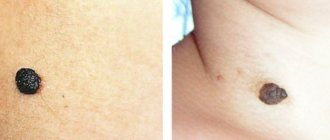
Skin lesions can come in different sizes, colors, and shapes. We are talking about moles (nevi), which can be either congenital or acquired in a person. These formations are benign, but sometimes they can become malignant (melanoma), so they require constant monitoring.
Redness around the mole may be alarming. It may indicate either the degeneration of a nevus into melanoma, or that it was simply subject to mechanical damage. In any case, this fact should not go unnoticed.
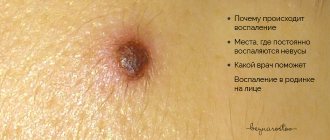
Why does redness occur?
In its normal state, the nevus does not show any changes in appearance; it does not hurt, does not itch, does not bleed or turn red. Any deviations from the norm should alert the owner of the tumor, as sometimes they indicate the onset of a serious illness. The causes of redness around a mole can be divided into four large groups.
Firstly, redness and inflammation can be caused by any damage to the nevus - mechanical, chemical and others. Moles are quite sensitive to any aggressive influences, so any, even minor, damage can lead to unpleasant consequences. Nevi are often damaged or rubbed by rough or synthetic tight clothing; in addition, they can be torn off during water procedures if the washcloth is too hard, or when combing if the tumor is on the head. Any cosmetics containing dangerous synthetic substances and household chemicals with an aggressive composition can cause irritation and redness of the skin around the mole.
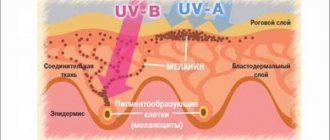
Secondly, a concomitant factor is irrational abuse of tanning. The desire for a bronze skin tone can result in skin problems for modern fashion followers, including the formation of new moles and changes in old ones. The maximum aggressiveness of the sun's rays is observed from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m., so experts do not recommend sunbathing during this time period. You should also treat the solarium with caution, because it uses artificial ultraviolet rays, and 10-15 minutes spent in such a booth is equivalent to a whole day on the beach.
Third, hormonal changes can influence the appearance of redness and inflammation. Unlike the previous reason, a disruption in hormonal balance affects the condition of moles quite rarely, but this possibility should not be ruled out. Especially violent surges of hormones are observed during puberty, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as with the onset of menopause in women.
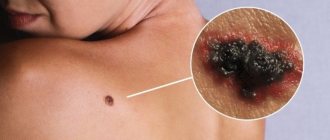
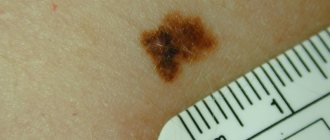
Fourthly, the reason may be the beginning of the process of malignancy. For the most part, nevi are benign neoplasms and rarely degenerate into a malignant melanoma tumor, but in some cases this does happen. If you notice suspicious changes occurring with a mole, you should contact a dermatologist or oncologist as soon as possible. When this disease is diagnosed at an early stage, the probability of recovery reaches 90%, but in advanced cases the possibility of recovery is much lower.
Knowing why the skin near the mole turns red, you can prevent this in the future if the cause lies in damage or excess ultraviolet radiation. Hormonal changes cannot be prevented; they occur randomly, but the degeneration of a nevus into melanoma can be prevented. Most often this happens due to the same damage and irrational tanning, so by treating the tumor with care, you can protect yourself from many unpleasant consequences.
Should we be afraid of such tumors?
Small capillary angiomas on the skin (hemangiomas) do not carry any harm if they are not touched or injured. The situation is more complicated with those that affect muscles, bones and internal organs. They can provoke disruption of body functions, such as breathing, vision, hearing and others.
Always protect external moles from direct UV rays. Use sunscreen creams locally or special sticks that are sold in solariums. Don't encourage them to grow.
They need to be feared in several cases if they:
- exist on a vulnerable and vital organ, such as the brain;
- located in a place that constantly rubs, for example on the heel;
- quickly increase in size and bleed constantly.
Red mole located in the rubbing area
Otherwise, they are harmless, like any other moles, but require constant monitoring and examination.
Other dangerous symptoms
If a mole begins to transform into melanoma, that is, become malignant, redness of the skin is not a single symptom; it is accompanied by some other negative manifestations. The presence of at least one of them should already serve as a signal to contact a specialist, and the combination of several factors literally obliges you to do this in the near future. Symptoms of nevus malignancy include:
- pain, itching, bleeding;
- change in color, structure, outline, shape;
- the appearance of asymmetry;
- the appearance of cracks on the surface;
- the appearance of black or red dots;
- thickening of the mole and the skin around it;
- inflammatory process;
- appearance of a white halo.
