What do liver spots look like on the body: description, names
It’s not for nothing that people call the liver the “filter” of our body.
It performs a number of important functions, such as neutralizing toxins and other harmful substances, producing glycogen (“gasoline” for our body), and also participates in digestion, synthesizing bile, which helps absorb nutrients, break down fats, etc. Thus, thanks to the liver, we can drink and eat whatever we want in unlimited quantities. However, everything in this world is not eternal. And our liver too. If you have an unhealthy diet, frequent consumption of alcohol, etc. the organ wears out and begins to malfunction, allowing harmful substances into the body. This is how various kinds of diseases arise that can harm a person to varying degrees, ranging from unpleasant sensations to a serious condition or even death. The skin is one of the organs that first gives signals about liver disease. And if you have a rash for no reason, you should think about whether these could be spots on the body due to liver disease?
What do rashes look like?
The nature of the skin rash depends on the type of dermatological problem. Many patients with hepatitis C ignore telangiectasia, chloasma, and lentigo. Without adequate therapy, the liver stops functioning, which causes irreversible consequences.
Symptoms of hepatitis C rashes
| Type of stains | Clinical manifestations | When spots appear |
| Lentigo | Multiple dark or light brown spots raised slightly above the skin. The shape resembles lentil grains. Does not cause burning or pain | Spots appear during a long course of hepatitis at the stage of subcompensated liver failure |
| Chloasma | Pigment spots do not rise above the skin and have a clear, uneven contour. The color varies from brownish brown to light yellow. Reach no more than 10 mm in diameter | Hyperpigmentation occurs after chronic inflammation |
| Erythema | Red spots cause itching or burning. Over time, they increase in diameter and have blurred boundaries. | Limited spots form in patients with hepatitis due to impaired protein and lipid metabolism, cirrhotic changes in the liver |
| Telangiectasia | The spots look like small spider veins. Their color ranges from pale red to light purple. Not accompanied by itching, pain or peeling of the skin | Persistent expansion of blood capillaries is more often observed with portal hypertension, the transition of liver fibrosis to cirrhosis |
If spots on the body are combined with itching and yellowing of the skin, this indicates cholestatic syndrome (stagnation of bile). It is additionally manifested by darkening of urine, upset stools and discoloration of feces.
Diseases affecting the appearance of spots on the body
The main diseases that cause redness and spots on the skin are:
- Hepatitis. Hepatitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the liver. They are usually accompanied by a variety of skin manifestations. This may include hives, changes in skin color, red-brown rashes, large pinkish-red spots, etc. The rash appears immediately after infection or during the transition to a chronic disease.
- Parasitic infections. Such diseases are divided mainly into echinococcosis, ascariasis, amoebiasis, etc., depending on the causative agent of the infection. Parasites and helminths not only damage the structure of the organ, but also stimulate neoplasms, disrupting the normal functioning of the liver. In this case, there is no jaundice, only red spots in the gland area and acne. Common symptoms are chronic fatigue, lethargy, exhaustion, sleep disturbances, bad breath, right upper quadrant pain, and enlarged liver.
- Cancer. The formation of metastases and tumors in liver cells leads to disruption of its functioning, and without treatment, to the death of a person. The development of such malignant neoplasms can be confused with other liver diseases, since their symptoms are similar: an unpleasant feeling of bloating, weakness, sometimes vomiting, loss of appetite, constant malaise. At a later stage, tumors inside the diseased organ reach such a size that they block the flow of bile into the intestines, and it goes straight into the blood. As a result, yellowing of the sclera and skin, darkening of urine, and itching occurs.
- Cirrhosis.
They are divided into: • Alcoholic; • Stagnant; • Viral. The vast majority of people get sick due to prolonged alcohol intoxication. The last two are much less common.
- Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, cholangitis are all diseases of the gallbladder. Basically, they are all associated with the formation of stones in the cavity of the bladder and its ducts.
Signs of the disease: • Itching of the epidermis; • Belching and bitterness in the mouth; • Heaviness under the right rib.
