumatization, which can subsequently lead to malignancy. In a short period of time, it can degenerate into melanoma. This is the most dangerous malignant tumor, prone to relapse and metastasis to the muscles. If a mole on your back itches a lot, itches, changes color and shape, and blood appears from it, this is an alarming signal. You should remember the main signs of the onset of the cancer process, which you should definitely pay attention to:
- color change, darkening or appearance of different shades;
- expansion of the spot, blurring of boundaries;
- increase by 2 mm per year;
- asymmetry, uneven growth;
- roughening of the skin, appearance of cracks;
- burning, itching, pain;
- discharge of colorless liquid, ichor, bleeding;
- becomes covered with crusts, tubercles, and ulcerations.
A white halo around a mole may mean that it is degenerating into a malignant form. At the same time, this may be a sign of depigmentation, which is not dangerous. In this case, you should definitely see a specialist.
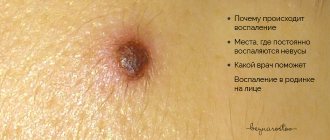
What is the danger of a mole?
Unfortunately, none of us is immune from the growth of a harmless nevus into malignant melanoma. This is a fairly serious pathology, which in the absence of timely treatment can lead to death.
So why are nevi on the skin dangerous? There are several points here:
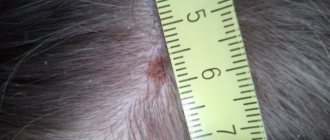
- The formation can develop into an atypical (precancerous form) at any time. Therefore, for example, it is important to know what dangerous moles on the head look like (we attach a photo to the article).
- Grows to large sizes.
- It turns into melanoma - a malignant tumor.
- It is very difficult to diagnose by appearance. Even if the nevus has only slightly changed visually, it can already widely spread metastases, which are spread by the lymph and bloodstream throughout the body.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of moles is carried out using a dermatoscope
If the formation begins to itch, swell or swell, or change color, you should immediately consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you treat a mole yourself at home, much less get rid of it. Until a diagnosis has been established, you should not sunbathe.
A dermatologist or oncologist examines the patient, determines the type of nevus, and treats the patient. Melanoform nevus has an ICD code of 10 D22. At the same time, the pathology of a single part of the body has its own class. To determine the species, a non-contact dermatoscopy method is used. The price for checking moles starts from 800 rubles, depending on the qualifications of the doctor and equipment.
For early diagnosis of transformation of moles and detection of cancer, computer epiluminescent dermatoscopy (CED) is used. A special camera examines the nevus and displays the image on the screen.
Patients who have many moles on the back and are at risk undergo automatic skin mapping. This allows you to record the location of the spots, their condition and boundaries. At the next inspection, an analysis of the changes that have occurred is carried out.
How to identify a malignant mole? Causes of rebirth
The presence of moles on the body will not surprise anyone. These skin elements, formed from melanocytes, can be very small and large, flat and convex, vascular and pigmented.
There are many varieties of nevi and they are all harmless until their owner begins to notice abnormal changes affecting the surface of the elements. Why do nevi gradually transform into malignant moles?
Factors contributing to the degeneration of moles
Experts call ultraviolet radiation the main culprit in the degeneration of pigmented spots. For this reason, the first to be at risk are those people who actively tan on the beach and in the solarium. The most dangerous time to be exposed to the sun's rays is considered to be between 11 and 16 hours.
Excess ultraviolet radiation harms the entire body, but the skin is the first to suffer. And if pigment spots and rapid skin aging are not too serious a problem, then sunburn, which provokes the development of melanoma, is really dangerous.
Look at the photo: dangerous moles with signs of skin cancer that appear after excessive sunbathing look like this. Don't be your own enemy, moderate your exposure to the sun.
The process of nevus malignancy can begin after a person has completed the following actions:
- pulled out a hair growing on its surface;
- received a thermal burn in a bathhouse;
- tried to delete the element yourself;
- injured a mole during hygiene procedures or due to wearing tight clothing.
Melanomatous moles are divided into such forms as: nevus of Ota, blue nevus, pigmented borderline mole, Dubreuil melanosis and giant pigmented mole. Differentiation of elements is carried out on the basis of their shapes, contours, color, location and size.
How to understand that a nevus is degenerating?
So that patients can figure out which moles are dangerous, experts have compiled the signs of malignancy into the acronym “ACCORD”.