If such symptoms occur, only a qualified specialist can help. You cannot self-medicate, giving preference to cheap pharmaceuticals or traditional medicine recipes, since melanoma can only be removed surgically. All other methods will only damage it, but the infected cells will continue to spread throughout the body at a faster rate, which will very soon cause complications.
Ways to remove moles
A dangerous diagnosis can be confirmed by undergoing a full examination. At the first stage, the doctor, armed with a dermatoscope, carefully examines the suspicious element. If the examination reveals atypical signs, the specialist invites his patient to do a biopsy and undergo histological tests. Only after this treatment tactics are developed.
What to do if malignancy is confirmed? The only way to save your life is to remove the atypical nevus along with the tissues adjacent to it. For these purposes, only standard surgery can be used. Neither cryodestruction, nor electrocoagulation, nor laser therapy allows, after the procedure, to obtain biological material that may be needed for laboratory examination of the tumor surface. Without it, it is difficult to understand the level of prevalence of the oncological process and make a prognosis.
Cancerous moles are removed taking into account the following recommendations:
- During the operation, the surgeon must excise the nevus along with a centimeter-long section of healthy tissue located on the sides of the periphery, and also remove the deep layer of skin down to the fatty tissue.
- If melanoma is up to two millimeters thick, the “margin” increases to two centimeters.
- If a cancerous mole is more than two millimeters thick, it is excised, including healthy skin up to three centimeters wide.
- When laboratory tests show the presence of a metastatic phase, the lymph nodes closest to the nevus are also removed during surgery. In later stages, chemotherapy is required after surgery.
The thickness of the tumor and the number of skin layers affected by the pathology are the main criteria that help make predictions about the level of survival. If the thickness of melanoma does not exceed one millimeter, oncology has high rates of cure. The higher this indicator, the worse the forecasts.
What to do if redness and inflammation appear
If you notice that the skin around one of your moles is red and inflamed, you should contact a dermatologist or oncologist for advice without panic. There is no need to be afraid of this, because in most cases the examination results can be obtained almost immediately. If the fears are confirmed and the redness turns out to be a symptom of malignancy, the necessary tests and subsequent surgery will be prescribed. If there is no cause for concern, the specialist will prescribe a pharmaceutical remedy that relieves inflammation.
YOUR DOCTOR WILL BE ABLE TO FIND OUT WHETHER CERTAIN FOLK RECIPES ARE SUITABLE FOR YOU, IT IS NOT RECOMMENDED TO USE THEM WITHOUT THE CONSENT OF A SPECIALIST TO AVOID COMPLICATIONS AND SIDE EFFECTS.
If the initial visual examination of the nevus is insufficient to make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe additional tests - dermatoscopy and siascopy. These are absolutely painless procedures that are performed non-invasively, that is, without damaging the skin. Dermatoscopy allows you to look at the tumor under magnification using a device that operates on the principle of a microscope. Siascopy is performed with a special scanner, which allows you to study the composition of the mole in more detail. In particularly difficult cases, a biopsy is prescribed, which involves taking a certain amount of nevus tissue for subsequent analysis of the nature of its occurrence.
Types of angiomas
Angioma is a collective name; it is divided into formations from capillaries and vessels - hemangiomas and those that grow from lymphatics - lymphangiomas. More often we meet the first type.
The main types of angiomas include:
- Simple.
The most harmless ones. Found on the surface of the skin. More often they appear singly. If they don't interfere, you don't have to remove them.
Simple angiomas
- Branched.
They are characterized by the presence of a constant pulsation, you will feel it if you lightly touch it. They appear from the plexuses of blood vessels. - Cavernous.
Most often they are located deep under the skin and increase with tension. They need to be constantly monitored and observed. If growth continues, it is better to remove.
Cavernous angioma
- Combined.
They are found on the surface and under the skin. Angiomas are a complex type, as they involve large surfaces.
According to the form they are distinguished:
- Flat
(not felt during palpation, because they are smooth). - Star-shaped
(visible vascular network extends from them).
Stellate angioma
- Nodular
(protrude above the surface like nodules, they can be easily palpated). - Serpiginous
(many red dots in one place).
Serpiginous angioma
These are just the main types that are most common. In medical practice, there are many more of them described.
Self-medication methods
Sometimes it happens that incomprehensible changes occur with a tumor, but it is not possible to see a doctor in the near future, for example, if the patient is on vacation. In this case, you can use some pharmaceutical drugs that will not cause harm in any case. However, before using them, it is advisable to consult at least with a nurse if you are prone to allergies.