- Liver failure. This disease occurs due to an overdose of alcohol or medications, or severe poisoning. It can manifest itself in the form of yellow spots, a purulent rash, spider veins, bitterness in the mouth, and general lethargy.
Associated symptoms indicating liver disease are:
- General weakness;
- Bitterness in the mouth;
- Fatigue quickly;
- Congestive acne;
- Hair loss and brittle nails;
- Weight loss;
- Pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Feverish state;
- Dry mouth;
- Yellowness of the sclera;
- Discomfort while eating;
- Smell of overripe fruit on the breath;
- Indigestion;
- Unpleasant smell of sweat.
How to cure?
Treatment of skin manifestations is part of complex therapy aimed at combating the main damaging factor, protecting and supporting intact areas of the liver parenchyma. The use of cosmetic procedures against the background of active disease does not produce results.
To prevent serious consequences, patients are advised to follow a strict diet with abstinence from alcohol, smoking, fatty and spicy foods, fried cooking methods, smoked sausages, meat, and fish. Preference in nutrition is given to vegetables and fruits, cereals, dairy products, low-fat boiled meat and fish dishes.
Anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed - antiviral drugs for viral hepatitis, antibacterial or antifungal drugs for other pathogens, specific drugs for tuberculosis, parasitic infestations, immunomodulators and corticosteroids in the case of an autoimmune process.
Long-term use of hepatoprotectors, vitamins, and herbal decoctions to improve the flow of bile is justified. During the inactive stage of the disease, you can consult with a cosmetologist about the possibility of eliminating spider veins and age spots on the face. It is not recommended to solve this problem yourself.
Where do spots appear on the body due to liver disease?
With diseases of the gland, the skin becomes a non-standard color, and this should never be ignored. Yellowish skin with an orange color indicates internal liver problems; lemon tint - about hematological disorders; brown means mechanical damage to the organ.
Basically, liver spots are localized throughout the body, depending on the disease and its manifestations:
- Rash – face, neck, chest, back;
- Red spots – in the liver, abdomen;
- Yellow spots – oral cavity, sclera, with transition to other parts;
- Bright red spots – palms;
- Pigment spots – palms, arms, face, neck;
- Yellow plaques – armpits, eyelids, arms, legs, feet;
- Spider veins – neck, back, arms, face;
Each skin rash is accompanied by itching.
What do liver disease spots look like?
There are different formations.
- Spider veins. They are blood vessels that rise above the skin level. They also have branches - vascular branches. The stars are usually dark red in color. The size can reach 15 cm. The photo shows blood spots on the body due to liver disease.
Upon palpation, you can notice how the stars pulsate. Sometimes they are quite painful and do not go away throughout the illness.
- Rash. It is not uncommon for a rash to appear with such diseases. It can be pustular, acne, or papulous. The main places of its concentration are the face, neck, back and chest.
The rash can also appear as an allergic reaction. For example, this happens with parasitic infections or an overdose of medical or other substances.
- Liver plaques. Most often they are a consequence of chronic diseases. They look like traces of healed burns and have clear edges.
What does a hepatitis rash look like?
Often, a rash due to viral hepatitis C is confused with an allergic one. With liver rashes, the skin is very itchy, especially in the evening and at night. Even if you take allergy medicine, the itching continues, causing scratching that does not heal for a long time. In addition to unpleasant spots, the following symptoms appear:
- The color of the skin changes, it often turns yellow, becomes darker or paler, thinner.
- Sweating increases.
- The skin begins to peel off.
- Swelling of the limbs and face appears.
- There is discomfort and heaviness in the liver area.
- The body is covered with cracks, scratches, and blue stripes.
With further progression of hepatitis C, a rash appears on any part of the body, limbs, face, and can have a different appearance and shape.
Liver spots
With liver failure and cirrhosis of the liver due to hepatitis C, the skin often becomes covered with a rash in the form of spots. This is the result of the release of toxins into the blood, which slow down metabolic processes. There are several types of liver spots:
- Chloasma (melasma) are voluminous brown or light brown spots of different sizes with clear boundaries. Often formed due to the use of antiviral drugs.
