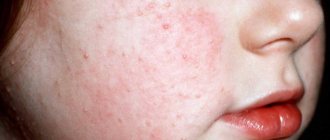
It occurs quite often in children and adults. Like any other virus, HPV enters the body unnoticed. It can manifest itself under favorable conditions.
Important! It is necessary to distinguish between Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and Papilloma formation.
- Papilloma is a benign formation.
- Exophytic condyloma (wart, anogenital wart), associated with HPV.
- Precancer and cervical cancer.
If the last two formations can and should be treated, then Papilloma PL is considered a benign formation. This virus causes troubles and problems when it manifests itself on internal organs - kidneys, urinary tract, vagina, mucous membranes. Papilloma, unlike warts (condylomas), has a stalk - thin, wide, and very rarely the stalk is absent.
A child may develop viral PL at the time of birth if the mother has such formations in the vagina or cervix. A child sometimes takes his first breath while walking along paths. At this moment, the virus can enter a small organism that does not yet have protective barriers.
Which doctor should a woman see for examination? Doctor dermatovenerologist is the first instance. It is possible to remove papillomas that are in the genital tract before pregnancy, after the end of breastfeeding. If the growths are located on the skin of the limbs and neck, then they will not affect the baby’s health.
If papilloma or other types of HPV growths are located along the path of the child during childbirth and reach the size of a chicken egg or a human fist, then removal is mandatory, but not earlier than 28 weeks of pregnancy.
The papilloma virus is transmitted mainly through sexual contact. You can also become infected at home in a sauna, gym or beauty salon. The virus is transmitted through household contact if the skin is broken, through abrasions, cracks and scratches.
Prepare for conceiving a child - get examined. Remember that being a carrier of the virus does not necessarily mean you will get sick. Remove papillomas that can affect your health and the health of your baby.
Causes of papillomas in children
There are a number of reasons why growths can form on a child’s body, namely:
- infection by the mother of the baby during childbirth;
- communication between children at home, in preschool and school institutions (use of common household items, toys);
- damage to warts by children themselves (self-infection);
- the presence of small wounds and abrasions, bumps on the arms and legs (they become infected);
- children's exposure to common colds;
- the baby has allergies;
- digestive problems;
- the presence of parasitic diseases;
- various stressful situations.
These reasons are not all. The period from the penetration of such an ailment as the human papillomavirus in children into this small organism until the formation of the first warts lasts up to six months. Adults may also suffer. However, if the baby is healthy and has a strong immune system, then he himself is able to defeat the bacteria, and as a result, papillomas will not appear anywhere in newborns. But even in those cases where formations are discovered, they can go away on their own over time, leaving no trace behind. The reasons for this have not yet been studied by scientists.
Clinical picture
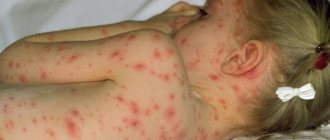
The main sign of the disease is the appearance of a tumor on the mucous membrane or skin. More often there are no symptoms. But small papillomas are capable of uniting into colonies of overgrown epithelium, the length of which reaches 6 centimeters. When they are damaged, the virus spreads throughout the skin, causing infection of the wound.
Pustules appear on the skin. The following signs are observed:
- problems swallowing;
- difficult nasal breathing;
- speech delay;
- problems with walking;
- decreased hearing and vision.
Some types of HPV (16, 18 and 52) are characterized by degeneration into a malignant process. To prevent papilloma from appearing in a child, Komarovsky advises vaccination at the age of 13, before the start of active sexual life. If the growth is already present on the skin or mucous membrane, a comprehensive diagnosis is indicated:
- PCR. Determining the concentration of the virus in the circulatory system using its DNA.
- Biopsy. Identification of the peculiarities of tissue formation and the nature of the localization of its layers.
- Histology. The diagnostic result helps make a prognosis by assessing the likely risk of cells transforming into cancer.
A blood test is prescribed to determine the type of virus. It is recommended to treat papillomas in a child after consultation with an oncologist and surgeon.
Types of child HPV and symptoms
The most common types of HPV that develop in children are:
- Papillomas in the larynx (when a baby becomes infected during childbirth from the mother). They are localized precisely in the throat and throat cleft, and are very dangerous; if their number increases, or an infant or older child gets an acute respiratory infection, they begin to swell and the baby may suffocate.
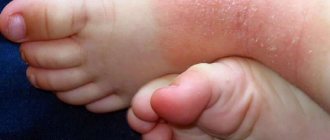
- Rough, red-brown spots on the feet and hands (called verrucous dysplasia) are the most dangerous form of HPV in children because these benign growths can develop into malignant tumors.
