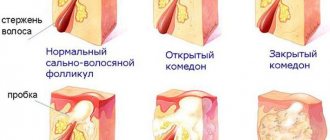
When the skin comes into contact with radioactive waves, damage occurs. Treatment of burns after radiation therapy is quite common because this side effect is not uncommon. This not only creates discomfort and pain, but is also dangerous due to the addition of a secondary infection with the development of an inflammatory process.
Radiation-induced skin changes are inevitable with long-term therapy and require care to prevent infection.
Types and stages of radiation burns after radiotherapy - symptoms of radiation burns
Depending on the area of the skin or mucous membrane that is involved in the pathological process, as well as based on the symptoms, there are 4 degrees of severity of radiation burns:
- First (mild) degree. Diagnosed if the radiation intensity does not exceed 1200 rad. The symptomatic picture is limited to redness of the skin and peeling. All of these manifestations make themselves felt after 14 days and are quite easily tolerated even by those whose body’s defense reactions are weakened.
- Second degree. May occur when exposed to radiation up to 2000 rads. Patients often complain of pain, blistering, redness, swelling and itching of large areas of the skin. The bubbles are initially small and numerous, filled with clear liquid. Subsequently, they merge into larger ones, and after spontaneous opening, an erosive area of bright red color forms in their place. Such conditions make themselves felt within 2 weeks after radiotherapy.
- Third degree. Characterized by a short latent period (3-4 days). Erosions, papules with or without pus, ulcers, necrosis are specific symptoms of the considered degree of radiation burns. Victims may also experience headaches, loss of energy, nausea, and increased body temperature. If the upper respiratory tract is affected, the nose, mouth, and throat dry out, causing coughing and pain. The mucous membrane in the area of the soft palate swells, and the neck visually increases in size. Often the overall picture is complemented by a secondary infection, which in advanced conditions leads to laryngeal stenosis.
- Fourth (extremely severe) degree. It is a consequence of extensive destructive processes in the upper layers of the skin and muscles, which manifests itself almost immediately after irradiation. In some cases, charring may occur.
Radiation burns, according to their clinical manifestations, go through several stages:
- Early reaction of the body. It may occur within a few hours or days. The skin at the site of the lesion peels, itches, and turns red. With moderate and severe radiation burns, victims' body temperature rises, blood pressure decreases, and pulse quickens. Nausea and vomiting may also occur. The duration and severity of such conditions will depend on the dose of ionizing radiation received - from 3 hours to 2 days.
- Hidden period. Characterized by the absence of any manifestations of the type of burn in question. The specified time period may last for 2-3 weeks - this indicates a mild degree of damage to the skin or mucous membranes. If the duration of the latent period is limited to several hours, the patient has received a severe radiation burn.
- The period of acute inflammatory phenomena. The skin in the area of negative impact changes color and density, swells and hurts - secondary erythema develops. Extensive degenerative processes are accompanied by the formation of ulcers, the bottom of which is gray in color and the edges are torn. This period may last for several months.
- Recovery. The swelling resolves, the pain decreases (until it completely goes away), the ulcers heal. If the wound is deep, it can take years to heal, and in its place a pigment mark and a scar form. Hair in this area falls out, the skin peels off and loses its elasticity. There are cases when the ulcer recurs, further provoking skin cancer.
Causes
Burns are caused by prolonged exposure to radioactive rays. The contact method of irradiation is used not only for oncological lesions of the skin, but also for diagnosing malignant neoplasms in internal organs.
In this case, the radiation effect is not only on the epidermis, but also on the subcutaneous tissue and other systems and structures. In this condition, the rays negatively affect not only atypical cells, but also healthy tissue.
Complications in the form of burns are promoted by X-rays and neutron rays, as well as gamma radiation. When passing through the skin, destruction of all tissues with which direct contact is established is noted.
On this topic
- Treatment
How to treat cystitis after chemotherapy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 4, 2021
This condition is accompanied by the development of severe inflammation.