- Lentigo is a yellow or dark brown rash in the form of spots with a diameter of 1 to 30 mm.
- Hepatic palms (palmar erythema). Persistent red spots appear on the palms of men and women. If you press on the palm, the redness disappears, and then returns again.
- Cutaneous porphyria is an itchy blistering rash accompanied by swelling and pain. Appears due to a mutation in the gene that is responsible for the production of hemoglobin.
- Atrophic stripes. Most often they form on the mammary glands, outer thighs, sides, and lower abdomen.
- Erythema is severe redness of the skin due to dilated blood vessels. The size of the rash depends on how severely the liver is affected.
Also, hepatitis C often results in the formation of angiomas - benign vascular tumors. They appear as a red rash that protrudes slightly above the skin surface.
Spider veins
This is an expanded network of capillaries that shines through the surface of the body. Outwardly it looks like a purple or red spider web. It is more often observed on the extremities, in the forearms, wings of the nose, cheeks, if a man or woman suffers from diseases of the hepatobiliary system and hepatitis C. Often this symptom provokes cirrhosis of the liver.
Asterisks can be large arterial, venous or capillary (the smallest).
Color can vary from blue to red. The diameter of the web reaches 30 mm. When pressing on the spot, a subtle pulsation is felt.
Hemorrhagic rash
These are small bright red or purple spots covering the abdomen, face, and neck. They do not protrude above the surface of the skin and do not change shade. Often formed as a result of taking medications against hepatitis C to the same extent in women and men. There are several types:
- small - petechiae that are small in size (about the size of a dot);
- medium - purple, ranging in size from 2 to 5 mm;
- volumetric - ecchymosis, reaching a diameter of 5-6 mm.
Elements of the rash often merge with each other. In this case, the color of the spots is purplish-blue with necrosis in the center. If hepatitis C develops with complications, gangrenous changes in the skin are possible.
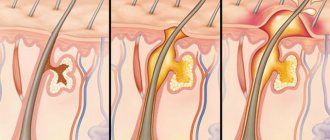
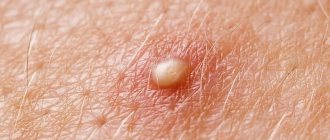
Pimples
With hepatitis C, pimples with liquid inside often form on the body - in medicine they are called papules. Ulcers may also appear. They become inflamed around them, hyperemia is noticeable, and the rash is very itchy.
This indicates disturbances in the functioning of the liver and bile ducts due to poor nutrition and intake of alcoholic beverages, which causes a decrease in detoxification function. Metabolic products are concentrated in the skin, and a pustular, vesicular, papular rash appears. Ulcers often occur due to steatosis, fibrosis, cirrhosis of the liver and the use of antiviral drugs. As a result of AVT for hepatitis C, an allergic rash sometimes occurs.
Xanthelasmas
These are benign formations that protrude above the surface of the skin. They look like yellowish plaques. Mostly observed in elderly people due to a malfunction of lipid metabolism. This is a sign of large deposits of cholesterol on organs, vascular walls and skin.
Xanthelasmas are often observed in chronic hepatitis C. There are several forms:
- Diffuse flat. In most cases, women with liver pathologies suffer from this type of formation. Xanthomas look like soft yellow wen of different shapes and sizes, with clearly defined boundaries. Formed on the neck, face, limbs.
- Tuberose. These are denser papules whose color varies from yellow to brown. This form of xanthelasma is painful. The formations are located in the area of the fingers, elbows, and buttocks.
- Eruptive when the papule has a color from red to yellow. Dimensions reach 7 mm. The rash has the appearance of small grains and is very itchy.
- Disseminated. Most often it affects the skin of the eyes (in the area of the lower and upper eyelids), the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and larynx, and the sclera. On the face, the rash appears as nodular formations, approximately 3 mm in size, from red to brown.
If the rash grows severely on the bridge of the nose and eyelids, it can affect vision.