Each letter carries a specific meaning:
- A, or asymmetry - any deviation from the original shapes and outlines requires urgent diagnosis of the neoplasm;
- K, or edges should ideally be smooth, so their blurring is a sign of degeneration;
- O - symbolizes color, and therefore any distortion of the color of the element and the appearance of atypical inclusions on its surface should serve as a reason for obtaining medical advice;
- P – a size that deviates from the initial values should also alert a person (a slight growth of a nevus in adolescence is not considered an anomaly);
- D, that is, the dynamics of changes, means the presence of pathological changes such as spontaneous bleeding from a mole, cracking of its surface and crusting.
In some people, cancerous moles manifest themselves through rashes on the surrounding tissue, pain in the area, and the formation of vascular clusters. The risk of developing cancer increases with significant growth of the nevus. Its diameter exceeding 6 mm already indicates a potential danger. Any nodules, hardening or softening of the element constitute an unfavorable clinical picture and require an early visit to the clinic.
Attempts to independently get rid of an unattractive “spot” can provoke the degeneration of a mole. Therefore, pulling it with a nylon thread or cauterizing it with vinegar or hydrochloric acid is not allowed.
Where to go with a problematic mole?
If a tumor is suspected of having malignant changes, people usually rush to see a surgeon. This action is not entirely correct, since the specialist excising the tumors will perform his work only if necessary.
What is the name of a mole doctor? A doctor specializing in skin problems has his own name - dermatologist. He is able to accurately determine the true nature of the problematic nevus and suggest the optimal way to eliminate it. An oncologist performs similar functions.
Where to check a mole for cancer? For diagnostic purposes, you can go to a specialized clinic or medical center, which is attended by qualified specialists. In small towns, the dermatologist's office is located in the local or district clinic.
After a visual assessment of the mole, a specialist may need to clarify the clinical diagnosis. To do this, he takes a biopsy specimen, that is, samples of nevus tissue and submits them for histological analysis. The method makes it easier to identify the nature of the element and helps differentiate it from other types of moles.
Atraumatic diagnostic methods include epiluminescent dermatoscopy of moles. The manipulation is performed using a dermatoscope - an optical instrument equipped with artificial lighting. On the eve of working with the device, the doctor lubricates the pigmented lesion with a small amount of vegetable oil.
New growths with a “leg” are subject to mandatory removal, as they can easily break off, convex elements with blurred edges and pigmented foci that appear on the head and in skin folds.
The advantages of dermatoscopy are:
- diagnosis of skin tumors;
- determination of surgical access to the element;
- detection of melanoma in the early stages of development;
- tracking the dynamics of skin treatment;
- examination of any pathologies affecting the skin;
- identifying potentially dangerous moles.
Video: You can find out if a mole is harmless using a dermatoscope.
This analysis is accurate in terms of determining the structure of the neoplasm, regardless of the changes affecting it, because the doctor has the opportunity to closely examine the problem surface and study it more deeply. Based on the information received, the dermatologist will set a time frame for removing the nevus and offer a rational option for performing the procedure.
kozhnyi.ru>
Indications for mole removal and methods
If malignant symptoms are present, surgery to remove the mole is indicated.
Nevi are removed when there is a risk of their transformation into a malignant form. Excision is performed for the following medical indications:
- a very large number of elements;
- increase in the size of the nevus;
- hair loss from pigment spots;
- inflammatory process and swelling, involving surrounding tissues;
- Hanging moles that are subjected to pressure can break off and bleed.
Birthmarks on the face are removed if they cause aesthetic discomfort. Elements larger than 1 cm require constant monitoring by an oncologist and must be removed.
Removal methods
After the examination, the doctor selects the appropriate method. If melanoma is suspected, treatment consists of surgical excision of the formation. This will remove about 3–5 cm of healthy skin. Scars remain after the procedure.
Operation with liquid nitrogen is used for cosmetic defects if the spot does not protrude above the surface of the skin. During the procedure, the nevus is frozen and shriveled. A crust forms on the surface, which prevents infection. Then it disappears, and the tissues are renewed.
The laser radiation method is the most effective and low-traumatic. The laser is used on open areas of the body. The device works with high precision. Thanks to this, healthy skin is not damaged and scars do not form.
Moles are also cauterized using a needle electrode. Formations protruding above the surface are removed using radio frequency waves.
Treatment
Treatment of dangerous moles involves removing them while simultaneously capturing adjacent tissue. In the case of early diagnosis of malignant dysplasia of nevus tissue, its removal makes it possible to prevent cancer cells from growing deep into the dermis and spreading throughout the body.
