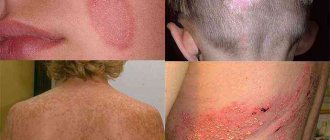
One of the main symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis is yellow dandruff on the head. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of crusts on the scalp and the formation of yellow dandruff after they peel off. The disease causes aesthetic discomfort, limits the supply of nutrients to the hair follicles and leads to severe hair loss. In the absence of effective treatment, the pathological process provokes baldness.
Yellow spots on the head, what are they?
A disease such as seborrheic dermatitis most often affects men, but this does not mean that it cannot affect women. The disease begins to develop gradually, and in winter the symptoms may intensify.
Yellow spots on the head of an adult can peel off, the size does not exceed twenty millimeters. You may feel wet and small cracks or crusts may appear. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, a visual examination of the patient is often sufficient.
The disease is quite common; it is believed that every fifth person on our planet suffers from it. When the scalp is affected, alopecia may occur. In the summer, relief usually occurs; many patients benefit from exposure to the sun.
In severe cases, erythroderma may develop. If you notice the first symptoms of the disease on your head, you must definitely visit a medical facility, in particular a trichologist or dermatologist.
Tips and tricks to resolve the problem
To get rid of crust on the scalp, it is important:
- find out from the doctor why the flaky areas appeared;
- strengthen the immune system. This will help: a course of vitamins, exercise, sufficient consumption of vegetables and fruits, giving up alcohol and tobacco;
- eliminate stressful conditions;
- drink about 2 liters of pure water per day;
- stick to a healthy diet (avoiding fatty, spicy, etc.). Normal activity of the gastrointestinal tract will reduce the formation of affected areas;
- choose shampoos and other caring cosmetics without aggressive ingredients. It is better to take plant-based products;
- get rid of the allergen, if we are talking about allergic manifestations of dandruff;
- use medicinal cosmetics prescribed by the doctor.
Folk remedies also give good results as a complete treatment, or complementing drug treatment.
After successful therapy, dandruff in the form of a crust on the epidermis may return, especially if you do not adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
Treatment
If yellow spots appear on your head, they must be examined. Since the disease is chronic, treatment takes a very long time. As mentioned above, the sun helps many people for treatment.
Shampoos containing selenium sulfide help a lot. Ketoconazole can be used only at the first stage of the disease, and subsequently it can be used as prophylaxis to avoid re-development of the disease.
When you wake up in the morning, you can remove the crusts that have formed on the stains. To do this, you need to dilute the shampoo in water and soak a cotton swab in it. After the scales are removed, you need to treat the skin with special products prescribed by the doctor.
On the shelves of pharmacies today there are a large number of different drugs that can be used to get rid of yellow spots on the head and cure such an unpleasant disease as seborrheic dermatitis. However, before using them, you must consult a doctor. In general, the treatment is successful, but only if it is correct and starts on time.
Preventive measures
There can be many reasons for the appearance of spots on the head, and they are all of a different nature, but compliance with certain preventive measures will minimize the risk of these symptoms.
The range of such events includes:
- Reducing the time spent under the influence of direct sunlight , as well as minimizing the receipt of ultraviolet radiation from any other sources.
- Use only high-quality detergents and cosmetics intended for application to the head, which do not have an aggressive effect, and which have not expired.
- Regular implementation of water procedures and taking other measures to maintain head hygiene.
- Wearing hats during hot or cold periods to provide protection from temperature changes.
- Use only personal combs , hats, towels, hairpins, combs, hair ties and other similar devices.
- Complete refusal or minimization of contacts with people if there is a suspicion that they have fungal or other diseases with similar symptoms.
- Author admin
- Causes and treatment
- No comments yet.
Yellow dandruff
One of the symptoms of the oily variety of seborrheic dermatitis is dandruff, which appears due to the fact that the sebaceous glands produce too much secretion, creating a favorable environment for the growth of the Malassezia fungus. With seborrheic dermatitis, the content of the fungus Malassezia Furfur increases. (1) Yellow dandruff is a sign of the oily variety of seborrheic dermatitis. We will now talk about the causes of its occurrence and methods of treatment.
Why does yellow dandruff appear on the head?