Alpha rays are less dangerous for the skin, since when exposed to them, only mucous membranes can be damaged. Penetration of beta rays is noted to a depth of the dermal layers of up to two centimeters. In this case, not only malignant, but also intact cellular structures are negatively affected.
Surgical care for stage 3 and 4 radiation burns - indications and types of operations
Surgical manipulations for this pathological condition can be prescribed for deep burns that affect the muscle layers.
If the wound is severely infected, antibacterial treatment is first carried out, and only then surgery is started.
The wound area is thoroughly cleaned of dead tissue. This all happens under general anesthesia. This type of surgery is called necrectomy.
Subsequently, the operator transplants a graft taken from another area of the patient's skin.
The essence of pathology
Radiation burns are injuries caused by side effects of radiation therapy. Ionizing radiation is used in the treatment of cancer. An increased dose of radiation provokes the development of injury.
Manifestations
A burn from radiation therapy differs from a thermal burn in the late onset of symptoms. They are divided according to the degree of injury.
Table. Characteristics of radiation burns depending on the degree of damage.
Important! The extent of damage largely depends on the patient's skin type. If a person quickly burns under the sun's rays, then there is a high probability of getting a burn even after low-intensity irradiation.
Traditional medicine methods for treating burns after radiotherapy
If after a radiotherapy session the patient receives a slight burn (not higher than 2nd degree), the following traditional medicine can be used to treat it:
- Sea buckthorn oil has anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties. They should soak a sterile napkin and apply it to the burned surface. This manipulation must be repeated every 3 hours. The affected tissues will recover faster, and pain will significantly decrease or go away altogether.
- A mixture made from beeswax and olive oil has a similar effect . These substances should be mixed in a ratio of 1:3 and applied to inflamed tissues 3 times a day.
- You can prevent the appearance of blisters by applying honey or potato pulp to the affected area. Honey, among other things, is an excellent disinfectant.
- You can ensure speedy healing of the burned area, as well as protect it from infection, using a mixture prepared from dry propolis (20 g) and vegetable oil (80 g). These ingredients are combined and placed in a water bath, where they must be infused until the propolis is completely dissolved. The resulting mixture is filtered through a fine strainer. After complete cooling, the ointment is applied to a sterile napkin and applied to the wound. You should be careful with such a medicine: bee products often provoke allergic reactions in people.
Video: Radiation therapy - what helped me with burns
3rd and 4th degree burns are treated exclusively in a hospital. Such conditions, in the absence of adequate treatment, can lead to serious complications that can cost the health and even the life of the patient.
All traditional medicine described above must be previously agreed with your doctor!
First aid
If the patient experiences redness or burning at the site of irradiation, it is necessary to contact a specialist, since burns may not appear immediately.
It is important to be able to connect radiation therapy and changes in the skin, since burns do not occur immediately after the treatment procedure, but after some time. Also, lesions on the integument are concentrated not in one place, but in different ones, which must be differentiated from other skin diseases. If the patient experiences redness, burning, ulcerative changes, or erosions in the area affected by the beam, he should immediately go to the hospital.
Affected skin must be protected from environmental influences. All procedures must be carried out with sterile gloves to avoid introducing infection to the burn site. Using clean or sterile dressing material, all affected surfaces are isolated from external irritants. After applying the bandages, it is necessary to take the patient to a doctor for further treatment of burn wounds.
Prevention of burns when prescribing radiation therapy – what should the patient and specialists do?
Preventive measures include the following:
- Radiotherapy should be prescribed on an individual basis . For each patient, the dosage and frequency of isotope radio emission will be determined by the general state of his health.
- In order to protect the eyes from burns before and after radiation therapy, they are instilled with artificial tears : 1-2 drops in each eye. This will minimize the risk of developing photophobia and dry eyes in the future.
- After each course of radiotherapy, the immediate areas of exposure must be treated with wound healing agents . A similar procedure should be performed before going to bed.