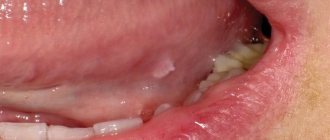
- Thin thread-like growths on the mucous membrane (tongue, palate, cheeks) - epithelial hyperplasia - cause discomfort in little ones, often get injured, which leads to secondary infections.
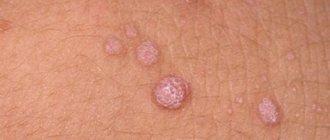
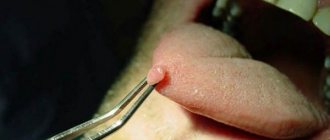
- Warts (simple papillomas or vulgar). These growths are small, roundish in shape, rough to the touch, and can reach up to 1 cm in diameter. They are mainly observed on the fingers, palms, and buttocks.
- Flat papillomas are neoplasms slightly raised above the skin, flesh-colored. Localized on the arms, knees, and lower part of the face. Sometimes they itch.
- Slightly elongated, flesh-pinkish color, droplet-like formations on the body are filamentous viral tumors. Most often found in the armpits, neck, face, chest. They are most susceptible to injury when dressing a child.
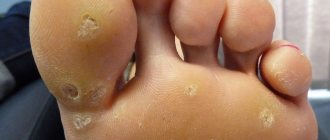
- Plantar warts are also not very large in size, dense, yellowish in color, and can sometimes look like dark dots. Appear on the foot.
Several types of HPV can appear on a child’s body at the same time. The first three types are the most dangerous; due to their location where they accumulate when exposed to external factors (infections, injury, etc.) they are difficult to treat. If a formation on the body is torn off or damaged by clothing, then you need to treat the wound with hydrogen peroxide until the bleeding stops, and then lubricate it with brilliant green. But for children of middle and high school age, iodine can be applied to the affected area, and then covered with an adhesive plaster.
Injuries to the mucous membrane (especially in the mouth - this is the first sign of starting treatment) can be rinsed with a disinfectant solution recommended for treating the oral cavity. But it is advisable to be extremely careful with such drugs, especially in young children whose symptoms have just begun to appear. Therefore, if you find such troubles in infants, it is better to consult a specialist.
What is HPV
Papillomavirus (HPV) is widespread among children. The infection occurs through close contact with a sick person or through communication with a carrier who does not have symptoms of the papilloma virus.
The virus enters the body and provokes papillomavirus on the child’s hands, face, neck and soles of the feet. Children who visit public places (swimming pool, bathhouse, kindergarten, educational institutions, etc.) are most often exposed to this pathology.
Routes of infection with papillomavirus
The human virus is transmitted very quickly; even a small amount of close contact between the skin of a healthy child and the skin of a virus carrier is sufficient.
A team of doctors identifies several main routes of HPV infection in children:
During delivery. If a young mother is a carrier of the genetic type of papilloma virus, then the risk of infection of the newborn at birth is very high. This type of infection occurs when the baby's skin comes into close contact with the vaginal lining of the mother giving birth to the baby.- Direct contact with the skin of an HPV carrier. If an adult has symptoms of the papilloma virus on his hands, then the child may be infected with the latter’s skin. The risk of infection increases in the presence of dermatological damage to the child’s skin - abrasions, bedsores, ulcers.
- Contact with household items. This cause of HPV infection is relevant for children attending sports clubs, swimming pools, schools, and kindergartens. The papilloma virus is transmitted to a healthy child with the help of other people's towels and combs. In kindergartens, healthy children are infected with HPV when playing with ordinary toys. Older children can become infected with the papilloma virus through water when they go to the pool or bath.
- Spontaneous infection of the body. If a child “suffers” from bad habits—biting his nails, constantly holding his hands in his mouth—then an infection that gets on the skin can easily be transmitted to the entire body. The risk of spreading the infection increases if the child's papilloma appears earlier or is already present.
are provocative factors for HPV infection:
Common colds and infectious diseases in children;- Allergy;
- Diabetes;
- Chronic diseases (tonsillitis, bronchitis, etc.). );
- Internal parasite infection;
- Tuberculosis;
- Failure of the digestive system (dysbacteriosis, etc.);
- Stress, nervous disorders;
- Long-term treatment with strong drugs (antibiotics, hormones, etc.).
The reasons given above show how the papilloma virus enters the body.
The pathological process of infection of the healthiest child’s body takes the following form:
The ideal conditions for virus activity are warm and humid conditions. In the external environment, as well as without contact with skin, the activity of the virus decreases.- As soon as the virus penetrates the surface layer of the child's skin, the incubation period begins, which can last up to 3 months. If the child’s body is weakened by the passive functioning of the immune system or other pathological changes, then the symptoms of papillomavirus may appear earlier.