Increased activity of the sebaceous glands and the proliferation of Malassezia, leading to the appearance of oily seborrhea, is only a consequence. Here are the main factors that directly affect the functioning of the sebaceous glands of the scalp:
- Hereditary factor. There is a genetic predisposition to various forms of seborrheic dermatitis, and this is one of the main reasons for its occurrence. Although predisposition does not mean that the disease will definitely develop
- Problems of the endocrine system and disorders of the body's secretions.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which also affect secretion.
- Stress. Constant experiences lead to malfunctions of various organs, and the internal and external secretion organs are no exception.
- Hormonal changes. With an increase in the amount of male hormones in the body, active production of sebum begins, which is typical during puberty. This may also be a consequence of taking hormonal drugs (2) (3).
Symptoms
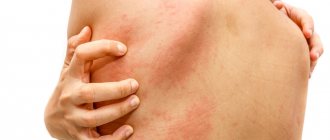
The presence of spots on the head, the appearance of which is accompanied by inflammatory processes, peeling of the skin, hair loss, severe itching or other symptoms, can be the cause of a variety of dermatological diseases or fungal formations.
It is recommended to consult a specialist, since only he can make an accurate diagnosis.
In most cases, such symptoms are evidence of one of the following ailments:
Ringworm
This is one of the most common and at the same time severe fungal diseases. A characteristic symptom is pathological hair loss, leading to partial baldness or the formation of large bald spots that are visible even to the naked eye.
The disease is highly contagious and can be transmitted to another person through direct contact with the patient or his personal belongings and hygiene equipment.
Infection through contact with sick animals is much less common, but there is still a risk. The difficulty of timely detection of the disease lies in the long incubation period, when there is no manifestation of the main symptoms; such a process can last from one week to several months.
Microsporosis
You can get infected both from sick people and from animals. In most cases, children under 12 years of age are infected and transmit the disease to their family members. A distinctive feature is the high rate of spread of spores, so isolated cases of infection can often be the first sign of an impending epidemic. Inflammatory processes rarely occur, but the affected areas usually become slightly swollen and covered with a purulent crust.
The main symptoms are very similar to the symptoms of other types of fungal infections, so an accurate diagnosis can only be made by a specialist.
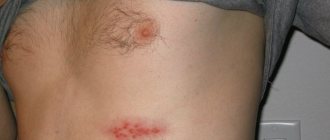
Scab
It is transmitted in exactly the same way as the other described diseases. The main manifestation is the appearance of characteristic yellow crusts, in the center of which hair usually grows. Lack of therapy can lead to severe spread of lesions, skin atrophy and complete baldness.
Psoriasis
Spots are already a secondary symptom that manifests itself in the presence of inflammation. First of all, excessive peeling of the skin, mild irritation and itching occurs, leading to scratching of the affected areas of the skin. As psoriasis develops, plaques with a gray crust or plaque form, so this disease is often confused with seborrheic dermatitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis
And other diseases of this type, which are caused by the activity of fungi, and provoke the occurrence of inflammatory processes. With timely detection and proper treatment in the initial stages, usually all symptoms go away fairly quickly.
Two forms of oily seborrhea
Oily seborrheic dermatitis can appear in liquid and thick forms. In the liquid form, the hair begins to become shiny, as if it had been generously lubricated with oil. Due to the increased activity of the sebaceous glands, pores expand and a large amount of sebum is released onto the surface of the skin. The active activity of the Malassezia fungus, which quickly multiplies in sebum, leads to keratinization of the epidermis (the upper cover of the scalp), resulting in the formation of yellow particles, that is, yellow dandruff, which is not shaken off as easily as dry white dandruff. In addition, the process of dandruff formation is accompanied by frequent itching, which is caused by chemically active waste products of Malassezia. If no measures are taken for a long time, a person’s hair may begin to fall out, acne, boils and other purulent formations may appear. This is due to the fact that in some places it is difficult for the secretion to escape.
The thick form of the oily variety of seborrheic dermatitis is more dangerous because the skin pores become clogged due to the fact that sebum mixes with keratinized particles of the epidermis and the surface of the head becomes covered with a yellow crust. As a result, plugs form in the sebaceous ducts and the secretion cannot come out, which leads to the appearance of large purulent formations, for example, atheroma. The thick form, like the liquid one, is accompanied by severe itching.
How to treat yellow dandruff?
