What is seborrheic keratosis?
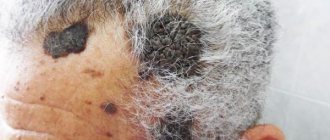
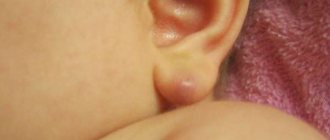
Seborrheic keratosis is a benign form of growth that appears on the skin; manifests itself as dark brownish spots, as a rule, the spots are slightly convex, raised (see photo below). The surface of areas affected by seborrheic keratosis tends to become scaly and form greasy crusts that are prone to flaking.
Unlike actinic keratosis , with which it should not be confused, seborrheic keratosis does not develop into a malignant pathology.
Features and danger
Keratopapilloma is usually called a benign formation. However, if the necessary treatment is not started, it can provoke the development of an oncological process. Therefore, we cannot talk about its complete safety.
Solar keratomas, although they look quite harmless, are a precancerous condition. If you ignore the disease for a long time, the disease will worsen, and treatment will not give the desired result.
The growth of skin horn is a rather dangerous phenomenon. In addition to the fact that keratinization is an advanced stage of the disease, there is a high risk of degeneration of benign cells into malignant ones. Typically, the growth is removed before it turns into a horn. But in certain cases, it is necessary to perform emergency amputation of the wart. After the doctor has neutralized the growth, the horn is sent for additional laboratory tests.
Elderly people need to be especially careful about their health. You should organize a proper balanced diet, protect exposed skin on sunny days, and protect yourself from bad habits. It is better to prevent a disease than to spend a lot of energy on its treatment. Moreover, performing operations in old age is dangerous in itself.
Causes
Etiopathological studies are still the basis for studying this disease. The only connection that scientists were able to prove was familiarity : seborrheic keratosis appears to be genetically transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner.
There is no doubt, however, that the growth, and therefore the development, of seborrheic keratoses is enhanced by hormonal changes or irritation, although it is not the trigger: for this reason, menopause , a time of high hormonal modulation, coincides with the intensification of seborrheic keratoses.
Finally, some studies also suggest the possible involvement of ultraviolet radiation in the etiology of the disease, as seborrheic keratoses have been noted to occur in people who have exposed their skin to the sun . However, since the disorder occurs even in people who have not been overexposed to ultraviolet radiation, the debate about the influence of sun exposure in the etiology of seborrheic keratoses is still open. Therefore, further and more in-depth research is needed in this area.
Prevention
Following a number of rules helps reduce the likelihood of keratoma:
- Avoid prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- Do not come into contact with hazardous chemicals;
- Treat chronic diseases;
- To live an active lifestyle;
- Provide yourself with a balanced diet;
- Protect skin from the sun, especially in summer.
If a person takes care of his own skin and the body as a whole, then he is unlikely to ever be bothered by keratopapillomas.
Clinical manifestations
Typically, seborrheic keratoses begin as yellowish papules that turn brown and flake off over time. In truth, the color of the lesions can vary from hazel to brown or blue depending on the subtype of seborrheic keratosis that affects the patient. Additionally, although the lesions are more common on the face and torso, depending on the subtype of seborrheic keratosis a person suffers from, they can also occur in other parts of the body. (see paragraph “classification”).
Classification
There are different subtypes of seborrheic keratosis:
- Seborrheic acanthotic keratosis : This is the most common form of this disease and presents with diffuse light brown to dark brown pigmentation with pseudocorneal cysts that tend to take on a yellowish color.
- Acropostic seborrheic keratosis : mainly affects the legs, the lesions are multiple.
- Hyperkeratotic seborrheic keratosis : A keratotic manifestation that tends to flake continuously.
- Pigmented seborrheic keratosis or melanoacanthema : this form manifests itself with multiple pigmentations, melanocytes are present in large numbers.
- Painful ( irritable ) seborrheic keratosis: The manifestation of seborrheic keratosis is accompanied by irritation and other possible skin changes. Bleeding and redness of the damaged areas occurs. Typically, infiltration of melanophages in the above-mentioned areas gives the spots a bluish color, sometimes causing diagnostic doubt (difficult to distinguish from basal cell carcinoma).
- Dermatosis nigra papularis ( seborrheic keratosis on dark skin ): Regarding this dermatological disease, it is not yet clear whether it can be considered a variant of seborrheic keratosis. It appears as small, multiple hyperpigmented spots.
