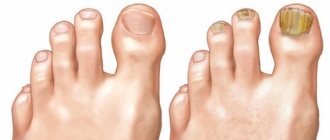
Lentigo melanoma is a rare variant of malignant melanoma, occurring in 5-10%. The most common place of formation is an open area of skin: face, ears, neck and palms. Only in 15% of cases melanoma affects the body: it occurs on the back or legs. In men, the pathology occurs 2 times less frequently, but at the same time the process more often becomes malignant.
As a rule, the disease develops after 45-50 years. The average age of the patient at diagnosis is 55-65 years. The risk of metastases is lower than with other types of melanoma, but with rapid vertical growth of the tumor, death is likely.
Classification of melanomas
Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor that develops from pigment cells. This is a dangerous type of tumor that can metastasize to almost all organs. Outwardly it looks like a nevus (birthmark), and sometimes grows out of it.
The following types of melanoma are distinguished:
- Superficial;
- Nodular or nodular;
- Lentiginous;
- Acral melanoma or acrolentiginous (subungual);
- Spindle cell;
- Achromatic.
Lentigo melanoma
Folk remedies
At home, folk remedies are an indispensable additional treatment, but only if lentigo maligna is completely excluded. Such methods can help if the spots are small and light.
For example, you can use products that contain acid on your facial skin:
- lemon, pomegranate, birch or rowan juice (just wipe the stains 1-3 times a day);
- strawberries (chop the fruits and make a mask for 15-20 minutes, rinse with warm water);
- fresh cucumber (vegetable slices should be applied to problem areas).
Such products are not harmful and can be used 1-3 times a day. They are safe for the skin and have no contraindications (except for allergies).
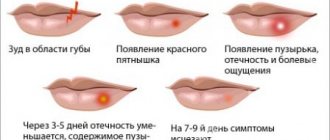
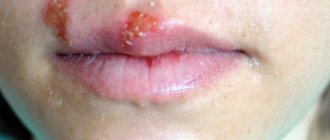
Symptoms and stages of lentigo melanoma
The disease is protracted. It can take up to 20 years from the first symptoms to the stage of malignancy (malignancy). In the initial phase, the neoplasm looks like a pale, large freckle. The size increases gradually, the growth rate varies from a couple of mm to several cm per year. The freckle gradually turns into a pigment spot, whose distinctive feature is an irregular shape with clear boundaries and a smooth surface that does not extend beyond the intact skin.
The color takes on a number of different shades of red-pink, yellow-brown and white, but the pigmentation is uneven. Therefore, the formation resembles a blot or the outline of an island on a geographical map. This is how lentigo maligna (lentigo maligna), a precursor to melanoma, develops. This is the first stage with a clear clinical picture of the pathology. Transition to full-blown melanoma occurs in 50%.
During vertical growth, cancer cells penetrate beneath the epidermis and deeper. This phase is characterized by blurring of the tumor boundaries. They become wavy and not so clear. The tumor becomes bulging. The surface of melanoma also undergoes changes: cracks and nodes appear. The skin peels and the color darkens. At this stage, patients complain of itching at the site of formation and periodic bleeding.
The inflammatory process in the immediate vicinity of the tumor is a sign of the last stage and the formation of metastases. Melanoma becomes blue-violet. The patient’s well-being in this phase is characterized by the signs of any cancer:
- Severe fatigue;
- Heat;
- Sudden loss of body weight;
- Swelling of the lymph nodes;
- Weakness.
Malignant lentigo melanoma progresses slowly even in the vertical growth stage. Compared to superficial melanoma, the likelihood of metastases spreading is much lower.
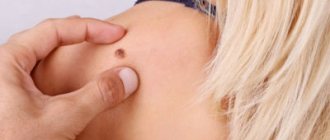
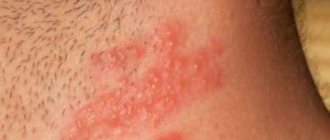
Clinical picture
Rice.