If you have yellow dandruff and an itchy head, the first thing you should do is see a trichologist - a doctor specializing in skin diseases. After examination and diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment, which usually includes taking antifungal medications, since the first task is to destroy the colonies of the Malassezia fungus, returning its content in sebum to normal levels (50% - (1). This will help cleanse the epidermis and hair from dandruff, and then you need to understand the cause of seborrheic dermatitis.
Since seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic disease, preventive therapy is necessary after a course of treatment. To eliminate the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis, ketoconazole, zinc-containing products, and tar are used at least twice a week for a month. Further, these same medications should be used for preventive purposes at least once every two weeks. This will keep the number of Malassezia fungus colonies in sebum within physiological limits and ensure an adequate level of secretion production (4).
Among the medicines, we will highlight medicated shampoos with ketoconazole. This substance has proven effective in controlling Malassezia colonies. (5) Ketoconazole suppresses excess fungal activity, thereby preventing the development of seborrheic dermatitis with yellow dandruff and other skin diseases that are often combined with various types of seborrhea. The medicinal shampoo "Perhotal", which contains ketoconazole, was tested by specialists from the Krasnoyarsk Regional Gerontological Center. https://perhotal.ru/wp-content/uploads/research-124.pdf. Among the subjects, 48 people suffered from various forms of seborrheic dermatitis, and after the second application of shampoo, the patients lost itching, flaking of the scalp decreased, and the amount of dandruff significantly decreased.
Perhotal shampoo is available in two forms: for treatment, shampoo with a 2% ketoconazole content is used, and for the prevention of seborrhea, a 1% form is used. Treatment is carried out with 2% ketoconazole 2-3 times a week (the shampoo is applied for 5 minutes) for 1 month, depending on the type of lesion and the severity of the disease. Preventive procedures using 1% ketoconazole are carried out once a week for a month.
What other types of dandruff are there?
(6)
- Yellow dandruff, caused by the related fungus Malassezia globosa, is characterized by flaking yellow scales. Some symptoms are similar to all types of dandruff: yellow particles peel off from the surface of the scalp, the functioning of the sebaceous glands is disrupted, hair loss and the development of other, more serious forms of dermatitis are possible.
- White or gray-white dandruff is characteristic of dry seborrhea. At the same time, the sebaceous glands do not work enough, not producing the required amount of secretion, as a result of which the skin begins to dry and peel, which leads to the appearance of white dandruff.
- Red, or rather, reddish dandruff is called so conventionally. Occurs when there is inflammation of the epidermis, which is affected by fungal infections or suffers from dermatitis. A person combs the diseased areas until they bleed, causing dead white-pink particles to fall off.
- Black dandruff is not actually dandruff, but acne peeling and remnants of acne and other formations protruding on the skin, as well as coagulated blood that was picked off while combing the head.
Brown dandruff may not be dandruff at all, since this color often develops with lice. (7)
References
Yellow spots on a child's headRate this post
Yellow spots on a baby's head are a completely normal phenomenon that almost all parents encounter. They mainly occur in children in the first months of their life. In medicine they have their own name - seborrheic dermatitis.
Scalp diseases leading to hair problems
Pathologies often appear not only on the scalp, but also affect the structure of the hair itself. Such diseases include:
- Trichokinesis or twisted hair, which is characterized by several thickenings overlapping each other. All this is accompanied by increased fragility with the appearance of areas of baldness.
- Monilethrix. A congenital defect that manifests itself already in the first months of a child’s life. Hair with this disease has several thickening and thinning along its entire length, even differing in color. Most often, the disease appears on the back of the head, but can even affect eyebrows and eyelashes.
- Trichoclasia. This defect affects the hair shaft, which breaks in several places at the tip. This disease is as familiar to us as split ends. The reason lies in physical or chemical influences.
- Hair loss.
- A large amount of hair is combed out after you wash your hair. The strands remain in whole bunches in your hands if you pull them.
- Obvious thinning hair.
- Baldness in men.
- Hair loss occurs at the temples.
- The bald spot gradually recedes, forming a shape reminiscent of the letter “M”.
- Alopecia Areata.
- Hair loss occurs in patches that have defined boundaries and varied shapes.
- Loss is observed in random, very different places on the head.
- Ringworm (Tinea Capitis).
- Itchy spots on the head.
- Scaly and red receding hairline.
- Hair fragility.
- Scalp soreness.
- Seborrheic eczema.
- The scaly spots are yellow or white and peel off.
