Types of fungus in children
Fungus can appear in children at any age for numerous reasons.
Fungal diseases in children can be caused by a variety of pathogens, each of which has its own symptoms, characteristics and reproduction pattern. However, doctors identify several types of fungus, which are most often diagnosed in children. These include:
- Keratomycosis. This pathogen causes fungal skin diseases in children. Externally it resembles tinea versicolor. The main symptom of the disease is severe peeling of the skin. Infants experience flaking on the scalp.
- Candidiasis. This disease develops as a result of the proliferation of a fungus of the genus Candida and manifests itself not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. This type of fungus is considered the most dangerous for a child, as it leads to discomfort, the formation of white plaque in the mouth, increased body temperature, conjunctivitis and other unpleasant consequences for the baby. Most often, when a mother-to-be is diagnosed with thrush, it is passed on to the baby during childbirth.
- Mold fungus. The causative agent of this type of fungus feels comfortable in a humid and warm environment, where it multiplies as quickly as possible. Mold spores constantly fill the environment where they reproduce and can cause a severe allergic reaction in a child.
Causes of infection
The fungus is very contagious, especially the feet are affected.
Fungus on a child’s skin and nails can occur for numerous reasons. Fungal pathogens surround us everywhere and are highly resistant to a number of aggressive factors. They are not afraid of high temperature, UV radiation and the drying process. Fungal infections in children are not as common as in adults, but often become epidemiological in kindergartens and schools.
Even babies can get fungus. This pathological process most often develops as a result of immaturity of the immune system. It appears upon contact with other children, for example, in kindergarten. Due to reduced immunity, stressful situations, and lack of vitamin D, the fungal pathogen quickly penetrates the weakened body and multiplies there, causing the development of the disease.
Animals can also become carriers of the fungal pathogen. Infection occurs after direct contact with the carrier. Sometimes this can even happen after using an infected item. Very often children can become infected with fungus:
- in a swimming pool;
- at the hairdresser;
- on the beach;
- in kindergarten or school;
- with uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
The risk of infection in a child is higher than in an adult, which is due to the structure of the skin. Children's skin is thinner and has a lower level of bactericidal activity of the gonads and high vascularity.
Prognosis and prevention
Particular attention should be paid to preventing the development of mycosis; for this, the following recommendations must be followed:
- After taking a bath or shower, the skin should be thoroughly dried with a towel.
- Clothing should be loose, made from natural, breathable fabrics.
- It is important to follow the rules of hygiene, regularly wash your hands and feet. Wear shoes in public places.
- Change diapers in a timely manner, if macerations occur, treat the skin with powder, and give the baby air baths.
- Do not use toys, dishes, personal hygiene items, or a comb from another child, especially if he or she has a fungus. Avoid contact with sick pets.
- The baby must have individual bed linen and dishes.
The prognosis of the disease is favorable. With timely treatment, complete recovery occurs.
Symptoms of fungus in a child
A characteristic sign of candidiasis is a white coating on the mucous membrane of the mouth or tongue.
Every child diagnosed with fungus complains of general weakness. That is why, having discovered persistent symptoms of illness, parents should carefully examine the child’s skin for any unusual changes. For different types of pathogens and their localization, the symptoms of manifestation directly depend. It will be different from each other, so it’s easier to make a table.
| View | Symptoms |
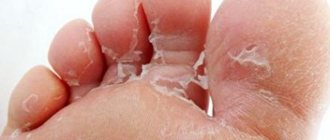
| Fungus on a child's feet | In this case, wounds and sometimes ulcers appear on the fingers and feet, around which inflamed areas of the skin are identified. In this case, the affected area is very flaky and itchy, causing severe discomfort in the child. If the disease is not treated in time, small redness turns into ulcers. It may become difficult to move normally, as even with the lightest pressure the wound begins to hurt. |
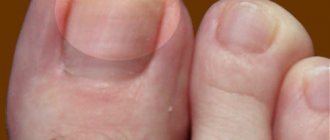
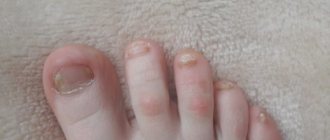
| Nail fungus in a child | The nail plate begins to peel off from the base of the finger. Then it darkens, thickens and simply moves away from the nail bed, which looks very unattractive. Nail fungus on the hands and feet of children provokes inflammation of the skin ridges around the affected nail, which cause pain when pressed. |
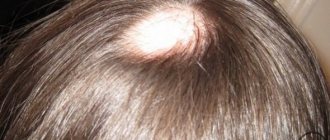
| Ringworm | Most often localized on the scalp and other areas of hair growth. The hair falls out a lot and becomes very fragile. The skin at the site of the fungal infection becomes red, flaky and itchy. When scratching, an additional infection often enters the wound, which can cause an increase in body temperature. |
| Pityriasis versicolor | This type of fungus manifests itself on the skin of the back with yellow or white spots. These areas of the skin may become covered with scales, but they do not cause unpleasant itching. |
| Candidiasis | Yeast fungus in children is localized on the mucous membrane in the oral cavity or intimate areas. A characteristic sign is a white coating of a cheesy consistency, which is difficult to remove even with mechanical removal, leaving behind an inflamed area, sometimes even a wound. Also, as the disease progresses, the child may have a temperature of up to 38 degrees. |
If a fungus develops on the toes or hands, a small rash of watery blisters can be seen on the skin, redness of the skin at the site of the lesion; if the itching is severe, the child can scratch the rash until wounds form.
