A developmental defect characterized by the appearance of a formation consisting of nevus cells is called a nevus. Nevus is more common in children and adolescents, and with age, as a rule, the number of tumors decreases. Such formations appear on the skin, infrequently on the mucous membranes, conjunctiva and choroid of the eyeball. These formations are considered benign and do not require serious treatment, but some of their types are precancerous conditions, which can later develop into a cancerous tumor.
The growth of moles in a person begins from the first days of life and this is not a pathology.
Why moles appear
When looking for an answer to the question of how moles appear, you can find out that they are congenital and acquired. Congenital nevi can be detected already in newborns. Acquired spots first appear, as a rule, in early adolescence and are associated with an active period of hormonal changes in the body. The age of appearance of moles is usually considered to be 10 years. Hormonal changes in the human body are associated not only with puberty and the rhythm of sexual life, but also with reproductive health, with the consequences of taking hormonal and other medications.
The number of nevi and the time of their appearance are unequal in males and females. The sudden appearance of moles is observed mainly in women due to the frequency of hormonal changes occurring in their bodies (the onset and course of pregnancy, the consequences of termination of pregnancy, the lactation period, the menopausal period in a woman’s life).
Prolonged unprotected exposure to direct sunlight also causes the appearance of nevi. “Favorite” places for pigment spots to appear include the face, neck, décolleté, back, arms, legs; in some cases they can be observed on the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, and genitals.
An increase in the size of the spot is a reason to consult a dermatologist for advice in order to eliminate a possible threat to health. Moles grow on the body under the following circumstances:
- mechanical injury (for example, during shaving, depilation, bruise, friction);
- intense ultraviolet exposure when in direct sunlight or in a solarium;
- active hormonal changes in the body;
- hereditary nature of the shapes and sizes of nevi.
What should I do to prevent the problem from returning again?
A mole is a congenital malformation of the skin or a benign tumor that forms at different stages of life. The following actions can be taken to prevent nevi:
control over exposure to the sun.
Your child should not be under the sun at dangerous times, namely from 11.00 to 16.00. if this cannot be avoided, it is important to wear clothes made from natural fabrics to protect the skin and also to avoid overheating. Don't forget about the need for a headdress.
- Using sunscreen. Despite the degree of dark skin, children are exposed to the sun much faster than adults. This is why it is worth applying sun protection cream to exposed areas of the body.
- Wearing loose and comfortable clothes and shoes made from natural materials. Nowadays, many modern parents are trying to buy stylish things for their children.
But during the summer season and hot days, it is important to consider not only the beauty, but also the safety of certain items of clothing. Often they protect against the harmful effects of the sun and the appearance of moles.
Varieties
There are conventional classifications of nevi based on their color, shape, size, origin, and the degree of threat of cancer development.
Based on color, including shades of color, moles are divided into brown, red, black, purple or blue. The appearance of a nevus of a certain color on a person’s body is associated with his skin color type.
Neoplasms can have the following typical forms:
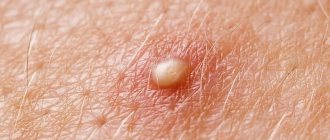
- flat appearance (such formations are considered absolutely safe);
- convex appearance, sometimes in combination with growing short hairs;
- oblong appearance;
- round view;
- with a smooth structure;
- with a rough structure.
Pigment spots are divided into three types based on size:
- small (up to 1.5 cm in diameter);
- medium (up to 10 cm in diameter);
- large (several times larger than average in diameter).
Large pigmented neoplasms have a congenital appearance on the human body.
Classification by origin:
- vascular (appear as a result of pathology in the development of blood vessels);
- pigmented (appear due to significant production of melanocyte cells containing pigment).
According to the degree of threat of cancer, nevi are divided into two types:
- melanoma-free;
- melanoma-hazardous.