- The affected areas may be red, itchy and greasy.
- The loss may occur in the affected area with a rash.
- Psoriasis manifests itself in different forms.
- Plaque: Brightly colored, extensive red patches on the skin.
- Guttata: small red spots on the trunk, limbs, face and scalp.
- Inverse: appears in the folds of the skin as a red, shiny and smooth rash.
- Pustulosis: White pustules surrounded by red skin.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis: resembles severe burns and covers large areas
- Head lice infestation.
- The head louse is the size of a sesame seed.
- Itchy head.
- Head wounds from scratches and insect bites.
- Feeling like something is crawling on your head.
- Body lice infection.
- These lice differ from head or pubic lice in being larger in size.
- The rash, caused by an allergic reaction to body lice bites, can spread to the scalp.
- Red bumps on the skin.
- Thickened or dark skin.
- Hashimoto's disease.
- Caused by underactive thyroid gland.
- Thinning hair, feeling sluggish, tired, and a hoarse voice.
- Constipation, high cholesterol, depression or muscle weakness in the lower extremities.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Symptoms gradually increase as the disease progresses.
- Brittle hair and nails, fatigue or weakness.
- Increased sensitivity to cold, constipation, depression.
- Addison's disease.
- Skin rash.
- Nausea, loss of appetite.
- Periodic vomiting.
- Hodgkin's disease.
- Painless swelling of the lymph nodes.
- Night sweats.
- Constantly itchy skin.
- Unexplained fever.
- Fatigue.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Constant cough.
- Ringworm Planus.
- Purple-colored bumps with flat tops (they most often appear on just the wrists, inner forearm, or ankles).
- Lesions that develop slowly and spread over two weeks to several months.
- Itching, blisters and white lines on the rash.
- Burning due to painful lesions in the mouth.
- Insufficiency of the pituitary gland (hypothyroidism).
- The pituitary gland secretes eight different hormones.
- Symptoms depend on which hormone is not synthesized in sufficient quantities.
- Only after the doctor has performed all the necessary blood tests will it be possible to find out which specific hormone is deficient.
- Malnutrition.
- Hair loss, paleness, fatigue or weakness.
- Difficulty breathing, unusual eating habits, or periods of lightheadedness.
- Constipation, drowsiness, or fast heartbeat.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Fast heart rate, weight loss and heat intolerance.
- Hair loss, itching, trouble sleeping, or irregular heartbeat.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Cranial fractures.
- Bleeding from a wound or eyes, ears or nose.
- Pain, swelling, redness, or heat at the site of injury.
- Headache, nausea or vomiting.
- Leishmaniasis.
- Transmitted through the bite of an infected gerbil. Infected sand flies are typically found in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis: Painless skin sores, shortness of breath or runny nose, nosebleeds or difficulty breathing.
- Visceral leishmaniasis: weight loss, weakness, enlarged spleen or liver.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- A symmetrical butterfly-shaped rash on the cheeks and nose.
- Massaging hair loss.
- Painful or swollen joints.
- Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma).
- In the early stages, thickening of the skin is observed.
- Narrow, shiny areas around the mouth, nose and fingers.
- As the condition progresses, limited movement develops in these areas.
- Syphilis.
- A small, painless pimple or ulcer that appears where bacteria enter the body.
- A rash that does not itch on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- Age-related arteritis.
- Occurs in people over 60 years of age.
- There are a variety of visual disturbances, sudden permanent loss of vision in one eye or drooping eyelid.
- Fever, weight loss, or facial pain.
- Ito syndrome (Incontinentia Pigementi Achromians).
- Loss of pigmentation on various parts of the body.
- Small lesions, white or discolored.
- Blaschko lines (long, spiral patterns around the arms and legs).
- Bamboo hair (Tricorrhexis nodosa).
- Hair that breaks easily.
- Eyelashes or eyebrows become noticeably thinner.
- Sparse hair growth or a pattern of massive hair loss.
- Short hair due to constant hair breakage.
- Celiac disease (gluten-sensitive enteropathy).
- Children and adults have different symptoms.
- In children: weight loss, vomiting, bloating or pain, persistent diarrhea.
- In adults: bone and joint pain, fatigue, numbness and tingling in the arms and legs, sores and ulcers in the mouth.
- Kwashiorkor.
- A form of malnutrition caused by insufficient protein in the diet.
