Pseudoscabies (pseudosarcoptosis) is a parasitic human disease caused by mites that live and reproduce on animals. The pathogen is transmitted primarily from dogs and cats, and less commonly from pigs, goats, sheep, poultry and horses. After contact with the carrier, the female parasites that get on the skin penetrate into its upper layers, causing severe itching. Unlike true scabies, with pseudosarcoptosis mites cannot gnaw tunnels in the skin and reproduce on the human body, so the disease is not contagious to other people.
Case history of scabies
The history of scabies dates back to ancient times. Scabies is the most common parasitic skin disease. Scabies was known 4000 years ago in China, Ancient Babylon, Egypt, and Assyria. Aristotle O. In 1687, the Italian physician Giovanni Cosimo Bonomo and the pharmacist Diacinto Cestoni first described the connection between scabies mites and the typical skin symptoms that develop following infection. It was they who established that the disease could be caused by a microscopic organism.
Causes of scabies: scabies mite in humans, photo
The reasons for the high incidence of scabies are factors such as poor personal hygiene, promiscuity, population migration, and deteriorating material conditions. Also in recent years, the number of low-symptomatic (erased) forms has increased. This is caused by the widespread use of ointments, creams with steroid hormones, antihistamines, and contact with chemicals. These are common causes of scabies in modern humans.
Scabies is caused by the scabies mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The scabies mite in humans is an obligate (permanent) parasite, the characteristic feature of which is transmission only from person to person. Ticks spend most of their lives in the skin of the host (females) and only during a short period of settlement they lead an ecto-parasitic lifestyle (males) on the surface of the skin. S. scabiei parasitizes the superficial layers of the skin, but with a complicated course it can also affect deeper layers.
We offer a photo of a scabies mite:
Pseudoscabies or pseudosarcoptosis: don’t relax!
Pseudoscabies (or false scabies) is defined in medicine by the term pseudosarcoptosis. This is a cutaneous parasitic dermatosis, the development of which is provoked by small mites of the genus Sarcoptes scabiei species S. s. canis, S. s. suis, S. s. bubulus, S. s. equi, S. s. dromedarii and others that actively colonize the skin of animals (rats, dogs, rabbits, pigs, cats, horses, goats and sheep, cows, buffaloes, camels) and birds (chickens, turkeys, pigeons). Today we will talk about the causes of such “pseudo” scabies in humans, its signs, symptoms and alternative treatment for pseudosarcoptosis.
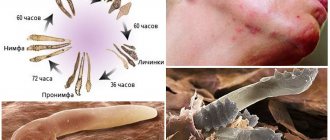
Life cycle of scabies mite
The length of the female scabies mite is 0.3-0.4 mm. The life cycle of the scabies mite is about 1 month. Females make passages under the stratum corneum of the epidermis, laying 2-3 eggs there daily. The eggs hatch into larvae. Within 2 weeks, the larvae, having gone through several stages, turn into adults. The latter rise to the surface of the skin and mate. The males, having fertilized the female, soon die. The fertilized female implants itself into the skin of the previous or new host. Thus, the clinical picture of the disease is caused exclusively by females.
The lifespan of a scabies mite at room temperature 22°C and 35 percent humidity is about 4 days. At a temperature of 60°C, ticks die within an hour, and at temperatures below 0°C almost instantly. The invasive stages of scabies mite development are only young females and larvae. The average survival time for female scabies mites reaches 3 days, and for larvae 2. It is in these stages that the mite can move from a host to another person and exist for some time in the external environment. Moreover, smoke dust, wooden surfaces, and natural fabrics are the most favorable habitats for S. scabiei outside the host.
Ways of infection with scabies
The incidence of scabies increases in the autumn-winter period. Scabies almost always occurs through prolonged direct skin-to-skin contact. In adults, sexual transmission predominates. Children often become infected when they sleep in the same bed with sick parents. In crowded groups, other direct skin-to-skin contacts are also realized (contact sports, children's games, frequent and strong handshakes). The low incidence of cases of indirect scabies infection is explained by the weak viability of the mite in the external environment.
Distinctive features of pathology
The development of pseudoscabies in humans occurs without an incubation period. Infection with the disease occurs through mite larvae; mature individuals are infected directly with scabies itself. The larvae are not able to gnaw passages under the epidermis; they only bite through the skin when infected and leave a wound in place. This produces saliva, the toxins of which cause severe itching.