Rate
—
Prevention
You can reduce the consequences of the procedure by using water, washing the irradiation site and thereby moisturizing it.
Radiation therapy always causes damage to healthy tissue. It is almost impossible to completely prevent the occurrence of burns due to contact exposure to rays. But if you follow a few rules, you can reduce the risk of their development. After each radiation therapy session, it is important to adhere to the hygiene rules of the areas where the rays influence. It is necessary to rinse with plenty of running water, which promotes hydration and prevents clogging of pores.
In the evening before bed, when the skin has calmed down, you need to apply ointments with regenerating abilities “Bepanten”, “Panthenol”. These products stimulate skin restoration, prevent the development of inflammatory processes and have a sedative effect. If redness, blistering, discomfort or pain is present, consult a doctor immediately.
How to behave during the rehabilitation period
The use of various medications is the basis of supportive treatment. An effective remedy is released, thanks to which the body quickly responds to regenerative therapy. We are talking about whey, which is enriched with lactates and is called “Hydrolactivine”.
Hydrolaactivin - recovery after irradiation
The distinctive features of this drug include the presence of:
- Complex impact on complications of radiation;
- Easy to digest by the body;
- Simplicity and safety of consumption;
- Compatible with many drugs.
If you accompany the radiotherapy process with the use of this drug and do not stop taking it during the period after surgery, the restoration of the skin exposed to radiation will be much faster. “Hydrolactivine” has an anti-inflammatory effect, enhances digestion, normalizes intestinal function, which restores the activity of the gastric and intestinal tracts.
Irradiation of the oral cavity often causes complications associated with the development of stomatitis. If you regularly rinse your mouth and throat with a solution of “Hydrolaktivina”, the mucous membranes of the oral cavity will recover faster. Dryness and discomfort will disappear, pain will decrease.
This drug normalizes metabolism, increases immunity and stress resistance, which is important for returning the body to normal after radiotherapy. This means that we recommend Hydrolaactivin as an accompanying therapy, as a drug that can mitigate many side effects.
The rehabilitation period should be accompanied by close supervision by the attending physician. He must be aware of all the changes that appear in the patient during the period of rehabilitation therapy. Special medications will be prescribed and taken according to a specific schedule.
Rehabilitation after radiation therapy
Light physical activity during this period will not hurt - this will provoke the restoration of the body's defenses. Of course, intense running will not do. But walking in the fresh air will have the desired effect. During the first month, you will feel general weakness and a desire to lie down, however, you do not need to allow the body to stagnate.
Plenty of fluid intake (at least three liters per day) is recommended to reduce the negative effects. You can drink both regular and mineral water. The consumption of natural juices, fruit drinks and compotes is also not excluded. You just have to avoid consuming sugary carbonated drinks.
It is necessary to eliminate bad habits - the body should not be saturated with toxins. True, to improve appetite, patients are allowed to consume beer (200 ml) or red wine (100 ml). But such a retreat is possible only after approval by the attending physician.
You'll have to start eating a balanced diet. You should adhere to the recommended ratio of carbohydrates, fats and proteins (4:1:1). A nutritious diet should exclude the consumption of sausage, smoked products and other harmful delicacies. The diet should consist only of natural food that does not contain flavoring additives.
Radiation treatment of basal cell carcinoma is always accompanied by damage to the surrounding tissues. This cannot be avoided even if you follow the rules of this method of therapy. The sensitivity of the skin to radiation depends on many factors. This:
- localization of the tumor, the anterior surface of the neck is more susceptible to radiation exposure than the skin of the wings of the nose and other areas of the face and back of the head; air temperature, in hot weather the blood supply to the epidermis improves, which increases the risk of developing the consequences of treatment; in cold weather this probability decreases; excess weight, it has been proven that the skin of obese people is more susceptible to the effects of radiation; cracks and scratches increase the permeability of the epidermis; age-related changes.