Removal is carried out:
- Classic method - removal with a scalpel (large formations)
- Laser destruction – laser evaporation (small)
- Cryodestruction – removal by freezing (flat formations)
- Electrocoagulation – cauterization with electric current (pedunculated nevi)
- Radio wave removal – removal by high frequency radio waves (for all types)
Note! Classical tissue excision is the most traumatic method of removing nevi, but it is preferred by many practicing surgeons as the safest and most effective.
What do moles mean?
Some experts believe that the location of spots on the body matters, just like the lines on the arms. There is a sign that those with a light nevus are lucky, and those with a dark nevus are unlucky. Zigzag-shaped birthmarks warn of unexpected negative events in life. A triangle-shaped spot speaks of both positive and negative stages.
The presence of a hairy mole on the left side of the body means that a person is prone to crime. Those with a nevus on the right are honest and highly spiritual people. Those with a mark in the middle of the spine can change their lives by joining one group or another.
A pigment spot on the lower back can mean that a person is successful in friendship and marriage. The mark on the shoulder blade, which a person cannot see without a mirror, brings good luck and happiness.
Types of melanomas
On the human body, malignant formations can be represented by several types:
- Connective. They combine several formations into one spot.
- Halo nevus. This type of pigment spot will be surrounded by a white ring in diameter.
- Spitz. This tumor is pinkish in color and dome-shaped. In its center you can see a small depression, a hole - through it secretions flow out.
- Blue. Seals of a characteristic shade that are located under the skin. They have clear boundaries and do not exceed 10 mm in diameter.
- Skin. They are distinguished by their pallor and convexity.
- Nodal. Flat and round formations of black or brown hue.
Prevention
One of the means of prevention is creams to protect the skin from the sun.
There are a huge number of interpretations of the meaning of age spots. Still, you shouldn’t get hung up on whether it’s located well or poorly. The main thing is to detect potentially dangerous nevi in time and prevent them from degenerating into cancer. As a preventive measure, you should follow some simple rules:
- tan before 10 o'clock or after 5 pm;
- use high-quality protective equipment against ultraviolet radiation;
- refuse to visit the solarium;
- do not injure, scratch, or tear off moles;
- Visit a dermatologist regularly.
To prevent the development of cancer, you need to carefully monitor the condition of your skin. At the slightest suspicion, consult a doctor and remove suspicious elements in a timely manner.
What a cancerous mole looks like: photo and description
There are moles on the body of almost every person with fair skin, so their appearance is not surprising, but in some cases these seemingly harmless neoplasms can give rise to a serious disease. Cancerous moles do not form very often, but such cases do occur, so you need to know when this happens, what treatment is required, and what preventative measures can be taken. This knowledge will reduce the risk of skin cancer and eliminate the consequences of nevus degeneration with minimal losses, if this does occur.
Education process
At first, any mole is a benign neoplasm that does not cause discomfort to the owner. It begins to degenerate into a malignant melanoma tumor when exposed to accompanying factors. Melanoma is a malignant tumor in which the presence of pathological proliferation of melanocytes occurs. These are cells that produce the coloring pigment melanin, accumulations of which give rise to moles. When melanoma grows sufficiently, melanocytes enter the blood, and along it reach the internal organs, forming metastases in them - secondary tumor foci.
Due to the seriousness of the disease, it is necessary to recognize a cancerous mole and consult a doctor as early as possible, this increases the chances of cure without consequences. When metastases have formed, there is a high probability of death, but in the early stages of melanoma it can be removed without complications. In some cases, self-diagnosis of the disease is complicated by the fact that the malignant tumor looks like a wart or spider vein in varicose veins. For this reason, it is better to consult a specialist as soon as you notice a suspicious nevus.
Provocateurs of malignancy
The process of degeneration of a benign mole into malignant melanoma is called malignancy. It does not occur without the intervention of certain factors; in any case, there must be an explicable reason. Knowing it, you can slow down the process and prevent relapse in the future.
The most common cause of malignancy of a benign mole is ultraviolet radiation. Current fashion trends suggest a bronze tan, but getting it can be fraught with skin problems. The most serious of them is the formation of melanoma from a potentially dangerous nevus. This does not happen very often, but this possibility must be taken into account; the risk factor is both natural solar radiation and artificial ultraviolet rays in a solarium.
Experts do not recommend sunbathing on the beach from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m., when the sun's rays are most aggressive.
All tanning enthusiasts need to take this process responsibly, but special attention should be paid to people at risk, which includes the following points:
- naturally fair-skinned people;
- overly sensitive skin;
- predisposition to sunburn;
- cases of cancer in close relatives;
- many pigment spots on the body;
- blond or red hair.
