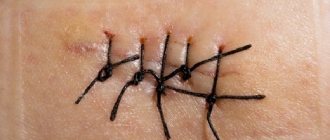
Main types of postoperative sutures
Any surgical intervention leaves behind a scar. The more complex the operation, the deeper the scar remains and the slower the healing process. In addition, the physiological characteristics of the human body play a huge role, in particular the supply of the skin with the necessary amount of blood.
Proper care of the scar left behind allows the wound to heal faster and more gently, leaving minimal damage. Caring for postoperative sutures is necessary so that they tighten well and do not give the person any unpleasant sensations. Postoperative scars are divided into several main types:
- Normotrophic scar. This type of scar is considered the simplest. It forms in most cases after shallow surgical interventions. As a rule, this scar has not too noticeable defects and has the same shade as the surrounding skin tissue.
- Atrophic scar. Formed when moles or warts are removed. The tissue of this type of scar slightly dominates the formation itself and looks like a hole.
- Hypertrophic scar. It is formed when suppuration appears or as a result of trauma. To avoid such a scar, it is necessary to care for the wound with ointment to heal the sutures after surgery.
- Keloid scar. This scar is formed on the skin, which is poorly nourished by blood, and in the case of deep surgical intervention. This scar is pinkish or white in color, protruding above the main level of the skin . Sometimes it gives off shine.
What to do if the wound does not heal
Inflammation of the wound after treatment occurs for several reasons: infection, boil formation, low immunity. In overweight patients, inflammation occurs due to improper drainage.
To prevent complications, consult your doctor. Before your visit, clean the incision, remove any exudate, and avoid lifting heavy objects. Only a specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis, prescribe treatment and correct treatment of the wound for inflammation after surgery.
The article has been verified by the editors
Treatment of scars at home
In order for postoperative scars to heal easily and quickly, without leaving behind painful complications, they must be properly cared for. You should know how to treat a postoperative suture for better healing. Basic care involves treatment with an antiseptic. The simplest means for processing:
- Zelenka, which is a disinfectant and antibacterial agent.
- Alcohol can remove any contaminants and kill all pathogenic bacteria.
- Thanks to iodine, healing can be accelerated.
You can use special products designed to speed up the healing of postoperative scars. These include:
- Fukortsin. With its help, high-quality treatment of the skin is carried out, providing proper care for postoperative scars.
- Levomekol ointment. Accelerates the healing process, nourishes the skin.
- Ointments with panthenol - helps tighten scars.
- Contractubex or Mederma. Used in the second or third month after surgery to smooth out the skin and tighten the stitches.
- Sea buckthorn and milk thistle oil. Nourishes the skin, heals wounds and promotes smoother tightening of postoperative sutures.
Wound care after specific operations
There are specific operations, the care for which is different and carried out carefully.
| Circumcision | The procedure is done for children, in adulthood due to phimosis and other diseases. Treatments are carried out within two days after leaving the hospital. The frequency of gauze renewal is from 3 to 6 times a day. As it heals, it is reduced to one. It is necessary to use special underwear with a frame. Fibrin may form during dressings; it is washed off with hydrogen peroxide. Maintain bed rest. |
| Trephine biopsy | The bandage is removed one day after surgery. The skin near the wound must be kept clean and treated promptly. |
| Tracheostomy removal | Pay special attention to preventing infection. Use sterile wipes. A bandage for the skin around the tube is impregnated with furatsilin or a solution of potassium permanganate. If mucus forms after surgery, it must be removed with a sterile catheter. To thin the secretions, 4% sodium bicarbonate is administered before cleansing. To avoid stomatitis and wound formation, the oral cavity should be rinsed with hydrogen peroxide. |
| Cryodestruction of basalioma | Treatment after surgery is carried out with antiseptic agents as prescribed by the doctor. Next, a sterile bandage is applied. The resulting bubble cannot be pierced with a syringe. Wear the bandage until complete healing. During the recovery process, do not visit the sauna, solarium or bathhouse. |
Taking medications in the form of tablets is prescribed by a doctor.
Self-removal of stitches
Sometimes postoperative sutures can be removed independently at home, but subject to the doctor's permission. You need to know that there are two main types of seams.