1. Skin of a woman with lentigo: single rounded formations of dark color, rising above the skin level (indicated by arrows). Rice. 2. Skin of a man with lentiginosis: multiple rashes in the form of small spots and formations rising above the skin level. L. appears more often already in the first years of life in the form of single (up to a dozen) elements (Fig. 1). A further increase in the number of rashes is observed either in adolescence (adolescent L.) or after 50 - 60 years (senile L.). Youthful L.—multiple, scatteredly located on any area of the skin, hyperpigmented oval-round sharply limited non-inflammatory formations of light brown or dark brown color. Senile L. is localized mainly on the back of the hands, forearms, face, neck and has a dark brown color, up to brown-black. There are no subjective sensations with L. In adults, the total number of lentiginous elements varies over a wide range, often reaching 20-30. The formation of a very large number of elements is possible, up to profuse (lentginosis) rashes (Fig. 2), which can also be located on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and genital organs.
Rare varieties of L. include: asymmetrical, or one-sided, lentiginosis, characterized by an asymmetrical location of the rash; midfacial Touraine's lentigo, which is characterized by localization of elements on the forehead with a transition to the bridge of the nose, nose, less often lips and neck; perioral L. - Peutz-Jeghers-Touraine syndrome (see Peutz-Jeghers syndrome). Certain elements of L. may, over time, take on a warty character or the character of pigmented hair nevi.
Diagnosis
placed on the basis of a characteristic wedge, pattern. Differential diagnosis is carried out with freckles (see), senile keratoses (see Keratoses).
Causes
One of the causes of lentigo melanoma is the degeneration of a benign nevus due to constant trauma. Therefore, doctors recommend removing birthmarks in areas of regular friction - on the neck, shoulders, skin of the feet and palms. A large number of moles is a reason to be wary and closely monitor their appearance and condition.
The tumor occurs due to Dubreuil's melanosis, a precancerous skin disease characterized by an increased number of pigment spots of various colors and shapes. Risk factors include prolonged exposure to the sun and excessive dryness and dehydration of the skin. Sunburn received in early childhood or adolescence can play a decisive role. Women over 65 years of age and light-skinned and light-eyed people (Fitzpatrick types 1 and 2) are most susceptible to the disease.
Lentigo melanoma appears due to the same reasons as others. It differs in that before the development of malignant tumors, a characteristic change in the skin occurs.
Drug therapy
Exfoliating products are required during the treatment of lentigo
Whitening (exfoliating) agents include preparations based on azelaic and kojic acid, licorice extract, arbutin, ascorbic acid, etc.
In addition, dermatologists quite actively prescribe low-potency corticosteroids (hormonal agents) in the form of creams and ointments to treat this condition. Hormones do not affect the process of photosensitization itself, but the inflammatory moment, if prescribed in a timely manner, is eliminated, which does not allow the spot to “fix” and prevents an increase in lentigo zones.
Retinoids are quite effective. These are synthetic analogues of retinol, i.e. vitamin A.
Retinoids - structural variations of vitamin A
Retinoids are structural variations of vitamin A (retinol) - Tretinoin, Isotretinoin, Accutane and their analogues. These drugs affect recovery processes, including skin regeneration after sunburn. They have effects comparable to hormonal drugs, i.e. prevent inflammatory changes in the skin.
Cream Iklen Melano-Expert is a combination drug that combines medicinal components
There are also combination preparations that include several active medicinal components at once, for example, Iklen Melano-Expert cream (rucinol, sophora, centaridin, ascorbic acid isomer).
Not all elements of lentigo are amenable to medicinal effects, so in some cases radical methods of treating this type of age spots are necessary.
Diagnostics
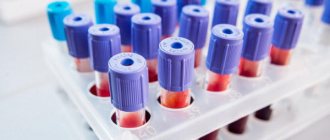
Timely diagnosis of lentigo reveals the disease at the stage of development, when the process of malignancy of melanoma has not begun. In this case, a complete cure is possible. The dermatologist examines the spot, measures it, and takes a photo. Non-invasive methods include dermoscopic examinations and computer diagnostics. The latter helps to analyze tumors over time. Dermatoscopy reveals structural features, which makes it possible to diagnose benign and malignant tumors.
A blood test shows the presence of tumor markers - enzymes that produce tumor cells.
Upon morphological examination, the initial stage shows atypical melanocytes - cells that produce melanin, which do not extend to the stratum corneum of the skin. When Dubreuil's disease transitions to lentigo-melanoma, changes affect all layers of the epidermis.