Itching and itchy spots
Almost all liver diseases are accompanied by itching on the epidermis. It especially manifests itself in combination with irritation and yellowness of the skin. This happens because bilirubin, which the liver should, but cannot, neutralize, lingers in the layers of the skin, irritating it. Thus, the body begins to itch due to stagnation of bile and, as a result, the occurrence of jaundice.
All skin rashes that appear on the skin as a result of liver disease, be it hives, plaques or red spots, are not without itching. It happens that itching occurs against the background of allergies, then in order to distinguish liver irritation from allergic irritation, you need to know that hepatic irritation is not eliminated by antiallergic drugs.
Types of skin changes
Liver diseases manifest themselves in different ways:
- dull arching pain in the hypochondrium on the right or a feeling of heaviness;
- heartburn, belching;
- diarrhea;
- change in urine color to darker, lightening of stool;
- temperature rise.
On the skin, changes appear in a latent period, when other signs can only be detected in the laboratory. In some patients, suspicious symptoms are detected already in the chronic advanced stage. In others, when the liver is overloaded due to acute poisoning, alcohol intake, or abuse of fatty and fried meats.
Treatment of liver spots
The most important thing is that you should not self-medicate. If you have liver spots, you should definitely contact a specialist who will examine you and prescribe the correct treatment.
A large number of cosmetic companies offer various medications and cosmetics for removing stains. However, the problem is within you, and after some time they will return again. It is better to focus efforts on combating the source of the problem than to mask it.
The liver is an amazing organ. She is capable of self-regeneration even in the most advanced cases, so if you help her, recovery will go faster. You should take medications as directed by your doctor, undergo procedures and follow a diet. Treatment of any of the diseases is carried out in various ways:
- In case of cirrhosis, treatment is aimed at stopping the processes of decay of organ structures. It includes the use of medications and diet.
- To get rid of diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts, you need to methodically take choleretic drugs. Also, one of the methods of non-surgical treatment is remote ultrasound lithotripsy. However, if the stones are too large, then only surgery will help. Now medicine offers the most modern methods of removing stones: crushing them with a laser, endoscopic cholecystectomy or open abdominal surgery.
- If a person has parasites, they are treated with antiparasitic drugs. If they do not help, surgical excision is used, then restorative measures.
- In the case of hepatitis, antiviral medications and a strict diet are used.
One way or another, the best option is to turn to a professional, if only to avoid making things worse. After all, health is one thing, and you need to preserve it with all your might. Take care of yourself!
Features of treatment
Therapy, if the patient has liver pigmentation, can be aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked its appearance. For this purpose, the functioning of the liver and all organs and systems is normalized. If this method does not give a positive result, then laser removal of areas of pigment accumulation or spider veins is indicated. Alternative medicine can be used as a complement to basic methods.
Treatment of the cause
The first stage of treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the skin defect.
Liver spots can be removed only after the functioning of all organs and systems has been normalized and the elimination of bilirubin breakdown products from the body has been enhanced. For this purpose, it is recommended to use hepatoprotectors “Essentiale” or “Phosphoglin”, which help restore hepatocytes and normalize blood flow in the liver. Also shown are agents that enhance the removal of toxins “Sirepar” and “Hepatosan”. The amino acids “Heptor” or “Heptral” will be useful.
Herbal products “Gepabena”, “Karsil” and “Hofitol” are also used. It is possible to treat gallstones using bile acid preparations, such as Ursofalk, Ursosan, Exhol and others. Patients must be prescribed a gentle diet, limiting the consumption of fatty, fried and spicy foods. It is important to get rid of bad habits - smoking and alcohol addiction, and also to avoid stress that puts stress on the liver.
Traditional methods
In combination with drug and surgical treatment, non-traditional methods can be used. They help to significantly improve the patient’s condition and reduce the severity of pigmentation. One such method is rubbing aloe, calendula and orange juice into the pigment. This should be done 3 times a day for 2 weeks. Once a week you can apply a mask of cottage cheese, ammonia, lemon juice and white clay. Ice cubes containing frozen decoction of mint, chamomile and aloe pulp will also be useful. They need to be rubbed into your face in the morning.
