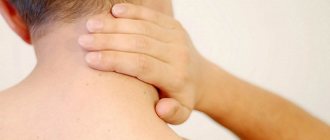
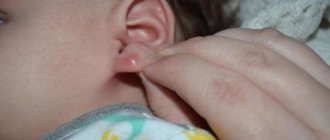
In most situations, the ball that appears behind the ear is an inflamed lymph node. Lymph nodes are a kind of filters that act as the body’s natural defense against pathogens.
When they increase in diameter and when painful sensations appear, there is a suspicion of some dysfunction in the lymphatic system or in a specific area. This is lymphadenitis. The diagnosis is made only by an experienced doctor after a preliminary diagnosis.
Possible reasons
Any person who has discovered some kind of tumor on his body wants to know what he is faced with and what to expect. What could cause a ball to appear behind the ear:
- Enlarged postauricular lymph nodes.
- Epidermal cyst.
- Benign neoplasm (atheroma, lipoma, etc.).
- Parotitis.
These are the most common reasons why a lump may occur in the behind-the-ear area. Other factors include trauma, malignant cancer, tuberculosis, etc. As you can see, if even a small formation appears under the skin, then it has to be differentiated from many quite serious pathological conditions and diseases. After all, it has long been known that without determining the exact cause of the disease, it is quite difficult to achieve a complete cure for the disease without consequences and complications.
If a ball (bump, tumor) appears behind the ear, there is no need to guess what it could be, but simply contact an experienced and highly qualified medical specialist.
Enlarged lymph nodes
It has been clinically proven that infection most often leads to enlargement of the postauricular lymph nodes. The following types of infectious diseases can trigger the development of lymphadenopathy:
- Sore throats.
- Measles and rubella.
- Inflammation of the palatine tonsils.
- Odontogenic infections.
- Infectious process on the head and neck.
- Tuberculosis.
- Toxoplasmosis.
- Infectious mononucleosis, etc.
In addition, enlargement of lymph nodes is observed during the oncological process, systemic diseases, adverse reactions to medications, etc. In the case of lymphadenopathy of an infectious nature, the following clinical picture will be noted:
- If swollen lymph nodes are caused by infection, a high fever is common.
- It can be seen that a rounded irregularity has formed behind the ear, which hurts when palpated.
- Weakness, increased fatigue, decreased appetite, headaches and other symptoms of general intoxication caused by an infectious process in the body may appear.
- In the presence of acute inflammation, the skin over the lymph node may be red, swollen, hot and tender to the touch.
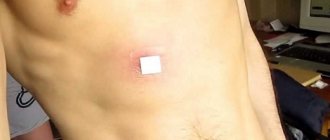
Epidermal cyst
As indicated in medical reference books, an epidermal cyst appears as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands and impaired outflow of sebum. External signs of an epidermal cyst:
- It looks like a round tumor behind the ear.
- Maintains normal skin color. In some cases, slight redness may be observed.
- The size of the epidermal cyst varies from 0.5 to 5 cm.
- Tends to grow quite quickly and increase in size.
- It often becomes infected due to a bacterial infection.
Benign neoplasm
Often a ball under the ear can turn out to be a banal wen or lipoma. They are formed from adipocytes, which are fat cells in the body. It is worth noting that the skin over the neoplasm looks unchanged. Lipoma does not have any specific clinical symptoms. A mobile round tumor of soft consistency is palpable. However, some benign growths may feel firm to the touch. Sometimes they hurt and cause some discomfort. If there is a fairly rapid growth of the lipoma, it is necessary to take prompt measures to eliminate it.
The appearance of a ball under your ear should alert you and force you to consult a doctor.
Parotitis
Another cause of swelling in the area of the auricle is mumps, or, as people say, mumps. Refers to acute viral diseases and is accompanied by a painful enlargement of the parotid salivary glands. Main symptoms of the disease:
- A sharp increase in temperature to high numbers.
- The parotid salivary glands become enlarged. Initially, the swelling is located in front and under the ear. The lesion can be either unilateral or bilateral.
- The swelling that appears spreads to the cheek and neck area.
- The patient feels severe pain while eating.