The most common way to quickly get rid of redness and inflammation of the skin around the tumor is to wipe it with medical alcohol. This must be done several times a day until the problem is completely eliminated or until you can make an appointment with a specialist. It is necessary to moisten cotton wool or a cotton pad with alcohol and apply it to the redness without pressure; there is no need to secure the compress with a bandage or plaster, just wiping is enough. If the pharmacy does not have medical alcohol, you can replace it with Septil.
One of the readily available ways to eliminate redness is streptocide powder. It is sold in pharmacies in finished form or in tablets that must first be crushed. Sprinkle the powder on the reddened mole, without wrapping it with a bandage or securing it with a band-aid, and leave it on for several minutes. This method is not suitable if you have previously used any cream to relieve inflammation, since streptocide will react with it.
Another remedy that allows you to quickly relieve redness and inflammation of the skin is calendula tincture - an anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, healing and regenerating agent. You can buy it at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself, for this you will need to pour 2 tablespoons of dried calendula flowers with 100 ml of alcohol or vodka, and then leave in a dark place. It is necessary to wipe the inflamed mole with the tincture several times a day until the problem is completely eliminated.
What are these red dots on the body?
When it comes to moles, we often think of a small dark brown spot, but in fact there are many types. Some you might not even suspect.
Normally, moles of different shapes and sizes are distinguished - from a millimeter to several centimeters; with clear oval outlines or shapeless. All of them are quite common and one person can have several species in one area. But small red dots and blue spots cause mistrust. What it is?
Red moles
The red blood spots that you may have noticed on your body or on someone you know are common angiomas. They are otherwise called red moles. In fact, these are vascular formations (vascular moles) or otherwise they can be called tumors, often pale pink or burgundy in color, sometimes the color turns blue. Depending on their location, they are flat or convex.
Red moles, also known as angiomas, are vascular formations, also called tumors.
They can be easily detected by performing a simple test: when pressed, they turn pale as blood stops flowing there. Small and superficial angiomas do not pose any danger, but often signal failures and disorders in the body. It would be a good idea to consult with a therapist; he can prescribe tests for you.
Folk recipes
If you do not like to use pharmaceutical drugs, but need to relieve redness, you can use traditional medicine recipes. By using them, you will be confident in the naturalness of the ingredients, and the cost will be significantly lower. You should use any of these recipes only after consulting with your doctor:
- Twice a day it is necessary to lubricate the red nevus with potassium permanganate until the problem is completely eliminated.
- A cucumber compress can help; for this you need to grate a small amount of the vegetable, wrap the resulting pulp in gauze and apply it to the tumor for 15-20 minutes.
- Fresh or sauerkraut applied to inflammation for 20 minutes can quickly get rid of the problem; the compress must be applied at least twice.
- If you boil juice from sour pomegranate and mix it in equal proportions with natural liquid honey, you will get another remedy for daily rubbing. The juice should be boiled for half an hour over low heat, and the redness should be lubricated with it several times a day.
- Grated raw or boiled potatoes can also help relieve redness and inflammation if applied as a compress for 20 minutes.
Reasons for conversion
Even an absolutely healthy person with a healthy lifestyle is not immune from the malignant degeneration of a nevus. Excessive sunbathing can contribute to the process of malignancy - malignant degeneration.
At risk are people with fair skin and hair, a large number of nevi on the skin, especially if among them there are those that are more than 5 mm in diameter. Also at risk are people who often develop new spots on their skin.
Other reasons for degeneration are:
- Constant contact of the mole with objects, friction of the mole against anything - jewelry, clothing, belt, underwear, etc.
- Injury, cut, scratching or burning of a mole.
- Removing hair from the surface of a mole.
- Removing a mole in non-medical conditions or trying to remove it yourself using traditional methods.
Content:
- White spot around the mole: Setton's nevus;
- consequence of injury;
- consequence of infection;
- melanoma;
- Halo of brown color (seborrheic keratosis, melanoma, Dubreuil's melanosis, dysplastic nevus, complex nevus);
Treatment
Therapy in this case has two directions. Symptomatic treatment simply relieves redness, and complete treatment involves removing the nevus from a given area of skin. Traditional medicine methods can be used as symptomatic treatment. Removal is carried out only on the basis of a medical institution after examination by an oncodermatologist.
Drug treatment
The following pharmaceutical products are used to relieve redness:
- Zinc ointment;
- Salicylic-zinc ointment;
- Tincture of calendula;
- medical alcohol;
- Syntomycin ointment;
- Streptocide ointment;
- Triple antibiotic ointment.