In addition to ultraviolet radiation, other factors can provoke malignancy. Firstly, these include frequent mechanical damage to the nevus, for example, from clothing, a comb, a razor, a washcloth and other items of daily use. One or two injuries will not provoke the formation of cancer, but systematic aggressive exposure is quite capable of causing malignancy. Secondly, chemical damage can affect, for example, when using low-quality cosmetics or personal care products, as well as aggressive household chemicals without proper protection. Thirdly, independent removal of hair growing from a mole using tweezers can provoke malignancy, since in this case the neoplasm is damaged. Hair can only be carefully cut with nail scissors if it is a cosmetic defect.
Symptoms of degeneration
A person may not feel internally that a pathological proliferation of melanocytes is occurring in his body, but there are always external signs. By noticing them in time, you can get the necessary help and prevent disastrous consequences. There is a system for visually determining the presence of melanoma, in English-speaking countries it is called “ABCDE”, in Russian-speaking countries it is “AKORD”, based on the first letters of the five symptoms.
The list begins with asymmetry, which should not exist on any mole. Ideally, if you draw an imaginary line through the nevus, the two halves of the neoplasm will be symmetrical. If it “slides” significantly to one side, this can be considered the first sign of a dangerous cancerous mole.
Under the letter “K” in the abbreviation are hidden the edges of the nevus, which should be smooth and clearly defined. When a tumor becomes malignant, its outline may become jagged or blurred, and this change will be clearly visible to the naked eye, as it will occur in a short time.
The color of the nevus plays an important role in determining the nature of its occurrence. Most types of moles remain unchanged throughout life, so a sudden change in shade should alert you. At first it may appear as small patches of red or black, which gradually merge to form a large spot.
The size of the mole must also fall within a certain range so that the new growth does not cause concern. Some varieties can grow with their owner, but this process is quite slow. A nevus that has exceeded 1 cm in diameter should alert its owner; a sharp increase in size is also a cause for concern.
The last sign noted by WHO is the dynamics of a mole, that is, a rapid, causeless change in any external characteristics. A white rim may appear around the neoplasm, hair may begin to grow, cracks or lumps may appear, and we must not forget about pain.
If you notice the listed signs, this should be a reason to see a doctor as soon as possible. If the description of the symptoms did not help you determine the nature of your nevus, you can look at photographs of melanoma and the process of its degeneration to compare them with your situation. Most cancerous moles look the same, and identifying them is not difficult.
Diagnosis of the disease
Having noticed signs of malignancy, not everyone immediately consults a doctor. Some do not attach much importance to this, others do not even suspect the possibility of developing melanoma, others are simply afraid of doctors and unpleasant tests. However, diagnosing a dangerous nevus is painless, so there is no need to postpone your visit to the clinic.
The doctor begins compiling an anamnesis with an initial examination and oral interview. During it, it is determined when the tumor appeared, whether it caused discomfort, whether it was damaged, and when the first changes appeared. To obtain a more complete picture of the disease, dermatoscopy and siascopy can be prescribed, which allow you to learn about the structure of the mole without damaging it. If blood or other discharge appears on it, a superficial smear is taken. Some include a biopsy in the list of diagnostic measures, that is, the removal of nevus tissue for detailed examination, but many doctors consider this analysis dangerous. A biopsy suggests damage to the growth, which can trigger an accelerated process of malignancy.
If a neoplasm on the patient’s body causes concern to the specialist, and there are signs of malignancy, removal of the mole may be prescribed, followed by a histological examination. With its help, it is determined whether the nevus was malignant, and whether it was possible to remove it completely.
Removal methods
If the process of malignancy has started, the doctor can only prescribe traditional excision of the tumor with a scalpel. All other procedures, which are carried out using modern equipment, cannot provide an absolute guarantee of complete removal of the mole along with its base. If this does not happen, the process of degeneration into melanoma may accelerate, and complications will appear.
The operation to remove a nevus is performed under local anesthesia, so the patient does not feel pain. The specialist removes the growth along with a small area of adjacent skin to prevent the growth of nevus cells after the procedure. The rehabilitation period lasts quite a long time, since the skin is damaged, and after healing, in most cases, scars remain.
You should not try to remove the tumor using traditional medicine or pharmaceutical drugs; this venture will not be successful. In addition to the fact that the desired result is unlikely to be achieved, and the degenerating mole will remain in place, it can begin to transform into melanoma much more quickly, since it has been damaged. Only an experienced doctor in a specialized medical institution licensed to carry out such activities can remove a malignant neoplasm.