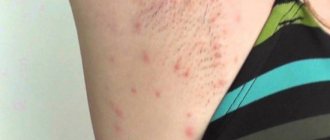
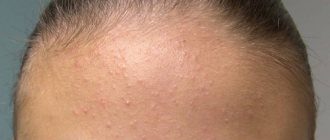
Rash on ears and face
The most common cause of rashes on the face and ears is allergies. In this case, damage to the epidermis and impaired immunity are observed. Rashes in this area can occur during stressful situations and skin injuries.
Allergic dermatitis in the initial stages is characterized by red or bright pink spots, in the place of which small blisters subsequently appear. Subsequently, these blisters burst, and the rash takes the form of small, weeping ulcers. The patient feels a burning sensation and severe itching, and not only the affected areas of the skin can itch, but also the entire surface of the ears. Skin eczema has similar symptoms, however, with this disease all the symptoms are more pronounced.
Contact dermatitis, which manifests itself as a rash on the ears and face, can occur when an irritating substance comes into contact with the skin. Some detergents, alkaline compounds, acids, etc. can have this effect.
When is it dangerous?
By and large, any growth on the skin should be a cause for concern. However, we list situations where delay in providing professional medical care is fraught with serious complications:
- The tumor behind the ear quickly increases in size.
- The neoplasm is painful and/or causes significant discomfort.
- Attachment of infection and development of purulent process.
- The temperature lasts for several days.
- The general condition suffers significantly.
- The swelling spreads to other areas of the head and neck.
A ball behind the ear - what is it?
A ball (seal) under the lobe or behind the ear can be a signal of quite serious problems in the human body. Such formations can be an integral part of the surrounding tissues or move when palpated with fingers. If a tumor appears on the organ of hearing, which does not cause discomfort, then a person may not immediately notice it.
However, in the case when a ball appears behind the ear or on it and it hurts, what it is, a person does not know, it is necessary to consult a specialist to be sure that this neoplasm is not a symptom of cancer. A lump near or under the ear can occur due to a variety of diseases.
Diagnostics
An experienced specialist begins the patient's assessment by assessing clinical signs and symptoms. Based on complaints, examination and palpation (palpation of the pathological area), one can completely determine the diagnosis. If necessary, additional research methods are used. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics include:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- X-ray examination.
- Ultrasound examination.
- Biopsy of the pathological focus.
- Histological analysis of biopsy material.
First of all, the doctor must exclude a more serious pathology, which, without timely treatment, can significantly aggravate the patient’s current condition (infection, cancer, etc.).
First aid
One or more blisters that appear behind the ears should not be touched with bare hands, especially without treatment with an antiseptic.
If blisters appear where contact with a bandage, headdress or hair is inevitable, remove these squeezing and rubbing objects, put the hair in a ponytail, pin it up, comb it - do everything to avoid contact.
If you suspect an allergic reaction, remove substances that could cause it away: rinse off the hair dye immediately with plenty of water so that the blister does not develop into Quincke's edema (a life-threatening syndrome, which is essentially an ordinary but giant blister that causes suffocation), Wash off shampoos or gels with plenty of clean water.
- If there is a significant deterioration in health or shortness of breath, take the victim out into the fresh air, into a well-ventilated area.
- Give any antihistamine to relieve an exacerbation.
- Treat the surface behind the ears with an antiseptic.
- If severe itching occurs, apply ice; you can lubricate it with any remedy that relieves this symptom, from soda solution to Finalgon.
- If you feel unwell, call emergency medical help; if you feel well, go to the hospital to find out the cause of the blister.
When applying symptomatic treatment to relieve itching, we must not forget that only a doctor can provide real help, as well as make a diagnosis. Even if the blister does not cause concern, you should not let the disease take its course.
Treatment
The choice of treatment tactics directly depends on the cause that provoked the appearance of a tumor-like formation in the ear area. The use of local therapy without making a correct diagnosis is usually inappropriate. Let's consider some features of the treatment of a ball behind the ear, depending on what could cause this pathological condition:
- If the lymph nodes are enlarged, then treat the infection that caused the lymphadenopathy. The pain behind the ear will go away when the underlying disease is cured. They use antibacterial, antiviral, immunostimulating and other drugs.