In more advanced cases, the wounds become rougher, the skin on them peels off and thickens, and cracks can form that cause pain when moving. In some babies, the fungus can even penetrate into the ear. In this case, the child becomes restless and capricious due to constant itching in the ear, which leads to neurosis and loss of sleep. The skin inside the ear becomes rough, and there is excessive secretion of earwax. Fluid of different colors may be discharged from the ear.
The mechanism of fungal nail disease
After the patient has learned what nail onychomycosis is, it is necessary to understand the mechanism of its development. The disease develops against the background of a fungal infection of the nail plate, as well as against the background of a weakening of protective immune mechanisms. The pathology progresses over time, can change shape, and also provokes the development of unpleasant symptoms in the nervous system. Fungal waste products have a toxic effect on the body beyond the nail plate, nail bed or foot.
Penetration of a fungal infection under the nail plate occurs at the point of its attachment, that is, in the nail bed. The development of microorganisms in such an environment occurs quickly. The fungus multiplies and uses nail cells as nutritional materials, simultaneously destroying it. All metabolic products that are formed after exposure to onychomycosis on the nail penetrate the blood and lymph, affecting the body as a whole.
If a person's immune system is weakened, then toenail fungus will require treatment after an incubation period of one to two weeks. Only in case of weakened immunity, as well as in old age, the risk of infection with onychomycosis of nails or nail plates is one and a half to two times higher than in a young and healthy body. Fungus of the nails and nail plate or foot is highly resistant to external conditions, which complicates the treatment of the disease.
Onychomycosis of the nail plates: main types of fungal pathogens
Fungus of the nail plate, nail bed and foot is caused by:
- Candida, their forms and types (1-8% of all cases);
- Trichophytons, their form is the most common (75-90%);
- Dermatomycetes of all varieties are found in 7-14% of cases;
- Other fungal infections.
Depending on the pathogen and its sensitivity, antifungal drugs are selected for the treatment of onychomycosis. This technique makes it possible to cure pathology quickly, without changing medications, but not in one day.
Onychomycosis of the nail plates is differentiated from a clinical point of view. There are such forms of pathology as
- Regional pathological process - the free nail edge is affected;
- Normotrophic form of fungal infection - without changes in the thickness of the plate;
- Hypertrophic onychomycosis - with thickening of the affected area;
- White superficial form - with visual modifications and the appearance of white spots on the skin or nails;
- Onycholytic fungal infection - with softening of the nail plate;
- The candidal form of the disease is a pathology with white spots;
- Atrophic onychomycosis - with atrophy of the nail plate or skin area.
The normotrophic form of the pathological process is considered the most common; it occurs even in children and requires adequate comprehensive treatment with new drugs. Trichophytons are fungi that most often cause onychomycosis of the nail plate and nail bed.
Pathology of any localization has characteristic signs of fungal infection. Namely, changes are observed on the skin: spots appear, most often white or yellowish, sometimes red. If the pathological process occurs on the nails, then they are characterized by stratification and changes in structure. Along with such symptoms, itching and painful sensations appear while walking.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of fungal infection is carried out under a Wood's lamp
If, during an examination, a pediatrician diagnoses a fungus of any kind in a child, then most likely he will write a referral to a mycologist. You can diagnose nail fungus in a child or mycosis of any other part of the body using the following methods:
- initial examination of the infected surface under a Wood's lamp;
- taking a piece of affected tissue for microscopic examination;
- sowing the scraping onto a nutrient medium. This method allows you to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to certain types of drugs;
If there is a suspicion of the development of mycosis, the doctor must carry out a differential diagnosis in order to exclude the development of psoriasis, dermatitis, vitiligo and other diseases, the signs of which are very similar to a fungus.
Symptoms
The description of symptoms depends on the form and location of the disease:
- A characteristic symptom for a fungal infection on the skin of the face and torso is the appearance of a scaly, ring-shaped rash with pustules and a clear outline . As the disease progresses, the number of elements increases and the affected area increases.
- A feature of a fungal infection of the scalp in a child is the appearance of itchy bald spots with remnants of broken, dull hair.
How to treat fungus
Treatment for fungus in children is different from the therapy that works in adults. When selecting a treatment regimen for young patients, a specialist must ensure that it is as safe as possible, but at the same time effective. In case of a complex course of the disease, the doctor may recommend a full examination in a hospital setting to exclude the presence of concomitant infections and problems that can cause complications and hinder a quick recovery.
Medications
Fungal skin diseases in children are treated with antifungal, antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory drugs. Depending on the location of the fungus and the advanced stage of the disease, the doctor may recommend complex treatment using several drugs or monotherapy.