Laser treatment
The advantage of the procedure is the quick result.
If it is not possible to eliminate liver stars, plaques or spots using medication, then surgical removal of these tissues is used. For this purpose, a laser is most often used. It causes minimal damage to the skin and leaves no scarring or wounds. This procedure is painful and is performed under local anesthesia. The effect is noticeable after several courses of laser removal of formations. At the same time, the problem in the liver remains and formations can develop again if their immediate cause is not eliminated.
What is cirrhosis of the liver?
Cirrhosis is an incurable pathology in which the parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue. The mechanism of formation is associated with lipocytes, or Ito cells. Lipocytes exist in two states: quiet - they are responsible for storing vitamin A reserves, activated - they form scar tissue in damaged areas of the liver.
With constant exposure to viruses, alcohol, poisons, and toxins on the gland, Ito cells have to become more active. Areas of connective tissue grow, the parenchyma becomes islands with a fibrous surrounding. The blood supply to the organ is disrupted, the vessels have to be rebuilt, bypassing the affected areas.
With a decrease in the amount of healthy parenchyma, the gland ceases to cope with its functions. Hormones and toxins are not neutralized, enter the bloodstream and poison other organs. Varicose veins of internal organs appear. The functioning of the kidneys and brain is disrupted. The final stage of cirrhosis is fatal.
Liver cirrhosis develops over a long period of time and has four stages.
- Compensated. The damage is minor, the healthy part of the parenchyma copes with the functioning of the organ. Manifestations of the disease are invisible.
- Subcompensated. The defeat is massive. The load on the preserved part of the liver increases, and malfunctions begin. The first signs appear - dyspepsia, disruption of sleep and wakefulness, increased fatigue, decreased appetite, jaundice, weight loss.
- Decompensated. Connective tissue makes up most of the liver. The remaining healthy cells cannot cope with their functions. Decay products, not neutralized toxins, poisons, hormones poison the body.
- Terminal. Complete replacement of parenchyma with fibrous scars. The organ doesn't work. Numerous complications develop.
In the early stages of cirrhosis, external signs are not noticeable; they appear later, when the damage is significant:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- Itchy skin, worse at night.
- Disturbance in sleep and wakefulness.
- Yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes, sclera.
- Redness of the palms and soles of the feet.
- Abdominal enlargement due to weight loss.
- Gynecomastia in men, decreased libido.
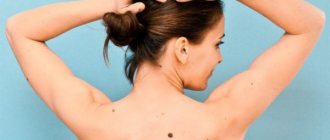
- Spider veins on the body.
Cause of spider veins
The reason for the appearance of stars in cirrhosis is the formation of collaterals, bypass paths for the passage of blood. Large vessels are compressed by scar tissue, and patency decreases. Additional highways from smaller vessels appear, compensating for the loss of blood supply. They become wider due to increased blood flow and lose elasticity. Dilated vessels shine through the skin, forming stars.
The causes of the appearance of stars in cirrhosis may be functional disorders of the liver, when toxins and hormones cease to be inactivated, and blood clotting is impaired. Smoking and alcohol aggravate the process. Stars are one of the skin manifestations that indicate a pathological condition. In combination with jaundice, this is a reason to seek medical help.
Why does itching occur?
Skin itching due to liver pathology worries the patient more than pain. It exhausts you and doesn't let you sleep. A man combs different parts of his body. Scratches appear on the skin, which quickly become infected and fester. Itching is not relieved by antihistamines and increases significantly with the appearance of jaundice.
The causes of itching are the combined effects of:
- stagnation of bile, blockage of ducts;
- increased concentration of bile acids in the blood;
- toxic and poisonous substances that are not neutralized by the liver.
What types of spider veins are there on the body?
Depending on the vessels undergoing pathological expansion, three types of asterisks, or telangiectasias, are distinguished:
- Capillary - inconspicuous, formed from small blood vessels.
- Venous - larger in size.
- Arterial - even larger, visible to the naked eye.
Asterisks in cirrhosis are red and blue. There are four types based on form:
- Spot. A dark dot surrounded by blue streaks of capillaries. Located on the legs. A significant amount is capable of forming spots.