Immersion - applied with thread, made of natural materials. Its advantages are that the material is independently absorbed by the human body and is not rejected. The disadvantage is that it is less durable. Removable - removed only when the edges of the incision are fused and are able to show how well the healing is proceeding. It is applied using silk, nylon, nylon, wire thread, and also a staple.
When removing threads at home, it is also necessary to take into account the timing after the operation. The approximate timing of suture removal after surgery will be as follows:
- From 1 to 2 weeks - for head surgery.
- From 2 to 3 weeks - in case of amputation.
- About 2 weeks - when opening the abdominal wall. In this case, the period will depend on the depth of penetration.
- From 1.5 to 2 weeks - on the chest.
- 2.5 weeks - for stitches in an elderly person.
- From 5 days to 2 weeks - after childbirth.
- From 1 to 2 weeks - for caesarean section.
As mentioned earlier, stitches can be removed at home yourself . Some rules must be followed:
- It is necessary to remove postoperative sutures carefully and carefully, remaining calm - only in the absence of an inflammatory process.
- To remove stitches, you will need two tools: tweezers and nail scissors. Before the process itself, the instruments must be thoroughly treated with alcohol.
- Before work, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water twice and put on medical gloves. You can treat your hands with an antiseptic.
- All manipulations must be carried out under a bright lamp in order to carefully see the entire process.
- Next, the seams are cut and the maximum number of threads is removed. The edges of the protruding threads need to be picked up with tweezers and gently pulled until the piece comes out of the skin.
- When absolutely all the pieces are pulled out, treat the wound with antiseptic ointment with antibiotics.
You need to have sterile bandages and tissues and a furatsilin solution with you - for the safety of the suture removal process, so that infection does not get inside.
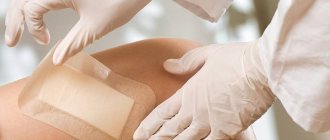
How to process seams
If the operation was successful, the patient is receiving home treatment and the sutures are not infected, their treatment should begin with thorough rinsing with an antiseptic liquid. To do this, you need to take a small piece of napkin with tweezers and moisten it generously with peroxide or alcohol. Then use a blotting motion to work the seam and the area around it. The next step is to apply a sterile bandage, previously soaked in a hypertonic solution and wrung out. You need to put another sterile napkin on top. At the end, the seam is bandaged and sealed with adhesive tape. If the wound does not fester, this procedure can be carried out every other day.
The use of folk remedies
To improve the condition of the skin, smoothing seams and reducing scars, it is necessary to act on problem areas in a comprehensive manner, using medications and folk recipes. In this case, the following folk remedies can help:
- Essential oils. The oil or mixture of oils will help speed up the healing of the scar by nourishing the skin and removing the effects of healing.
- Seeds of melons - for example, pumpkin, melon, watermelon. They are rich in essential oils and antioxidants. You need to make a paste from fresh seeds of these plants, apply it as a compress to the affected areas of the body.
- Compress made of milk and pea flour. From these ingredients you need to make a dough, which is applied to the damaged areas and kept there for at least 1 hour. The resulting composition tightens the skin well.
- Cabbage leaf is considered an old but very effective remedy. If you apply a cabbage leaf to a wound, it has a healing and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Beeswax can nourish the skin well at the scar site, relieving inflammation, swelling, and smoothing the skin.
- Sesame or olive oil well moisturizes and nourishes the skin, brightens, smoothes and tightens scars.
How does rapid healing occur?
Wound healing occurs differently in each patient, depending on the type of suture and the severity of the surgical intervention performed. You should never leave a wound untreated. Treatment is needed to ensure a quick recovery and the stitch to heal without complications.
Ointments and other medications with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, and regenerating effects help to quickly get rid of the unpleasant consequences after skin surgery. They are necessary in order to:
- rapid tissue regeneration occurred (recovery, wound closure);
- no inflammatory process occurred due to antibacterial and antiseptic properties;
- improve the quality of newly formed tissue;
- reduce internal intoxication.
Healing occurs in several stages, they are clearly visible during processing manipulations. Firstly, the wound is disinfected, which promotes healing; bacteria cannot prevent the wound from healing. Secondly, the ointments and creams used help speed up regeneration, that is, help the skin recover and improve the quality of the new tissue being formed.
Taken together, all actions lead to the fact that the seam heals soon.