Preventive measures
In most cases, mole cancer is treatable if pathological changes are noticed in time. However, it is much easier to prevent the occurrence of a dangerous disease; to do this, you only need to follow some recommendations. They need to pay special attention to people who are at risk.
The most important rule applies to bronze tan lovers. There is no need to fanatically get involved in this activity, because even if you do not take into account the possibility of melanoma, the frequent aggressive influence of ultraviolet rays negatively affects the skin. It can cause premature aging and the appearance of age spots.
You should also monitor the composition of the products you use. It is not recommended to use cosmetics and hygiene products that contain many synthetic components that negatively affect the health of the body. When using aggressive household chemicals, you need to wear gloves and prevent solutions from coming into contact with your skin. In addition, you should regularly inspect potentially dangerous moles; you can do this yourself.
BezPapillom.ru>
How dangerous is this?
The first action of a person if his mole becomes rough and dry should be to see a doctor .
Peeling and dryness of a mole can be a consequence of certain factors:
- traumatic mechanical damage (usually due to regular friction of the formation against items of clothing, especially if they are made of synthetic fabric, or due to careless cosmetic procedures);
- influence of ultraviolet radiation (due to prolonged exposure to the open sun or frequent visits to the solarium);
- the use of cosmetics (this effect can be achieved by foundation creams that are used to disguise moles, as well as some natural oils used for massage, and components in body care lotions);
- hormonal changes (during long-term use of hormonal drugs, as well as at the stages of puberty, pregnancy and menopause).
When a mole becomes rough for one of the listed reasons, the situation is considered reversible. If you wear clothes made from natural fabrics, loose enough so as not to injure moles, if you exclude cosmetics and protect your skin from ultraviolet radiation, and also restore the balance of hormones, the formations will no longer cause concern, they will no longer be dry and flaky.
A situation that is dangerous to health is when the roughness and dryness of a nevus is caused by its degeneration into a malignant neoplasm:
- soreness when touched;
- peeling of the upper skin cells;
- the appearance of a swollen crown around the nevus ;
- bleeding of the formation (sometimes with the release of pus);
- change in color and texture;
- hair loss.
It is important! The listed symptoms indicate the beginning of a serious pathological process; a person should definitely see a dermatologist, and then, if necessary, an oncologist.
Should I delete
Removal of a scaly spot is indicated when a transformative process into a malignant tumor is identified or a nevus is located in a place that spoils a person’s appearance. There are several effective methods that can be used to get rid of dangerous or unwanted stains:
- Laser removal. The impact of the laser helps the mole fall off. Among the advantages of the method are the absence of scars and pain during the procedure.
- Radio wave removal. Using a radio knife, the doctor excises the formation and cauterizes the vessels to prevent bleeding.
- Cryodestruction method. Liquid nitrogen freezes cells and blood vessels, causing the nevus to disappear. Used for small formations.
- Electrocoagulation. Excision occurs using alternating or high-frequency current, which cauterizes vessels and tissues, as a result the growth dies and falls off.
- Removal using a scalpel. The method is used for large formations. The disadvantage of surgical intervention is the presence of scars and scars after the operation. It is not recommended to remove nevi located in a visible place with a scalpel. Among the advantages is the low cost of the procedure.
The need for removal and the choice of method are determined by the doctor based on the examination.
Rough mole on the skin of adults photo
- 01 August
- 0 rating
A nevus is a limited area of accumulation of cells that produce the pigment melanin. This is an area of the skin that is sensitive to external factors and requires special attention. It is believed that if a mole begins to peel off, this is an unfavorable sign, meaning a change in its structure and possible degeneration.
Causes
The causes of peeling nevi in adults, children and adolescents are divided into external and those occurring inside the human body.
External causes of peeling include:
- Exposure to the sun.
This is one of the most common factors influencing changes in the surface layer of an age spot. If a mole begins to peel off due to overheating, this is a process of natural change of epithelium. The color does not change, the shape remains convex or flat as it was originally. It is recommended to protect the nevus from prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. - The influence of ultraviolet radiation when visiting a solarium.
After the procedure, the mole may begin to peel off, since the impact of UV radiation with artificial tanning is much stronger than with natural tanning. If the spot remains rough and continues to peel for a long time, you should consult a dermatologist. - Aggressive exposure to caustic chemicals. If chemicals come into contact with the surface of the nevus, irritation or burns may occur.
- Allergy to components of cosmetic products.