- Tree-like. They look like a twig with branches, the color is blue, and are found in the thigh and lower leg area.
- Arachnids. They have a center, an arteriole, from which “spider legs” diverge - capillaries. Of red color.
- Linear. They look like parallel lines, of any color, favorite places of localization are the nose and cheeks.
Treatment of spider veins
To remove stars as a cosmetic defect, different techniques are used:
- Therapeutic. Wearing compression clothing, massages, using masks that strengthen facial blood vessels.
- Medicinal. Taking medications aimed at strengthening vascular walls - ascorutin.
- Surgical. Removing stars. Electrocoagulation is used - cauterization of localization sites. Radio wave surgery – removal using high frequency radio waves. Sclerotherapy is the introduction of a sclerosant into the vessels, a gluing agent that stops blood flow in the vessel. Ozone therapy is an injection of an oxygen-ozone mixture. Laser photocoagulation – burning with a laser beam.
- Traditional methods.
How do liver problems affect the skin?
The liver is a vital internal organ; it is responsible for the destruction and evacuation of toxic substances, cleansing the blood of impurities harmful to humans. The liver produces bile, which takes part in the breakdown of lipids and stimulation of the intestines. Minerals and vitamins are deposited in the tissues of the organ, without which adequate functioning of the human body is impossible.
The peculiarity of the liver is the absence of nerve endings, therefore, even with the development of serious diseases, it does not give such a symptom as pain. By the time obvious signs of the disease appear, the tissues of the organ are seriously affected, and the disease is difficult to treat. For this reason, it is extremely important to know and learn to identify the main signs of liver disorders.
What are the types of liver diseases?
According to statistics, over 200 million people all over the planet have experienced liver disease at least once in their lives.
Problems with the filtering organ cause human death in every tenth case of death. In terms of mortality, hepatitis is equated to pulmonary tuberculosis and AIDS. Most often, liver diseases occur due to viral infections, intoxication with toxic substances, and alcoholic beverages. Chronic pathologies become a predisposing factor in the complete degeneration of organ tissue, cirrhosis.
Hepatitis takes first place in the list of diseases, they can be:
The disease is also divided into acute and chronic forms.
With prolonged exposure to toxic substances, cirrhosis develops in the human body. This disease can be the result of genetic diseases, oncology of the hematopoietic system, necrotic processes.
Various benign and malignant neoplasms can develop in the liver. Doctors diagnose cancerous tumors of liver cells or metastasis from other internal organs, tissue abscesses, cysts.
What liver diseases cause changes in the skin?
Liver diseases vary in cause. All of them lead first to the functional inferiority of hepatocytes, then they destroy the organ and replace it with scar tissue.
- Inflammatory pathologies include: viral and toxic hepatitis, damage from tuberculosis and syphilis, abscesses, autoimmune diseases.
- Metabolic disorders are characterized by: alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatosis (fatty degeneration), alcoholic liver disease.
- Consequences of blunt trauma in the abdomen, ruptures, stab wounds, crushing from gunshot wounds.
- Diseases of large vessels: hepatic vein thrombosis, pylephlebitis (portal vein suppuration), portal hypertension in cirrhosis, fistulas and arteriovenous fistulas.
- Pathology of the bile ducts: intrahepatic congestion, acute and chronic purulent cholangitis, formation of stones from salts, congenital dilation of the ducts inside the liver with increased stone formation and small abscesses in the parenchyma.
- Tumor processes: cyst, hemangioma, hepatocellular and intraductal cancer, sarcoma, metastases.
- Parasitic diseases with localization of the focus in the liver are caused by: alveococcus, echinococcus, roundworms, opisthorchiasis, leptospirosis.
- Hereditary anomalies: complete absence or underdevelopment of the organ, narrowing of the ducts, fermentopathy with disruption of various types of metabolism.
In addition, differential diagnosis always takes into account the possibility of secondary liver damage caused by changes in other organs. Therefore, signs of congestion in heart failure, amyloidosis, blood diseases, renal and hepatic failure in diseases of the urinary organs are excluded.