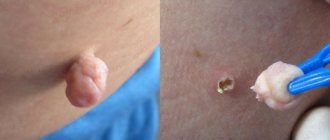
Postoperative fistula: how to treat?
After surgery, complications are possible - the formation of a postoperative fistula. Pus accumulates in the hole. He can't go outside. The reasons for the appearance of formations can be different:
- chronic inflammation
- infection during surgery
- intolerance of the body to suture threads
Patients often experience reactions to the suture material. Threads envelop tissues - seals. Fistulas can form immediately after surgery or several months later. Symptoms:
- redness
- the appearance of a compaction
- pain and swelling
- purulent discharge
- increase t
Treatment of pathology is possible in two ways:
- Local. Cleaning the seam from dead tissue, treating the wound, taking antibiotics
- Surgical. The doctor makes an incision, cleans the wound of pus, and removes the ligature. Complete excision of the suture is possible. Antibiotics and immunotherapy are prescribed
Folk remedies:
- Mix mummy with aloe juice. Apply a bandage and make a compress for 2-3 hours
- wash the wound with a decoction of St. John's wort
- apply cabbage leaf
Rating of the best ointments for healing sutures after surgery in 2019
When thinking about which company is better to buy ointment, pay attention to the Nizhpharm brand and their well-known wound healing agent Levomekol. The drug has an antimicrobial and bactericidal effect, helps accelerate cell regeneration. The functionality of the product is that it is an antibiotic and a reparant. Thanks to its effective healing properties, the ointment has the laudable status of “the surgeon’s favorite assistant.” Levomekol has the ability to penetrate deeply into cells, creating a healing, therapeutic effect. In this case, cell membranes are not damaged and retain functional activity.
The product is classified as a low-hazard substance for humans. The ointment is used for both treatment and preventive purposes. The main indication for the drug is the treatment of purulent wounds; the drug is also used for burns of 2 and 3 degrees, for the occurrence of trophic ulcers and for the treatment of boils. For prevention, the product is applied to a bandage or cotton wool and applied to sutures, as a result of which healing is accelerated and infection is prevented. The ointment is used externally, applied once or twice a day, the treatment process lasts from 5 to 10 days.
Cost: about 150 rubles.
- Accelerates the process of cell regeneration;
- Accelerates cell renewal;
- An effective remedy for deep wounds prone to suppuration;
- Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial;
- Suitable for healing postoperative sutures;
- Itching and irritation of the dermis are eliminated;
- Budget.
- Over time, bacteria develop resistance to the active substance of the drug;
- Allergic reactions are possible.
An excellent hypoallergenic gel is Mederma, which helps smooth out scars. Its amazing functionality includes improving blood circulation, antibacterial effects and accelerating skin cell renewal. The product is not a hormonal substance and can be purchased without a prescription. Available in tubes in the form of a transparent gel, it has a herbal aroma.
Many buyers praise Mederma for smoothing out scars and scars and returning the skin to its original state. Mederma is prescribed for post-operative scars, marks from tattoo removal, consequences of skin peelings and to combat stretch marks of various origins. But you need to remember that it helps only with fresh scars, and will not cope with old ones. Apply the product externally, rub until completely absorbed; treatment of problem areas of the skin is needed about 4 times.
You can buy it for about 700 rubles.
- Anti-inflammatory ointment;
- Accelerates the process of cell regeneration;
- Suitable for removing fresh scars;
- Helps with acne scars;
- Hypoallergenic.
- Expensive;
- There are complaints that it rolls into lumps.
The Swiss drug Solcoseryl is very popular among the Russian population, and all thanks to its effectiveness and versatility. The product is used for many different purposes, even as a rejuvenating elixir, but we are concerned about its use for the healing of postoperative sutures. The functionality of Solcoseryl is such that it helps to increase collagen production and perfectly activates the process of tissue metabolism. The drug is available in different formats: gel, ointment, dental adhesive paste and solution.
This medical product belongs to the group of products that stimulate tissue regeneration. Allowed to be applied to a wet seam. A thin and even layer is carefully applied to the washed and disinfected wound. The course of use is a month. For a fresh wound, it is advisable to use a gel; if the wound has already crusted over, then you need to purchase an ointment. Numerous surveys regarding the drug revealed that thanks to Solcoseryl it was possible to avoid scars and cicatrices.
