Many birthmarks are harmless and do not require any treatment. They either disappear as the child grows or remain on the skin, but do not pose a health hazard.
Other moles can grow very quickly. Without medical treatment, they can become large, permanent areas of discoloration that can affect the deeper layers of the skin. If the birthmark is located in a very visible location, parents may decide to keep its appearance to a minimum while the child is young.
Drug and laser therapy can be very effective in reducing the size of birthmarks and preventing them from recurring.
Diagnosis of nevi
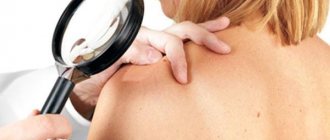
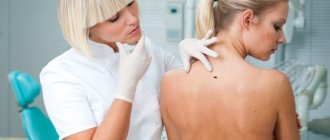
How to determine whether a mole is dangerous or not? To do this, you should contact a dermatologist and undergo a detailed examination. Since it is not possible to independently determine dangerous nevi in a child. Diagnostics includes the following research methods:
- Detailed survey of parents. Taking an anamnesis helps determine the genetic predisposition to the formation of moles in a child. If there have been cases of dangerous moles in the family, then the baby is also likely to have them.
Visual inspection. The doctor carefully examines and palpates the tumor. Atypical moles with uneven edges and uneven color require additional research in the laboratory.- Dermatoscopy. This research method involves the use of a dermatoscope. This is a device that enlarges a fragment of the skin several times. Thanks to this, pathological changes in the nevus can be seen.
- Histological analysis. It is performed after surgical removal of a mole. This material is sent for thorough examination, after which a pathological process is excluded or confirmed.
If the pathology extends beyond the mole, the child is sent for the following studies:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- Ultrasound diagnostics of lymph nodes;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- biopsy.
It is important to know! A biopsy is not performed until the tumor is completely removed! Because after taking a fragment of a mole, a part of it remains, which can develop into melanoma.
The danger of nevi on the feet
The worst place for a mole is the soles of the feet, because they are used every day for walking and are often susceptible to injury when wearing low-quality shoes. These factors together increase the risk of degeneration of an initially benign tumor into a malignant formation. An even more unfortunate place for a mole on the foot is the space between the toes.
The formation of nevi in such places should alert the owner and become a reason to visit a doctor. Those who have or have had relatives with skin cancer should definitely not delay consultation with a specialist. The main rule when detecting these formations is that you cannot self-medicate. Even understanding how to remove a mole at home is not considered a sufficient argument in favor of self-medication.
Harmless moles in children
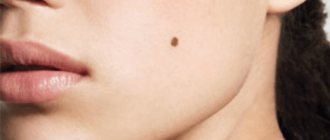
Safe moles can vary in size and shade. You should not worry about your child if the tumors look like this:
- flat;
- uniform color;
- diameter less than 5 mm;
- the relief corresponds to the skin;
- hair is present.
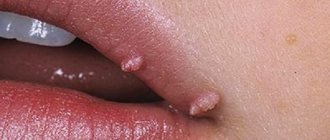
Convex moles in most cases also do not pose a danger to children. But they are more susceptible to damage, especially if they are located in areas where friction occurs regularly. A child can inadvertently tear off these nevi and injure them. In such situations, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Indications for removal
Birthmarks are benign phenomena on the body, do not cause harm, and are not dangerous.
But there are dangerous malignant nevi. Experts classify such moles as formations with a diameter of 20 centimeters or more. They have a risk of developing into malignant tumors. Every spot has a risk of becoming malignant, but the risk of degeneration is 15% higher for large lesions. It is recommended to remove flat birthmarks that cover the skin. Formations appear in the area of the baby’s head and face. The spot can change in size throughout a person's life. During growth, the color of the nevus does not change. It is advisable to remove formations immediately after detection.
It is recommended to remove stains with symptoms:
- pain appeared;
- increased size;
- there is itching on the formation;
- texture, color, density changed.
It is recommended to remove those tumors that are located in areas subject to damage.
Dangerous neoplasms
Dangerous tumors can develop into melanoma. Therefore, they require constant monitoring. At the first pathological changes, you should contact a specialist. Dangerous nevi in children include:
Blue mole.
It has a bluish tint, uncharacteristic for such neoplasms. Located in the deep layers of epithelial tissue. The risk of cancer increases if the blue mole is located in a place that is subject to friction.- Borderline neoplasm. It has a black or brown tint and does not protrude above the surface of the skin.
On such nevi, unlike other birthmarks, there is no hair.
Mole Ota. It is a type of blue nevus.
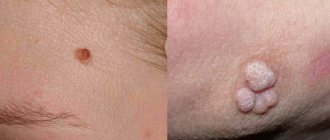
It is a large spot with an uneven color. Most often localized in the facial area. Initially, such a neoplasm resembles a bruise, but then begins to increase for no apparent reason.- Large pigmented mole. In appearance, this neoplasm resembles a wart.