Complex treatment includes the following drugs:
- antifungal;
- hormonal;
- antihistamines;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamin complexes.
In this case, along with tablets, it is necessary to use ointments and gels that will help increase the effectiveness of the course. Fungus in children on their toes or hands will go away faster if, in parallel with taking tablets that fight pathogenic microflora inside the body, you use topical treatment products (ointments, gels).
The affected areas must be lubricated 2-3 times a day (in the morning and evening necessarily). Usually the course of treatment lasts at least a month. For systemic therapy, doctors often use the following drugs: Diflucan, Terbinafine, Griseofulvin.
For lichen in a child, it is recommended to use ointments that contain zinc, tar and salicylic acid. In advanced cases of skin infections that develop against the background of a fungus, hormonal therapy may be required.
If yeast is found on the child’s mucous membranes, it is necessary to include Monistat or Mycelex suppositories in the course of treatment.
Traditional medicine recipes
Baths with sea salt composition are an effective folk remedy for fungal infections
You can cure toenail fungus in children, on the hands and mycosis on different parts of the body using traditional medicine recipes. This method, in addition to its effectiveness, is safe, but also long-lasting. How to treat fungus in children with folk remedies? Use the following recipes to help get rid of unpleasant symptoms without causing additional harm to your health.
- 20 grams of crushed celandine herb are poured with a liter of boiling water and left for about an hour. After this, the product is additionally heated before use. They moisten a natural cloth or cotton swab and wipe the affected areas of the skin. If fungus is diagnosed in children on the toes or hands, the infusion is used for baths. The affected limbs are lowered into it for 10-15 minutes;
- natural liquid honey. A liter of honey is diluted in 10 liters of water and the solution is used as a lotion on the affected areas of the skin;
- herbal baths. To prepare medicinal infusions, it is recommended to purchase sage, oak bark, chamomile and St. John's wort at the pharmacy. Each herb is used separately. You need to take 20 grams of the herb and pour a glass of boiling water over it, then bring the medicine to a boil and remove from the heat. After the herb has been infused for a quarter of an hour, it can be used for compresses and baths;
- sea salt baths. To prepare the composition, take warm water in which 4-5 tablespoons of sea salt are dissolved. The temperature of the solution must be selected at such a temperature that you can soar your feet in it for 15 minutes without severe burning or discomfort;
- Tea tree oil works as a powerful antifungal and anti-inflammatory natural remedy. Lightly soak a cotton swab with oil and lubricate the affected areas of the skin. Thus, fungus on the hands of children is well treated when you do not want to use toxic ointments.
Antifungal diet
We have figured out what is the best way to treat a child’s nail fungus, but in parallel with local and drug treatment, the doctor will advise you to follow a special diet that will help defeat the fungus faster. The child's daily diet should include:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- seeds;
- chicken eggs;
- fermented milk products.
Minimize sweets and even try to put less sugar in tea. Junk foods and heavy fatty foods will cause additional harm to the body and delay treatment. It is advisable to completely exclude the following from the child’s menu:
- fresh baked goods;
- yeast baked goods;
- sweets;
- milk.
These products create a breeding ground for the development of pathogenic microorganisms and inhibit the treatment process.
Features of the treatment of mycosis in children of different ages
With newborn children the situation is very simple. They become infected with the fungus directly from their mother or father, who are carriers of the pathogen. In these cases, your doctor will recommend using topical antifungal ointments or gels. Systemic treatment in newborns is not practiced because such therapy is too severe for babies. At the same time as the child, it is necessary to treat the adult who spreads the fungus.
Another important point. It is not enough to cure nail fungus in children; treatment involves eliminating the possibility of relapse.
Children of primary preschool age can become infected with fungus in kindergarten, school or while attending sports clubs. In each case, fungus on a child’s feet, hands or other parts of the body is treated according to an individual scheme, which is selected by the attending physician. The basis of any systemic therapy is special mild antifungal drugs to suppress symptoms without harming the child’s health.
How to treat nail fungus in a teenage child? Therapy in this case does not differ from the treatment of an adult. Antifungal drugs are used to destroy pathogenic microflora in the same volumes as in adult patients.
What drugs are used for treatment?
Typically, as part of the treatment of children, the following medications are prescribed:
- Griseofulvin . It is considered the most gentle remedy. However, its effectiveness is low. Effective only in the first stages;
- Terbinafine For children weighing up to 20 kg, up to 63 mg of the drug is prescribed, weighing 20-40 kg - 125 mg. This dosage is quite safe;
- Fluconazole You will need 3 mg of active substance per 1 weight. This dosage is for a week. The average course of treatment is 3 months;
- Clotrimazole . It is a local drug that is applied to the affected plates;
- Amorolfine . This is a medicinal varnish that can be prescribed to infants.
Travogen cream is recommended for a young child. Its action can be supplemented with Loceryl varnish. When using local products, you need to make sure that they do not come into contact with the baby’s mucous membranes.