Common liver signs and symptoms of liver disease
If liver function is disrupted, there is insufficient production of cholesterol and bile, a decrease in the efficiency of toxin evacuation, and difficulty in digesting food. Various liver pathologies have many similar symptoms.
Deterioration of health, asthenia
As a result of nitrogen metabolism, the body releases toxic substances that are dangerous to human health.
For normal functioning of the body, toxins are neutralized in the liver.
If there is a decrease in the ability to neutralize, the patient suffers from general malaise, deterioration of health for no obvious reason, and decreased performance.
- drowsiness increases;
- weakness is felt throughout the body;
- the person becomes overly irritable.
The patient gets tired quickly and has trouble sleeping at night. Even a long rest does not help to cope with disorders and feel better.
Dyspeptic phenomena
Among the common symptoms and dysfunction of the digestive system is dyspepsia.
For a number of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the symptoms may vary, but for liver diseases there is a general trend.
The diseases are expressed by stool instability, attacks of nausea, vomiting, successive alternation of constipation and diarrhea, and stool distortion.
In addition, problems with the liver can be suspected by a feeling of bitterness in the mouth or loss of appetite.
Pain in the right hypochondrium
You can talk about the development of pathologies of the filtering organ by a feeling of heaviness in the right side under the rib, discomfort. Soreness radiates to the area:
The nature of the sensations can be acute, pulling, it all depends on the etiology of the disease.
With partial or complete blockage of the intrahepatic bile duct, colic appears, accompanied by severe stabbing pain in the right side under the rib.
Hepatic lesions of the skin and its appendages
Problems with liver function can also appear on the integument; liver disease and skin symptoms are inextricably linked. Signs of damage to the filtering organ on the skin are varied; these can be rashes, severe itching, dermatitis, or even irreversible changes.
Hepatic skin itch
Itchy skin is a constant symptom of jaundice and occurs due to an increase in the level of bile acids in the bloodstream.
Some non-obstructive diseases make themselves felt precisely by intense itching, for example, hemochromatosis.
However, other ailments may not show signs of liver disease on the skin at all; they sometimes appear only before the appearance of jaundice or other specific symptoms of the pathological condition, accompanied by:
- rashes;
- unhealthy skin;
- peeling.
The skin itches briefly and paroxysmally, while other patients complain of constant and persistent discomfort. More often than others, the arms, legs, and torso are affected. Traces of scratching and round subcutaneous plaques of a yellowish color are visible on the integument, located on the folds of the skin and the face around the eyes.
Yellow discoloration of the skin or jaundice
With a diseased liver, symptoms on the skin are manifested by a change in the color of the integument, this is due to a sharp increase in the level of bilirubin.
At first, jaundice is visible on the sclera and oral cavity, then it spreads to the face, palms, soles, and gradually covers the entire body.
The distribution of yellowness on the integument is uneven; the majority of changes occur on the body and sclera. The symptom is much less pronounced on the lower and upper extremities.
Liver stars
An important diagnostic sign is the appearance of vascular:
Multiple pulsating areas slightly rise above the skin and are light in color.
Small vessels radiate from the stars, resembling the legs of a spider or a cobweb. They can appear on the back, neck, arms, shoulders.
Hepatic purpura
In liver diseases, hemorrhagic spots appear on the integument; in some patients, they are also detected on the mucous membranes. With mechanical pressure, hepatic purpura does not disappear, which distinguishes it from other types of rash.
Liver palms
A specific sign of liver pathologies is a change in the color of the palms to a bright red color. The symptom occurs with almost any type of chronic liver disease. If you press lightly on the stain, it will first fade a little and then recover.
- the thumb becomes smooth;
- significant elevation of the little finger.
Some patients are diagnosed with plantar erythema - staining of the soles of the feet.
Liver tongue
When chronic, the patient's tongue acquires a bright red color, it becomes swollen with a seemingly varnished surface. In some cases, the color of the tongue may appear dark red or even purple. A dry tongue will be a harbinger of liver failure. The lips and mucous membranes of the oral cavity acquire a specific carmine-red color.