This is a convex mole with a bumpy surface. Over time, it tends to grow. Therefore, it can reach significant sizes at some point.
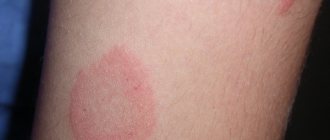
Red moles. They are formed from blood vessels.
Hemangiomas are very common in children. They pose a danger only if they begin to grow dynamically and cause discomfort in the child.
In any case, all moles in children should be under close attention. For any pathological changes, you need to contact a specialist. Despite the fact that their removal in a child occurs in extremely rare cases, in some situations surgery is the only way to avoid the development of melanoma.
Why do they appear?
Nevi are essentially benign skin formations.
Some people get scared when they see many moles on their body. What does this mean for a specialist? Only that the patient’s body is prone to accumulation (accumulation) of melanin in the surface layers of the epidermis.
The reasons for the appearance of numerous or single nevi are varied.:
1. External:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation, one of the most common factors in the formation of moles due to increased melanin levels during tanning;
- traumatic damage to the epidermis, systematic violations of the integrity of the skin contribute to the appearance of pathological changes in it;
- exposure to radiation, which rapidly changes normal skin cells;
- consumption of harmful products (GMOs, fast food, alcohol) and smoking, these habits negatively affect metabolic processes in the body.
2. Internal:
- endocrine disorders and diseases, any changes in hormonal levels can cause the appearance of skin pathologies, pigmentation, moles;
- hereditary predisposition, the presence of various nevi in the family.
The appearance of moles can be triggered by inflammatory and autoimmune skin diseases, toxic lesions, burns and frostbite, as well as the constant use of low-quality cosmetics and preparations for face and body care.
Alarming symptoms
Pathological neoplasms, when actively developing, can cause skin cancer. Therefore, any uncharacteristic changes in nevi in a child should not be ignored. So, when is there a reason to visit a specialist? Presence of the following symptoms:
- Growth of neoplasm. An active, unnatural increase that does not correspond to the baby’s growth indicates the development of a pathological process. Such nevi need to be gotten rid of.
- Sudden color change. Regardless of whether the nevus becomes brighter or paler, this is an atypical symptom.
- Seal. The mole should not become hard over time. When this sign appears, you should pay attention to at what point the compaction appeared and in what part of the neoplasm.
- Change in the nature of the nevus. Cracks or a white coating may appear on the mole, which most often causes bleeding.
- Bleeding. If a child’s nevus begins to bleed, then it is necessary to treat it with an antiseptic, apply a sterile bandage and contact a specialist for help.
- Discomfortable sensations in the area of the tumor. The child should not feel itching, burning, pain or other discomfort. Safe moles do not cause them.
Why are the above symptoms dangerous to health? They indicate the development of an atypical pathological process that can lead to melanoma.
What may the appearance of a large number of moles indicate?
A large number of age spots may indicate:
- frequent exposure of the baby to the sun;
- hormonal surge (typical in adolescence);
- exposure to x-ray radiation;
- consequences of past illnesses and injuries.
The location of moles can be inherited.
The following are more likely to form birthmarks:
- children with light skin color;
- girls (5 times more than boys);
- premature babies.
Frequent age periods of children that are characterized by the appearance of pigmentation: 0.5-2 years, 5-6 years, 12-16 years.
Development of melanoma in a child
This serious disease does not always develop in moles. Sometimes a stain may appear. The disease also appears as a result of improper removal of the nevus. In moles, melanoma develops gradually and does not cause discomfort in the early stages.
Over time, the patient may experience the following pathological signs:
the tumor is growing rapidly;- change in the shape of the mole, a healthy nevus should be round in shape;
- the birthmark changes color, brown and black shades begin to predominate;
- the appearance of plaque, peeling, crust formation on the nevus;
- bleeding;
- burning, itching and other discomfort.
A birthmark that has reached 5 mm or more in a short period of time may also indicate the development of melanoma.
These symptoms require immediate consultation with a doctor for help.
What should parents be wary of?
In these cases, you urgently need to show the child to a dermatologist or oncologist:
- the nevus has changed consistency or color;
- tubercles, ulcers, depressions, and ulcerations appear on the surface of the nevus;
- the surface of the nevus peels off, crusts form;
- the skin pattern disappears on the surface of the nevus;
- the formation rises above the surrounding tissues;
- softening of the nevus;
- inflammation appeared;
- bleeding, the surface becomes wet;
- pink or pigmented daughter formations appear;
- nevus grows horizontally;
- the surface becomes glossy and shiny;
- burning or itching appears;
- hairs fall out from the surface of the nevus or are absent;
- depigmentation is observed (the color becomes paler) in some areas;
- small nodules appear.
How to check a mole?