This applies to cosmetics that cause dry skin, and is also important for people with severe allergic reactions. In addition to peeling, allergies may cause local tissue swelling and itching (scalp, face). After 14 days, the rough layer should recover. - Exposure to X-rays.
Changing the surface is possible after taking multiple pictures during the examination. - Mechanical injuries. Constant friction can cause irritation or damage to the mole, and then peeling off its upper covers.
It is necessary to reduce the impact of foreign factors on the surface of the mole . This is especially true for large and convex nevi.
Reasons related to internal processes of the body include:
- Phenotype. If a person has a light color of eyes, skin and hair, and there are a large number of moles on the body, then he belongs to a group at increased risk of degeneration of nevi. Changes in color (the spot becomes a darker color), texture (the skin cracks or peels) or size are a good reason to visit a dermatologist.
- Age exceeding 50 years. Due to changes in hormonal balance in a person, the structure of nevi may change.
- Immunity. Significant decrease in immune defense due to previous diseases or active phases of chronic diseases.
- Smoking and drinking large amounts of alcohol. Toxic substances negatively affect the entire human body, including the condition of the skin.
- Congenital predisposition. Hereditary changes increase the likelihood of malignant transformation.
If a pigment spot cracks, bleeds, enlarges or changes color, this is a reason to consult an oncologist as soon as possible for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Signs of degeneration of a mole do not always appear together. Often only one or two may be noticed, but severe discomfort or a significant change in the appearance of the skin should not go unnoticed.
Diagnostic methods
To identify the reason why a mole peels off, a study consisting of 2 stages is used:
- carrying out an external inspection;
- dermatoscopy.
The second method allows you to detect melanoma in the initial stages. After excision of the nevus, the tissue is sent for additional histology examination.
Treatment
There are several methods for eliminating degenerating formations if the rough mole has not recovered, but has continued to change its structure.
- Laser removal is used for skin spots larger than 2 centimeters in diameter. This is a virtually painless procedure with the option of local anesthesia. The healing period is 14 days.
- Cryodestruction - removal using liquid nitrogen. It is considered a painful procedure. The nevus disappears, but a long healing period is required.
- Electrocoagulation, or exposure to electric current. A rather painful method, after which the formation of scar tissue is observed on the skin.
- Radio wave method - removal without contact and bleeding during the operation process. The healing period is from 9 to 14 days.
- Surgical removal.
Severely dry or rough moles that have begun to degenerate are a dangerous sign of the onset of cancer. Human skin is penetrated by a network of blood vessels, and the penetration of metastases into the blood often leads to the formation of foci of disease in other systems and organs.
It is important to remember that normally the age spot should not itch or show other symptoms of discomfort. If it changes significantly, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4q_FgHF7-II
The degeneration of a mole in an adult, child or teenager can be stopped by removing a section of skin.
Why children and teenagers are at greater risk:
- a small child is not able to take care of his health on his own, this means that examination and determination of changes must be under the control of parents;
- a child’s skin is very delicate, it is less protected from exposure to external factors;
- most nevi appear in childhood;
- During adolescence, a complex restructuring of the hormonal balance occurs in the body, which is responsible for all processes, including those occurring in the nevus.
Source: https://papillomnet.ru/papillomy/shershavaja-rodinka-na-kozhe-u-vzroslyh-foto.html
Factors contributing to peeling of a mole
If a mole has become rough and loose, this is a symptom that requires consultation with a dermatologist or oncologist. With timely detection of melanoma and its removal, health consequences can be avoided. The main reasons that result in rough moles appearing on the body of an adult and a child are:
- The influence of sunlight. With prolonged exposure to direct ultraviolet rays, the top layer of the nevus acquires a rough structure. With regular overheating, the spots become dry, so it is recommended to reduce or eliminate exposure to the sun, especially in the summer.
- Reduced immunity. The presence of chronic diseases that have caused a deterioration of the immune system provokes the formation of a crust on the nevus. The mole flakes and flakes off if you scratch it or rub it with tight shoes or clothing.
- Frequent visits to the solarium. Artificial tanning has a more intense effect on the birthmark than sun rays. The risk of exfoliation of the surface of the formation and its further increase increases.
- Heredity. If parents have changed the structure of the nevus on the face or neck, their child may experience a similar transformation.
- Damage to the nevus. If the growth is located on the back or head, it is subject to accidental scratching, which will lead to the growth beginning to become inflamed and peel off. If the nevus is located on the leg, it can be shaved off when removing hair or damaged by tight shoes.
- If the person’s age exceeds 45–50 years. As the body ages, its hormonal balance changes, which causes a disruption in the structure of the birthmark.