Treatment
The vast majority of skin and other manifestations on the patient’s body regress with treatment of the underlying disease.
Perhaps the most emotionally unpleasant manifestation of liver pathology is skin itching. Treatment of skin itching in liver diseases comes down to eliminating the root cause. However, according to the results of scientific research, drugs that inhibit the absorption of bile salts by hepatocytes (rifampicin, fusidic acid) or prevent intrahepatic cholestasis (metronidazole) can be effective. The use of these and some drugs significantly improves the quality of life of patients.
It has been established that pulse therapy with metronidazole leads to rapid disappearance of itching in patients who are insensitive to therapy with other drugs. The antipruritic effect of metronidazole is also associated with changes in the metabolism of bile acids by small intestinal bacteria. However, itching may return 4–6 weeks after stopping metronidazole therapy. A repeated short course of treatment with metronidazole eliminates itching.
It is also known that metronidazole reduces the level of low-density lipoproteins by 10–20%, i.e. improves lipid metabolism. At the same time, metronidazole derivatives have not been studied as possible drugs for monotherapy of lipid metabolism disorders.
Modern medicine has achieved certain successes in the treatment of liver diseases and their complications. However, the possibilities of medicine are not limitless, so the chances of success are much higher with timely diagnosis.
Dermatologists and cosmetologists, when treating patients about unclear skin rashes, begin the examination with questions and tests characterizing the functioning of the liver. It is known that many chronic diseases of this organ proceed secretly for a long time. People may not be aware of the pathology, and skin changes are associated with age, infection, and hormonal fluctuations.
Skin rashes due to liver disease are a sign of damage to hepatocyte cells and their initial functional failure. But external manifestations can be indirectly related to the liver, since failure and overload in work contribute to a decrease in protective forces and often provoke other diseases.
Liver disease syndromes
A syndrome refers to several symptoms characteristic of a particular disease. The signs may fully correspond to the disease; more often the clinical picture consists of a pair of symptoms of varying degrees of intensity.
Mesenchymal inflammatory syndrome
Liver signs include mesenchymal-inflammatory syndrome, in which the patient:
- body temperature rises;
- lymph nodes swell and hurt;
- joint pain appears.
In a man, if he is addicted to alcoholic drinks, the spleen swells, the lungs and skin are affected, and lumps appear.
Cytolytic syndrome
As you know, the liver consists of hepatocytes. Membranes and cell walls under the influence of negative factors, viral infections, toxins and starvation undergo cytolysis and death. In this case we talk about cytolytic liver syndrome. Laboratory tests will show changes in bilirubin levels. The syndrome has diagnostic and prognostic significance for hepatitis, oncology, and cirrhosis.
Cholestasis
A sign such as cholestasis is observed when the outflow of bile from the external or intrahepatic bile ducts is impaired. There is simple and cholestasis of pregnancy. Symptoms help identify congestion in the bile ducts:
- skin itching;
- plaques on the upper eyelids;
- jaundice with a hint of green.
Cholestasis is characterized by abundant pigmentation of the skin, lightening of stool, and severe darkening of urine.
Portal hypertension
The occurrence of portal syndrome is provoked by a violation of blood flow in the veins of the liver.
As a result of the pathological condition, blood flow decreases and pressure inside the organ increases. The causes include mechanical damage, neoplasms, the presence of pathologies of blood vessels, chronic hepatitis, and parasitic infestations. There are several stages in the development of portal syndrome: initial, moderate, severe, complicated. The initial stage is characterized by moderate dyspepsia of the digestive tract, pain in the liver, increased gas formation, and loss of appetite.
At a moderate stage, the spleen swells and varicose veins of the esophagus develop. At an advanced stage, there are symptoms of ascites; a large amount of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. Noted:
- general swelling;
- subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- soreness.
If the situation worsens, portal hypertension enters a complicated stage. It is expressed by internal bleeding in the abdominal cavity, a significant disruption of the functioning of the digestive system.