Types of nevi
It is customary to classify moles as follows:
| Type of moles | Description |
| Angiomas | They are formations that appeared due to the expansion of blood vessels. They have a red-blue color. |
| Flat | Pigmented spots located in the upper layers of the skin. Formed due to increased accumulation of melanocytes. |
| Convex | They occur in the deep layers of the skin and have a bumpy surface. The diameter of such nevi is no more than 1 centimeter. Sometimes hairs grow from such moles. |
| Blue | Smooth formations whose shade varies from blue to light blue. They can be either small or quite large. |
| Large pigmented spots | Most often they are observed in a baby at birth and do not stop growing until old age. There are beige, brown and black. |
Causes of moles
The appearance of nevi (their color, shape, size) makes them quite noticeable on the human body, especially if their presence was not initially indicated in any way, that is, they were simply absent. The appearance of new moles along with existing ones, as a rule, arouses curiosity and certain concerns about their safety and aesthetics. Assistance in conducting a diagnostic study of nevi can be provided by a dermatologist, who, in the process of collecting the necessary medical history, can clarify when the mole appeared, whether there are growing moles on the body, whether the color of the nevus has changed, whether pain or itching has occurred even occasionally in the areas where pigmented formations are located , burning, strange discharge.
The factors that provoke the appearance of nevi are different and have age-related characteristics.
Often, parents notice the presence of moles or birthmarks on the body of a newborn child and experience certain concerns about their origin and safety for the baby. In most cases, newborn girls become carriers of nevi. An infant or newborn is considered a child from the moment of birth to 1 month of life.
The reasons for the appearance of moles in infants are as follows:
- hereditary factor (genetic predisposition, since genetic information is encoded in DNA and is transmitted from parents to offspring);
- premature birth of a baby or prematurity (fetal maturity factor);
- level of skin pigmentation (very light skin of the baby and his parents);
- disturbances in the functioning of the mother's hormonal system during pregnancy (hormonal surges);
- the mother of the baby suffers a genitourinary tract infection during pregnancy;
- adverse chemical effects and exposure to various types of radiation (including ultraviolet radiation) on a pregnant woman;
- traumatization of an area of the baby’s skin with a hidden mole due to external influences (for example, insect bites and/or abrasions received, for example, during childbirth);
- targeted exposure to ultraviolet sunlight on the baby's skin.
- Nevi and birthmarks can also occur in infants. An infant is considered a child from the neonatal period to 1 year.
The appearance of moles in infants is explained by similar reasons for the appearance of moles in infants.
The appearance of moles in a child is a natural process that accompanies the growth and formation of a young body. Such neoplasms, most often, do not pose a threat to the baby’s health, but require passive monitoring.
The reasons for the appearance of moles in children can be outlined as follows:
- genetic factor or hereditary predisposition;
- period of active physiological development of the child;
- regularity of exposure to direct sunlight on the child’s body;
- chronic nature of certain diseases of internal organs and systems;
- inflammation of the skin;
- mechanical damage to skin tissue.
Moles tend to actively appear in adulthood. The appearance of moles in adults can be explained by the following reasons:
- hormonal surges. Hormonal imbalance provokes the appearance of an accumulation of melanin cells in the body of women (during pregnancy, its termination, in the postpartum period, during menopause). In men (in case of malfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, during surgery or negative effects on the groin area, with an increased amount of estrogen hormones). Regardless of gender - in a situation of significant stress, during a severe course of a somatic illness;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays (in the form of direct sunlight, when visiting a solarium, in the process of getting sunburn);
- disruption of the functioning of internal organs and systems (susceptibility to viral, dermatological diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, lipid metabolism disorders);
- insect bites and abrasions (external mechanical impact leads to the appearance of microwounds, microcracks in the skin, which, in turn, provokes the grouping of melanin cells at the site of injury);
- genetic predisposition (inheritance of moles along a related line);
- natural aging of the body (moles act as a sign of biological deterioration of the body).
Is the appearance of new moles dangerous?
The appearance of new individual moles or new clusters of nevi on the skin cannot go undetected and can cause some concern regarding their potential danger to the health of a particular person. An accurate conclusion about the nature of nevi on human skin can be made by a qualified specialist in the field of dermatology and oncology after conducting a series of special diagnostic studies. A simple initial physical examination of your own moles can be carried out independently, focusing on certain criteria for their examination. The following moles are considered melanoma-free:
- there are no discharges from the neoplasm (including bleeding), it has a complete appearance;
- throughout the entire period of existence of the neoplasm, its color, size, and shape are constant;
- the nevus is not covered with scales;
- there is no pain, itching, or inflammation in the area where the nevus is located.