Antiseptics in powder form
Antiseptic in powder form is used to treat superficial purulent wounds, bedsores, and skin ulcerations. They have astringent, anti-inflammatory, bactericidal effects; the dry form relieves swelling, reduces the amount of mucus, dries, and prevents the formation of purulent discharge.
It is not very convenient to use drugs in powder form, so pharmacies use them to prepare pastes, ointments, solutions, and compresses for application to the skin. These antiseptics include: Collargol, Ethacridine, Protargol, Resorcinol, Phenol.
Solutions and ointments based on powders in small concentrations of 0.2-2% have an epithelializing effect; in the form of lotions and compresses they are applied to weeping lesions for regeneration and elimination of the inflammatory process.
At higher concentrations, 5-10% solutions and ointments have a keratolytic and cauterizing effect..
Contraindications to the use of powder products are deep wounds, burns, allergic skin reactions and intolerance to the components of the drug.
Victor Systemov - expert of the 1Travmpunkt site
Fighting surgical infection is the key to successful treatment and wound healing. In addition to observing the rules of asepsis, antiseptics must also be observed. This includes a whole range of procedures for treating postoperative sutures with antiseptic solutions. Treatment begins immediately after surgical procedures and continues until a dense scar forms on the skin.
What to take to increase endurance
To increase performance, the following minerals are recommended:
- P - normalizes the functioning of all organs, improves blood circulation;
- Ca - strengthens the skeletal system, teeth, reduces nervous tension;
- Fe - supports immunity, due to its participation in the synthesis of hemoglobin, ensures cellular respiration;
- Mg - makes the skeleton strong, does not allow blood glucose levels to rise, increases stress resistance;
- I - improves metabolism and thyroid function.
Necessary vitamins for recovery after surgery:
- A - takes part in intracellular protein synthesis, helps maintain the reserve of carbohydrates in the body;
- B - helps to gain muscle mass, speeds up metabolism and prevents fatigue syndrome;
- C - saturates tissues with oxygen, helps to recover after physical activity;
- D - improves the condition of bone and cartilage tissue;
- E - protects the cell membrane from damage;
- H - participates in energy processes.
You can take essential nutrients both in the form of a multivitamin complex and with food.
Processing methods
Methods for treating scars
The key to successful healing of the suture is timely, regular and correct therapy. The time and effectiveness of the result are affected by:
- sterility
- processing agents
Before you start treating a seam, you need to understand that if an infection enters an open wound, it will not be so easy to cure the process. Therefore, scar treatment begins only after disinfection of hands, instruments and all additional equipment.
Treatment of seams begins with the use of antiseptic drugs:
- iodine. It is not recommended to use frequently or in large quantities. The wound is lightly soaked with cotton wool slightly moistened with iodine.
- potassium permanganate. Use strictly according to the instructions in compliance with the dosage
- brilliant green
- medical alcohol
- hydrogen peroxide
- special anti-inflammatory drugs
Read: What do the instructions for Clindacin cream tell you?
In addition to pharmaceutical drugs, you can use home remedies:
- tea tree oil
- Mix beeswax 100 g, sunflower oil 400 g and cook on the stove for 15 minutes. Apply the cooled compound to the seams
- Mix calendula extract with petroleum jelly or cream, add a little orange or rosemary.
The choice of medication should be coordinated by a doctor. To avoid the patient's individual intolerance to the drug or allergic reactions. To maximize healing time, the following rules for treating scars should be followed:
- disinfect all necessary tools for processing
- Slowly release the scar from the bandage. If the wound is still fresh and the bandage does not want to come off, then you need to pour a little peroxide on the bandage
- take a cotton swab or gauze and treat the scar with the selected antiseptic
- Apply a new clean bandage on top and secure it so that it does not fall off
Important! Treatment is carried out in the morning and evening. Treatment can be increased only after consultation with your doctor. Constantly getting the seam wet is not always beneficial. The scar should be carefully monitored for the absence of inflammatory and putrefactive processes. There is no need to try to remove the scabs from the wound ahead of time; it is better to wait until they fall off on their own. When washing, be careful not to accidentally damage the seam with a washcloth.