- Contact with a chemical substance on the area of the nevus can cause a burn or inflammation, as a result of which the mole itches and flakes off.
- X-rays. An examination that involves frequent exposure to X-rays will provoke a disturbance in the surface structure of the spot.
- Hormonal imbalance. During pregnancy, lactation, menopause, and puberty, changes in hormones occur in the body. This will cause the mole to peel off.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking. Toxins that penetrate inside with alcohol or tobacco poison the body. The toxic effect affects not only the internal organs, but also the skin, as a result of which the mole will begin to crumble.
- Nevi in a person with light eyes, skin and hair are more exposed to external factors. As a result, multiple nevi on the human body will begin to dry out, crust over, and itch.
- Allergic reaction to used cosmetics and hygiene products. Cosmetics can cause itching and flaking. The rough mole persists for two weeks, after which the symptom disappears on its own. The condition for this is to stop using cosmetics that caused the allergy.
Can a mole become dry, rough and change size: causes and dangers
A rough mole is a seborrheic keratosis on the surface of the skin; the disease has nothing to do with a birthmark and is expressed in excessive thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. A nevus consists of melanocytes - special cells containing melanin that have a direct connection with the nervous system. Seborrheic papilomatosis can last for decades and progress.
What is a seborrheic mole, is it dangerous?
The element, rough to the touch, is distinguished by a peculiar, greasy coating and has a direct connection with the hair follicles. It can grow on the scalp, face, neck, and affect the body - back, chest, back of the hands, forearms and external genitals.
Never develops on the soles and palms. The main group of patients is in the age range from 30 to 40 years. The color of the seborrheic keratosis lesion darkens due to the increased density of exfoliating cells.
In some cases, single melanocytes are found, which gives the spots a dark color.
The tumor-like formation is benign. Shape - oval or round. The boundaries are clear, protruding above the surface of the surrounding tissues. The size ranges from 2 to 6 mm. The growth may itch periodically.
The color palette is pink, black, dark or light brown. On the surface there are many small warts with a thin flaky crust that tends to bleed.
As it develops up to 1-2 cm in diameter, it becomes covered with cracks.
Seborrheic keratosis has a soft structure, but the top layer is dense and hard. Keratoma can take on a convex or pointed appearance. The top contains white or black keratin. The edge is uneven.
The formation is benign, the degeneration of cells into cancer is not excluded. Keratosis externally resembles some types of oncology, which can be determined by histology. A dangerous type of growth, occurring like a cutaneous horn, represents the first stage of skin cancer.
Causes of roughness on a mole
Doctors have not yet been able to establish with certainty what causes the appearance of rough formations.
For a long time, doctors adhered to the version about the viral origin of the disease and its reaction to exposure to solar radiation. Numerous studies have not provided conclusive evidence. There is no reliable information that the disease develops in patients with oily seborrhea, in people who consume insufficient amounts of animal, vegetable fats and vitamins.
It was found that keratosis often appears in people whose relatives have previously suffered from the disease. Predisposition is transmitted by heredity. Manifests itself during the aging period of the skin and under the influence of internal and external irritants:
- endocrine diseases of a chronic nature;
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- pregnancy;
- regular mechanical damage to the skin;
- psoriasis;
- HPV;
- eczema;
- genetic mutations;
- taking hormonal medications, immune disorders;
- exposure to aerosols containing chemicals.
By eliminating the negative factor, you can reduce the likelihood of keratoma growth.
How to distinguish a seborrheic mole from dangerous symptoms
A rough mole can frighten the wearer with its unusual appearance. Outwardly, it may resemble melanoma; only a doctor and diagnostic measures can accurately determine the type of tumor.
The main differences between seborrheic keratosis and an oncological tumor:
| Factor | Keratosis | Melanoma |
| Risk group | People over 30 years of age whose skin is susceptible to aging. | Can be diagnosed at any age. The patient may be a small child, an able-bodied adult, or an elderly person. |
| Form | A round or oval growth with clear boundaries. It has the ability to grow and thicken up to 1-2 cm. | Formation over 6 mm. |
| View | Flaky mole. Flat or slightly convex appearance. It may look waxy, as if painted on the body. | A spot or raised element that is in the stage of active growth. |
| Symmetry | Complied with. | Violated. |
| Color | Uniform or interspersed with white and black. | It changes and takes on several shades. |
| Borders | Smooth. | Vague with jagged edges. |
The dry growth is dense to the touch, like a dangerous nevus, but it does not hurt when touched, at rest. A painful syndrome can develop when irritated or damaged, then the skin around it itches, and secondary infection can occur.