In most cases, radiation treatment of basal cell carcinoma does not cause systemic consequences. Most of the side effects are due to a skin reaction, which manifests itself in the form of epidermatitis. First, during each session, swelling, redness, and itching occur. As treatment continues, symptoms become more pronounced and reach a maximum by the third week of therapy and disappear 1 - 1.5 months after its completion.
Blisters filled with exudate form on the affected area of the skin. They burst, revealing an inflamed, bright red epidermis. This serves as a gateway for pathogenic flora, and if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed, a bacterial infection can develop. The appearance of wounds covered with crusts is also noted.
A dangerous consequence of such treatment for basal cell carcinoma is a radiation ulcer. Under the influence of radioactive isotopes, microcirculation in the blood vessels located under the skin is disrupted. The risk of complications increases in proportion to the depth of penetration of the pathological process and the strength of radiation. The onset of ulcerative changes in the skin is indicated by the following symptoms:
- dryness and flaking; disappearance of the surface pattern of the epidermis; the appearance of spider veins; pigmentation disorder.
If basal cell carcinoma is located near the mucous membranes of the nose or mouth, inflammation may occur - mucositis. It is characterized by dry epithelium, burning and pain when touched. However, such consequences are rare. During radiation treatment of a tumor in the eye area, recurrent conjunctivitis is noted.
To prevent radiation dermatitis, the skin around the basal cell carcinoma is regularly lubricated with Vaseline, metacil emulsion, or treated with a cotton swab moistened with a mixture of Shostakovsky Balsam and vegetable oil (prepared in a ratio of 1:4). Moreover, this should be done from the first irradiation session. If, despite the measures taken, ulcers form, it is necessary to prevent bacterial inflammation.
To prevent damage to the mucous membrane, rinsing or washing with chlorhexidine, chamomile or sage decoction is prescribed. Antibacterial drops are indicated for the treatment of conjunctivitis. If it is not possible to avoid exposure to sunlight on the skin of the face or other area of the body where the basal cell carcinoma is located, so-called indurative edema may appear.
It is worth noting that with radiation treatment of basal cell carcinomas located on the face, the risk of relapse is higher than in other areas of the skin. According to oncology clinics in Russia and foreign countries, this probability is up to 30%. It is particularly difficult to target tumors localized on a textured surface, since radiation is unevenly absorbed by cells.
http://www. rakneprigovor. ru/ozhogi-posle-luchevoj-terapii
http://kakiebolezni. ru/kozhnyie-zabolevaniya/bazalioma/obluchenie-bazaliomy. html
Useful articles:
- Life prognosis with glioblastoma of the brain Glioblastoma of the brain One of the most aggressive and most common malignant brain tumors is glioblastoma. Glioblastoma is diagnosed in half of cases [...]
- Test drawing a clock when determining the degree of dementiaTest drawing a clock when determining the degree of dementia Published Editorial on 1/31/13 • Categories 04. HAVE AN OPINION Memory becomes more and more dynamic with age: you won’t have time for something […]
- How to cure COPD at homeCoPD - treatment with folk remedies and our recommendations Not in all areas, official medicine has yet reached such heights as to completely cure diseases that can disrupt normal […]
- How long does a course of chemotherapy for lymphoma last? All important information about chemotherapy for lymphoma Malignant tumor of the lymphatic system is a disease that does not spare even small children. Lymphoid tissue is present in every [...]
Radiation damage to the oral cavity, treatment
Natural and artificial radioactive isotopes are widely used in almost all industries, agriculture, medicine, especially in scientific research.
Careless handling, the use of significant doses for therapeutic purposes, as well as industrial accidents can lead to local and general exposure with the development of painful manifestations in the oral cavity in the form of burns, ulcerative, necrotic and aphthous stomatitis with impaired oral function. The effects of ionizing radiation can be detected immediately or after a certain period of time.
The course of acute radiation sickness is divided into 4 periods. The first period occurs several hours after irradiation. Against the background of general symptoms (dizziness and general weakness), dry mouth, a dull tint of the mucous membrane and pinpoint hemorrhages appear in it.