If during the postoperative period the suture begins to bother you, it hurts too much or putrefactive processes form, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Types of antiseptic solutions for external use at home and in the hospital
- Group of halogens. These include aqueous and alcoholic tinctures of iodine, potassium iodide, and Lugol's solution. Used for treating and washing wound cavities. They have a cauterizing effect. Sutures are treated with iodine preparations no more than once per knock.
- Salts of heavy metals. Currently, bandages and ointments with the addition of silver nitrate are widely used, as well as a 0.1-0.2% solution of silver nitrate for the external treatment of postoperative wounds. At a concentration of 5%, this solution has a cauterizing effect, so it is used only in cases of severe inflammation and weeping of the wound.
- Alcohols. Ethyl alcohol in solutions with a concentration of 40% is used extremely rarely. It is not recommended to use it on a dry, non-inflamed seam. It is used primarily for treating wounds that are in the phase of active inflammation.
- Dyes. This group includes the most widely used solution - brilliant green, better known as brilliant green. For external use, an aqueous or alcoholic 1-2% solution is used. It is used both on mucous membranes and on the skin. The wound is treated daily, at least 2 times a day.
- Acids. Here, a weak solution of boric acid (2-4%) is most often used. Boric acid is a good antiseptic that is used in the form of solutions, ointments, powders, and powders. Local treatment with boric acid is applicable to both mucous membranes and skin. Treatment of postoperative wounds is carried out at least 2 times a day: in the morning and in the evening.
- Oxidizing agents. Also widely used in medical practice. The most well-known drugs from this group are potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide.
Hydrogen peroxide is an active oxidizing agent used for the treatment and treatment of purulent wounds. It is more often used in hospitals to separate purulent contents and completely clean the wound surface.
Important information! The advantage of hydrogen peroxide is its hemostatic properties. Therefore, in case of suppuration and bleeding from a wound after discharge from the hospital, this is the first resort of medical aid.
Potassium permanganate has cauterizing properties. In low concentrations it is suitable for washing sutures in the oral cavity, in higher concentrations - for treating postoperative wounds. It is used for processing no more than 1 time per day.
- Detergents. 0.1-0.2% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine is one of the drugs in this group. It is used externally for processing and washing postoperative sutures, at least 2-3 times a day.
- Antibiotics. To combat bacterial infection, ointments have been developed with the addition of antibiotics and hygroscopic agents. They are used to apply bandages to purulent postoperative wounds. Use at home only in case of suppuration of the sutures. An example of such ointments is Levomekol ointment, Vishnevsky ointment.
What to do if a fistula forms?
A fistula is a kind of channel that connects cavities. Purulent discharge comes out through it. If they are absent, an inflammatory process develops.
The cause of a fistula is an infection that has entered the wound. The same applies to a chronic inflammatory process, a foreign body. A fistula also forms if the infection has not been completely cured or the threads have been rejected.
For treatment, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. It is necessary to wash the wound with antiseptic agents and also drink vitamins.
How to treat a wound
At the present stage, many groups of antiseptic solutions are used in clinical practice. The choice of one or another antiseptic depends on the nature of the wound, the presence or absence of pus in it, the timing of healing and the final goals of treatment.
Important! The antiseptic for use at home and in the hospital is determined by the attending physician. The name of the drug is given in the recommendations, and the duration and frequency of treatment of the postoperative wound are also indicated there.
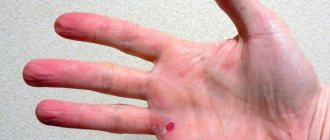
Symptoms of suture inflammation
Some impressionable patients get scared if the seam turns a little red, and immediately try to anoint it with something or bandage it. There is also a category of patients who, on the contrary, do not pay attention to any changes, believing that everything is normal. Therefore, every person who has undergone surgery should know the main symptoms of suture inflammation:
- skin redness;
- swelling of tissues;
- local pain (aching, bursting, aggravated by tension of the skin);
- bleeding that doesn't stop;
- suppuration of the postoperative suture: discharge of white or yellow foul-smelling plaque;
- fever, chills;
- increased heart rate;
- increase in pressure.
We can talk about inflammation only if 5 or more of the listed symptoms are detected. Fever without redness and suppuration is a sign of another disease. Likewise, slight bleeding and swelling without an increase in temperature may be just a temporary phenomenon caused by mechanical damage to the seam (the bandage was abruptly pulled off, clothing touched the wound, accidentally scratched, etc.).