At the first signs of malignancy and vertical growth, a biopsy is performed. Part of the intact tissue is cut off and sent for biopsy. Examination of the site of the disease is not recommended, as this may cause uncontrolled growth of malignant cells. At this point, cancer cells penetrate the dermis and the inflammatory process begins.
Histology confirms the fact of a malignant tumor and determines the structure and stage of the process. It is carried out after excision. It reveals the proliferation and thickening of the epidermis.
Types of lentigo melanoma
The task of differential diagnosis is to distinguish pathology from diseases that are similar in external manifestations, but are not malignant. In this case, it is important not to confuse it with hyperkeratosis or actinic lentigo, which occur in the same areas of the skin as melanoma.
Laser therapy for senile lentigo
A slightly more aggressive version of the previous method. Allows you to carefully remove pigment spots. The skin regenerates, after a few months there is not even a stain left.
Phototherapy and laser therapy for lentigo require mandatory prior consultation with a dermatologist.
Laser therapy for lentigo should be carried out after consultation with a dermatologist.
This is due to the fact that a diagnostic error can be very costly for the patient. Destroying a melanoma-dangerous nevus or the superficial layer of lentigo maligna sometimes leads to the development of one or another form of skin cancer (melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma).
These methods are contraindicated for mycoses and other inflammatory diseases of the affected skin area, since there is a high risk of infection spreading in the treated area.
Treatment and prognosis
The type of treatment for lentiginous melanoma directly depends on the stage of the disease. The course of therapy is drawn up by the oncologist after an initial examination and consultation.
Surgical method
Surgery is the main method of treating melanoma. The neoplasm is removed, capturing adjacent tissues that have not undergone changes. This reduces the risk of relapse. It is recommended to perform surgery before the vertical growth stage begins, while the tumor affects only the top layer of skin cells. It is performed under local anesthesia, then stitches are applied. Subsequently, it is possible to carry out cosmetic surgery to eliminate the appearance defects that have arisen.
If the tumor has managed to metastasize, a regional lymphadenectomy is recommended, during which all malignant nodes in a specific organ are removed. For metastases in distant anatomical areas, treatment is tailored to the individual patient. The degree of development of the oncological process and the location of secondary foci are important. Individual metastases and those that threaten the patient’s life are removed.
Radiation therapy
If the size of the spot or the location of the tumor on the face makes surgical removal impossible, close-focus radiotherapy is performed. Lentigo melanoma is poorly responsive to chemotherapy and radiation therapy, so options are limited. The methods are justified in case of a significant number of metastases or as a step in combination therapy. Using X-rays, tumor development is stopped.
The average five-year survival rate for skin cancer was 92% in 2010 and rising. In the case of lentigo melanoma, due to the long period of horizontal spread, it is characterized as favorable. With the superficial growth of melanoma, it is 100%, but when the vertical growth phase is reached, it begins to rapidly deteriorate, and after surgery it drops to 15-25%, despite the fact that metastasis occurs only in 10% of cases.
How to treat lentigo
At the first stage of ridding the client of hyperpigmentation, it is necessary to take control of melanogenesis. For this purpose, the cosmetologist has in her arsenal procedures and products that include tyrosinase blockers.
The second stage of treatment will be work to balance pigmentation: lightening/whitening and healing. At this stage, the most effective means in the cosmetologist’s arsenal will be AHA acids, and preparations for restoring the antioxidant capabilities of the skin, lipid metabolism and barrier function will be an indispensable aid in tissue regeneration processes. Now let's talk in more detail about each stage and its “main characters”. Tyrosinase blockers are substances that block the hyperactivity of melanocytes. Pigment spots appear due to the intense interaction of tyrosine (an amino acid) and tyrosinase (an enzyme that catalyzes the first stage of melanin synthesis). The most important role in the treatment of lentigo is played by biologically active substances that influence the suppression of melanin production and its destruction in epidermal cells. Active tyrosinase blockers include: mulberry and bergenia extract, glabridin, as well as kojic and phytic acids.
The most famous blocker is arbutin (hydroquinone glycoside). It is found in bearberry leaves, wintergreen and licorice root. Arbutin is identical to vaccinin, a bitter substance first extracted from lingonberry leaves. The vaccine does not cause skin irritation and does not have a photosensitizing effect, which allows its use for a long time.