The second period is imaginary well-being. All symptoms observed in the first period disappear, there are no changes in the oral cavity.
The third period is the height of the disease. It is characterized by the appearance of a number of symptoms from the oral mucosa, which becomes pale and dry. The gingival papillae, especially their edges, become swollen, and a pink border appears in the form of a fringe. The mucous membrane of the gums bleeds.
A reduced content of platelets in the blood and increased permeability of the vascular wall lead to the appearance of extensive hemorrhages, especially in the area of the floor of the oral cavity. The swelling of the oral mucosa increases, and tooth marks are visible on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue.
The mucous membrane is covered with whitish viscous mucus mixed with blood with an unpleasant odor.
Against the background of a pale and edematous mucous membrane, areas of limited tissue necrosis appear in the form of a white spot, primarily in places adjacent to metal fillings and prostheses. After the necrotic epithelium is rejected, an ulcer is formed, the bottom of which has uneven elevations, is covered with a gray-dirty coating and has reddened edges. The edges of the ulcer without sharp boundaries merge into the surrounding tissue. In case of infection, more extensive necrosis is formed on the mucous membrane of the gums, cheeks, and at the root of the tongue, sometimes reaching the bone. The papillae of the tongue swell, the tongue becomes rough, and cracks appear. The interdental bone septa dissolve, the teeth become loose and fall out. All this is accompanied by painful phenomena. On the 8-10th day of illness, the submandibular lymph nodes enlarge and become painful. The fourth period is recovery. All symptoms slowly begin to disappear, but a recurrence of stomatitis is possible, which stops with general recovery. Metal dentures and fillings worsen the condition of the oral cavity during radiation sickness. Ulcers formed on the mucous membrane in places adjacent to metal fillings and dentures do not heal until the dentures and fillings are removed.
In the chronic course, ulcers resemble aphthae, which appear on the vestibular surface in the area of transitional folds, gums and lower lip. The tongue swells and deep furrows appear on it. In some patients, glossalgia persists. After 5-7 days, these phenomena may disappear, and then reappear for a long time.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis, the general condition of the blood picture and the clinical picture.
Treatment is mostly general. Due to the significantly reduced protective function of the body and the possibility of secondary infection, it is necessary to carefully care for the oral cavity.
The mucous membrane is irrigated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, furatsilin, and applications are made with antibiotic solutions (200,000 units of penicillin in 10 ml of 0.5% novocaine, an aqueous solution of biomycin - 100,000 units in 20 ml of distilled water).
A gentle diet, milk, a large amount of vitamins, raw egg white (lots of lysozyme) are prescribed. Partial sanitation of the oral cavity is performed.
Tooth extraction and the use of cauterizing substances are contraindicated.
The prognosis is always serious.
Prevention. Carrying out preventive measures to prevent gingivitis, stomatitis and other manifestations of the disease in the oral cavity play an important role in the process of curing radiation sickness.
Persons in contact with X-rays must be constantly under the supervision of a doctor and at least once every 3 months must come for examination and sanitation by the dentist. All workers with radioactive isotopes must be familiarized with personal preventive measures. Persons who, due to the nature of their diseases, require radiation therapy, in order to prevent complications from the oral cavity, must be appropriately prepared. It is necessary: 1) undergo complete sanitation of the oral cavity; 2) do not wear removable dentures at the time of irradiation; 3) remove metal prostheses and fillings; 4) do not use a toothbrush to avoid injury to the mucous membrane during radiation therapy; perform morning oral hygiene with a cotton ball moistened with a solution of hydrogen peroxide; 5) eat food that does not irritate the oral mucosa; do not smoke or drink alcohol; 6) rinse your mouth thoroughly before a radiation therapy session. Irrigation of the oral cavity with a solution of adrenaline (1:1000) in physiological solution (2:100) with the addition of 3 ml of a 40% glucose solution significantly reduces the sensitivity of the mucous membrane to radium rays.
Source: https://www.blackpantera.ru/stomatologiya/34334/