It is believed that it is advisable to independently examine your own body to exclude anomalies in the appearance of nevi at least once every three months. Such an examination can be carried out with the assistance of close relatives.
Thus, the very fact of the appearance of new moles is a natural process of physiological change in the human body, but due to the unpredictability of the impact of unfavorable external or internal factors, occasional passive monitoring of the condition of the nevi is necessary.
Video consultation with a pediatrician
Watch the video for a detailed consultation with Dr. Komarovsky about moles, warts, molluscum contegium and other skin problems for children. Parents, most importantly, don’t panic!
When do children get moles? Most often, dark spots on the skin form some time after birth. This is influenced by many external and internal factors. Parents need to understand this issue well in order to promptly identify possible violations.
Difference from melanoma
Ordinary moles are quite harmless to the human body, but when exposed to unfavorable factors, they can degenerate into an aggressive malignant neoplasm called “melanoma” or skin cancer.
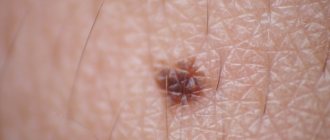
Characteristic signs of the degeneration of an ordinary mole into melanoma are:
- surrounding the nevus on the skin with a rim of a cluster of red or shades of red cells;
- microdamages on the surface of the nevus, visible to the ordinary eye;
- the originality of the color of the nevus on its entire surface, inclusions of blue, red, black colors;
- the appearance of ordinary or numerous scales on the surface of nevi;
- change in the shape of the nevus due to its growth to the sides;
- fuzzy or sharp-angled edges of the nevus;
- sensations of thickening of the skin area in the area of the nevus or an increase in the diameter of the tumor (especially more than 1 cm);
- inflammation, painful tingling, itching at the site of the nevus;
- bloody and other discharge from the neoplasm;
10) accumulations of cells in the form of nodules along the edge of the nevus.
Thus, knowledge of the critical features of malignant formations can contribute to the timely identification of dangerous nevi during their independent examination.
When should I delete it?
Often acquired types of formation in children do not require any treatment, but there are indications when a nevus needs to be removed:
- cosmetic defect;
- if education is located in places where it is difficult to control;
- if the boundaries are unclear or the size of the formation is large;
- nevi, which have a high risk of developing into a malignant tumor;
- small congenital formations of an unusual appearance must be removed before reaching 12 years of age;
- when there is a significant number of neoplasms;
- nevi with intense color, which are located on the extremities, mucous membranes, and conjunctiva.
- if the shape and size changes;
- frequent nevus injury.
Indications for immediate removal of nevus
- increasing its area and height;
- when the intensity of pigmentation increases;
- if a halo of pigment appears around the nevus;
- with inflammation of the formation;
- if the nevus itches;
- when erosion or bleeding occurs.
How does the removal take place?
Removal of skin tumors is carried out by a qualified specialist in the field of dermatology and oncology. If it is necessary to remove a mole for aesthetic purposes, no preliminary preparation is required. When removing a pathological mole, it is necessary to first undergo certain tests and conduct a specialized study. During the removal process, the specialist may suggest the use of local anesthesia. The most common methods for removing nevi are the following:
- using a laser;
- using nitrogen (cryodestruction);
- surgical intervention;
- using radio waves (radio wave removal);
- using high frequency current (electrocoagulation).
When a pathological mole is removed, its element must be sent for histological examination. Medical observation continues to monitor the patient's condition in the postoperative period.
Diagnostic methods
When a suspicious mole is detected in a child, the doctor uses the following diagnostic procedures to determine its condition:
- Visual inspection. The doctor examines the formation, measures its diameter, evaluates its shape and color.
- Dermatoscopy. Using a special instrument, a dermatologist can examine the mole at multiple magnification. Dermatoscopy allows you to determine the presence of oncology in the early stages.
- Digital dermatoscopy. The latest diagnostic method, during which a skin formation is displayed on the screen, magnified thousands of times.