Symptoms
Recognizing the disease is not so easy. Patients realize that they are sick only after strange growths begin to form on their body. They protrude slightly above the top layer of skin. After some time, the tumor may increase in size. A dense crust will appear on it, which will begin to peel off.
Keratoma is often multiple. Growths appear on exposed areas of the body, which is why people perceive them as a cosmetic defect. The injured rash will begin to hurt and bleed. If these symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor immediately. He will tell you how to treat a benign tumor, avoiding serious complications.
Diagnostics
A dermatologist must properly diagnose the disorder by analyzing each individual seborrheic wart to avoid misunderstandings: the signs left behind by seborrheic keratoses actually resemble those of much more serious skin diseases (squamous melanoma, spinocellular carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma).
If the diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis is made correctly, removal of the warts will be futile (unless the disorder is a serious aesthetic problem in the eyes of the affected subject). Through dermatoscopy, a specialist can make the correct diagnosis and differentiate seborrheic keratosis from other skin diseases. Of course, the physician will also need to determine what type of seborrheic keratosis the patient has.
Treatment
As already mentioned, treatment by removing seborrheic warts is not necessary except for aesthetic reasons. In fact, the lesions are usually asymptomatic and cause no discomfort to patients. However, if seborrheic keratoses show unregulated and excessive growth, the disorder can have significant aesthetic consequences.
In this case, diathermocoagulation, cryotherapy, laser therapy, curettage or electrocoagulation are possible solutions to eliminate seborrheic keratosis. At the same time, these therapeutic approaches may be used if the lesions become irritating, causing itching, pain and/or bleeding.
After seborrheic keratosis removal, the skin usually appears lighter than the surrounding skin. This hypopigmented area may remain hypopigmented throughout the patient's life. However, treatment results in permanent removal of the lesion, as it will no longer appear in the area where it was removed. However, this does not prevent the appearance of new seborrheic keratoses in other untreated areas of the body.
Prevention
There are currently no specific methods for preventing this pathology. It is recommended to limit exposure to the sun, avoid heavy tanning, follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle, avoid drinking alcohol and cigarettes, and maintain good hygiene.
Traditional methods
Severe psoriasis - neck, close-up
You can try to treat seborrheic keratosis at home. For these purposes, folk medicine has several recipes, which we will share with you.
Aloe
For the procedure, we will need the leaves of a plant that is more than five years old. You need to wash them thoroughly and put them in the refrigerator for several days. Then take out one at a time and cut into thin plastic pieces.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Apply these plates to the affected area of the skin, secure them with cling film and bandage.
Leave everything overnight, and in the morning you need to wipe the skin in this area with a weak solution of salicylic alcohol. After half an hour, you can apply a new compress.
Propolis
You need to roll out a piece of propolis into a thin leaf and apply it to problem areas, securing it with a bandage. Leave it like this for several days, maximum five. Then the bandage needs to be changed. The procedure must be repeated at least three times.
Raw potatoes
Make a paste by grating a potato on a fine grater, place it on gauze folded in several layers and bandage it to the affected area of the skin. After an hour, the potato pulp should be replaced with fresh one. This should be repeated three times.
Onion peel
Take 4 tbsp. l. clean dry onion skins and pour a glass of vinegar over it. You need to insist in a dark place for two weeks. Then strain the infusion and make lotions from it.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
For the first procedures, 30 minutes will be enough.
Then, with each new procedure, add another half hour. The total duration should be three hours.
To summarize
To consolidate the material, see the table below...
| Disease | Seborrheic keratosis or seborrheic wart. |
| Clinical aspects | The disease is not contagious, non-infectious, benign. Appears as raised dark brownish spots; The surface of the papules is rough, characterized by scales and uneven crusts. Typically, the diameter of the spots varies from 1 mm to 1 cm. Sometimes the skin disease is associated with an irritating itching sensation. |
| Prevalence | Seborrheic keratoses occur in subjects who have reached advanced middle age, with no gender preference; The dermatological disorder occurs primarily in the Caucasian population, while it is rare in Oriental and black people. |
| Affected areas | Often the face and torso. |
| Differences from actinic keratosis | Seborrheic keratosis is not a malignant form of cancer and does not result from exposure to ultraviolet rays, like the actinic form. |
| Causes | The reasons are not clear. It is probably genetically transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner. Increased by hormonal changes and immunosuppression (weak immunity). |
| Damage | Purely aesthetic |
| Classification |
|
| Possible treatments to eliminate seborrheic keratoses. |
|