By blocking tyrosinase, you can slow down the formation of melanin for an extended period of time in areas of hyperpigmentation and remove old, excess melanin that usually gets trapped and accumulated in the upper layers of the epidermis. Alpha hydroxy acids are most commonly used to treat acne, dry skin, actinic keratoses, and to improve skin color and texture. However, AHAs are also actively used to treat hyperpigmentation of various etiologies.
Low concentrations of AHAs promote exfoliation by breaking the bonds between corneocytes and stimulate the growth of new cells in the basal layer, while high concentrations of AHAs promote epidermolysis and the removal of melanin from the basal layer. Alpha hydroxy acids serve as stimulants to the basement membrane, which is the producer of new skin cells. Under the influence of AHA acids, the dermis thickens and the epidermis becomes thinner, the stratum corneum becomes elastic and firm.
The undisputed leader among alpha hydroxy acids in the matter of whitening age spots is glycolic acid : it improves the outflow of sebum and causes exfoliation of keratinized scales covering the skin. Glycolic acid has the smallest molecular weight and easily penetrates the skin, which allows it to produce the most noticeable effect. External products based on glycolic acid are used during periods of light solar activity, from October to April. During the sunny period, it is better to use home remedies with antioxidants and photoprotectors. Glycolic acid is found in green grapes and sugar cane.
Antioxidants. The formation of persistent hyperpigmentation is associated with a decrease in the antioxidant capacity of the skin in a certain area. The main antioxidant of the skin is hyaluronic acid. It is part of the skin and is involved in tissue regeneration. With excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation, inflammation occurs - sunburn, while the synthesis of hyaluronic acid in the dermal cells stops and the rate of its decay increases. Due to its high content in extracellular matrices, hyaluronic acid plays an important role in tissue hydrodynamics, processes of cell migration and proliferation, and is also involved in a number of interactions with cell surface receptors.
Hyaluronic acid and proteoglycan, in combination with the action of natural active ingredients, affect the production of melanin, and after 30-40 days of daily use, pigment spots become noticeably lighter, the skin acquires an even color, smoothes out and looks radiant and healthy. To restore antioxidant status, not only external application of antioxidants is indicated, but also procedures that stimulate the synthesis of one’s own hyaluronic acid. Vitamins C and E play a huge role in restoring natural skin regeneration. They stimulate collagen synthesis, protect the skin from infections and the appearance of new age spots.
An excellent assistant in skin restoration is oat protein, which promotes the healing of microcracks, eliminates itching and irritation, and supports the whitening effect of active ingredients. Jojoba oil optimizes lipid metabolism, restores skin barrier function, softens it, relieves tension and irritation, mulberry extract inhibits tyrosinase, and niacinamide improves skin barrier function and vascular function, inhibits the transfer of melanin to keratinocytes. Turmeric extract - curcumin - is a safe and effective skin lightener. Kojic acid contains melanin inhibitors that block tyrosinase.
In cosmeceuticals, there are often examples when certain components have a complex effect. For example, Emblica officinalis extract effectively fights the appearance of age spots and has a long-lasting antioxidant effect. And licorice extract acts as a powerful antioxidant, tyrosinase blocker and has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
When choosing an effective anti-pigmentation technique, it is important to take into account the presence of anti-inflammatory drugs and components (both in the protocol itself and in long-term home care products), and a complex of complementary antioxidants.
In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the severity of exfoliation aggression in the technique or its traumatic nature (possibility of burns, thermal damage), as well as to the capabilities of the daytime product, but not only to the parameters of the filters, but also to the antioxidants, moisturizers, soothing and cooling components included in the composition , non-toxic depigmenting components.
Vitamin C. Cosmetics with ascorbyl tetraisopalmitate (a fat-soluble derivative of vitamin C) lightens the skin, radically solving pigmentation problems: it inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase, preventing the synthesis of melanin from tyrosine, and also slows down the transfer of pigment to skin keratinocytes.