Bites are usually localized on open areas of the skin in contact with the skin or fur of animals. A person can only become infected from animals; a sick person is not contagious. Pseudosarcoptosis can be eliminated on its own if the cause is eliminated.
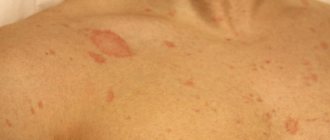
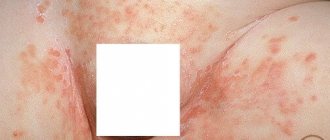
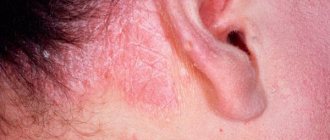
Manifestations and symptoms of scabies with photos
The first and main subjective symptom of scabies is itching, which gets worse in the evening. Its intensity, as a rule, increases as the duration of the disease increases, which, in turn, depends on the number of the parasite and the individual characteristics of the organism. Manifestations of scabies include: sensitization of the body to the mite and its waste products and the state of the patient’s nervous system. The number and distribution of scabies in the skin is not random and is determined by the rate of regeneration of the epidermis, the structure and thermal regime of the skin. Mostly scabies burrows are located on areas of the skin of the hands, wrists and feet that have a low temperature, minimal or absent hair and the maximum thickness of the stratum corneum of the epidermis (hands, wrists and feet).
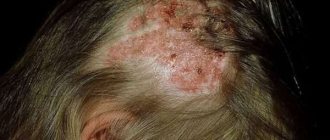
Rashes in infants due to imperfect immunity often affect areas of the skin that are extremely rarely affected in adults: the face and head, soles and palms. Moreover, sometimes the symptoms of scabies on the face and head are “masked” by the clinical picture of acute weeping eczema, resistant to conventional therapy. In children, scabies can be complicated by severe pyoderma and sepsis.
Scabies can occur in different ways. Symptoms of scabies depend on its form :
Typical scabies , the most common. It is characterized by the presence of all of the above symptoms (itching, scabies, etc.).
Scabies without moves . Its difference from typical scabies is that there are no scabies on the skin, but there are bubbles up to 2-3 mm in diameter. Scabies without burrows develops in people who have been in contact with someone with scabies, but they were infected not by adults, but by larvae, which take time to develop.
Clean scabies is similar to typical scabies, but it develops in people who wash frequently and remove most of the scabies mites from their bodies. Thus, their scabies are not as severe as typical ones.
Norwegian scabies develops in people with weakened immune systems (for example, with AIDS, tuberculosis), drug addicts, and people with Down syndrome. Norwegian scabies is very severe, affects the entire body, including the head, and is highly contagious.
You can see the main symptoms of scabies in the photo:
Treatment of scabies
Treatment of scabies in patients identified in one lesion should be carried out simultaneously.
Anti-scabies are rubbed into the entire skin of children under 3 years of age; in other patients, the exception is the face and scalp. Rubbing in anti-scabies drugs is done only with your hands - for better penetration into the passages.
Treatment is carried out in the evening, which is associated with the daily rhythm of pathogen activity.
It is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of contact persons. It consists of a single treatment with any anti-scabies drug.
It is recommended to wash the patient before and after the course of treatment. If necessary, the drug can be washed off every morning, and its exposure on the skin should be at least 12 hours, including the night period.
Change of underwear and bed linen is carried out at the end of the course of therapy.
Forecast
After isolation of the carrier animal and uncomplicated pseudoscabies (without infection or acute allergy), the prognosis is favorable. In such cases, anti-scabiosis (anti-mite) therapy is not necessary - it is enough to take a soap bath and wash thoroughly with a washcloth, followed by treating the bite sites with antiseptics - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide.
If itching, hyperemia, inflammation around the bites does not go away for several days or signs of pseudoscabies appear in other places, you should contact a parasitologist, infectious disease specialist or dermatologist to make an accurate diagnosis.