- Changes in skin and hair color (red-orange tint).
- Fatigue, diarrhea, muscle loss or swelling.
- Allergy.
- A dark red rash on the body, including the head.
- Redness and itching.
- Dry and irritated eyes.
Causes of spots
Why do yellow spots appear on a child’s head? Children have fairly delicate skin; the epidermis is not yet developed as well as in adults. The sweat glands work very weakly, while the sebaceous glands, on the contrary, actively work, which is why such an imbalance occurs in the work of the glands. The skin becomes very vulnerable to environmental factors and it’s easy to catch some infections.
Most often, yellow flaky spots on a child’s head appear when the head sweats frequently. It is possible that mothers dress their children very warmly.
A sweaty head simply cannot cope with such an imbalance on its own, so the development of dermatitis cannot be avoided.
Yellow spots on a baby's head photo
Even a mother’s poor diet can lead to illness. The thing is that an allergic reaction may develop to the introduction of new complementary foods, and this is a provoking factor for the development of dermatitis.
Take a close look at the spots and crusts on your head; they should come off easily. If, after you have removed them, abrasions or wet areas remain, you must consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
Children with these diseases do not need treatment. To wash your hair, you must use hypoallergenic shampoos, they should be for children. The crusts need to be removed, but this procedure must be carried out correctly.
A few hours before bathing, you need to treat your baby's head with baby oil. Almond or olive oil works well for this. If you don’t have it on hand, you can use Vaseline.
Wash your hair well and then dry it with a towel. In order to remove the crust, you need to use a special brush, the teeth of which should be round. By combing your hair, the crusts will be removed.
Do not under any circumstances try to remove them, otherwise you may injure the head. It's not always possible to delete everything in one session, so there's no need to get upset. Maybe they just haven't softened enough. Next time, hold the oil longer and repeat the procedure again.
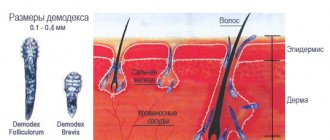
What does the diagnosis mean: mycelium of a pathogenic fungus in humans
The mycelium of a pathogenic fungus in humans is often not immediately noticed. The spores first lengthen and take the form of a tube. Over time, they thin out and turn into hyphae. Pathogenic fungi appear already from the mycelium. Their cells are covered with a wall of carbohydrates. It determines the species affiliation.
The danger of the mycelium of a pathogenic fungus lies in its resistance to various physical and chemical influences. Sometimes a course of serious treatment is required to permanently cure the disease. The most sensitive to therapeutic effects are microspores, and the least sensitive are candida.
Epidemiology
Infection occurs in two main ways:
- Straight. It is characteristic of human interaction with the earth, plants, sick animals or people.
- Indirect. The mycelium of the pathogenic fungus enters the dermis upon contact with clothing and objects that the patient had previously used.
There are varieties of pathogenic fungi found in children. These include superficial trichophytosis and microsporia. There are also varieties of mycelium that primarily affect adults. There are fungal diseases that appear at certain times of the year. In autumn, the likelihood of contracting microsporia increases. In summer – zoophilic trichophytosis.
Features and types of pathogenic fungi
The mycelium of a pathogenic fungus poses the greatest threat when the body’s protective properties are reduced. It can provoke the development of various infectious diseases. All pathogenic fungi are divided into several genera and classes. According to the method of reproduction, 8 classes are distinguished, but only 4 are considered dangerous to humans:
- Ascomycetes. These include dermatophytes, yeast-like and moldy species.
- Zygomycetes. In the absence of medication, this variety can cause significant harm to health.
- Basidiomycetes. One variety of this class causes the development of meningoencephalitis.
- Deutremycetes. They lead to the development of various skin mycoses.
Regardless of the class, mycelium appears in the reproductive phase of the life of the fungus. It is formed by filamentous fibers with different shapes. They are arranged sequentially or in a chaotic order. Reproduction in a favorable environment occurs quickly. Therefore, fungal diseases are characterized by their transience and progression.
Symptoms
Spores and mycelium of a pathogenic fungus may manifest themselves or go unnoticed. If itching appears, changes in the color and structure of the dermis become noticeable, then the development of the disease can be assumed. Most often, symptoms appear later. At the stage of mycelium and spores, pathogenic fungi do not manifest themselves in any way.