- Papilloma becomes a provocateur of pathological changes, which leads to visually unaesthetic growth on the surface of the skin.
What if you have papillomas on your chest?
Types of papillomas
There are several subtypes of papilloma that can develop in children of different age categories:
- warts (simple papillomas). In accordance with their appearance, the new formations are rounded small cones, covered with a hard cornea on top. The size of warts can vary from a few millimeters to 1 centimeter. The color of the simple papillae is light or dark brown. Such neoplasms most often occur on the child’s palms, buttocks and fingers.
Warts on the hand - Flat papillomas. The photograph shows the tumor as a small, rounded nodule that only briefly rises above the skin. Flat papillomas are identical in color to the natural skin tone. In most cases, new growths “grow” in the lower part of the face and on the child’s knees or palms. It is important to note that in newborns, flat papillomas itch and itch, all this leads to severe irritation of the body area, which is suppressed by the virus.
Flat papillomas - Viral tumor of sewing thread. The external feature of the neoplasm is a small teardrop-shaped tumor that adheres to the skin with an elongated leg. The color of the tumor is often identical to the natural skin tone, but may also have a pinkish-red tint. In most cases, the viral tumor is located in the child's groin, neck, chest and face. A filamentous viral tumor poses a danger to a child, since upon contact with clothing it easily injures itself and bleeds, and open wounds easily penetrate due to infection.
Papilloma in the form of threads on a child’s nose - Papilloma in the basement. The external feature of the knots are small hard cones that are located at the base of the toes. The color of the nodes varies from fleshy to pale yellow. Epithelial hyperplasia
Single wart - . Formation on the oral mucosa - on the tonsil, tongue, palate, inner cheeks. As for the external features, such papillomas are thin, stretched threads, which is very unpleasant for the child. The growths are easily flammable, injured and susceptible to infection, so they must be treated promptly. Epithelial hyperplasia in a child
Which doctor can help with papilloma in a baby?
It should be understood that HPV in children is of a bacterial nature, and treatment must be carried out in a complex manner: simultaneously aimed at both getting rid of “surprises” and strengthening the child’s immunity. If growths are detected, first of all you should contact your pediatrician. During the initial examination, the doctor will determine the type of neoplasm and refer you for tests to determine the causes of infection. If necessary, will issue a referral to more specialized specialists:
- dermatologist;
- surgeon;
- immunologist;
- in rare cases, see an oncologist.
There is no need to be afraid of this. After all, in any treatment the main thing is to get rid of problems, and not to create new ones. Therefore, a timely examination can protect the growing body from very serious problems in the future.
How dangerous is the human papillomavirus in a child?
The lack of necessary therapy in the early stages leads to a significant growth of papillomas in adulthood, leading to physical discomfort and complexes due to the appearance of their disease. A person will repeatedly try to get rid of them on his own. With frequent injuries, the risk of secondary infection increases. It is necessary to follow all recommendations and doctor’s advice, monitor the health of a child with HPV, provide him with vitamins, adequate nutrition, and teach him to maintain personal hygiene in order to avoid the possibility of infection.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Most suitable treatments for children
Treatment of papilloma in children with mild stages of HPV infection (single warts that do not cause much harm other than external discomfort) does not require radical measures. Often it is enough to take a course of vitamins, antiviral and immune-strengthening drugs. If complications occur:
- papillomas increase in size;
- their number increases;
- new areas of skin are affected;
- the growths change (swell, pus begins to ooze out, etc.);
- are often exposed to various injuries.
Treatment must be started immediately. Especially when laryngeal papillomatosis is detected.
To disappear common warts on the hands and feet in children, you can use antiviral and immunostimulating ointments, creams, gels, for example,
- "Viferon" (the most gentle of all drugs).
- "Oxolinic ointment."
- "Salicylic ointment" (from 12 years of age).
- other.
They should only be bought in pharmacies, used according to a doctor’s prescription and in full accordance with the instructions. Apply only to the formation, and under no circumstances should you apply burning or cauterizing medications to the delicate baby skin.
How the virus spreads
- A child can become infected with the virus while still in the womb, as well as during childbirth.
- Papilloma can be transmitted through contact with an infected person. If parents or someone they know is a carrier of the virus, it can easily be passed on to the child.
- Due to the lack of basic hygiene, the papilloma virus can also arise. Therefore, a child from an early age must be taught to keep his body clean.
Statistics show that the congenital virus in children is most often localized on the mucous membrane. And the acquired one is on the face, hands, feet and armpits.