If a person is accustomed to unusual spots on the body, he may miss cancer. Patients with keratosis are recommended to regularly visit a dermatologist and undergo diagnostics.
Melanoma is on the rise. Its increase occurs quickly: by 1-2 mm per month or more.
Mole removal methods
Seborrheic keratosis and other benign formations that are assessed as dangerous are usually excised. Removal serves as a prevention of degeneration or as a method of combating the early stages of dysplasia. The doctor chooses the method in accordance with the nature of the growth.
Popular and effective methods of destruction:
- laser removal. The instrument is a high power beam of light. It destroys cells, evaporating them from the surface of the skin. The advantage is maintaining the integrity of neighboring healthy tissues. Laser radiation parameters are selected individually for each patient. A crust remains at the treatment site, which comes off on its own after 7-14 days. During the procedure there is no pain and no bleeding. The laser prevents the formation of new elements. Disadvantage: lack of material for histology due to its complete destruction;
- cryodestruction. It is used in cases where the body of the growth is located in the upper layers of the epidermis. The dermatologist treats it with liquid nitrogen, which is applied to the surface and removed after 3 minutes. During the process, pain and discomfort are felt. In the first days, decomposition of the pigment is noted, the formation of a crust, which will come off after a few weeks;
- radio wave therapy. The rough element is cut off from the surface using a non-traumatic method. The main advantage is the cauterization of tissue during the incision, which prevents bleeding. Thanks to coagulation, the wound heals quickly. The technique cannot be used by patients in a feverish state, with herpes and a pacemaker;
- diathermoelectrocoagulation. The skin lesion is cut off with a red-hot metal loop. Then the area of the skin affected is cauterized with a coagulator. As a result, there is no blood and the risk of infection is reduced. A crust remains at the treatment site and comes off naturally. A small mark may remain;
- surgical destruction. The most reliable way to remove a large or hanging mole. It is prescribed to the patient when other methods are powerless or a change has begun at the cellular level (the onset of melanoma). The doctor works with a scalpel, cutting off the problematic growth and the tissue underneath it. After healing, a scar remains on the surface, increasing the chance of stopping the cancer.
Symptoms of nevus malignancy
If moles become dry and rough, conduct an independent study of their condition.
Malignization is an autonomous process prone to progression and the appearance of cancerous tumors in the body. They develop by degenerating healthy cells into malignant ones.
The cell structure is rebuilt, active growth is observed - the first sign of a dangerous disease. The nevus may enlarge without other symptoms or discomfort.
Diagnosis of pathology at this stage is difficult.
With active development, the following symptoms appear:
- diameter becomes more than 6 mm;
- the surrounding skin turns red and a halo appears;
- dryness, peeling appear on the surface of the growth, the color changes from uniform to uneven with different shades and tints;
- the structure changes to a nodular pattern or the skin pattern is completely smoothed out;
- when pressed, blood, fluid or pus is released;
- itching, pain at rest or when touched;
- the form blurs and loses its outline, symmetry disappears;
- the color changes to black or colorless.
Timely detection of changes significantly increases the chances of defeating a dangerous, intractable disease.
Seborrheic keratosis appears in older people and is perceived as a natural process. Patients rarely seek help from doctors and self-medicate. Improper handling of rough growths and lack of protective and preventive measures are the main reason for the violation of the integrity of the tumor surface. The spot grows, hurts and bleeds.
Any skin formation requires careful examination by a specialist and regular monitoring. A malignant tumor develops rapidly and affects the entire body. You need to be careful about your health to prevent complications.
The article was approved by the editors Link to the main publication
articles:
(1 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Didn't find suitable advice?
or see all questions...
Source: https://ProMelanin.ru/rodinki/shershavye.html
Features of the appearance of moles in children
A child may develop a mole in the first year of life; they can be small, medium or large. A child's mole is most often brown or dark brown, has smooth edges, a smooth structure that does not protrude above the skin. Light moles are formed from children's frequent exposure to the sun. But the peak formation of nevi in a child is the period of puberty.
Moles in children appear in the first years of life, and some may disappear after a while.
If your baby has large moles, it is important to constantly monitor their behavior, degree of growth and surface structure. If a rapidly growing mole changes its boundaries, color, or begins to bleed, you should urgently show the baby to a dermatologist, who will help determine the nature of the formation and, if necessary, prescribe treatment. Timely detection of pathology will help prevent dangerous complications and preserve the health and life of the child.