As the lesion progresses, yellow spots appear on the nails. Such formations can be single or multiple. In the latter case, they merge into one large spot that does not have smooth edges. The process begins from the edge of the nail plate, gradually spreading to its entire surface. The nail itself becomes thicker and more fragile.
If the mycelium of a pathogenic fungus does not appear on the nail plate, then the following is noted:
- Peeling of the skin;
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- Itching;
- Burning;
- Development of areas of inflammation.
Diagnostic procedures
Usually, a doctor only needs to examine the affected area to draw conclusions about the development of the disease. If in doubt, additional methods are used:
- Ultraviolet. A special lamp allows you to accurately detect not only the presence of fungus, but also mycelium. The technique is also used to monitor the effects of medical procedures. This method has one drawback: the type of fungus cannot be immediately identified.
- Microscopy. To carry it out, skin scales, parts of hair and nails affected by mycosis are taken. To identify pathogenic fungi, native and staining compounds are used.
- PCR. The method is one of the most modern, but expensive. To make a diagnosis, you need to take several tests at once.
- Bac sowing. The surest way to identify the causative agent of the disease. The full result is ready only after two weeks.
Treatment
Fungal mycelium on nails always requires prolonged exposure. Combination therapy is more often used. For this purpose, special preparations are used. If necessary, the affected nail is removed and prosthetic. To get rid of mycelium, you need to take antifungal drugs orally. This is the only way to protect your body from further damage. Sometimes special patches and ointments are used.
When pathogenic fungi spread to hair and nails, systemic and external antimycotics are used. Additionally, laser therapy is used. This method has been used since 2010. Practice has shown that when the nail is carefully heated to a temperature of 60-70 degrees, the mycelium and pathogenic microorganisms die. Heat waves without affecting surrounding tissue can be achieved exclusively with the help of a laser.
Hardware processing can be used as additional techniques. Using wave radiation, the fungus is affected. He gradually dies. The peculiarity is that hardware methods must be used for a long period of time.
Drug therapy to combat the mycelium of a pathogenic fungus includes:
- Nystatin;
- Application of sulfur ointment;
- Use of iodine and hydrogen peroxide;
- Taking Fluconazole.
Thus, the mycelium of a pathogenic fungus in humans leads to the development of serious pathologies. Sometimes mycelium threads are discovered by chance. They are not a death sentence, but identifying them allows you to start treatment on time. Infection occurs in different places, but the most striking clinical picture is observed with reduced immunity.
Forms of the disease
Seborrheic crusts (gneiss) are a common phenomenon among infants. As the baby grows, this problem disappears on its own. But it happens that gneiss bothers older children, and such situations require special attention.
Let's look at how seborrhea manifests itself. There are three forms of the disease:
- Mild - when only the top of the head is affected, sometimes the ears. The children's general health is normal.
- The moderate form is when the entire face and neck become red and peel, and the body and limbs are partially affected by dermatitis. The scales on the head are large, children become capricious, diarrhea appears, and regurgitation becomes more frequent.
- The severe stage is accompanied by the appearance of a continuous plaque on the head or “baby cap.” An infection occurs, causing suppuration. The baby loses his appetite, is lethargic and does not gain weight well.
Reasons for appearance
There is no definite answer to the question of why children have a crust on their heads. Doctors identify only possible provoking factors, which include:
- Development of the endocrine system. In the newborn period, endocrine functions malfunction - the sebaceous glands begin to secrete intensely. This leads to the formation of gneiss.
- Poor hygiene. Scales on the head appear after prolonged wearing of hats. Sweaty skin, too frequent washing, inappropriate washing gels and shampoos - all this provokes the formation of the disease.
- Inappropriate diet. Seborrhea occurs due to poorly tolerated formula or early introduction of complementary foods. Improper nutrition of the mother during breastfeeding can also lead to a malfunction of the baby’s endocrine system.
- Fungal infection. The fungus is constantly present in human skin, but hormonal imbalances contribute to its proliferation. This provokes the appearance of yellow scales.
- Weakened immunity. When the immune functions of the body are weakened, children experience disruption of the sebaceous glands and proliferation of fungus.
Dermatitis in children and adolescents
“Crusts appeared on the head of a 2-year-old child. What to do?" - parents panic on the forums. First of all, you need to remember that before the age of three, this phenomenon is very common. This affects the increased work of the sebaceous glands.