According to WHO, 8 out of 10 people are carriers of the virus. However, it does not manifest itself immediately. Serious disruptions must occur in the child’s body, only then unpleasant growths will begin to appear on the surface. Here's what can trigger virus activity:
- weakened immune system;
- stress;
- change in climatic conditions;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- allergy;
papilloma in a child's nose
Unconventional treatment of papillomas
Recently, the unconventional daily method of suggestion and self-hypnosis has become increasingly popular. The child is told that all his “warts” (warts, in the sense) go away on their own, so that he imagines that they are not there at all, and never happened. This is a kind of training.
When the damage to the body by HPV is more serious, or it directly concerns the papillomavirus, which is actively multiplying (progressing), then it is highly advisable to begin radical treatment of papilloma in children. Modern medicine offers several ways to remove tumors:
- using a laser beam;
- freezing with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction);
- electric shock (electrocoagulation);
- surgical (conventional operation with a scalpel using anesthesia).
Each method has its pros and cons, side effects and contraindications. In any case, radical treatment is prescribed and carried out by a specialist doctor, taking into account the age and other characteristics of the child’s body.
Tips for parents
The danger of neoplasms in a child often lies in the fact that he can accidentally damage it or deliberately pick it apart. The parents’ task is to explain to the child that under no circumstances should the sore be touched. In addition, it is important to know:
- papillomas cannot be removed independently at home, as the virus will spread even more;
- any damage to the growths can provoke their further growth and proliferation over a larger surface of the skin or mucous membrane;
- the child needs to be taught regular hygiene, since he can catch the virus almost anywhere;
- Neoplasms do not go away on their own or without the help of specialists, so self-medication is not recommended.
Is it possible to use folk remedies?
The answer to this question is very ambiguous. On the one hand, these methods are akin to self-medication, which sometimes leads to complications and other unsightly consequences. Such methods require regularity and many procedures; they take a long time (sometimes from 1 to 2 months). On the other hand, natural substances are much harmless than medications. Therefore, if the baby steadfastly endures all the hardships of such “executions,” then you can try it at your own peril and risk.
Warts on the legs and arms are most amenable to this treatment. They get rid of them using compresses of grated raw potatoes, red rowan berries; for older children, gruel of crushed garlic is used. All mixtures should be applied only to the growths, covering healthy skin with an adhesive bandage. And grated potatoes are first laid out on paper, then attached to the wart and kept overnight. You can also make compresses and rubs every day from the juices of celandine, dandelion, green varieties of apples, and milkweed.
Methods for treating papilloma
Komarovsky argues that treatment of the virus cannot be neglected. And here he is right. This disease will have to be constantly monitored and all possible preventive measures must be used so that the papillomavirus does not begin to progress.
Medical professionals recommend using an integrated approach to treating pathology. Treatment for human papillomavirus involves strengthening the immune system, administering antiviral therapy, and removing skin lesions if necessary.
- The doctor may prescribe ointments to get rid of benign tumors. Good ones are Oksolin, Viferon, Panavir, Salicylic and Zinc ointment, Balsamic Liniment (according to Vishnevsky), Malavit, Bonafton, Hydrocortisone, Solcoseryl.
- Treatment with folk remedies in childhood improves immunity well and can cope with the resulting growths in the larynx. For example, inhalations with celandine. Take 15 ml of fresh plant juice, pour it into 300 ml of boiling water, ask the child to breathe in the steam for 10 minutes.
- Papilloma of the tongue is treated by rinsing the mouth. Squeeze the Kalanchoe juice and rinse for a few minutes. This remedy is also suitable for growths in the mouth.
The appearance of a formation on the body is an unpleasant sight. You can get rid of them using the resin of coniferous trees. Treatment with resin has antiseptic and healing properties. Recipe:
- in a 1:1 ratio, combine resin with any oil (olive, castor, burdock, vegetable);
- Place the product in a water bath and heat until warm.
Apply the resulting balm to the growth using a bandage, rubbing a little. Secure with a bandage and leave for 20 minutes. Home remedies are less safe than medications, but no less effective.
Prevention of occurrence
The best and main preventive method in the fight against any viruses (including HPV) is to strengthen the body’s protective functions. And this means:
- mandatory daily walks in the fresh air;
- strict adherence to all norms and rules of personal hygiene in public places;
- eating healthy foods;
- timely treatment of small wounds, cuts and abrasions on the skin with antiseptic substances;
- maintaining a healthy atmosphere in the family, in kindergarten, at school (do not expose children to stress, pay attention to depressive states).
Teach your baby to a healthy lifestyle. This will save both you and him from many life problems and troubles. You should never pick or cut off the growths yourself, even when symptoms of proliferation, blackening or inflammation have already manifested themselves. Contact your pediatrician.
The article has been verified by the editors