Preparations for the treatment of scabies
Before starting treatment, it is advisable to take a hot shower using a washcloth and soap to mechanically remove mites and sebaceous gland secretions from the skin and to loosen the stratum corneum of the epidermis, which improves the absorption of anti-scabies. However, in the presence of secondary pyoderma, water procedures are contraindicated. We offer you to familiarize yourself with some medications for the treatment of scabies.
Treatment according to the Demyanovich method is carried out with two solutions: No. 1 (60 percent sodium thiosulfate solution) and No. 2 (6 percent hydrochloric acid solution).
Benzyl benzoate , emulsion (10% for children, 20% for adults).
Ointments containing sulfur or tar: Wilkinson's ointment, 20-30% sulfur ointment. Among the disadvantages of this method of treatment are: duration of therapy, unpleasant odor, frequent development of complications. These ointments are not prescribed to persons suffering from eczema and children.
Lindane lotion (1%) is highly effective . Due to toxicity, it is prohibited for children (under 2 years of age), pregnant women, patients with multiple scratches, and those suffering from eczema and atopic dermatitis.
Crotamion is used as a 10% cream, lotion or ointment.
Spregal is used in all age groups and has no contraindications.
Malathion is used as a 0.5% lotion (1% shampoo is used for head lice).
Permethrin is an effective and safe drug for the treatment of scabies. After a single treatment at night, the number of patients cured is 89-98%.
When treating with any of the listed methods, underwear and bed linen must be boiled and ironed on both sides! Sanitary treatment of things, clothing and premises increases the effectiveness of therapy, as it prevents possible relapses of the disease.
Therapeutic measures
If pseudoscabies is not complicated by a bacterial infection, then the process can self-limit. For severe itching and rashes, treatment is used for scabies. The main antiparasitic drugs include:
water-soap emulsion;- Benzyl benzoate;
- Spregal (used for pregnant women);
- Medifox;
- Lindan.
Next, antihistamine and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. For this purpose, local ointments Akriderm, Videstim are used, as well as antihistamines, which are usually taken orally in the form of tablets:
- Suprastin.
- Loratadine.
- Zodak.
Timely drug therapy will help cure the disease in a short time.
Traditional medicine methods are widely used for illness. However, they should be used only for adults, since the child’s body can give an unexpected reaction, which will aggravate the child’s general condition. At home, soap baths for 5 minutes several times a day help well; birch tar can be applied topically in a thin layer, which should be washed off after 2 hours under running water. A good effect is observed after using a mixture of sulfur and fat.
Many people use a product made from onions and garlic mixed with a bar of laundry soap. To do this, grate the soap into warm water and mix thoroughly. Add grated onion and garlic to the resulting mixture. The resulting composition is cooled and rolled into balls. Apply soap until the itching stops.
If not treated in a timely manner, pseudosarcoptosis can lead to the development of purulent processes due to the secondary attachment of bacteria; prolonged scabies leads to the development of skin eczema. An allergic reaction can cause critical symptoms such as choking. That is why it is important to recognize and treat the disease in time.
Prevention of scabies
Prevention of scabies involves active identification of sources of infection and persons in contact with the patient, identification of foci of scabies and their elimination, preventive treatment of persons who were in close contact with patients with scabies, clinical observation of patients, and ongoing disinfection at the source of infection.
Control of cure is carried out 3 days after the end of treatment, and then every 10 days for one and a half months. The success of treatment is determined both by the drug itself and its concentration, the choice of which depends on the age of the patient, the degree of development of the process, the presence of complications and their severity.
Preventive measures
To prevent your pet from becoming infected with scabies mites, you should limit its contact with street animals.
At least once every six months, it is recommended to carry out preventive treatment of wool against ectoparasites using antiparasitic drops, solutions, and sprays based on selamectin.
For preventive purposes, during the bathing process, special animal shampoos and insecticidal agents are used, which can be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy, veterinary clinic or pet store. For the same purpose, you can purchase a special collar for your cat.
After each walk, inspect the animal's fur. Do not forget about hygiene procedures and support your pet’s body with products aimed at strengthening the immune system. To do this, introduce mineral and vitamin complexes into your cat’s diet.
Ticks do not survive if the house is regularly cleaned, cleaned, and laundry washed. Preventive measures will minimize the risk of your pet becoming infected with scabies. Take care of your cat one hundred percent, and then the tick is unlikely to be able to settle in her fur and in your home for a long time.