Perhaps the problem is a lack of vitamin B (biotin), which is responsible for metabolism in the body. The very appearance of the crust does not cause discomfort, and with appropriate treatment and compliance with hygiene rules, they disappear without a trace.
When a crust forms on the head of a 3-year-old child, this fact should alert parents. There may be several reasons for this:
- improper hair care;
- overheating in the headdress, when the head begins to sweat;
- use of unnatural cosmetics that cause irritation;
- dry scalp from frequent bathing;
- allergies to new foods.
If all these factors are excluded, and seborrhea in 3-year-old children does not go away, then the reasons may be much more serious, for example, disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland or the central nervous system. In this case, you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
There are situations when, at a young age, the child’s parents do not face such a problem, but first learn about dermatitis when their child is 5-6 years old. A crust on the head of a 5-year-old child is quite rare, just like in teenagers. But it still happens. This phenomenon is often associated with a bacterial infection. It is treated with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
If the onset of the disease is accompanied by increased weight gain, doctors suspect Leiner's disease in a young patient. In addition, scales on the skin in children 5-6 years of age and older may be symptoms of diathesis, psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
How to get rid of crusts
Parents are wondering how to remove crusts on their child’s head, and whether this can be done. It is necessary to remove them, because careless movement can accidentally tear off the crust. This will lead to infection of the resulting wound on the skin.
To get rid of crusts on a child’s head, you should:
- wash your hair with baby shampoo;
- blot with a towel;
- moisten a cotton pad with sunflower or olive oil and gently rub the crusts;
- put the baby to sleep in a cotton bonnet or hat;
- In the morning, comb out the crusts with a soft comb or brush;
- wash your hair, comb it.
These actions should not be carried out more than twice a week. The procedure is also repeated for seborrhea behind the ears and on the eyebrows.
There is also another method in which an hour (or at least 20 minutes) before taking a bath, slightly heated oil (burdock, baby, olive) is rubbed onto the baby’s head. Then they put on a hat.
While bathing, wash your hair with shampoo and remove flakes. Then comb out the remaining scabs.
Let's look at how to comb out the crust in more detail. Take a blunt-tooth comb and comb your hair from front to back. After this, use a soft brush. The fontanel area requires special attention; crusts must be removed from it, only with caution. When combing, the scales may become separated from the hair.
If seborrheic dermatitis appears regularly, the presence of diathesis or other allergies is suspected. In this situation, you should contact a dermatologist and allergist.
Medicines
In general, gneiss does not require drug treatment, with the exception of the severe stage. In this case, children are prescribed antibiotics (for skin infection) and antihistamines to reduce itching.
Since the reasons for the appearance of scales differ in each case, treatment is selected individually.
To eliminate various forms of the disease, use:
- antifungal ointments (Lamisil, Mycospor and others);
- anti-fungal shampoo (Nizorex, Sebazol, Dermazol);
- corticosteroid ointments (“Ecolom”);
- zinc ointment to relieve inflammation;
- preparations for diseased skin (“Topicrem”, “Bioderma Sensibio”);
- vitamin complexes;
- antihistamines (Citrine, Diazolin).
Mustela shampoo or foam helps get rid of yellow crusts. Its composition is hypoallergenic, the shampoo softens scales and also has an antibacterial effect.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. It is extremely difficult to establish why pathology develops in a particular patient. It is believed that factors that weaken a person’s immune system can provoke a relapse of the disease:
- infectious, viral and other diseases;
- severe stress;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight (useful in small doses);
- taking medications and more.
After an exacerbation, the pathology goes through several stages of development, each of which is characterized by certain signs:
- itching and redness of the dermis, over time the skin itches more and more;
- peeling of the skin;
- the appearance of large spots covered with white flakes (dead tissue);
- cracks and abrasions on the head.
The elasticity of the skin in the problem area decreases, as a result of which the dermis is easily injured.
Treatment
Psoriasis requires an integrated approach to treatment. Therapy of the disease involves the use of:
- corticosteroids and cytostatics (in severe cases);
- antihistamines;
- sedative and hyposensitizing drugs;
- vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
The use of these drugs is intended to relieve symptoms characteristic of psoriasis and increase the duration of the remission stage. However, it is impossible to completely get rid of the pathology. In case of secondary infection, treatment of psoriasis is supplemented with local antibacterial drugs.