Prevention
Measures to prevent skin diseases include constant protection from ultraviolet radiation. The UVI (UV Index) helps with this. It was developed by the World Health Organization as part of the international program to combat cancer and prevent cancer. This is a special indicator (0-10) characterizing the potential danger to a person in a specific geographical location during solar noon, i.e. between 12-14 noon. According to it, with a value above 3 (average radiation level), sun protection is required - cream with a high SPF factor, long sleeves and a hat. When the index is 8 or higher, it is recommended to stay in the shade.
If you have a large number of birthmarks, you should undergo regular examinations with a dermatologist to evaluate the condition of the nevi. Regular self-diagnosis helps to be alert in time if moles increase in size or change color.
Early detection of pre-melanoma formations is a type of prevention. Detection of lentigo melanoma in the radial growth stage leaves the possibility of a favorable outcome.
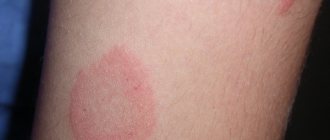
The nature of senile lentigo
Senile lentigo is a consequence of skin damage from ultraviolet radiation
It occurs predominantly in people of the white race, as a delayed consequence of skin damage from ultraviolet radiation. At a young age, this kind of phenomenon is atypical, because The compensatory capabilities of the skin and the level of general metabolism are significantly higher.
Lentigo develops faster in people with existing metabolic disorders, in particular diseases of the digestive system, bad habits (alcoholism, hepatitis, peptic ulcer).
Senile lentigo does not pose a health risk, but in some cases it is an unpleasant cosmetic defect (and also indicates age).
In some cases, a borderline nevus or lentigo maligna tries to masquerade as this harmless condition. Sometimes ordinary freckles are mistaken for senile lentigo. To make a correct diagnosis, you need to visit a dermatologist.
Photo gallery: formations similar to senile lentigo
Etiopathogenesis
Lentigo senile is a benign proliferation of melanocytes in older adults. In this case, a stain is formed, the appearance of which is caused by the influence of UV rays.
From this point of view, lentigo is similar to freckles and pigment spots vulgaris, which appear as a result of age-related hyperkeratosis. A distinctive feature of lentigo is the mixed nature of pigment formation, that is, the spot appears as a result of sunburn, hormonal changes and age-related changes.
According to statistics, more than half of people over 60 years old have one or two such spots. It is more common in patients with very light skin.
Hyperinsolation is the cause of the problem
The pathology has no gender differences and can occur with equal probability in both men and women. The debut can take place at any time of the year. The urgency of the problem is determined by aesthetic discomfort, especially in the case when multiple age spots are located on the face.
Important! Senile lentigo never becomes malignant. However, accurate diagnosis is necessary to distinguish it from borderline nevus or lentigo maligna.
The immediate reason why a senile lentiginous spot is formed is UV rays that affect the epidermis. This layer contains up to 85% of keratinocytes; they are responsible for tanning, that is, the skin's response to the sun's rays.
Ordinary epidermal cells do not produce melanin; it enters them by transport from melanocytes. They are the main source of pigment and the second most numerous cells of the epidermis. People with fair skin have little melanin in their skin, which means they have less protection from UV rays.
How does UV radiation affect the skin?
Due to hyperinsolation, the formation of melanin is stimulated and a tan appears. Some of the cells that are filled with pigment rise to the surface, while some remain at the level of the granular layer. Melanin accumulates.
Keratinocytes, which are filled with melanin and have already performed a protective function against radiation, become horny scales and peel off. A month after exposure, these cells are replaced by new ones with a normal amount of melanin, and the skin returns to its usual shade.
Melanin performs antioxidant functions, inhibits oxidative processes, binds free radicals, which generally prevents skin aging. But over time, this substance can become a source of free radicals, and melanocytes acquire the ability to become malignant.
After 50 years, the pro-oxidant properties of melanin begin to prevail over the protective ones. It is during this period that senile lentiginous spots form on the skin. They appear both after tanning and spontaneously, as a result of a cumulative effect.
Scheme of melanin formation and skin pigmentation
In addition, patients who have diseases of the digestive system, as well as alcoholism, suffer from disorders of bilirubin metabolism. This substance accumulates in the skin, epidermal cells perform a protective function worse, and the rate of metabolic processes decreases. Because of this, chronic inflammation occurs, which further stimulates the appearance of senile lentigo.