- Conservative methods of treating epidermal cysts are ineffective. Only surgical treatment is indicated. Laser coagulation or complete removal of the cyst using the traditional surgical method can be used.
- In case of purulent inflammation (abscess), it is necessary to open the pathological focus. Then the wound is cleaned of pus and drainage is installed.
- The lipoma may not be touched if it does not cause discomfort. Otherwise, it is removed surgically.
- For mumps, supportive therapy is used. The patient is provided with an optimal regimen, diet and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to reduce pain and local inflammation. After receiving permission from the attending physician, place a warm compress on the parotid area.
If the ball behind the ear hurts without stopping, there is absolutely no point in delaying visiting the hospital.
Rash on earlobe
The appearance of a rash on the earlobe may be associated with constant or periodic wearing of jewelry that causes inflammation. The phone may also be the cause of this phenomenon. In the latter case, it should be thoroughly treated with antibacterial agents. Another common cause of rashes on the lobe is insufficient hygiene. In addition, shampoos, masks and other hair products often cause a rash in this area.
If a rash does appear on the earlobes, you should not touch it, so as not to cause a secondary infection and prevent suppuration. Periodically, pimples should be treated with alcohol or aloe juice. Differin and tar soap can be used to treat rashes on the earlobe. Folk remedies are also suitable for these purposes: a decoction of celandine or plantain, an infusion of calendula or chamomile and others.
Small rash on ears
A small rash on the ears occurs as a result of an allergic reaction or irritation. The cause of such rashes can be various allergens, earrings, products used for skin and hair care, washing powders and other household chemicals, cosmetics, etc. To treat such a rash, it is desirable to establish the factor that caused its appearance and eliminate it. In addition, external use of such products as Advantin and Elokom in the form of cream gives good results.
How to treat if the appearance of a blister still cannot be avoided
Modern pharmaceuticals and traditional medicine recipes come to the aid of the sick.
Medicines to combat illness
Broad-spectrum antimicrobial ointments such as Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Levomekol ointment, the root cause of the appearance of a blister is unknown, because they act on almost any group of bacteria.
Furacilin solution will help disinfect the surface of the skin.
Treatment of blisters caused by the herpes virus
Antiviral ointments are used to treat blisters caused by the herpes virus. They act precisely, reach the source of inflammation faster, and many of them have healing properties.
The most commonly prescribed are Oxolinic ointment, Viferon, Zovirax, Cycloferon.
Treatment of blisters - signs of allergies
Other types of neoplasms
In addition to the above diseases, there are (albeit much less common) other formations with outwardly similar symptoms:
- Fibroma. It looks as if a mushroom has appeared on a stalk, separate from the adjacent skin. Most often it is painless. It is recommended to consult a doctor if fibroids grow or become inflamed.
- Hemangioma. This is a pathology of blood vessels that grow together. It can be hard or soft, and has a reddish tint. It is capable of growing rapidly, capturing neighboring tissues.
- Malignant tumors. May be sarcoma, neurofibromatosis, or basal cell carcinoma. Such formations can adhere to nearby tissues and become painful; their color is slightly darker than that of healthy skin.
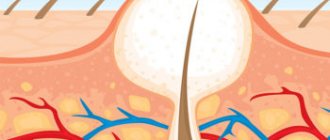
Atheroma
This is a clogged sebaceous gland, stretched due to continued production and accumulation of secretions in it. In fact, it is a cyst on the exit duct of the gland. It can reach a diameter of several centimeters and occasionally degenerate into a malignant neoplasm. The main reasons for the appearance of atheroma:
- heredity;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- a consequence of prolonged stay in contaminated premises;
- excessive sweating;
- seborrhea;
- hair follicle injury.
Unlike lipoma, the chance of infection and inflammation is much higher. Therefore, if a ball is inflated on your ear and it hurts, then most likely it will have to be removed. This is done in the sterile conditions of a clinic or hospital.
At an early stage, the contents of the cells may be evaporated by high-frequency radio waves or burned out by a laser beam. In case of suppuration, the capsule is removed using a traditional scalpel under local anesthesia in 15-20 minutes.