It is not possible to independently distinguish a safe neoplasm from an emerging melanoma. To do this, you need to contact a qualified oncologist who will conduct a thorough diagnosis. It is aimed at conducting the following research:
- histological analysis. To do this, a fragment of mole tissue is taken from the child for study.
- Biopsy. It helps determine the type of malignant tumor.
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
If, after the tests, malignant cells are found in the child, a blood test is required, after which the method of treatment is determined.
After diagnosis, only a specialist can decipher the research results and also establish a diagnosis: a dangerous mole or a non-dangerous one.
Contraindications and precautions
Contraindications to this procedure in a child are:
- the presence of infectious skin diseases in the area of the mole being removed;
- poor blood clotting;
- severe heart defects.
Precautionary measures include preparation for the operation, namely the collection of additional tests, which include a general blood test, as well as a blood clotting test. In addition, children need to be tested for an allergic reaction to anesthesia.
Appearance
What do dangerous moles look like? Based on the appearance of the nevus, you can determine whether there is cause for concern. The reasons for visiting a dermatologist are the following neoplasms:
A mole with uneven edges. A safe nevus should have a clear round shape.
If the edges become uneven and nicks appear, this is a cause for concern. Pathology is also indicated by the loss of round shape in convex moles.
Rough mole. A degenerating nevus may begin to peel off, and also become covered with plaque and cracks will form on it, which may bleed.
Such moles often cause discomfort in the child and require prompt medical attention.
Large moles. They are most often called birthmarks.
They tend to grow with age. But too dynamic growth indicates an atypical process that can lead to dangerous consequences.
Vascular tumors do not pose a danger to the child; they disappear over time on their own. But their increase, the appearance of a brighter shade can also be a dangerous sign.
Oral therapy
Propranolol is a medication taken by mouth that can be very effective in reducing the size and lightening the color of hemangiomas, which are vascular birthmarks caused by malformed blood vessels. Propranolol inhibits the growth of new blood vessels inside hemangiomas and shrinks existing blood vessels.
Dermatologists may prescribe propranolol if the hemangioma is located in the airway or near the eyes or mouth and threatens to impair functions such as vision or breathing. Your doctor may also prescribe this medication to shrink hemangioma for cosmetic purposes.
Propranolol comes as a liquid medicine and is taken two to three times daily during the child's first year of life, when hemangiomas tend to grow more aggressively. These birthmarks often become smaller or lighter in color within a few weeks.
After the first year of treatment, dermatologists evaluate the size and color of the hemangioma before recommending additional treatment. The goal of treatment with propranolol is to continue therapy until the hemangioma no longer grows and to gradually discontinue treatment as soon as possible after one year. However, stopping treatment too early may result in regrowth.
What happens if you rip off a mole?
You cannot remove a nevus yourself.
Firstly, it is dangerous, and secondly, it is simply ineffective. If the mole is located close to blood vessels, prolonged bleeding may develop. Often such self-medication leads to re-formation of the nevus, its growth or malignancy.
Therefore, it is difficult to predict what will happen if a mole is torn off. It may have no consequences, or it may cause serious complications for the health and life of patients.
Doctors warn that any trauma to the nevus is extremely undesirable, but pedunculated moles or small convex formations can be accidentally removed with nails or hard items of clothing.
What to do if you rip off a mole:
- cauterize the wound with an alcohol solution;
- stop the bleeding by applying a gauze bandage;
- come to see a specialist.
In cases of partial removal of a mole, do not touch the remaining formation, do not cut it off or tear it off.
Sometimes such pigmentation appears before the disappearance of a mole (as a sign of depigmentation), and in other cases it may signal its degeneration. White spots around the mole appear as a characteristic sign of Setton's nevus. This formation is considered harmless in terms of degeneration into a more malignant form, however, melonomas (aggressive cancerous formations) can also have such a white rim, so the appearance of white spots is a reason to contact a medical specialist.
How to remove nevi on the feet
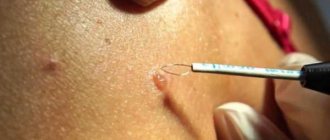
Modern medicine offers five ways to remove moles. The appropriate option is selected jointly with the attending physician; it depends on the type and characteristics of education:
- Laser removal. It has proven itself due to the complete absence of pain and rapid operation, safety and the impossibility of recurrence of the formation.
- Scalpel. It is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor captures some of the healthy tissue. After the operation, a scar remains.
- Cryodestruction. Removal occurs under the influence of ice, carbonic acid or liquid nitrogen. The operation is good because it is painless, but it is expensive.
- Electrocoagulation. Using the method of exposure to high temperatures, the mole is cauterized along with a healthy area of skin. Cannot be performed with high pain sensitivity.
- Radiosurgery. The nevus is destroyed due to the action of radioactive radiation. Completely eliminates moles and has a disinfecting effect. There are no complications.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. But if you ask a doctor about how to remove a mole at home and whether it is worth doing, he will definitely recommend any available operation performed by professionals.